| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
The pharmacokinetics of intravenously administered gadodiamide in normal subjects conforms to an open, two-compartment model. Gadodiamide is eliminated primarily in the urine with 95.4 ± 5.5% (mean ± SD) of the administered dose eliminated by 24 hours. The volume of distribution of gadodiamide (200 ± 61 mL/kg) is equivalent to that of extracellular water. Following GBCA administration, gadolinium is present for months or years in the brain, bone, skin, and other organs. The renal and plasma clearance rates of gadodiamide are nearly identical (1.7 and 1.8 mL/min/kg, respectively), and are similar to that of substances excreted primarily by glomerular filtration. The objective of this study was to determine the gadolinium (Gd) concentration remaining in human bone tissue after administration of standard clinical doses of 2 Gd-based contrast agents: ProHance and Omniscan. After administration of 0.1 mmol/kg of Gd chelate to patients undergoing hip replacement surgery, bone specimens were collected and analyzed, and compared with an age-matched control population without a history of Gd chelate administration. Bone specimens were collected fresh, refrigerated, and subsequently frozen. After grinding and freeze-drying, tissue digestion was performed using Teflon bombs and concentrated nitric acid. A method for analysis of Gd in bone specimens was developed and validated using inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy (ICP-MS). Results were compared with a previous study using a different technique for analysis of the same tissue specimens. Tissue retention was 1.77+/-0.704 microg Gd/g bone (n=9) for Omniscan and 0.477+/-0.271 microg Gd/g bone (n=10) for ProHance measured by ICP-MS. These findings confirmed results from the previous ICP-AES study. Omniscan (Gd[DTPA-BMA]) left approximately 4 times (previous study 2.5 times) more Gd behind in bone than did ProHance (Gd[HP-DO3A]). Twenty-seven patients--nine with severely reduced renal function (glomerular filtration rate, 2-10 mL/min), nine undergoing hemodialysis, and nine undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis--were followed up for 5, 8, and 22 days, respectively, after receiving gadodiamide injection (0.1 mmol per kilogram body weight). Gadodiamide injection caused no changes in renal function. In patients with severely reduced renal function, the elimination half-life of gadodiamide injection was prolonged (34.3 hours +/- 22.9) compared with data in healthy volunteers (1.3 hours +/- 0.25). An average of 65% of the gadodiamide injected was eliminated during a hemodialysis session. After 22 days of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis, 69% of the total amount of gadodiamide was excreted; this reflects the low peritoneal clearance. In all patients, no metabolism or transmetallation of gadodiamide was found. ... The pharmacokinetic behavior of gadodiamide was consistent with its extracellular distribution. ... Gadodiamide was shown to be excreted rapidly, primarily through the kidneys. In rats, 94% of the administered dose was excreted in the urine within the first 24 hours after administration. Approximately 1% to 4% appeared in the feces during the same period. ... /In rats/ following iv dosing of gadodiamide (NaCa DTPA-BMA) (0.015 mmol/kg) in a (14)C-labeled form, plasma concentrations of the drug declined rapidly with an elimination half-live of 0.31 hr, a distribution volume of 244 mL/kg and a plasma clearance of 9.2 mL/min/kg. These results demonstrate that NaCa DTPA-BMA distributes into the extracellular fluid compartment and is renally excreted via glomerular filtration. Of the dose of radioactivity given, 86.6% was excreted in urine by 4 hr after injection, and 95.3% in urine and 3.3% in feces by 120 hr. ... For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for GADODIAMIDE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites There is no detectable biotransformation or decomposition of gadodiamide. In addition, experiments were done /in rats/ to clarify the in vivo metabolism of gadodiamide (NaCa DTPA-BMA). Results show small quantities of transchelated forms of NaCa DTPA-BMA in urine. HPLC analysis demonstrated these metabolites were the Zn and Cu forms of the drug, resulting from displacement of the Ca ion in the NaCa DTPA-BMA molecule by endogeneous Zn or Cu. Further analyses by HPLC and ICP-AES demonstrate that the unchanged parent drug, the Zn and the Cu forms occur in relative quantities of approximately 92%, 7%, and 1%, respectively. This demonstrates that the Ca ion in caldiamide sodium can be replaced by Zn or Cu ions in vivo, but only to a small extent. Biological Half-Life The mean distribution and elimination half-lives (reported as mean ± SD) were calculated to be of 3.7 ± 2.7 minutes and 77.8 ± 16 minutes, respectively. ... /In rats/ following iv dosing of gadodiamide (NaCa DTPA-BMA) (0.015 mmol/kg) in a (14)C-labeled form, plasma concentrations of the drug declined rapidly with an elimination half-live of 0.31 hr ... The pharmacokinetic behavior of gadodiamide was consistent with its extracellular distribution. Its half-life in rats, rabbits, and monkeys was short, 18, 38, and 75 minutes, respectively. The pharmacokinetics of intravenously administered gadodiamide in normal subjects conforms to an open, two-compartment model with mean distribution and elimination half-lives (reported as mean + or - SD) of 3.7 + or - 2.7 minutes and 77.8 + or - 16 minutes, respectively. ... The average half-time of gadodiamide was 1.93 hr (SD 0.55) /in thirteen hemodialysis patients with abdominal disease receiving iv gadodiamide (0.1 mmol/kg body weight)/. Twenty-seven patients--nine with severely reduced renal function (glomerular filtration rate, 2-10 mL/min), nine undergoing hemodialysis, and nine undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis--were followed up for 5, 8, and 22 days, respectively, after receiving gadodiamide injection (0.1 mmol per kilogram body weight). Gadodiamide injection caused no changes in renal function. In patients with severely reduced renal function, the elimination half-life of gadodiamide injection was prolonged (34.3 hours +/- 22.9) compared with data in healthy volunteers (1.3 hours +/- 0.25). ... |
|---|---|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Gadodiamide is a contrast agent for intravenous use in MRI to visualize lesions with abnormal vascularity (or those thought to cause abnormalities in the blood-brain barrier) in the brain (intracranial lesions), spine, and associated tissues. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: The possibility of a reaction, including serious, life threatening, fatal, anaphylactoid or cardiovascular reactions or other idiosyncratic reactions should always be considered especially in those patients with a known clinical hypersensitivity, a history of asthma, or other allergic respiratory disorders. Gadolinium-based contrast agents increase the risk for nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) in patients with acute or chronic severe renal insufficiency and in patients with acute renal insufficiency of any severity due to the hepato-renal syndrome or in the perioperative liver transplantation period. In these patients, avoid use of gadolinium-based contrast agents unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrast enhanced MRI. Among the factors that may increase the risk for NSF are repeated or higher than recommended doses of a gadolinium-based contrast agent and the degree of renal function impairment at the time of exposure. Inadvertent intrathecal use of Omniscan has occurred and caused convulsions, coma, sensory and motor neurologic deficits. Following 1157 gadodiamide-enhanced examinations, measured serum calcium spuriously dropped from 8.65 to 8.33 mg/dL and 34 patients had spurious critical hypocalcemia (<6 mg/dL). Of 60 patients with high-dose gadodiamide injection and renal insufficiency, 36.7% had spurious critical hypocalcemia immediately post MRI. In 216 patients with renal insufficiency, the mean serum magnesium level increased slightly from 1.69 to 1.77 mEq/L following gadodiamide injection. ANIMAL STUDIES: Gadodiamide injection has been shown to have a remarkably low acute lethal toxicity, superior to that of gadopentetate dimeglumine injection or gadoterate meglumine. In comparison with gadopentetate dimeglumine injection, gadodiamide injection had fewer effects on cardiovascular and hemodynamic function after rapid iv injection in anesthetized dogs. Similar to all known iv administered diagnostic imaging agents, gadodiamide injection produces vacuolization of the proximal tubular cells in the kidney, without any change in renal function. The vacuolization was only moderate in degree and was shown to have regressed partially during the 7 days after administration. Gadodiamide injection produced no significant irritation when administered by a variety of intravascular and extravascular routes. In monkeys, administration of gadodiamide daily for 28 days had no effect on the kidney . The compound was well tolerated in monkeys for 28 consecutive days. In rats, significant toxicity occurred only at high doses, particularly in male animals, and the pattern of toxicity (involving the stomach, testes, and skin) suggested a disturbance of zinc metabolism. Studies in rabbits showed that gadodiamide at doses 5 times the maximum recommended human dose increased the incidence of skeletal and visceral abnormalities in the offspring. Gadodiamide has been shown to have an adverse effect on embryo-fetal development in rabbits that is observed as an increased incidence of flexed appendages and skeletal malformations administered for 13 days during gestation (approximately 2 times the maximum human cumulative dose) . Skeletal malformations may be due to maternal toxicity since the body weight of the dams was significantly reduced in response to gadodiamide administration during pregnancy. The results of the following genotoxicity assays were negative: bacterial reverse mutation assay, CHO/HGPRT forward mutation assay, CHO chromosome aberration assay, and the in vivo mouse micronucleus assay. Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Gadodiamide releases more free gadolinium than some other gadolinium-containing contrast agents. Some European guidelines recommend a 24-hour interruption of breastfeeding after a dose, but guidelines developed by several North American professional organizations state that breastfeeding need not be disrupted after a nursing mother receives a gadolinium-containing contrast medium. Other agents may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants A mother with neuromyelitis optica was nursing her 38-day-old male infant. Each breastfeeding session was about 15 minutes every 2 hours. She was given gadodiamide (dose not specified) before an MRI scan. She withheld breastfeeding for 6 to 8 hours after the injection. Her infant experienced no immediate adverse effects. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Gadodiamide does not bind to human serum proteins in vitro. Interactions ... Urine and serum profiles were monitored for 24 days after iv injections of saline, diatrizoate, iohexol, gadopentetate dimeglumine, and gadodiamide in high doses (4.59 mmol/kg body weight) in rats that received a weekly intraperitoneal (ip) injection of cisplatin (1 mg/kg) for 10 weeks. There were 10 rats in each group. ... Light and electron microscopy showed severe morphologic changes, including tubular dilatation, atrophy, and necrosis induced by cisplatin; however, the contrast media did not induce any additional morphologic changes. Gadopentetate dimeglumine, diatrizoate, and iohexol significantly increased (3-20 times) albuminuria compared with iv saline in cisplatin nephropathy, whereas gadodiamide did not. Albuminuria was highest after diatrizoate injection. All four contrast media caused an immediate and transient significant increase in the excretion of the brush border enzymes alkaline phosphatase and gamma-glutamyltransferase (125-500 times) and the cytoplasmatic enzymes alanine aminopeptidase and lactate dehydrogenase (16-100 times). Compared with saline, the ionic agents significantly increased the excretion of both glucose (two times) and sodium (three to five times), whereas the nonionic agents did not. /The authors concluded that/ high doses of radiologic and magnetic resonance contrast agents cause temporary dysfunction in rats with cisplatin nephropathy. Gadodiamide caused the least dysfunction and diatrizoate the most. ... /The case of/ a 54-year-old woman in whom a /spuriously/ "critically low" serum calcium level was measured with standard colorimetric assay after gadodiamide-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging /is reported/. The same phenomenon was noted in 2 other patients ... Repeat serum calcium measurements performed several hours later were within normal limits. Commercially available gadolinium-based contrast agents might precipitate critically low serum calcium values when measured by standard colorimetric assay. Physician awareness of gadodiamide-induced spurious hypocalcemia might prevent unnecessary therapeutic interventions. ... A case in which a 78-year-old man had a /spuriously/ "critically low" serum calcium level measured with use of standard colorimetric assay after gadodiamide administration during magnetic resonance angiography /is reported/. Reanalysis of the same serum specimen using absorption spectroscopy revealed normal calcium values, confirming the diagnosis of spurious hypocalcemia. Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Mouse iv 14 mmol/kg LD50 Mouse iv 34 mmol/kg /Gadodiamide injection/ |
| 其他信息 |
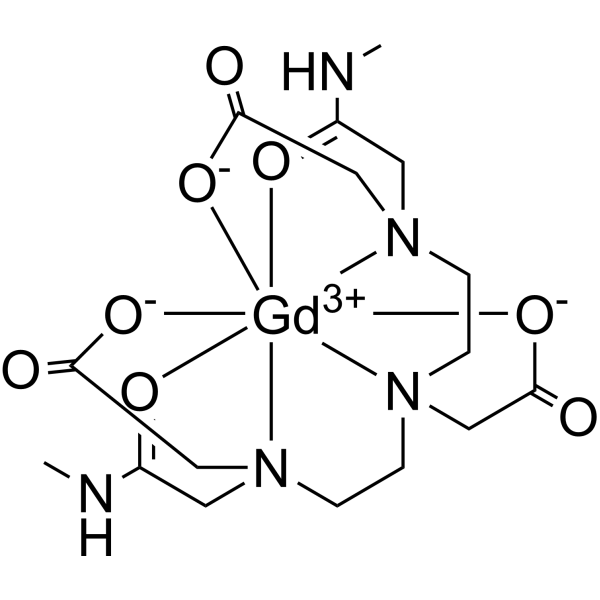
Gadodiamide is a linear, non-ionic gadolinium-based contrast agent (GBCA) that is used in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) procedures to assist in the visualization of blood vessels. GBCAs constitute the largest group of MR agents, and they are thought to be safer than nonionic iodinated contrast agents. Approved by the FDA in 1993, gadodiamide is the first non-ionic GBCA to be used. However, since linear, non-ionic GBCA is less stable than macrocyclic or ionic GBCA, gadodiamide can potentially lead to more gadolinium retention in the brain and thus more likely to cause side effects.
Gadodiamide is a Paramagnetic Contrast Agent. The mechanism of action of gadodiamide is as a Magnetic Resonance Contrast Activity. Gadodiamide is a paramagnetic gadolinium-based contrast agent (GBCA), with imaging activity upon magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). When placed in a magnetic field, gadodiamide generates a large local magnetic field, which can enhance the relaxation rate of nearby protons. This change in proton relaxation dynamics, iincreases the MRI signal intensity of tissues in which gadodiamide has accumulated; therefore, visualization of those tissues is enhanced. Drug Indication Gadodiamide is indicated for the visualization of lesions with abnormal vascularity in the brain (intracranial lesions), spine, and associated tissues and the body (including the thoracic (noncardiac), abdominal, pelvic cavities, and retroperitoneal space) by the FDA and Health Canada. Additionally, gadoliamide is approved by Health Canada to detect and localize tenosis in renal arteries and aorto-iliac arteries in magnetic resonance angiography (MRA). Mechanism of Action Gadodiamide paramagnetic molecule that develops a magnetic moment when placed in a magnetic field. The magnetic moment alters the relaxation rates of water protons in its vicinity in the body. Its use in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows to selectively increase contrast in tissues where gadodiamide accumulates. Therapeutic Uses Contrast Media Omniscan is a gadolinium-based contrast agent indicated for intravenous use in MRI to visualize lesions with abnormal vascularity (or those thought to cause abnormalities in the blood-brain barrier) in the brain (intracranial lesions), spine, and associated tissues. /Included in US product label/ Omniscan is a gadolinium-based contrast agent indicated for intravenous use in MRI to facilitate the visualization of lesions with abnormal vascularity within the thoracic (noncardiac), abdominal, pelvic cavities, and the retroperitoneal space. /Included in US product label/ ... To evaluate the safety and effectiveness of gadodiamide-enhanced magnetic resonance (MR) angiography with single and triple doses in the assessment of abdominal arterial stenoses ... One hundred five patients were included in the randomized, double-blind, phase III multicenter trial. Results of MR angiography with 0.1 mmol/kg and 0.3 mmol/kg doses of gadodiamide were compared with those of digital subtraction angiography (DSA) and according to dose ... No serious adverse events were observed. The mean contrast index at the region proximal to the primary stenosis was significantly higher in the triple-dose group (P = 0.03). Mean 95% CI values for the difference in depicted degree of stenosis between DSA and postcontrast MR angiography improved from -3.4% +/- 4.7 (SD) in the single-dose group to -1.2% +/- 4.7 in the triple-dose group. Mean values for overall image quality on the visual analogue scale improved with the triple dose (P = 0.02). Confidence in diagnosis was high at postcontrast MR angiography in 88% and 96% of cases in the single- and triple-dose groups, respectively ... Gadodiamide-enhanced MR angiography performed with single and triple doses is safe and effective for assessing major abdominal arterial stenoses. Although high agreement between MR angiography and DSA was achieved with both doses, triple-dose MR angiography was superior in the evaluations of image quality, degree of arterial stenoses, and confidence in diagnosis. ... The safety and diagnostic efficacy of MultiHance (gadobenate dimeglumine) in the central nervous system (CNS) were evaluated in a double-blind, multicenter, phase III clinical trial ... Two hundred five patients highly suspected of having a CNS lesion (by previous imaging exam) were enrolled at 16 sites in the United States. Patients were randomized to one of three incremental dosing regimens. Magnetic resonance imaging with Omniscan (gadodiamide) at doses of 0.1 and 0.3 mmol/kg was compared with MultiHance (gadobenate dimeglumine) at doses of 0.05 and 0.15 mmol/kg and at 0.1 and 0.2 mmol/kg ... Compared with predose images alone, efficacy was demonstrated in each of the gadobenate dimeglumine and gadodiamide groups (single and cumulative doses) as indicated by the level of diagnostic information, number of lesions detected, and contrast-to-noise ratio measurements. The level of diagnostic information from gadobenate dimeglumine at 0.1 mmol/kg was equivalent to that with gadodiamide at the same dose. One of the two blinded reviewers found equivalence between the gadobenate dimeglumine 0.05 mmol/kg dose and gadodiamide at 0.1 mmol/kg. Both reviewers found the level of diagnostic information to be equivalent after the second dose of contrast for all three dosing regimens. The cumulative doses of gadobenate dimeglumine were well tolerated and as safe as gadodiamide ... Gadobenate dimeglumine is comparable to gadodiamide in terms of safety and efficacy for imaging of CNS lesions, with a possible advantage in imaging applications owing to enhanced T1 relaxivity. Drug Warnings /BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: NOT FOR INTRATHECAL USE AND NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS (NSF). NOT FOR INTRATHECAL USE: Inadvertent intrathecal use of OMNISCAN has caused convulsions, coma, sensory and motor neurologic deficits. NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS (NSF): Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of GBCAs in these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrasted MRI or other modalities. NSF may result in fatal or debilitating fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle and internal organs. Do not administer Omniscan to patients with: chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 sq m), or acute kidney injury. Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (e.g., age > 60 years, hypertension or diabetes), estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) through laboratory testing. Do not exceed the recommended Omniscan dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug from the body prior to any readministration Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) increase the risk for nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of GBCAs among these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrast enhanced MRI or other modalities. The GBCA-associated NSF risk appears highest for patients with chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 sq m) as well as patients with acute kidney injury. Do not administer Omniscan to these patients. The risk appears lower for patients with chronic, moderate kidney disease (GFR 30-59 mL/min/1.73 sq m) and little, if any, for patients with chronic, mild kidney disease (GFR 60-89 mL/min/1.73 sq m). NSF may result in fatal or debilitating fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle and internal organs. ... Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. Features of acute kidney injury consist of rapid (over hours to days) and usually reversible decrease in kidney function, commonly in the setting of surgery, severe infection, injury or drug-induced kidney toxicity. Serum creatinine levels and estimated GFR may not reliably assess renal function in the setting of acute kidney injury. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (e.g., age > 60 years, diabetes mellitus or chronic hypertension), estimate the GFR through laboratory testing. Among the factors that may increase the risk for NSF are repeated or higher than recommended doses of a GBCA and the degree of renal impairment at the time of exposure. Record the specific GBCA and the dose administered to a patient. When administering Omniscan, do not exceed the recommended dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug prior to any readministration Anaphylactoid and anaphylactic reactions, with cardiovascular, respiratory and/or cutaneous manifestations, resulting in death have occurred. Personnel trained in resuscitation techniques and resuscitation equipment should be present prior to Omniscan administration. If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, stop Omniscan Injection and immediately begin appropriate therapy. Observe patients closely, particularly those with a history of drug reactions, asthma, allergy or other hypersensitivity disorders, during and up to several hours after Omniscan Injection. FDA Pregnancy Risk Category: C /RISK CANNOT BE RULED OUT. Adequate, well controlled human studies are lacking, and animal studies have shown risk to the fetus or are lacking as well. There is a chance of fetal harm if the drug is given during pregnancy; but the potential benefits may outweigh the potential risk./ For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for GADODIAMIDE (24 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics In magnetic resonance imaging, visualization of normal and pathologic tissue depends in part on variations in the radiofrequency signal intensity. These variations occur due to: changes in proton density; alteration of the spin-lattice or longitudinal relaxation time (T1); and variation of the spin-spin or transverse relaxation time (T2). Gadodiamide is a paramagnetic agent with unpaired electron spins which generate a local magnetic field. As water protons move through this local magnetic field, the changes in the magnetic field experienced by the protons reorient them with the main magnetic field more quickly than in the absence of a paramagnetic agent. By increasing the relaxation rate, gadodiamide decreases both the T1 and T2 relaxation times in tissues where it is distributed. At clinical doses, the effect is primarily on the T1 relaxation time and produces an increase in signal intensity. Disruption of the blood-brain barrier or abnormal vascularity allows the accumulation of gadodiamide in lesions such as neoplasms, abscesses, and subacute infarcts. The pharmacokinetic parameters of gadodiamide in various lesions are not known. |
| 分子式 |
C16H29GDN5O8
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
576.68
|
| 精确质量 |
574.102
|
| CAS号 |
131410-48-5
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Gadodiamide hydrate;122795-43-1
|
| PubChem CID |
153921
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| 沸点 |
769.1ºC at 760mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
419ºC
|
| 蒸汽压 |
6.54E-26mmHg at 25°C
|
| tPSA |
146.82
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
11
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
13
|
| 重原子数目 |
30
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
527
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
CNC1=O[Gd+3]([N]2(C3)CC4)([N]5(C6)CC2)(O=C(NC)C5)([O-]C7=O)([O-]C6=O)([O-]C3=O)[N]4(C7)C1
|
| InChi Key |
HZHFFEYYPYZMNU-UHFFFAOYSA-K
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C16H29N5O8.Gd/c1-17-12(22)7-20(10-15(26)27)5-3-19(9-14(24)25)4-6-21(11-16(28)29)8-13(23)18-2;/h3-11H2,1-2H3,(H,17,22)(H,18,23)(H,24,25)(H,26,27)(H,28,29);/q;+3/p-3
|
| 化学名 |
2-[bis[2-[carboxylatomethyl-[2-(methylamino)-2-oxoethyl]amino]ethyl]amino]acetate;gadolinium(3+)
|
| 别名 |
DV-7572; DV 7572; Gadodiamide
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
H2O : ≥ 100 mg/mL (~174.32 mM)
DMSO : ~5.56 mg/mL (~9.69 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 0.56 mg/mL (0.98 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 5.6 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 0.56 mg/mL (0.98 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 5.6 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入 900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 0.56 mg/mL (0.98 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7341 mL | 8.6703 mL | 17.3406 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3468 mL | 1.7341 mL | 3.4681 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1734 mL | 0.8670 mL | 1.7341 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。