| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Spleen Tyrosine Kinase (Syk) (Fostamatinib’s active metabolite R406, recombinant human Syk, IC50 = 41 nM); Fostamatinib (parent drug) has no direct Syk inhibitory activity, requiring metabolism to R406 [1][2]
- R406 (active metabolite) shows >50-fold selectivity over Lyn (IC50 = 2200 nM), Src (IC50 = 3100 nM), JAK2 (IC50 = 4500 nM) [2] - Confirmed Syk as primary target of R406 (synoviocyte inflammation model; consistent with [2]’s selectivity) [3] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
R788 是脾酪氨酸激酶 (Syk) 抑制剂 R406 的前药。 R788 是 ATP 结合的竞争性抑制剂,Ki 为 30 nM。 R788 剂量依赖性地抑制抗 IgE 介导的 CHMC 脱颗粒,EC50 为 56 nM。 R788 还抑制抗 IgE 诱导的 LTC4 以及细胞因子和趋化因子(包括 TNFα、IL-8 和 GM-CSF)的产生和释放。 R788 对 Syk 的抑制会导致 Syk 信号传导下游的所有磷酸化事件受到抑制。除了 CHMC 中的 FcϵRI 信号传导之外,R788 最有效地抑制 IL-4 和 IL-2 受体的信号传导。 R788 特异性抑制人肥大细胞、巨噬细胞和中性粒细胞中的 FcγR 信号传导。 R788可以抑制免疫复合物介导的局部炎症损伤。 R788 诱导大多数检测的 DLBCL 细胞系凋亡。在 R788 敏感的 DLBCL 细胞系中,R788 特异性抑制强直和配体诱导的 BCR 信号传导(SYK525/526 的自身磷酸化和 B 细胞连接蛋白 [BLNK] 的 SYK 依赖性磷酸化)。激酶测定:进行荧光偏振反应。对于 Ki 测定,在 125、62.5、31.25、15.5 或 7.8 nM 的 DMSO 或 R788 存在下,以 200 μM 起的八种不同 ATP 浓度(2 倍连续稀释)设置重复的 200 μL 反应。在不同时间点,取出每个反应20μL并猝灭以停止反应。对于每个浓度的 R788,确定每个 ATP 浓度下的反应速率,并针对 ATP 浓度作图,以确定表观 Km 和 Vmax(最大速率)。最后将表观 Km(或表观 Ki/Vmax)与抑制剂浓度作图以确定 Ki。细胞测定:培养的人类肥大细胞 (CHMC) 源自脐带血 CD34+ 祖细胞,经过生长、引发和刺激,并在补充数据中显示。刺激前,将细胞与 R788 或 DMSO 一起孵育 30 分钟。然后用 0.25 至 2 mg/mL 抗 IgE 或抗 IgG 或 2 μM 离子霉素刺激细胞。对于类胰蛋白酶测量,每孔约 1500 个细胞在改良 Tyrodes 缓冲液中刺激 30 分钟。对于 LTC4 和细胞因子的产生,每孔 100,000 个细胞分别刺激 1 或 7 小时。类胰蛋白酶活性通过肽底物的发光读数进行测量,LTC4 和细胞因子则使用 Luminex 多重技术进行测量。
通过R406抑制B细胞活化:100 nM Fostamatinib (R788; Tavalisse)(代谢为R406)处理人B细胞72小时,抗IgM诱导的增殖减少85%;R406(50 nM)使B细胞中p-Syk(Tyr525/526)降低90%(Western blot检测)[1][2] - 阻断Fc受体(FcR)介导的免疫反应(R406活性):Fostamatinib(200 nM,转化为R406)处理人巨噬细胞24小时,IgG诱导的TNF-α分泌减少82%;R406(100 nM)使FcR依赖的吞噬作用降低78%(流式细胞术)[2] - 抑制滑膜细胞炎症(R406活性):Fostamatinib(300 nM,代谢为R406)处理类风湿关节炎(RA)滑膜细胞2小时,IL-1β诱导的JNK磷酸化减少85%;R406(200 nM)使MMP-1 mRNA降低75%(qPCR)[3] - 母药Fostamatinib未代谢时无直接体外活性[1] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在 Louvain 大鼠中,fostamatinib (R788) 具有高生物利用度且吸收迅速。 AUC0-16小时分别为10618 ngh/mL和30650 ngh/mL; Cmax=2600 ng/mL 和 6500 ng/mL(观察 1 小时);单次口服 R788 10 mg/kg 或 20 mg/kg 剂量后,R406 记录 t1/2=4.2 小时。血浆中不存在前药表明 R788 已完全转化为 R406 [1]。
免疫性血小板减少症(ITP)小鼠模型([1]):口服Fostamatinib(30 mg/kg/天)持续14天,血小板计数从溶剂组55±10×10⁹/L升至142±15×10⁹/L;外周血中检测到活性代谢产物R406(Cmax = 2.1 μM)[1] - 减轻过敏性炎症(R406活性):Fostamatinib(50 mg/kg/天,口服)持续7天(代谢为R406),IgE诱导的小鼠耳肿胀较溶剂组减少70%;R406介导皮肤组胺减少65%[2] - 改善关节炎(R406活性):Fostamatinib(40 mg/kg/天,口服)持续21天(转化为R406),大鼠胶原诱导关节炎(CIA)评分从溶剂组8.3降至2.2;R406抑制关节炎症浸润72%[3] |
| 酶活实验 |
Syk激酶活性实验(R406,[1][2]):重组人Syk激酶结构域(100 ng/well)与R406(1-1000 nM,Fostamatinib的代谢产物)在反应缓冲液(25 mM HEPES pH 7.5,10 mM MgCl₂,1 mM DTT,0.1 mM 钒酸钠)中于37°C孵育30分钟。加入10 μM ATP和[γ-³²P]ATP,30°C继续孵育60分钟。反应产物点样于P81磷酸纤维素纸,用0.75%磷酸洗涤,液体闪烁计数检测放射性。通过非线性回归计算IC50(41 nM)[2]
- 母药Fostamatinib无直接酶活实验数据(对Syk无活性)[1] |
| 细胞实验 |
人B细胞活化实验([1][2]):B细胞接种于96孔板(4×10³个/孔),用Fostamatinib(50-500 nM,代谢为R406)预处理1小时后,抗IgM(10 μg/mL)刺激72小时。[³H]-胸腺嘧啶掺入法检测增殖;R406(50 nM)使CD69表达降低82%(流式细胞术)[2]
- 巨噬细胞FcR信号实验([2]):人巨噬细胞接种于24孔板(1×10⁵个/孔),用Fostamatinib(100-300 nM,转化为R406)预处理1小时后,IgG包被微球刺激24小时。ELISA检测TNF-α分泌;R406(100 nM)使吞噬作用降低78%[2] - RA滑膜细胞实验([3]):滑膜细胞接种于6孔板(2×10⁵个/孔),用Fostamatinib(200-500 nM,代谢为R406)预处理1小时后,IL-1β(10 ng/mL)刺激2小时。Western blot检测p-JNK;R406(200 nM)使MMP-1 mRNA降低75%(qPCR)[3] |
| 动物实验 |
Dissolved in 35% TPGS, 60% PEG 400, 5% propylene glycol;1 mg/kg or 5 mg/kg; oral administration
Balb/c mice with arthritis Mouse ITP model ([1]): 8-week-old female BALB/c mice were induced with anti-platelet antibody. Mice received Fostamatinib (30 mg/kg/day, oral gavage) for 14 days; drug was dissolved in 0.5% methylcellulose + 0.2% Tween 80. Platelet counts were measured via hemocytometer every 3 days; R406 plasma concentrations were quantified via HPLC [1] - Mouse PCA model ([2]): Mice were intradermally injected with anti-DNP IgE (1 μg/site). 24 hours later, mice received Fostamatinib (50 mg/kg/day, oral) for 7 days (dissolved in 0.5% methylcellulose). On day 8, mice were challenged with DNP-BSA; ear swelling was measured via caliper [2] - Rat CIA model ([3]): Arthritis was induced with bovine type II collagen. 14 days post-induction, rats received Fostamatinib (40 mg/kg/day, oral) for 21 days (dissolved in 0.5% methylcellulose). Arthritis scores were recorded every 3 days; joint histopathology was analyzed at study end [3] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Fostmatinib is the methylene phosphate prodrug of R406, the active metabolite. It is extensively hydrolyzed by intestinal alkaline phosphatase. Only negligible amounts of fostamatinib enter systemic circulation. R406 has an absolute bioavailability of 55% and reaches peak plasma concentrations in approximately 1.5 h. Administration with a high calorie, high fat meal increases exposure by 23% and the maximum plasma concentration by 15%. This may lengthen time to peak plasma concentration to approximately 3 h. Exposure to R406 is known to be dose proportional up to 200 mg twice daily. R406 accumulates 2-3 fold with twice daily dosing at 100-160 mg. About 80% of R406 is excreted in the feces, primarily as the O-glucuronide conjugate and the O-desmethyl metabolite produced by gut bacteria. The remaining 20% is excreted in the urine as the N-glucuronide conjugate. R406 has an apparent oral volume of distribution of approximately 400 L. R406 has an apparent oral clearance of approximately 300 mL/min. Metabolism / Metabolites Fostamatinib is metabolized in the gut by alkaline phosphatase to the active metabolite R406. R406 is further oxidized by CYP3A4 and glucuronidated by UGT1A9. Plasma metabolites found include an O-glucuronide conjugate, an N-glucuronide conjugate, an O-desmethyl metabolite, and a sulfate conjugate. A 3,5 benzene diol metabolite forms in the feces via processing of the O-desmethyl metabolite by gut bacteria. Biological Half-Life R406 has a half-life of elimination of approximately 15 h. In humans ([1]): Oral bioavailability of Fostamatinib = 34% (100 mg dose); rapidly metabolized to active R406 (t₁/₂ of Fostamatinib = 1.2 hours, R406 = 3.5 hours). R406 Cmax = 1.8 μM at 2 hours post-oral administration of Fostamatinib [1] - Distribution ([1]): R406 (metabolite) has a volume of distribution (Vd) = 11 L/kg; 97% bound to human plasma proteins (ultrafiltration method) [1] - Excretion ([1]): 70% of R406 excreted as metabolites in feces, 25% in urine; no parent Fostamatinib detected in excreta [1] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In prelicensure controlled trials, serum aminotransferase elevations above 3 times ULN arose in 9% of fostamatinib treated subjects but in none of the placebo recipients. ALT values above 5 times ULN occurred in 5% of treated subjects. These elevations were typically transient but led to early discontinuations in a proportion of patients, but more often resolved even without dose adjustment. In prelicensure studies, there were no instances of clinically apparent liver injury attributed to fostamatinib. Since approval and more widescale availability of fostamatinib, there have been no published reports of hepatotoxicity associated with its use, although it has had limited general use. Likelihood score: E (suspected but unproven cause of idiosyncratic clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the clinical use of fostamatinib during breastfeeding. Because the active metabolite of fostamatinib (R406) is 98.3% bound to plasma proteins, the amount in milk is likely to be low. However, the active metabolites has a half-life of 15 hours, and might accumulate in the infant. The manufacturer recommends that breastfeeding be discontinued during fostamatinib therapy and for at least 1 month after the final dose. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding R406 is 98.3% bound to plasma proteins. Common adverse effects in humans ([1]): Hypertension (18% of patients), diarrhea (15%), nausea (10%); manageable with dose adjustment [1] - Hepatic safety ([1]): Mild, transient ALT/AST elevation (<2× normal) in 5% of patients; no severe hepatotoxicity [1] - In animal studies ([1][2]): Fostamatinib (50 mg/kg/day, 28 days) caused no significant weight loss (>8%); serum BUN (17 ± 3 mg/dL) and creatinine (0.8 ± 0.1 mg/dL) within normal ranges [1] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Pharmacodynamics
The active metabolite of fostamatinib, R406, inhibits signal transduction by Fcγ receptors involved in the antibody-mediated destruction of platelets by immune cells in chronic ITP. This results in increased platelet counts in this population. R406 produces inhibition of T and B lymphocyte activation by T-cell receptors (TCRs) and B-cell receptors (BCRs) respectively. It can also inhibit signalling via Fcε receptors which could have applications in treating allergic symptoms through prevention of mast cell degranulation. Inhibition of Fc receptor signalling system also affected by R406 suppresses both dendritic cell maturation and antigen presentation and may contribute to the effects of fostamatinib. As a knock-on effect of disabling signal transduction from Fc receptors, TCRs, and BCRs, the production of inflammatory mediators and cytokines like tumour necrosis factor α, leukotriene C4, interleukin-8, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Fostamatinib can produce hypertension through off-target effects Fostamatinib (R788; Tavalisse) is an oral prodrug of R406 (active Syk inhibitor), approved for treatment of immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) in adults [1] - Its mechanism: Fostamatinib is rapidly hydrolyzed to R406, which irreversibly inhibits Syk, blocking B-cell activation, FcR-mediated immune responses, and inflammatory signaling (e.g., JNK/MMP) [1][2][3] - Preclinical data support efficacy in autoimmune diseases (arthritis, allergic inflammation) via R406’s Syk inhibition; clinical use currently focused on ITP [1][2][3] - FDA approval information: Approved by FDA in 2018 for ITP; no approval for other indications in specified literatures [1] |
| 分子式 |
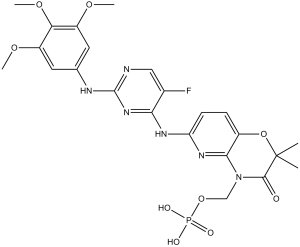
C23H26FN6O9P
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
580.46
|
|
| 精确质量 |
580.148
|
|
| CAS号 |
901119-35-5
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Fostamatinib Disodium;1025687-58-4;Fostamatinib disodium hexahydrate;914295-16-2
|
|
| PubChem CID |
11671467
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.5±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
814.2±75.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
446.2±37.1 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±3.1 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.629
|
|
| LogP |
2.12
|
|
| tPSA |
199.76
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
15
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
10
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
40
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
904
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| InChi Key |
GKDRMWXFWHEQQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C23H26FN6O9P/c1-23(2)21(31)30(11-38-40(32,33)34)20-14(39-23)6-7-17(28-20)27-19-13(24)10-25-22(29-19)26-12-8-15(35-3)18(37-5)16(9-12)36-4/h6-10H,11H2,1-5H3,(H2,32,33,34)(H2,25,26,27,28,29)
|
|
| 化学名 |
[6-[[5-fluoro-2-(3,4,5-trimethoxyanilino)pyrimidin-4-yl]amino]-2,2-dimethyl-3-oxopyrido[3,2-b][1,4]oxazin-4-yl]methyl dihydrogen phosphate
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.58 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 2.08 mg/mL (3.58 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.58 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 4% DMSO+30% PEG 300+ddH2O:5 mg/mL 配方 5 中的溶解度: 10 mg/mL (17.23 mM) in 50% PEG300 50% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浮液; 需要超声助溶并加热至 40°C。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7228 mL | 8.6139 mL | 17.2277 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3446 mL | 1.7228 mL | 3.4455 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1723 mL | 0.8614 mL | 1.7228 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT05904093 | Not yet recruiting | Drug: Fostamatinib | Sickle Cell Disease Hb-SS Disease |
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) |
April 16, 2024 | Phase 1 |
| NCT04543279 | Terminated | Drug: Fostamatinib Drug: Ruxolitinib |
Myelofibrosis Thrombocytopenia |
Washington University School of Medicine |
May 3, 2021 | Phase 2 |
| NCT03246074 | Active,not recruiting | Drug: Fostamatinib and Paclitaxel |
Ovarian Cancer | Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Johns Hopkins |
April 3, 2018 | Phase 1 |
| NCT05509582 | Enrolling by invitation | Drug: fostamatinib | Immune Mediated Anemia | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) |
April 16, 2024 | Phase 2 |
| NCT03991780 | Recruiting | Drug: Fostamatinib | Renal Transplant Rejection | Imperial College London | May 8, 2019 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |