| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 100μg |
|
||
| 500μg |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
GLS1 (IC50 = 31 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
GLS-1,也称为肾型或 KGA,和 GLS-2,也称为肝型或 LGA,是谷氨酰胺酶的两种已知亚型。 GLS-2 的表达似乎主要局限于肝脏,而 GLS-1 则广泛表达。 IPN60090 对 GLS-2 没有作用,IC50 > 50000 nM,并且在双偶联酶测定中抑制纯化的重组人 GLS-1(GAC 亚型),IC50 为 31 nM [2]。 IPN60090 的 IC50 为 26 nM,可防止 A549 细胞增殖[2]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
IPN60090(静脉注射 3 mg/kg;口服 10 mg/kg)表现出优异的药代动力学特征,包括 CL=4.1 mL/min/kg、t1/2=1 小时、Cmax=19 μM 和 F%=89%。 2]。当以 250 mg/kg 剂量每天两次口服时,IPN-60090(口服给药;100 mg/kg;每天两次;30 天)表现出与 CB-839 相当的有效性和与靶点的结合。此外,对于即将进行的模型研究,IPN-60090的耐受剂量为100 mg/kg BID[2]。 IPN-60090(口服;100 mg/kg;每天两次;30 天;单一疗法或与 TAK228 联合)抑制肿瘤生长。 IPN-60090 以剂量依赖性方式表现出强大的体内靶点参与能力。第 4 天和第 28 天显示服药后 4 小时较低的谷氨酸/谷氨酰胺比率和 IPN-60090 游离血浆浓度[2]。此外,单独使用 IPN-60090 可抑制 28% 的体内肿瘤生长,而 IPN-60090 与 TAK228 组合可强烈抑制 85% 的肿瘤生长[2]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
GLS-1酶测定。[2]
谷氨酰胺酶双偶联荧光测定在384孔、黑色、Greiner、非结合板(Greiner,目录号784900)中进行,其测定缓冲液由50 mM Hepes(pH 7.4)、250μM EDTA(pH 8)和0.12 mM Triton-X 100组成。所有最终浓度均指20μL的体积。在100%DMSO中制备测试化合物的储备溶液,并使用100%DMSO以1:3的比例连续稀释。化合物在测定缓冲液中额外稀释1:50,并将5μL/孔转移到测定板上。将稀释在测定缓冲液中的4x谷氨酰胺酶和磷酸氢二钾三水合物在室温下预孵育10分钟。将5μL/孔的谷氨酰胺酶和磷酸氢钙三水合物加入微孔板(终浓度分别为2 nM和50 mM),然后在室温下孵育10分钟。偶联反应由谷氨酸氧化酶、Amplex UltraRED、谷氨酰胺和辣根过氧化物酶组成。在弱光下将稀释在测定缓冲液中的5μL/孔谷氨酸氧化酶和Amplex UltraRED(终浓度分别为100 mU/mL和75μM)和稀释在测定缓冲器中的5µL/孔谷氨酰胺和辣根过氧化物酶(终浓度为1 mM和100 mU/mL)加入微孔板,然后在室温下孵育20分钟。使用PerkinElmer Envision平板读数仪测量再硫酸镁信号:激发-535 nm,发射-590 nm。使用Genedata Screener软件通过四参数逻辑斯谛曲线拟合计算IC50值。[2] GLS-2酶测定。[2] GLS2双偶联荧光测定在384孔、黑色、Greiner、非结合的平板上进行,平板上的测定缓冲液由50 mM Hepes(pH 7.4)、250μM EDTA(pH 8)和0.12 mM Triton-X 100组成。所有最终浓度均指20μL的体积。在100%DMSO中制备测试化合物的储备溶液,并使用100%DMSO以1:3的比例连续稀释。化合物在测定缓冲液中额外稀释1:50,并将5μL/孔转移到测定板上。将稀释在测定缓冲液中的4倍GLS-2和磷酸氢二钾三水合物在室温下预孵育10分钟。将5μL/孔的GLS-2与磷酸氢二钠三水合物加入微孔板(终浓度分别为33 nM和50 mM),然后在室温下孵育10 min。偶联反应由谷氨酸氧化酶、Amplex UltraRED(分子探针,目录号A36006)、谷氨酰胺和辣根过氧化物酶组成。在弱光下向微孔板中加入在测定缓冲液中稀释的5μL/孔谷氨酸氧化酶和Amplex UltraRED(终浓度分别为100 mU/mL和75μM)以及在测定缓冲溶液中稀释的每孔谷氨酰胺和辣根过氧化物酶(终浓度分别为3 mM和100 mU/mL)。使用PerkinElmer Envision平板读数器连续测量间苯二酚信号20分钟:激发-535 nm,发射-590 nm。使用Genedata Screener软件通过四参数逻辑斯谛曲线拟合计算IC50值。[2] 微软稳定性。[2] 微粒体稳定性测定在Beckmann Biomek FXp实验室自动化系统上进行。肝微粒体孵育混合物由磷酸钾缓冲液(100 mM,pH 7.4)中的肝微粒剂(0.5 mg微粒体蛋白/mL)、试验化合物(1 uM)、MgCl2(3 mM)和EDTA(1 mM)组成。咪达唑仑和氯胺酮用作测定对照底物。通过加入NADPH再生溶液(1.3 mM NADPH)引发反应,并在37°C下振荡。在0至45分钟的五个时间点,取出等分试样(50μL),用含有内标(丙咪嗪)的乙腈(100μL)淬灭。涡旋和离心后,通过LC-MS/MS分析样品。体外半衰期和清除率的计算遵循文献指南。[2] 血浆蛋白结合。[2] 使用快速平衡透析(RED)装置进行血浆蛋白结合(PPB)测定。华法林和美托洛尔被用作对照底物。向接收器侧加入350μL磷酸盐缓冲盐水(pH 7.4,1x)。向供体侧加入200μL掺有试验化合物(5μM)的血浆。同样的血浆/试验化合物溶液(50μL)也用于回收样品。用Immunoware密封带覆盖平板,在37°C下以100 rpm的速度摇晃5小时。孵育后,对受体和供体侧进行取样(50μL),并与另一侧相同体积的基质相匹配。回收物、供体和受体样品用300μL含丙咪嗪的冷ACN作为内标提取。涡旋和离心后,对上清液(150μL)进行LC-MS定量。PPB(结合百分比)计算为结合百分比=100×([供体]-[受体])/[供体]。[2] CYP抑制试验。[2] 在人肝微粒体中进行了研究(CYP 1A2/2C9/2D6/3A4为0.1 mg/mL;CYP 2C19为0.5 mg/mL)。肝微粒体购自BD Gentest。用乙腈将化合物储备溶液的等分试样稀释至4mM,然后在加入肝微粒体(0.2mg/mL)后进一步稀释。将30μL稀释的试验化合物溶液与15μL底物溶液混合。将平板预热至37°C,然后加入15μL 8 mM NADPH(也预热至37℃)。将平板在37°C下孵育以下孵育时间:3A4孵育5分钟,1A2/2C9/2D6孵育10分钟,2C19孵育45分钟。在指定时间点加入乙腈停止反应。将分析板在振动器(IKA,MTS 2/4)上摇动10分钟(600 rpm),并在5594 g下离心15分钟(Multifuge×3R)。取上清液的等分试样,用1:3稀释到蒸馏水中,通过LC-MS/MS分析代谢物浓度,并与内标进行比较。1A2使用的底物为非那西丁(30μM),2C9使用双氯芬酸(10μM)、2C19使用S-美芬妥因(35μM);3A4使用咪达唑仑(10μM)或睾酮(80μM)。测定的代谢产物为1A2的对乙酰氨基酚、2C9的4'-羟基双氯芬酸、2C19的羟基美芬妥、3A4的1-羟基咪达唑仑或奥沙米,以及2D6的1-羟基-氟尿嘧啶。使用的阳性对照抑制剂为CYP1A2的α-萘黄酮、CYP2C9的磺胺苯唑、CYP2C19的奥美拉唑、CYP2D6的奎尼丁和CYP3A4的酮康唑。将所需时间点测试化合物样品中代谢物与代谢物内标的峰面积响应比(PARR)与对照样品中的PARR进行比较,以确定每个时间点对照样品的百分比(%对照)。%抑制率计算为100%对照。 |
| 细胞实验 |
A549细胞活力测定。[2]
使用加湿培养箱(37°C,5%CO2和环境O2)将A549细胞常规保存在补充有10%透析FBS的过滤RPMI培养基中。在准备存活率测定时,收集细胞并将其重新悬浮在补充有10%透析FBS的过滤RPMI培养基中。将细胞以1000个细胞/孔的密度接种到384孔的黑色PerkinElmer组织培养板上,体积为40μL。组织培养板在37°C、5%CO2和环境O2下孵育24小时。在100%DMSO中制备测试化合物的储备溶液,并使用100%DMSO以1:3的比例连续稀释。将化合物在培养基中额外稀释1:40,并将10μL/孔转移到组织培养板上。添加化合物后,将微孔板在37°C下孵育72小时。向板中加入10μL Promega的CellTiter Fluor试剂,即在测定缓冲液中稀释的GF-AFC底物,使其达到1x终浓度。0.5%DMSO和20μM依托泊苷分别用作对照,以确定100%和0%的存活率。然后在室温下以300RPM在轨道振荡器上摇动该板15分钟,然后在37°C下孵育30分钟。使用PerkinElmer Envision平板读数器测量CellTiter Fluor信号:激发-400nm,发射-505nm。使用Genedata Screener软件通过四参数逻辑斯谛曲线拟合计算IC50值。[2] A549靶点结合试验。[2] A549细胞常规保存在添加了10%透析FBS的过滤RPMI培养基中,使用加湿培养箱(37°C,5%CO2和环境O2)。在准备靶点参与试验时,收集细胞并将其重新悬浮在补充有10%透析FBS的过滤RPMI培养基中。将细胞以15000个细胞/孔的密度接种到96孔组织培养板上,体积为100μL。组织培养板在37°C、5%CO2和环境O2下孵育24小时。在100%DMSO中制备测试化合物的储备溶液,并使用100%DMSO以1:3的比例连续稀释。将化合物在培养基中额外稀释1:200,并将200μL/孔转移到组织培养板上。添加化合物后,将微孔板在37°C下孵育24小时。然后使用YSI 2900生物化学分析仪测量培养基中的L-谷氨酰胺和L-谷氨酸水平。使用Genedata Screener软件通过四参数逻辑斯谛曲线拟合计算IC50值。[2] 肝细胞稳定性。[2] 在DMSO中制备10mM的供试化合物储备溶液。将储备溶液的等分试样用DMSO稀释至200μM,然后用KHB缓冲液进一步稀释至2μM。程序如下:计数肝细胞,然后将细胞悬浮液稀释至适当密度(活细胞密度=2×106个细胞/mL)。在不同时间点指定的孔中加入50μL预热(37°C)的2μM测试化合物。在0分钟内,向孔中加入100μL含ACN的内标(IS),然后加入50μL肝细胞溶液,然后密封孔。在指定的孔中加入50μL预热的肝细胞溶液,持续15分钟、30分钟、60分钟和120分钟,并开始计时。将测定板置于37°C的培养箱中。在15分钟、30分钟、60分钟和120分钟时,分别向孔中加入100μL ACN,然后密封相应的孔。淬火后,将平板超声处理5分钟,然后在5594×g下离心15分钟(Thermo Multifuge×3R)。将50μL上清液从每个孔转移到含有120μL超纯水的96孔样品板中,用于LC/MS分析。将化合物在15分钟、30分钟、60分钟和120分钟时的峰面积响应比(PARR)与IS与0分钟时的PARR进行比较,以确定每个时间点剩余的测试化合物的百分比。使用Excel软件计算半衰期,拟合单相指数衰减方程。[2] Caco-2渗透性。[2] Caco-2细胞购自美国组织培养物保藏中心。细胞在37°C的CO2中,在含有10%热灭活FBS和1%非必需氨基酸的改良Eagle培养基(MEM)中维持。将细胞接种在聚碳酸酯过滤器插件上。在运输实验之前,细胞培养了21-28天。在测定前后检查上皮电阻(TEER)和Lucifer Yellow通透性。将化合物以10mM溶解在DMSO中,并在Hank's平衡盐溶液(HBSS)中用25mM HEPES(pH 7.4)稀释以进行研究。在10μM下,在心尖到基底外侧(A-B)和基底外侧到心尖(B-A)方向上测试化合物,并在37°C下进行90分钟。孵育结束时,用测定缓冲液将供体样品稀释10倍,然后将60μL受体和稀释的供体样品与60μL乙腈混合,通过LC-MS/MS与标准曲线进行浓度分析。 |
| 动物实验 |
Female CD-1 mice[2]
3 mg/kg for i.v.; 10 mg/kg for p.o. (Pharmacokinetic Analysis) Intravenous injection and oral administration In vivo pharmacokinetics.[2] Mouse: Female mice weighing 20–30 g were used for studies. Food and water were available to all animals ad libitum. The test article was dosed via tail vein (IV doses) or oral gavage (PO doses), respectively. Blood samples were collected from all animals at predose and at 0.083, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, and 24 h postdose into tubes containing the anticoagulant K2EDTA (3 animals per time point with 3 time points collected per animal). Plasma was separated from the blood by centrifugation at 4 °C and stored at −70 °C until analysis. Test article concentrations in plasma were quantified using a liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method. Rat: Male rats weighing 200–300 g were used for studies. Animals were fasted overnight and fed 4 h postdose. Water was available ad libitum for all animals. Test article was dosed via dorsal foot vein (IV doses) or oral gavage (PO doses). Blood samples were collected via tail vein from all animals at predose and at 0.083, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, and 24 h postdose into tubes containing the anticoagulant K2EDTA. Plasma was separated from the blood by centrifugation at 4 °C and stored at −70 °C until analysis. Test article concentrations in plasma were quantified using a liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method. Dog: Male Beagle dogs weighing 7–10 kg were used for studies. Animals were fasted overnight and fed 4 h postdose. Test article was administered to dogs via the cephalic vein (IV doses) or oral gavage (PO doses). Blood samples were collected via the saphenous vein or cephalic vein from all animals at predose and 0.083, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, and 24 h postdose into tubes containing the anticoagulant K2EDTA. Plasma was separated from the blood by centrifugation at 4 °C and stored at −70 °C until analysis. Test article concentrations in plasma were quantified using a liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method. Monkey: Male Cynomolgus monkeys weighing 3–5 kg were used for studies. Animals were fasted overnight and fed 4 h postdose. Test article was administered to monkeys via the cephalic vein (IV doses) or nasal gavage (PO doses). Blood samples were collected via the saphenous vein or cephalic vein from all animals at predose and 0.083, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, and 24 h postdose into tubes containing the anticoagulant K2EDTA. Plasma was separated from the blood by centrifugation at 4 °C and stored at −70 °C until analysis. Test article concentrations in plasma were quantified using a liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method.[2] In Vivo Models.[2] All experiments were conducted in compliance with institutional guidelines. Glutamine and Glutamate Levels in H460 Xenograft Model. [2] NSG female mice were implanted with H460 cells (5×105 cells/mouse diluted with matrigel 1:1). Mice were between 6–10 weeks old. All animals received LabDiet 5053 chow ad libitum. Tumors were allowed to grow to 300–400 mm3, and animals were treated with compound 27 (bis-hydrochloride) formulated in 0.5% methylcellulose in sterile water. Animals were euthanized via CO2 at 8 or 24 h after a single dose of compound 27 by oral gavage, and tumors were harvested. Each group contained 6 animals. Tumors were weighed and snap frozen. Tumor sections were homogenized using an OmniBEAD Ruptor 24 at 100 mg tissue/mL in MeOH/Water (80:20) containing 13C5-L-glutamine and 13C5-L-glutamate as internal standards. Homogenates were centrifuged at 15,000 rpm at 4 °C for 10 min An aliquot of 10 μL of the supernatant was diluted with 190 μL of 0.1% formic acid in ACN/water (50:50), vortexed for 15 sec, and centrifuged at 15,000 rpm at 4 °C for 5 min Samples were analyzed on an Agilent 1290 infinity LC system coupled with an Agilent 6460 triple quadrupole mass spectrometer operated at positive mode (ESI+). A Waters XBridge Amide column (3.5 μm; 4.6 × 100 mm) was used for analyte separation. The HPLC buffer A was 95% (v/v) water/ACN containing 20 mM ammonium hydroxide and 20 mM ammonium acetate. The HPLC buffer B was 100% ACN. The gradient was 80% B (0–1 min), 80–10% B (1–3 min), 10% B (3–5 min), 10–80% B (5–5.3 min), 80% B (5.3–10 min). The column temperature was 40 °C and the flow rate 0.5 mL/min. The sample injection volume was 2 μL. The detection conditions of the mass spectrometer were as follows: capillary voltage 4000 V, nebulizer pressure 35 psi, cell accelerate voltage 4 V, sheath gas temperature 400 °C, sheath gas flow 11 L/min, source gas temperature 300 °C, source gas flow 11 L/min, fragmenter voltage 80 V, collision energy 26 V (glutamate) and 14 V (glutamine). Metabolites were detected by compound specific multiple reaction monitoring transition (MRM) and retention time (RT): Glutamine (m/z 147>84, RT 4.93 min), 13C5-Glutamine (m/z 152>88, RT 4.93 min), Glutamate (m/z 148>84, RT 4.78 min), 13C5-Glutamate (m/z 153>88, RT 4.78 min). The method was validated with an analytical range of 10 – 5000 ng/mL for both glutamine and glutamate in ACN/Water (1:1). GraphPad Prism was used for generation of graphs, and data is expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. Efficacy in Ru337 PDX model. [2] 8 week old NSG female mice were implanted with Ru337 (Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center) patient derived xenografts (PDX) subcutaneously on the right flank. Tumors were allowed to grow to an average volume of 100 mm3 as monitored by caliper measurements. Animals were then randomized into groups of 8. All animals received chow ad libitum. Mice were treated with compounds on a 5 day-on/2 day-off schedule. Compound 27 was formulated in 0.5% methylcellulose in sterile water and dosed at 100 mg/kg, PO, BID (doses administered approximately 8 hours apart (8:00 and 16:00) each dosing day followed by a 16 hour gap before the next day’s dose). TAK-228 was formulated in 5% sucrose and 0.5% methylcellulose in sterile water and dosed at 1 mg/kg, PO, QD. Body weights were monitored twice per week. Tumor volume was calculated using the formula: V=l2*L/2 (l=length; L=width). GraphPad Prism was used for generation of graphs, and data is expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. For the combination arms, standard deviations were very low (bars smaller than the size of plotted datapoints). |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
The pharmacokinetic properties of compound 27 (IPN60090) in rat and dog are superior to its properties in mouse and monkey, with rat and dog showing lower in vivo clearances and 5–6x longer half-lives. Because of the low volumes of distribution across species, half-lives are short unless clearances are extremely low, as is the case for rat and dog. Clearances across species are qualitatively in agreement with in vitro metabolic stabilities. Given that the in vitro clearances in human microsomes and hepatocytes are very low (similar to or lower than values for rat and dog), we expect low in vivo clearances and favorable half-lives in humans, more similar to rat and dog than to mouse and monkey.[2]
compound 27 (IPN60090) was further tested in ascending single dose oral PK experiments in mouse, rat and dog (Figure 6). Across the dose ranges tested (up to 200 mg/kg in mouse, 100 mg/kg in rat and 10 mg/kg in dog), maximal concentrations and total exposures continually increased with dose, with high exposures achieved across species. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Glutaminase-1 Inhibitor IACS-6274 is an orally bioavailable inhibitor of the metabolic enzyme glutaminase-1 (GLS1), with potential antineoplastic and immunostimulating activities. Upon oral administration, IACS-6274 selectively targets, binds to and inhibits human GLS1, an enzyme that is essential for the conversion of the amino acid glutamine into glutamate. Blocking glutamine metabolism inhibits proliferation in rapidly growing tumor cells and leads to an induction of cell death. Unlike normal healthy cells, glutamine-dependent tumors heavily rely on the intracellular conversion of exogenous glutamine into glutamate and glutamate metabolites to provide energy and generate building blocks for the production of macromolecules, which are needed for cellular growth and survival.
|
| 分子式 |
C24H27F3N8O3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
532.518194437027
|
| 精确质量 |
532.22
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 54.13; H, 5.11; F, 10.70; N, 21.04; O, 9.01
|
| CAS号 |
1853164-83-6
|
| 相关CAS号 |
IPN60090 dihydrochloride;2102101-72-2; IPN60090;1853164-83-6; 2102101-78-8 (mesylate); 2102101-77-7 (sulfate); 2102101-80-2
|
| PubChem CID |
118627280
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to yellow solid powder
|
| LogP |
1.6
|
| tPSA |
137
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
11
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
11
|
| 重原子数目 |
38
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
804
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
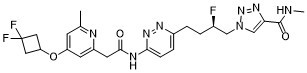
CC1=CC(=CC(=N1)CC(=O)NC2=NN=C(C=C2)CC[C@H](CN3C=C(N=N3)C(=O)NC)F)OC4CC(C4)(F)F
|
| InChi Key |
GEHZIZWHNLQFAS-OAHLLOKOSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C24H27F3N8O3/c1-14-7-18(38-19-10-24(26,27)11-19)8-17(29-14)9-22(36)30-21-6-5-16(31-33-21)4-3-15(25)12-35-13-20(32-34-35)23(37)28-2/h5-8,13,15,19H,3-4,9-12H2,1-2H3,(H,28,37)(H,30,33,36)/t15-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
1-[(2R)-4-[6-[[2-[4-(3,3-difluorocyclobutyl)oxy-6-methylpyridin-2-yl]acetyl]amino]pyridazin-3-yl]-2-fluorobutyl]-N-methyltriazole-4-carboxamide
|
| 别名 |
IACS-6274; IACS6274; IACS 6274; IPN60090; CHEMBL4741924; 1-[(2R)-4-[6-[[2-[4-(3,3-difluorocyclobutyl)oxy-6-methylpyridin-2-yl]acetyl]amino]pyridazin-3-yl]-2-fluorobutyl]-N-methyltriazole-4-carboxamide; IACS6274; O6ZT4D087I; IPN 60090; IPN-60090
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: 5~31.4 mg/mL (9.4~59.0 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 3.14 mg/mL (5.90 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 31.4 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8779 mL | 9.3893 mL | 18.7786 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3756 mL | 1.8779 mL | 3.7557 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1878 mL | 0.9389 mL | 1.8779 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT03894540 | Terminated | Drug: IPN60090 Drug: pembrolizumab |
Solid Tumor | Ipsen | March 22, 2019 | Phase 1 |