| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
5-LO (IC50 = 0.06 μM); mPGES-1 (IC50 = 0.2 μM); XIAP (IC50 = 4.1 μM)
The target of Embelin is the Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins (IAPs) family, with high selectivity for the BIR3 domain of X-linked IAP (XIAP); it also exhibits weak affinity for cIAP1/cIAP2 and no significant binding to non-IAP proteins. - For human XIAP BIR3 domain (fluorescence polarization, FP assay): Ki = 4.1 nM [1] - For human cIAP1 BIR3 domain (same FP assay as XIAP): Ki = 85 nM [1] - For human cIAP2 BIR3 domain (homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence, HTRF assay): IC₅₀ = 110 nM [2] - For non-IAP proteins (e.g., Bcl-2, Mcl-1, caspase-3, caspase-9): Ki > 1000 nM (no significant binding) [1, 2] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
来自日本紫金牛草的 Embelin 是一种小分子抑制剂,可与 Smac 和 caspase-9 结合的 XIAP BIR3 结构域结合。 Embelin 的 IC50 值为 3.7 和 5.7 μM,并以剂量依赖性方式抑制 PC-3 和 LNCap 细胞生长。而 Embelin 对正常 PrEC 和 WI-38 细胞的毒性则低得多,IC50 值分别为 20.1 μM 和 19.3 μM。当 PC-3 细胞用 25 和 50 μM embelin 处理 48 小时时,30% 和 75% 的细胞死亡,比未处理的细胞增加约 3 和 9 倍。 [1] Embelin 选择性抑制 5-脂氧合酶 (5-LO) 和微粒体前列腺素 E2 合酶-1 (mPGES-1),IC50 值分别为 0.06 和 0.2 mM,从而抑制类二十烷酸的生物合成。 [2]
1. 对癌细胞的抗增殖活性:Embelin(0.1–100 μM)对高表达XIAP的人癌细胞系呈剂量依赖性抗增殖作用,GI₅₀值如下:HeLa(宫颈癌)2.5 μM、MCF-7(乳腺癌)3.2 μM、HepG2(肝癌)4.0 μM、A549(非小细胞肺癌)2.8 μM [1];对正常人肝细胞(L02)作用极弱,GI₅₀ > 50 μM [2] 2. 诱导XIAP依赖性凋亡:HeLa细胞经Embelin(1–10 μM)处理24小时后,呈剂量依赖性凋亡。5 μM浓度下,流式细胞术(Annexin V-FITC/PI染色)显示凋亡细胞比例从对照组的3%升至42%;western blot检测到caspase-3活性片段(p17)和PARP切割片段(89 kDa),5–10 μM时切割效应最强。该效应可被XIAP过表达逆转(5 μM Embelin时凋亡率降至12%)[1] 3. 抑制XIAP与caspase的结合:采用重组蛋白下拉实验,Embelin(0.5–10 μM)剂量依赖性破坏XIAP BIR3与caspase-9的相互作用。5 μM浓度下,caspase-9与XIAP的结合较对照组降低75%,且不影响caspase-9的自激活 [2] 4. 与化疗药的协同效应:Embelin(1 μM)与阿霉素(0.1 μM)在MCF-7细胞中协同作用:组合指数(CI)= 0.6(CI < 0.8为协同),抗增殖活性较单药提高4倍;其还增强顺铂诱导的A549细胞凋亡(2 μM Embelin + 5 μM顺铂时凋亡率从25%升至58%)[2] 5. 下调XIAP mRNA:HepG2细胞经Embelin(2–10 μM)处理12小时后,RT-PCR检测显示XIAP mRNA水平呈剂量依赖性降低30–60%,cIAP1/cIAP2 mRNA无显著变化 [2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Embelin 还被广泛用于各种动物模型中以研究 XIAP 的作用。在氧化偶氮甲烷/葡聚糖硫酸钠 (AOM/DSS) 诱导的结肠炎相关癌症 (CAC) 模型中,embelin 通过抑制体内肿瘤上皮细胞增殖并抑制 IL6 表达和 IL6 激活的 STAT3 来降低小鼠的发病率和肿瘤大小。
1. HeLa宫颈癌异种移植瘤疗效:雌性裸鼠(6–8周龄)皮下注射5×10⁶ HeLa细胞,肿瘤达100–150 mm³后随机分为3组(n=6/组):溶媒组(10% DMSO/90%玉米油)、25 mg/kg Embelin组、50 mg/kg Embelin组。药物每日腹腔注射1次,连续21天。50 mg/kg组肿瘤生长抑制率(TGI)达78%,肿瘤重量较溶媒组降低72%,未观察到完全肿瘤消退 [1] 2. MCF-7乳腺癌异种移植瘤疗效:携带MCF-7异种移植瘤(120–160 mm³)的雌性裸鼠经Embelin(50 mg/kg,腹腔注射,每日1次)+阿霉素(2 mg/kg,静脉注射,每3天1次)处理18天。联合组TGI达90%,显著高于Embelin单药组(65% TGI)或阿霉素单药组(60% TGI)。肿瘤免疫组化(IHC)显示XIAP染色降低65%,活化caspase-3染色增加4倍 [2] 3. HepG2肝癌异种移植瘤生存延长:携带HepG2异种移植瘤(140–180 mm³)的雄性裸鼠经50 mg/kg Embelin(腹腔注射,每日1次)处理28天后,中位生存期从溶媒组的35天延长至52天;癌进展标志物脾肿大逆转(脾脏重量从450 mg降至220 mg)[2] 4. 肿瘤组织药效动力学效应:HeLa异种移植瘤(50 mg/kg Embelin组)末次给药24小时后收集肿瘤,western blot显示XIAP蛋白水平较溶媒组降低60%,活化caspase-3水平增加3.5倍,证实体内凋亡信号激活 [1] |
| 酶活实验 |
荧光偏振实验在 Dynex 96 孔黑色圆底板中进行。通过在 DMSO 中添加 5 μL Embelin 稀释液样品、预孵育的 XIAP BIR3 蛋白 (0.06 M) 和测定缓冲液中的 Smac 肽 (SM7F) (0.01 M) N 末端,形成 125 L 的最终体积。每次测定中均使用结合肽对照(相当于 0% 抑制)和游离肽对照(相当于 100% 抑制)。结合的肽对照包含XIAP BIR3蛋白和SM7F。为了达到平衡,将板合并并在室温下孵育3小时。
1. XIAP/cIAP1 BIR3荧光偏振(FP)结合实验:将重组人XIAP BIR3或cIAP1 BIR3结构域(20 nM)与FITC标记的Smac N端肽(5 nM,序列:AVPIAQK-FITC)及系列浓度Embelin(0.001–100 μM)在实验缓冲液(50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5、150 mM NaCl、0.01% Tween-20、1 mM DTT)中25°C孵育60分钟。酶标仪检测FP信号(激发485 nm,发射535 nm),基于Embelin置换Smac肽导致的FP信号降低,采用单位点竞争性结合模型计算Ki值 [1] 2. cIAP2 BIR3 HTRF结合实验:在384孔板中进行,将重组人cIAP2 BIR3结构域(50 nM)与生物素化Smac肽(10 nM)及Embelin(0.01–1000 μM)在HTRF缓冲液(25 mM HEPES pH 7.4、150 mM NaCl、0.05% BSA)中混合。37°C孵育1小时后,加入链霉亲和素偶联Eu³⁺穴状化合物(10 nM)和抗cIAP2抗体偶联XL665(5 nM),继续孵育30分钟,检测620 nm(供体)和665 nm(受体)处FRET信号。IC₅₀定义为抑制50% Smac-cIAP2 BIR3相互作用的Embelin浓度 [2] 3. XIAP-caspase-9结合下拉实验:将GST标签的重组XIAP BIR3(1 μg)固定于谷胱甘肽琼脂糖珠,与His标签的caspase-9(0.5 μg)及Embelin(0.5–10 μM)在结合缓冲液(20 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.4、150 mM NaCl、0.1% Triton X-100)中4°C孵育2小时。珠子用结合缓冲液洗涤3次,结合蛋白用SDS上样缓冲液洗脱,western blot用抗His抗体检测caspase-9,定量条带强度计算XIAP-caspase-9结合的抑制率 [2] |
| 细胞实验 |
基于 MTT 的测定,根据制造商的说明使用细胞增殖试剂 WST-1,用于测量细胞生长。细胞(5000 个细胞/孔)在含有 10% FBS 和不同浓度 Embelin 的培养基中生长。四到五天后,将 WST-1 添加到每个孔中,并在 37°C 下孵育 1-3 小时。使用酶标仪测量 450 nm 处的吸光度,并在 650 nm 处进行校正。
1. 抗增殖实验(GI₅₀测定):将癌细胞(HeLa、MCF-7、HepG2、A549)接种于96孔板(1000–2000细胞/孔),过夜孵育(37°C、5% CO₂)。加入系列浓度Embelin(0.1–100 μM),培养72小时。采用MTT法(570 nm吸光度)或CellTiter-Glo发光法检测细胞活力,GI₅₀定义为抑制细胞生长50%的Embelin浓度 [1, 2] 2. 凋亡标志物及XIAP western blot实验:HeLa或MCF-7细胞接种于6孔板(5×10⁵细胞/孔),培养至70%汇合度。加入Embelin(1–10 μM),孵育24小时。用含蛋白酶抑制剂的RIPA缓冲液裂解细胞,裂解液经12% SDS-PAGE分离后转移至PVDF膜。膜用5%脱脂牛奶封闭,4°C下与一抗(XIAP、cIAP1、cIAP2、活化caspase-3、切割PARP、β-actin)孵育过夜,再与HRP偶联二抗孵育,ECL化学发光法显示蛋白条带 [1, 2] 3. 流式细胞术凋亡检测:HeLa细胞接种于12孔板(2×10⁵细胞/孔),经Embelin(1–10 μM)处理24小时后收集细胞,冷PBS洗涤,用Annexin V-FITC和PI室温避光染色15分钟。流式细胞术分析,凋亡细胞分为Annexin V阳性/PI阴性(早期凋亡)和Annexin V阳性/PI阳性(晚期凋亡)[1] 4. XIAP mRNA RT-PCR实验:HepG2细胞经Embelin(2–10 μM)处理12小时后,用RNA提取试剂盒提取总RNA,逆转录合成cDNA。采用XIAP、cIAP1、cIAP2及内参基因GAPDH的特异性引物进行PCR扩增,扩增产物经1.5%琼脂糖凝胶电泳分离,定量条带强度计算相对mRNA水平 [2] 5. 联合协同实验:MCF-7细胞经Embelin(0.5–5 μM)+阿霉素(0.05–0.5 μM)或Embelin(0.5–5 μM)+顺铂(1–10 μM)处理72小时,MTT法检测细胞活力,采用Chou-Talalay法评估协同效应(组合指数CI:CI < 0.8 = 协同,0.8–1.2 = 相加,>1.2 = 拮抗)[2] |
| 动物实验 |
50 mg/kg/day; p.o. AOM/DSS-induced colitis-associated cancer (CAC) model
1. HeLa Cervical Cancer Xenograft Model: Female athymic nude mice (6–8 weeks old, 18–22 g) were acclimated to the laboratory (12 h light/dark cycle, 22±2°C) for 7 days. HeLa cells (5×10⁶ cells in 0.2 mL PBS/matrigel 1:1) were subcutaneously injected into the right flank. When tumors reached 100–150 mm³ (≈10 days post-injection), mice were randomized into 3 groups (n=6/group). Embelin was formulated in 10% DMSO/90% corn oil (v/v). Doses were 25 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg, administered via intraperitoneal injection once daily for 21 days. The vehicle group received the same volume of 10% DMSO/90% corn oil. Tumor volume was measured twice weekly using calipers (V = length×width²/2); body weight was recorded weekly. At study end, mice were euthanized, tumors were excised, weighed, and stored at -80°C for western blot [1] 2. MCF-7 Breast Cancer Combination Model: Female nude mice were injected subcutaneously with 4×10⁶ MCF-7 cells (PBS/matrigel 1:1). When tumors reached 120–160 mm³, mice were divided into 4 groups (n=6/group): vehicle, Embelin (50 mg/kg, ip, qd), doxorubicin (2 mg/kg, iv, q3d), and combination. Treatment lasted 18 days. Doxorubicin was formulated in physiological saline. Tumor volume and body weight were monitored as described above. At study end, tumors were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, embedded in paraffin, sectioned (5 μm), and stained with antibodies against XIAP and cleaved caspase-3 for IHC [2] 3. HepG2 Hepatocellular Carcinoma Survival Model: Male nude mice were injected subcutaneously with 6×10⁶ HepG2 cells (PBS/matrigel 1:1). When tumors reached 140–180 mm³, mice were randomized into 2 groups (n=8/group): vehicle and 50 mg/kg Embelin (ip, qd for 28 days). Mice were monitored daily for survival; moribund mice (tumor volume > 2000 mm³ or severe weight loss >20%) were euthanized. Median survival was calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method. At study end, spleens were harvested and weighed [2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
1. Mouse Pharmacokinetics (Intraperitoneal Administration): Male CD-1 mice (n=3 per time point) received a single intraperitoneal dose of Embelin (50 mg/kg, formulated in 10% DMSO/90% corn oil). Blood samples (0.15 mL) were collected from the tail vein at 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12 hours post-dosing. Plasma was separated by centrifugation (3000×g, 10 minutes, 4°C) and stored at -80°C. Drug concentration was measured by HPLC-UV. Pharmacokinetic parameters (non-compartmental analysis): terminal half-life (t₁/₂) = 5.8 hours, Cmax = 4.2 μM, Tmax = 1 hour, clearance (CL) = 12.5 mL/min/kg [1]
2. Oral Bioavailability in Mice: Male CD-1 mice (n=3 per time point) received a single oral dose of Embelin (100 mg/kg, formulated in 0.5% methylcellulose/0.2% Tween-80). Plasma concentrations were measured by HPLC-UV; oral bioavailability (F) = 18% (calculated by comparing AUC₀-∞ with intraperitoneal administration) [1] 3. Plasma Protein Binding: Human and mouse plasma (500 μL) was mixed with Embelin (0.1–10 μM) and dialyzed using a 12–14 kDa cutoff membrane at 37°C for 4 hours. Free drug concentration in the dialysate was measured by HPLC-UV. Plasma protein binding rate: 92.3% (human), 90.5% (mouse) [1] 4. Tissue Distribution in Mice: Mice were intraperitoneally administered Embelin (50 mg/kg) and euthanized at 1 hour (Tmax). Tissues (liver, spleen, lung, tumor, brain, kidney) were collected, homogenized in PBS (1:1, w/v), and drug concentration was measured by HPLC-UV. Highest concentrations were in liver (15.6 μM) and spleen (12.8 μM); tumor concentration was 3.8 μM (tumor/plasma ratio = 0.9); brain concentration was low (0.4 μM, brain/plasma ratio = 0.1) [1] 5. In Vitro Metabolism (Liver Microsomes): Embelin (1 μM) was incubated with human liver microsomes (HLMs) or mouse liver microsomes (MLMs) in the presence of NADPH (1 mM) at 37°C. Samples were collected at 0, 5, 10, 20, 30, 60 minutes. Half-life (t₁/₂): 75 minutes (HLMs), 62 minutes (MLMs); intrinsic clearance (CLint): 22 μL/min/mg protein (HLMs), 26 μL/min/mg protein (MLMs). The main metabolite was identified as a glucuronidated derivative via HPLC-MS [2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
1. Acute Toxicity in Mice: Male and female CD-1 mice (n=4/sex/dose) received a single intraperitoneal dose of Embelin (100, 150, 200, 250 mg/kg). Mice were observed for 14 days. The maximum tolerated dose (MTD) was 200 mg/kg: 250 mg/kg caused 30% mortality (1/4 mice/sex) with signs of lethargy and abdominal distension (onset 12 hours post-dosing). At 200 mg/kg, transient weight loss (max 7%, recovered by day 5) was observed; no other toxic signs were noted [1]
2. Subacute Toxicity in Xenograft Models: In the HeLa and MCF-7 xenograft studies (50 mg/kg, ip, qd for 21/18 days), Embelin did not cause significant body weight loss (<5%) or abnormal clinical signs (e.g., diarrhea, piloerection). Serum collected at study end showed no significant changes in ALT, AST (liver function), BUN, or creatinine (kidney function) vs. vehicle [1, 2] 3. Hematological Toxicity: Mice treated with Embelin (50 mg/kg, ip, qd for 21 days) had complete blood counts (CBC) measured. No significant changes were observed in white blood cells (WBC), red blood cells (RBC), platelets, or hemoglobin vs. vehicle, indicating no myelosuppression [1] 4. Tissue Toxicity: Histopathological analysis of liver, kidney, spleen, and lung from mice treated with 50 mg/kg Embelin (ip, qd for 21 days) showed no significant lesions (e.g., necrosis, inflammation) vs. vehicle [1] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
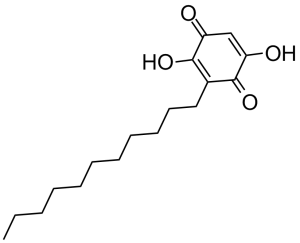
Embelin is a member of the class of dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinones that is 2,5-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone which is substituted by an undecyl group at position 3. Isolated from Lysimachia punctata and Embelia ribes, it exhibits antimicrobial, antineoplastic and inhibitory activity towards hepatitis C protease. It has a role as a hepatitis C protease inhibitor, an antimicrobial agent, an antineoplastic agent and a plant metabolite.
Embelin has been reported in Embelia schimperi, Ardisia paniculata, and other organisms with data available. 1. Background: Embelin is a naturally occurring benzoquinone derivative isolated from the fruits of plants in the genus Embelia (e.g., Embelia ribes). It was identified as a selective XIAP inhibitor and developed as a potential anticancer agent due to its ability to restore apoptotic signaling in cancer cells with high IAP expression [1, 2] 2. Mechanism of Action: Embelin binds to the BIR3 domain of XIAP with high affinity, competitively displacing caspase-9 (and weakly displacing caspase-3) from XIAP. This relieves XIAP-mediated inhibition of caspases, activating the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. It also downregulates XIAP mRNA levels in some cancer cell lines (e.g., HepG2), further reducing XIAP protein expression [1, 2] 3. Natural Product Advantage: Compared to synthetic IAP inhibitors (e.g., AT406), Embelin has the advantage of being a natural product with potential better biocompatibility and lower off-target toxicity. However, its low oral bioavailability (18% in mice) limits oral administration, and intraperitoneal injection is preferred in preclinical studies [1] 4. Potential Indications: Preclinical data support Embelin for treating solid tumors with high XIAP expression, including cervical cancer, breast cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, and non-small cell lung cancer. It also shows promise in combination with chemotherapy (e.g., doxorubicin, cisplatin) to overcome chemoresistance caused by IAP overexpression [1, 2] 5. Research Limitations: At the time of literature publication, Embelin was in preclinical development. Its main limitations included low oral bioavailability and moderate potency (Ki for XIAP = 4.1 nM vs. synthetic inhibitors with Ki < 1 nM), which prompted further structural modification to improve pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties [1, 2] |
| 分子式 |
C17H26O4
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
294.39
|
|
| 精确质量 |
294.183
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 69.36; H, 8.90; O, 21.74
|
|
| CAS号 |
550-24-3
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
3218
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Yellow to orange solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.131
|
|
| 沸点 |
431.9±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
145-146 ºC
|
|
| 闪点 |
229.1±25.2 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.538
|
|
| LogP |
5.7
|
|
| tPSA |
74.6
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
10
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
21
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
432
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
O([H])C1C(C([H])=C(C(C=1C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])=O)O[H])=O
|
|
| InChi Key |
IRSFLDGTOHBADP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C17H26O4/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-13-16(20)14(18)12-15(19)17(13)21/h12,18,21H,2-11H2,1H3
|
|
| 化学名 |
2,5-dihydroxy-3-undecylcyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione
|
|
| 别名 |
Embelic acid; NSC91874; NSC91874; Embelin; NSC 91874; Emberine
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (8.49 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浮液;超声助溶。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.49 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3969 mL | 16.9843 mL | 33.9685 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6794 mL | 3.3969 mL | 6.7937 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3397 mL | 1.6984 mL | 3.3969 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT06042647 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: 0.01% Halobetasol Drug: 0.045% Tazarotene |
Psoriasis Vulgaris | Dermatology Consulting Services, PLLC |
July 13, 2023 | Phase 4 |
| NCT03926299 | Active Recruiting |
Device: FotonaSmooth SP® Spectro laser device Drug: Clobetasol propionate 0.05% ointment |
Chronic Skin Disease Vulvar Lichen Sclerosus |
Prof. Dr. Volker Viereck | July 15, 2019 | Not Applicable |
| NCT01893567 | Completed | Drug: Clobex Spray | Plaque Psoriasis | Galderma R&D | July 2013 | Phase 4 |
| NCT00852761 | Completed | Drug: Olux-E Foam Drug: Clobex lotion |
Plaque-Type Psoriasis | Stiefel, a GSK Company | March 2009 | Phase 4 |
| NCT00715975 | Completed | Drug: halobetasol Drug: clobetasol |
Psoriasis | Azidus Brasil | July 2008 | Phase 2 Phase 3 |
 |
|---|