| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Naturalproduct; ferroptosis
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
铁死亡是一种由铁诱导的脂质氢过氧化物积聚引起的坏死,涉及多种分子事件,与帕金森病有关。天麻素是天麻的一种成分,具有很强的抗氧化活性。我们研究了天麻素是否可以预防H2O2诱导的大鼠胶质瘤细胞系C6的细胞毒性。为此,C6细胞用天麻素(1、5、25µM)预处理,然后暴露于100µM H2O2中。结果表明,用天麻素预处理C6细胞可减少H2O2诱导的乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)释放和细胞死亡。此外,天麻素在H2O2处理后降低了细胞内丙二醛(MDA)水平,而增加了谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GPX)活性和谷胱甘肽(GSH)水平。此外,去铁胺(DFO)、ferrostatin-1和liproxstatin-1的治疗消除了H2O2或erastin预处理引起的铁死亡。天麻素治疗减弱了H2O2诱导的C6细胞铁死亡,降低了脂质活性氧(ROS)(C11-BODIPY)的产生。此外,天麻素增加了经H2O2处理的C6细胞中核因子红系2相关因子2(Nrf2)、GPX4、铁蛋白-1(FPN1)和血红素加氧酶-1(HO-1)的蛋白质表达。RSL3是一种GPX4抑制剂,可抑制天麻素和100µM H2O2共处理细胞中的GPX4蛋白水平。这些发现表明,天麻素可以通过其在C6细胞中的抗氧化作用抑制H2O2诱导的铁死亡。[2]
接受二甲双胍治疗的急性高眼压患者视网膜中 TNF-α 和 iNOS mRNA 表达水平较低[1]。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
腹腔注射天麻素10 mg/kg或50 mg/kg,每日1次,连续15天,可有效预防急性高眼压(AOH)损伤引起的视网膜神经节细胞(RGC)损失。 AOH后两周,腹腔注射天麻素1 10 mg/kg和50 mg/kg的大鼠视网膜中Iba1阳性小胶质细胞数量显着减少,分别达到231.3±54.3 cells/mm2和201.9±43.1 cells/mm2。 1]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
逆转录定量聚合酶链式反应[1]
术后第14天,在用NS或不同剂量的gastrodin/天麻素治疗后收集视网膜。通过逆转录定量聚合酶链反应(RT-qPCR)测定TNF-α和iNOS的mRNA表达水平。根据制造商的说明,使用Trizol试剂分离总RNA,并使用一种商业试剂通过逆转录产生第一链cDNA。在Lightcycler 480系统上使用Fast Start Universal SYBR Green Master进行定量PCR。使用的引物如下:TNF-α引物:forwad(5′-CAGGTCCGTCCCTCTCATA-3′)和reverse(5′-TGCCGGTCCACATCTCG-3′),iNOS引物:forawad(5’-GCAGCCCTCCTACTCTC-3′)与reverse。使用大鼠β-actin内源性参考基因引物和其他引物。所有反应均进行三次,平均阈值周期(Ct)值>35被视为阴性。采用比较Ct法计算mRNAs的相对表达水平。将每组标准化为对照组,然后设置为100%。 |
| 动物实验 |
AOH rat model was performed in a randomly selected eye by anterior chamber perfusion and either received an intraperitoneal injection with various concentrations of gastrodin or normal saline. After 2wk, the rats were sacrificed. FluoroGold was used to label survival RGCs. Immunostaining with anti-Iba1 in the retinal flat mounts to calculate the microglia density in the ganglion cell layer (GCL). Changes in microglial cytokines, tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and inducible NO synthase (iNOS) were examined with Western blot and reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Expression levels of total and phosphorylated p38 mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) were determined by Western blot.[1]
Adult female SD rats (age, 8wk; weight, 200-250 g) were used for all the experiments and every possible measure was performed in order to minimize animal suffering. The animals were caged individually in an environmentally controlled room (22°C-26°C) with an alternating 12h/12h light/dark cycle and enough food and water. The rats were divided into 4 groups: 1) control group; 2) normal saline (NS) group who were exposed to AOH and received intraperitoneal injection of 0.9% NS; 3) G10 group who were exposed to AOH and received intraperitoneal injection of 10 mg/kg gastrodin; 4) G50 group who were exposed to AOH and received intraperitoneal injection of 50 mg/kg gastrodin. Significant loss of RGCs is known to take place in a delayed fashion after the acute high IOP. The number of RGCs decreased to less than 50%, meanwhile, the retina microglial cells also increased significantly in number and displayed an activated morphology, as revealed by Iba1-positive cell on day 14 after acute high IOP[6]. Therefore, the loss of RGCs and the number of Iba1-positive retina microglia were determined at 2wk after rapid ocular hypertension. gastrodin), dissolved in NS, was administered intraperitoneally for 1d at the respective doses before the induction of AOH model.[1] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Gastrodin is a glycoside.
Gastrodin has been reported in Anoectochilus formosanus, Pyrus communis, and other organisms with data available. See also: Gastrodia elata tuber (part of). Many reports have indicated that gastrodin can act upon multiple pathways, such as NF-κB, ERK1/2, and iNOS, among others, except on the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Thus, gastrodin could possibly inhibit the microglia activation dependent on different pathways, including the p38 MAPK pathway. As expected, the phosphorylation level of p38 was significantly decreased as a result of continuous gastrodin treatment. Therefore, the p38 MAPK signaling pathway is the major signaling pathway through which gastrodin exerts its anti-inflammatory effects. In addition to its anti-inflammatory effect, gastrodin can prevent the enhancement of extracellular glutamate level, which may provide extra insights to explain the neurochemical effects of gastrodin against RGCs damage induced by AOH. Further investigations are needed to elucidate the direct effect of gastrodin on cultured primary RGCs. In conclusion, we showed that gastrodin exerted its neuroprotective effects on RGCs in the AOH rat model. Gastrodin treatment significantly attenuated the production of microglia-mediated pro-inflammatory mediators, including TNF-α and iNOS. Furthermore, the level of phosphorylated p38 MAPK was significantly decreased by continuous gastrodin treatment. Taken together, these findings support our belief that the therapeutic potential of gastrodin in neuroprotective therapy for glaucoma and gastrodin can promote the survival of RGCs and may have a therapeutic potential in other degenerative optic neuropathies characterized by RGC apoptosis. [1] |
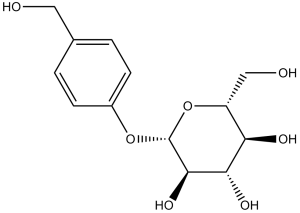
| 分子式 |
C13H18O7
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
286.28
|
|
| 精确质量 |
286.105
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 54.54; H, 6.34; O, 39.12
|
|
| CAS号 |
62499-27-8
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
115067
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.5±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
563.2±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
154-157ºC
|
|
| 闪点 |
294.4±30.1 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.638
|
|
| LogP |
-1.85
|
|
| tPSA |
119.61
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
5
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
20
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
292
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
5
|
|
| SMILES |
C1=CC(=CC=C1CO)O[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O2)CO)O)O)O
|
|
| InChi Key |
PUQSUZTXKPLAPR-UJPOAAIJSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C13H18O7/c14-5-7-1-3-8(4-2-7)19-13-12(18)11(17)10(16)9(6-15)20-13/h1-4,9-18H,5-6H2/t9-,10-,11+,12-,13-/m1/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
4-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl β-D-glucopyranoside
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.73 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.73 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.73 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 100 mg/mL (349.31 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4931 mL | 17.4654 mL | 34.9308 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6986 mL | 3.4931 mL | 6.9862 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3493 mL | 1.7465 mL | 3.4931 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。