| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
多奈哌齐(E2020 游离碱)的毒蕈碱拮抗剂活性通过其浓度依赖性抑制人 SHSY5Y 神经母细胞瘤细胞中卡巴胆碱刺激的细胞内 Ca2+ 浓度增加来证明。一旦大鼠腹腔注射多奈哌齐,震颤和流涎就会出现剂量依赖性增加,表明明显的胆碱能行为,ED50为6μmol/kg。多奈哌齐的 ED50 为 50 μmol/kg,口服时效果稍差 [2]。根据最近的一项研究,多奈哌齐可以保护人脐静脉内皮细胞 (HUVEC) 免受 H2O2 造成的细胞损伤。这有可能用于治疗与心脏和大脑相关的疾病中的氧化应激[3]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
将新型乙酰胆碱酯酶抑制剂多奈哌齐和NXX-066的体外和体内效果与他克林进行了比较。使用电鳗中纯化的乙酰胆碱酯酶,他克林和多奈哌齐都被证明是可逆的混合型抑制剂,与酶上的类似位点结合。相反,NXX-066是一种不可逆的非竞争性抑制剂。所有三种化合物都是大鼠脑乙酰胆碱酯酶的有效抑制剂(IC50[nM];他克林:125+/-23;NXX-066:148+/-15;多奈哌齐:33+/-12)。他克林也是一种强效的丁酰胆碱酯酶抑制剂。多奈哌齐和他卡林取代了大鼠脑匀浆中[3H]哌仑西平的结合(IC50值[微M];他卡林:0.7;多奈哌齐尔:0.5),但NXX-066在该M1毒蕈碱位点的效力约低80倍。对卡巴胆碱刺激神经母细胞瘤细胞[Ca2+]i增加的研究表明,多奈哌齐和他克林都是M1拮抗剂。配体结合表明,在其他神经递质位点,任何药物都没有可能具有药理学意义的活性。对大鼠腹膜内施用这些化合物产生了唾液分泌和震颤的剂量依赖性增加(ED50[微mol/kg];他克林:15,NXX-066:35,多奈哌齐:6),其中NXX-066对震颤具有最持久的影响。口服给药后,NXX-066起效最慢,但作用持续时间最长。相对效力也发生了变化,他克林的效力较低(ED50[微摩尔/千克];他克林:200,NXX-066:30,多奈哌齐:50)。唾液分泌仅在他克林治疗的动物中严重。使用大脑皮层的体内微透析,发现NXX-066和他克林都会产生细胞外乙酰胆碱的显著增加(至少30倍),在他克林后2小时和NXX-066后4小时内,细胞外乙酰胆碱保持升高[2]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
本研究旨在比较多奈哌齐和其他一些用于治疗阿尔茨海默病的胆碱酯酶(ChE)抑制剂对乙酰胆碱酯酶(AChE)和丁酰胆碱酯酶(BuChE)的体外抑制作用。氨基甲酸酯衍生物毒扁豆碱和利瓦斯汀需要预培养以表现出适当的抗ChE活性。毒扁豆碱对ChE的最大抑制作用在30-60分钟内出现,而利瓦斯汀对AChE和BuChE活性的抑制作用分别在48和6小时后达到峰值。在每种ChE抑制剂的最佳测定条件下,对AChE活性的抑制效力(IC50)的顺序为:毒扁豆碱(0.67 nM)>利瓦斯汀(4.3 nM。苄基哌啶衍生物多奈哌齐和TAK-147对乙酰胆碱酯酶表现出比BuChE高的选择性。氨基甲酸酯衍生物表现出中等的选择性,而4-氨基吡啶衍生物tacrine和ipideacrine没有表现出选择性。这些ChE抑制剂对AChE活性的抑制效力可能说明了它们在体内的潜在活性[1]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
胆碱酯酶抑制剂对SHSY5Y人神经母细胞瘤细胞钙通量的影响[2]
将SHSY5Y细胞维持在Eagles Minimum Essential Medium和Hams F-12培养基(1:1)中,所述培养基补充有10%胎牛血清、2%l-谷氨酰胺、1%非必需氨基酸和20mM Hepes pH 7.4。为了收获细胞,取出培养基,用10ml Hank平衡盐溶液冲洗单层,并用细胞刮刀从烧瓶底部刮去。将得到的悬浮液在4°C下以250×g离心5分钟,并将得到的颗粒重悬在由6ml磷酸盐缓冲盐水组成的负载缓冲液中,该缓冲液含有2mM EDTA、10μM Fluo-3AM和0.02%pluronic F-127 pH 7.4。在37°C下用Fluo3的乙酰乙酸乙酯衍生物(Fluo-3AM)加载细胞15分钟。在4°C下以250×g离心5分钟后,将所得颗粒重悬于含有CaCl2(0.5 mM)和葡萄糖(10 mM)的pH 7.4的含氧Hepes Ringer缓冲液中。然后将细胞悬浮液在室温下再孵育20分钟,以使Fluo-3AM水解,以250×g离心5分钟,并如前所述重新悬浮在氧化的Hepes–Ringer缓冲液中。将等分试样(2ml)的细胞悬浮液置于石英试管中,并在室温下搅拌平衡1分钟。记录基础荧光,之后加入测试试剂。使用Hamilton注射器进行20微升的添加,允许连续测量荧光信号。背景荧光不受该过程的影响。在激发505nm:发射530nm下测量荧光。通过加入10μM钙离子载体4-溴钙霉素测量最大荧光。然后使用MnCl2(1mM)猝灭荧光信号。 |
| 动物实验 |
Behavioural observations[2]
Tremor and salivation were assessed using the methods described by Hunter et al. (1989). Briefly, groups of animals were injected with various doses of cholinesterase inhibitor and observed. Tremor (score 0–3) and salivation (weight in 10 mg units) were noted. 2.9. Measurement of extracellular acetylcholine in rat brain using in vivo microdialysis. Individually prepared concentric probes, essentially as described by Hutson et al. (1985), were used except that they were implanted without the use of a guide assembly and the internal glass capillary tubes were replaced by fused silica tubes (VS-150-075-1D). The dialysis membrane was 4mm long and had an approximate diameter of 0.2 mm. The in vitro efficiency of ACh recovery when the microdialysis probes were placed in an ACh (60 μM) solution at room temperature and perfused at 1.0 μl/min, was 17.9±2.4%. Probes were implanted transversely into the cortex of rats anaesthetised with halothane (2%) in O2/N2O mixture (1: 2) and secured in Kopf stereotaxic frame with the tooth bar at −3.3 mm below interaural zero. Probes were implanted horizontally into the right cortex: +7.7 mm anterior and +4.2 mm lateral from interaural zero and −1.3 mm from the skull surface and secured to the skull with two screws and dental cement. Following surgery, the animals were housed in perspex boxes until the beginning of microdialysis procedures the next day. Placement of the probe was verified by visual inspection of the probe track at the end of each experiment by injecting Luxol Fast blue. Dialysis probes were perfused at a rate of 1 μl/min with artificial CSF (composition mM: NaCl 125, KCl 2.5, MgCl2, 1.18 and CaCl2 1.26), or high K+CSF (composition mM: NaCl 27.5, KCl 100, MgCl2 1.18 and CaCl2 1.26) using a model 22 Harvard Microlitre syringe pump. The artificial CSF did not contain an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Thirty minute fractions were collected which were then stored on ice. Dialysate from the first 60 min was discarded and the next three collections of 30 min were baseline samples prior to the i.p administration of tacrine (21 μmol/kg) or NXX-066 (106 μmol/kg). Acetylcholine was measured by a hplc method similar to that originally described by Potter et al. (1983). Following its separation on an analytical ion exchange column ACh was converted to hydrogen peroxide inside a 4.1×30 mm analytical column, filled with polymeric matrix to which AChE and choline oxidase enzymes has been covalently linked. The hydrogen peroxide formed was detected electrochemically by oxidation on a platinum electrode at +500 mV versus a Ag/AgCl reference. The mobile phase composition was 3.4 mM H3PO4 (85%) and 5 mM Kathon CG (1%); the pH was adjusted to 8.5 by addition of NaOH. The flow rate of 0.6 ml/min ensured quantitative conversion of ACh to H2O2 within an enzyme reactor. Peaks were recorded on a Kontron integrator. ACh in brain dialysates was quantified by the standard curve method. A lower level of 0.6 pmol of ACh on the column could be reliably detected. Donepezil were dissolved in 0.9% w/v NaCl (saline) before injection. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Donepezil is slowly absorbed via the gastrointestinal tract after oral administration. Tmax is 3 to 4 hours with a bioavailability of 100% and steady-state concentrations are attained within 15 to 21 days of administration. The Tmax in one pharmacokinetic study determined a Tmax of 4.1 ± 1.5 hours. The Cmax of 5 mg donepezil tablets is estimated to be 8.34 ng/mL, according to the Canadian monograph. The AUC of 5 mg donepezil tablets has been determined to be 221.90-225.36 ng.hr/mL. In a study of radiolabeled administration donepezil in healthy adults, 57% of measured radioactivity was identified in the urine, and 5% was identified in the feces. The volume of distribution of donepezil is 11.8 ± 1.7 L/kg for a 5-mg dose and 11.6 ± 1.91 L/kg for a 10-mg dose. It is largely distributed in the extravascular compartments. Donepezil crosses the blood-brain barrier and cerebrospinal fluid concentrations at the above doses have been measured at 15.7%. The volume of distribution at steady-state according to the FDA label for donepezil ranges from 12 - 16 L/kg. According to the FDA label, the average apparent plasma clearance of this drug is 0.13 – 0.19 L/hr/kg. A 5 mg dose of donepezil in healthy patients was shown to have a plasma clearance of 0.110±0.02 L/h/kg. In 10 patients diagnosed with alcoholic cirrhosis, showed a mean decrease in clearance by 20% when compared to the clearance in 10 healthy subjects. In 4 patients with severe renal impairment compared to 4 healthy subjects, no significant change in clearance was noted. Donepezil is well absorbed with a relative oral bioavailability of 100% and reaches peak plasma concentrations in 3 to 4 hours. Pharmacokinetics are linear over a dose range of 1 to 10 mg given once daily. Neither food nor time of administration (morning vs. evening dose) influences the rate or extent of absorption of donepezil hydrochloride tablets. ... The mean apparent plasma clearance (Cl/F) is 0.13 L/hr/kg. Following multiple dose administration, donepezil accumulates in plasma by 4 to 7 fold and steady state is reached within 15 days. The steady state volume of distribution is 12 L/kg. In a study of 10 patients with stable alcoholic cirrhosis, the clearance of donepezil hydrochloride was decreased by 20% relative to 10 healthy age and sex matched subjects. In a study of 11 patients with moderate to severe renal impairment (ClCr < 18 mL/min/1.73 sq m) the clearance of donepezil hydrochloride did not differ from 11 age and sex matched healthy subjects. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Donepezil (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Donepezil is metabolized by first pass metabolism in the liver, primarily by CYP3A4, in addition to CYP2D6. After this, O-dealkylation, hydroxylation, N-oxidation, hydrolysis, and O-glucuronidation occur, producing various metabolites with similar half-lives to the unchanged parent drug. A study of the pharmacokinetics of radiolabeled donepezil demonstrated that about 53% of plasma radioactivity appeared as donepezil in the unchanged form, and 11% was identified as the metabolite 6-O-desmethyl donepezil, which exerts similar potency inhibition of the acetylcholinesterase enzyme. This drug is heavily metabolized to four primary metabolites, two of which are considered pharmacologically active, as well as to multiple inactive and unidentified metabolites. Donepezil is both excreted in the urine intact and extensively metabolized to four major metabolites, two of which are known to be active, and a number of minor metabolites, not all of which have been identified. Donepezil is metabolized by CYP 450 isoenzymes 2D6 and 3A4 and undergoes glucuronidation. Following administration of 14C-labeled donepezil, plasma radioactivity, expressed as a percent of the administered dose, was present primarily as intact donepezil (53%) and as 6-O-desmethyl donepezil (11%), which has been reported to inhibit AChE to the same extent as donepezil in vitro and was found in plasma at concentrations equal to about 20% of donepezil. The aim of this study was to investigate the metabolism and elimination of donepezil HCl in humans, following the administration of a single 5 mg (liquid) oral dose containing a mixture of unlabelled and 14C-labelled donepezil. ... Unchanged donepezil accounted for the largest component of the recovered dose in each matrix. Three metabolic pathways were identified: (i) O-dealkylation and hydroxylation to metabolites M1 and M2, with subsequent glucuronidation to metabolites M11 and M12; (ii) hydrolysis to metabolite M4; and (iii) N-oxidation to metabolite M6. In plasma, the parent compound accounted for about 25% of the dose recovered during each sampling period, as well as of the cumulative dose recovered. The recovered residue showed higher levels of the hydroxylated metabolites M1 and M2 than of their glucuronide conjugates M11 and M12, respectively. In urine, the parent compound accounted for 17%, on average, of the dose recovered from each pooled sample, as well as of the total recovered dose. The major metabolite was the hydrolysis product M4, followed by the glucuronidated conjugates M11 and M12. In feces, the parent compound also predominated, although it accounted for only 1%, of the recovered dose. A large percentage of the radioactivity in feces consisted of unidentified very polar metabolites, which were retained at the TLC origin. Of the extracted metabolites, the hydroxylation products M1 and M2 were the most abundant, followed by the hydrolysis product M4 and the N-oxidation product M6. Donepezil is hepatically metabolized and the predominant route for the elimination of both parent drug and its metabolites is renal, as 79% of the recovered dose was found in the urine with the remaining 21% found in the feces. Moreover, the parent compound, donepezil, is the predominant elimination product in urine. The major metabolites of donepezil include M1 and M2 (via O-dealkylation and hydroxylation), M11 and M12 (via glucuronidation of M1 and M2, respectively), M4 (via hydrolysis) and M6 (via N-oxidation). Donepezil has known human metabolites that include 6-O-Desmethyl Donepezil, 5,6-dimethoxy-2-(piperidin-4-ylmethyl)-2,3-dihydroinden-1-one, and 5-O-Desmethyl Donepezil. Donepezil is metabolized by CYP 450 isoenzymes 2D6 and 3A4 in the liver and also undergoes glucuronidation. The main metabolite, 6-O-desmethyl donepezil, has been reported to inhibit AChE to the same extent as donepezil in vitro. Route of Elimination: Donepezil is both excreted in the urine intact and extensively metabolized to four major metabolites, two of which are known to be active, and a number of minor metabolites, not all of which have been identified. Half Life: 70 hours Biological Half-Life The average elimination half-life of donepezil is about 70 hours according to the results of various studies and the FDA label for donepezil.. One pharmacokinetic study determined the average terminal half-life to be 81.5±22.0 h The elimination half life of donepezil is about 70 hours. A 79-year-old woman with Alzheimer's disease was admitted due to acute cholinergic symptoms induced by overdose (45 mg) of donepezil (DPZ) ... The plasma concentration of DPZ was 54.6 ng/mL on admission and gradually decreased to the normal limits in about 90 hr. The calculative half-life of DPZ was about 55 hr ... |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
Donepezil is a cholinesterase or acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor. A cholinesterase inhibitor (or 'anticholinesterase') suppresses the action of acetylcholinesterase. Because of its essential function, chemicals that interfere with the action of acetylcholinesterase are potent neurotoxins, causing excessive salivation and eye-watering in low doses, followed by muscle spasms and ultimately death. Nerve gases and many substances used in insecticides have been shown to act by binding a serine in the active site of acetylcholine esterase, inhibiting the enzyme completely. Acetylcholine esterase breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which is released at nerve and muscle junctions, in order to allow the muscle or organ to relax. The result of acetylcholine esterase inhibition is that acetylcholine builds up and continues to act so that any nerve impulses are continually transmitted and muscle contractions do not stop. Among the most common acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are phosphorus-based compounds, which are designed to bind to the active site of the enzyme. The structural requirements are a phosphorus atom bearing two lipophilic groups, a leaving group (such as a halide or thiocyanate), and a terminal oxygen. Hepatotoxicity In several large clinical trials, donepezil therapy was not associated with an increased rate of serum enzyme elevations compared to placebo treatment. Furthermore, escalation of the dose from 10 to 23 mg daily was not followed by an increased rate of ALT elevations compared to patients maintained on the lower dose. Nevertheless, since its introduction into clinical use, donepezil has been implicated in several isolated case reports of clinically apparent hepatotoxicity. The time to onset was short (1 to 6 weeks) and the pattern of serum enzyme elevations was cholestatic or mixed. The course of illness can be severe with prolonged jaundice and itching (Case 1), but fatal instances have not been published. Immunoallergic and autoimmune features are not common. Likelihood score: D (possible, rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Protein Binding Donepezil is 96% protein-bound, with approximately 75% binding to albumin and approximately 21% binding to alpha-1-glycoprotein. Interactions Ketoconazole and quinidine, inhibitors of CYP450, 3A4 and 2D6, respectively, inhibit donepezil metabolism in vitro. Whether there is a clinical effect of quinidine is not known. In a 7 day crossover study in 18 healthy volunteers, ketoconazole increased mean donepezil concentrations (AUC0-24 and Cmax) by 36%. The clinical relevance of this increase in concentration is unknown. A synergistic effect may be expected when cholinesterase inhibitors are given concurrently with succinylcholine, similar neuromuscular blocking agents or cholinergic agonists such as bethanechol. Inducers of CYP 2D6 and CYP 3A4 (eg, phenytoin, carbamazepine, dexamethasone, rifampin, and phenobarbital) could increase the rate of elimination of donepezil hydrochloride. A 75-year-old man with Alzheimer's disease, treated with the cholinesterase inhibitor donepezil for 14 months, was scheduled for left colectomy under general anesthesia. During the procedure, succinylcholine-induced relaxation was prolonged and the effect of atracurium besylate was inadequate even at higher doses than those indicated for the patient's weight. Cholinesterase blood tests performed 10 months, 1 month and 10 days before surgery had demonstrated a gradual decrease in the duration of activity of the enzyme. Such an effect, which has been described for cholinesterase inhibitors like neostigmine and donepezil, would explain the prolonged effect of succinylcholine. After ruling out other causes for resistance to atracurium, we conclude that donepezil or its metabolites acted on muscle plaque, blocking acetylcholine hydrolysis and antagonizing atracurium. For more Interactions (Complete) data for Donepezil (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
Cholinesterase Inhibitors; Nootropic Agents Donepezil hydrochloride tablets are indicated for the treatment of dementia of the Alzheimer's type. Efficacy has been demonstrated in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's Disease. /Included in US product label/ /EXPTL Ther:/ ... Officially approved for mild-to-moderate and severe /Alzheimer's Disease/ (AD), donepezil has also been shown to be effective in early-stage AD, vascular dementia, Parkinson's disease dementia/Lewy body disease and cognitive symptoms associated with multiple sclerosis. In addition, one study suggested that donepezil may delay the onset of AD in subjects with mild cognitive impairment, a prodrome to AD. Drug Warnings Donepezil hydrochloride tablets are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to donepezil hydrochloride or to piperidine derivatives. Because of their pharmacological action, cholinesterase inhibitors may have vagotonic effects on the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes. This effect may manifest as bradycardia or heart block in patients both with and without known underlying cardiac conduction abnormalities. Syncopal episodes have been reported in association with the use of donepezil hydrochloride. Syncopal episodes have been reported in association with the use of donepezil hydrochloride. Through their primary action, cholinesterase inhibitors may be expected to increase gastric acid secretion due to increased cholinergic activity. Therefore, patients should be monitored closely for symptoms of active or occult gastrointestinal bleeding, especially those at increased risk for developing ulcers, eg, those with a history of ulcer disease or those receiving concurrent non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS). Donepezil hydrochloride, as a predictable consequence of its pharmacological properties, has been shown to produce diarrhea, nausea and vomiting. These effects, when they occur, appear more frequently with the 10 mg/day dose than with the 5 mg/day dose. In most cases, these effects have been mild and transient, sometimes lasting one to three weeks, and have resolved during continued use of donepezil hydrochloride. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Donepezil (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics By inhibiting the acetylcholinesterase enzyme, donepezil improves the cognitive and behavioral signs and symptoms of Alzheimer's Disease, which may include apathy, aggression, confusion, and psychosis. |
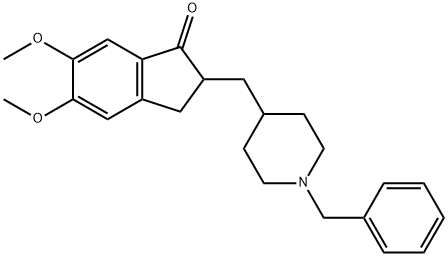
| 分子式 |
C24H29NO3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
379.492
|
| 精确质量 |
379.214
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 75.96; H, 7.70; N, 3.69; O, 12.65
|
| CAS号 |
120014-06-4
|
| 相关CAS号 |
(R)-Donepezil;142698-19-9;(S)-Donepezil;142057-80-5;Donepezil-d7 hydrochloride;1261394-20-0;Donepezil-d5;1128086-25-8;Donepezil Hydrochloride;120011-70-3
|
| PubChem CID |
3152
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.1±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
527.9±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
207ºC
|
| 闪点 |
273.1±30.1 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.578
|
| LogP |
4.71
|
| tPSA |
38.77
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
28
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
510
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
ADEBPBSSDYVVLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C24H29NO3/c1-27-22-14-19-13-20(24(26)21(19)15-23(22)28-2)12-17-8-10-25(11-9-17)16-18-6-4-3-5-7-18/h3-7,14-15,17,20H,8-13,16H2,1-2H3
|
| 化学名 |
2-((1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl)-5,6-dimethoxy-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-one
|
| 别名 |
HSDB 7743; HSDB-7743; HSDB7743
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮和光照。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~33.33 mg/mL (~87.83 mM)
H2O : ~2 mg/mL (~5.27 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.59 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.59 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.59 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6351 mL | 13.1756 mL | 26.3512 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5270 mL | 2.6351 mL | 5.2702 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2635 mL | 1.3176 mL | 2.6351 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Safety and Efficacy of Donepezil in Mild to Moderate Alzheimer's Disease
CTID: NCT02787746
Phase: Phase 4 Status: Completed
Date: 2024-08-23