| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
1β-hydroxylase (CYP11B1) (IC50 = 35 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
皮质醇和醛固酮被奥西洛司他抑制(LCI699;0.01-10 μM;HAC15 细胞、17 种原代人肾上腺皮质细胞培养物、垂体腺瘤细胞)。奥西洛司他对肾上腺雄激素影响较小,并抑制皮质酮和 11-脱氧皮质醇的积聚 [2]。
体外酶抑制[1] LCI699/Osilodrostat剂量依赖性地抑制重组人醛固酮合酶的活性(IC50 = 0.7 nmol/L)的选择性是11β-羟化酶的3.6倍(IC50 = 2.5 nmol/L)(表1)。Lineweaver–Burk图(图1)显示,LCI699是重组人醛固酮合酶(Ki = 1.4 ± 0.2 nmol/L,平均值 ± SEM)和更高浓度的11β-羟化酶(Ki = 2.4 ± 0.3 nmol/L)。 使用大鼠重组酶的体外酶研究表明,LCI699抑制大鼠醛固酮合酶的效力比人酶低约230倍(表1)。然而,与重组人酶相比,LCI699对重组大鼠醛固酮合酶和11β-羟化酶具有相似的弱选择性(2.6倍的差异)。 在猴子肾上腺匀浆中,LCI699对醛固酮合酶的IC50比人重组酶高17倍,但比大鼠肾上腺匀浆中测量的IC50低67倍。在猴肾上腺匀浆中,醛固酮合酶的选择性是11β-羟化酶的5.2倍。 总之,LCI699/Osilodrostat抑制醛固酮合酶的相对物种排名顺序是人类 > 猴子 > 大鼠,而醛固酮合酶对11β-羟化酶的3至5倍选择性在这些物种中是相似的。 背景:美替卡松和酮康唑是治疗库欣综合征的常用类固醇生成抑制剂,可能与副作用和疗效有限有关。Osilodrostat是一种CYP11B1和CYP11B2抑制剂,对其他类固醇生成酶的影响尚不清楚。 目的:比较奥司他、美曲朋和酮康唑对体外肾上腺类固醇生成和垂体腺瘤细胞的影响。 方法:将HAC15细胞、17种原代人肾上腺皮质细胞培养物和垂体腺瘤细胞与Osilodrostat、Metrapone或酮康唑(0.01至10µM)一起孵育。皮质醇和促肾上腺皮质激素采用化学发光免疫测定法测定,类固醇谱采用液相色谱-质谱法测定。 结果:在HAC15细胞中,osilodrostat对皮质醇产生的抑制作用(IC50:0.035µM)明显强于美曲朋(0.068µM;P<0.0001)和酮康唑(0.621µM;P<0.001)。osilodrostat和metrapone对基础皮质醇产生的IC50值分别相差25倍和18倍,具有相当的效力。与美曲普酮和酮康唑相比,奥司他对醛固酮的抑制作用更强。Osilodrostat和metrapone治疗导致皮质酮和皮质醇的强烈抑制,11-脱氧皮质醇的积累,以及对肾上腺雄激素的适度影响。未观察到osilodrostat对垂体的直接影响。 结论:在我们的研究条件下,osilodrostat是人类肾上腺皮质细胞中一种强效的皮质醇生成抑制剂,与甲氧基吡咯烷酮相当。所有类固醇生成抑制剂在原代肾上腺皮质培养物之间的敏感性存在很大差异。Osilodrostat可能抑制CYP11B1和CYP11B2,在某些情况下抑制CYP17A1活性的程度较小,是类固醇生成的近端步骤。Osilodrostat是库欣综合征的一种有前景的治疗选择,与美曲普龙的体内差异可能是由药代动力学差异引起的[2]。 Osilodrostat、美曲普龙和酮康唑对体外基础和促肾上腺皮质激素刺激的皮质醇产生的影响[2] HAC15细胞系[2] 3天后,与美曲朋(0.0678µM;95%CI,0.0543至0.0848;P<0.0001)和酮康唑(0.621µM;95%CI,0.488至0.833;P<0.00001)相比,奥司他在显著较低的浓度下抑制了皮质醇的产生(IC50为0.0347µM;95%CI,0.0294至0.0410)(图1A)。在所有实验中,ACTH对皮质醇的平均刺激率为42%(±4%)(图1C)。对于osilodrostat,当HAC15细胞被ACTH刺激时,IC50值增加了1.7倍(与基础条件相比,P<0.0001),而甲氧基帕酮和酮康唑在ACTH刺激下的效力没有显著变化。比较三种化合物在ACTH刺激下的抑制作用,奥司洛司他抑制皮质醇产生的效果与美曲普酮一样强(IC50 0.0605µM;95%CI,0.0514至0.0714 vs IC50 0.0739µM;95%CI,0.0645至0.0847;P=0.0669),与酮康唑相比更有效(IC50 0.709µM;95%CI,0.523至0.962;P<0.0001)。添加类固醇生成抑制剂不会影响细胞数量。 原代肾上腺皮质培养[2] 在17种原代培养的人类肾上腺皮质组织中也评估了Osilodrostat、美曲普龙和酮康唑的影响:8种产生皮质醇的ACA,3种ACTH依赖性肾上腺增生,2种ACTH非依赖性肾上腺增殖,2种产生皮质醇和2种Conn综合征相关肾上腺增生。患者和组织特征如表1所示。表2列出了osilodrostat、metrapone和酮康唑对原代肾上腺皮质培养物中皮质醇产生的IC50值;剂量反应曲线如图2和(26)所示。在58个肾上腺培养板中的37个中进行了DNA测量,其中评估了化合物对皮质醇或醛固酮的剂量反应,结果显示任何药物对这些培养物中的细胞数量都没有影响。在原代肾上腺皮质培养物中,85pM ACTH诱导的皮质醇增加从48%到737%不等(表2)。 在未受刺激的原代ACA培养物中,Osilodrostat对皮质醇产生的IC50值差异为25倍(表2,图2A;0.0217,95%CI,0.0102至0.0461;0.534,95%CI,0.360至0.793),而美曲普酮的IC50值相差18倍,酮康唑的IC50值差别为84倍。与肾上腺增生的平均IC50(n=2;0.0269µM,95%CI,0.0210至0.0346;P<0.0001与ACA相比)相比,奥司罗司他在ACA中的平均IC50更高(n=7;0.104µM;95%CI,0.0716至0.151),尽管组数较小,但与ACC的IC50没有统计学上的显著差异。与ACC相比,osilodrostat在肾上腺增生中的平均IC50较低(P=0.0007)。在八种情况下(基础或促肾上腺皮质激素刺激),可以对osilodrostat和metrapone进行直接比较(表2)。与osilodrostat相比,Metyrapone在三种情况下更有效地抑制皮质醇的产生(P<0.05),而osilodrosta在ACTH依赖性肾上腺增生1号中更有效地控制皮质醇(P<0.0001)。在11种培养物中,有8种在基础条件下研究了Osilodrostat和酮康唑的疗效,与酮康唑相比,Osilodrosta对皮质醇的抑制作用更强(P<0.05至P<0.0001)。在促肾上腺皮质激素刺激下,与酮康唑相比,六种原代培养物中有两种对osilodrostat的IC50较低(P<0.01和P<0.001)。 在基础和ACTH模拟条件下比较疗效的三种培养物中,有两种培养物的疗效发生了变化,其中一种培养物在ACTH刺激条件下效力更高,另一种培养液效力更低(分别为P<0.01和P<0.05)。 Osilodrostat、美曲普龙和酮康唑对人肾上腺皮质细胞醛固酮生成的影响[2] 在血管紧张素II刺激的HAC15细胞中(图3D;醛固酮平均增加282%;P<0.0001),与美曲朋相比,Osilodrostat抑制醛固酮水平的浓度低10倍以上(图3A;IC50,0.0354μM;95%CI,0.0269至0.0465 vs 0.413μM;95%CI,0.306至0.557;P<0.00001)。未刺激的HAC15细胞中的醛固酮浓度太低,无法充分评估化合物的抑制作用。在导致Conn综合征的醛固酮生成性肾上腺增生中,Osilodrostat对醛固酮生成的抑制作用也比美曲普龙强得多(图3B;IC50,0.00281μM;95%CI,0.000910至0.00866 vs 0.822μM;95%CI,0.471至1.433;P<0.0001)。在第二例醛固酮生成性肾上腺增生中,在两种测试浓度(0.1和5μM,数据未显示)下,奥司罗司他和美曲朋对基础醛固酮浓度的抑制作用没有差异。在基础状态下的ACTH依赖性肾上腺增生1号中,奥司前列素对醛固酮的抑制作用明显强于美曲普酮(图3C;IC50,0.00469μM;95%CI,5.516E-5至0.398 vs 0.364μM;95%CI,0.05515至2.397;P<0.0001)和酮康唑(0.315μM;95%CI,0.05%至1.916;P<0.0011 vs奥司前列醇)。在这种原代培养中,与皮质醇抑制所需的浓度相比,osilodrostat在显著较低的浓度下抑制醛固酮的产生(IC50醛固酮为0.00469μM;95%CI为5.516E-5至0.398,而皮质醇为0.0311μM;95%CI为0.0242至0.0399;P=0.0164)。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在 Ang-II 和 ACTH 刺激的 Sprague Dawley 大鼠中,奥西洛司他(LCI699;0.1-100 mg/kg;口服;一次)抑制醛固酮和皮质酮的合成 [1]。 Osilodrostat(LCI699;3-100 mg/kg;口服;每天一次,持续 52 周)通过降低平均动脉压来延长 dTG 大鼠的生存期 [1]。
背景:醛固酮合酶的抑制有可能减弱醛固酮的盐皮质激素受体依赖性和非依赖性作用。重组人酶的体外研究表明,LCI699是一种强效、可逆、竞争性的醛固酮合酶抑制剂(人体内K i=1.4±0.2 nmol/L),对11β-羟化酶具有相对选择性。 方法:在促肾上腺皮质激素(ACTH)和血管紧张素II刺激醛固酮释放的大鼠和猴子体内模型中,研究了口服Osilodrostat/LC699的激素作用,并在一项随机、安慰剂对照研究中与盐皮质激素受体拮抗剂依普利酮进行了比较。在过表达人肾素和血管紧张素原的双转基因大鼠(dTG大鼠)模型中,研究了LCI699和依普利酮对醛固酮过量所致心脏和肾脏后遗症的影响。 结果:刺激醛固酮释放的大鼠和猴子体内模型预测了人类剂量和暴露反应关系,但高估了Osilodrostat在人类中的选择性。在dTG大鼠模型中,LCI699剂量依赖性地阻断醛固酮的增加,防止独立于血压变化的心肾功能异常的发展,并延长生存期。依普利酮在相似程度上延长了生存期,但在预防心脏和肾脏损伤方面效果较差。在健康人类受试者中,LCI699 0.5 mg选择性降低血浆和24小时尿醛固酮分别为49±3%和39±6%(第1天,平均值±SEM;与安慰剂相比P<0.001),这与钠尿症和血浆肾素活性增加有关。大于1mg的LCI699剂量抑制了基础皮质醇和ACTH刺激的皮质醇。100 mg依普利酮可增加血浆和24小时尿醛固酮,同时刺激钠分泌和增加肾素活性。与依普利酮相比,LCI699增加了醛固酮前体11-脱氧皮质酮和尿钾排泄。 结论:这些结果为实验模型中抑制醛固酮合酶的心脏和肾脏作用以及激素作用对人类的转化提供了新的见解。选择性抑制醛固酮合酶似乎是治疗醛固酮过量相关疾病的一种有前景的方法。[1] 生长抑素类似物帕瑞肽和11β-羟化酶抑制剂Osilodrostat(LCI699)通过不同的作用机制降低皮质醇水平。研究这两种药物联合使用的临床疗效是有科学依据的。这份手稿报告了一项大鼠毒理学研究的结果,评估了不同剂量的单独和联合使用的osilodrostat和pasireotide。将60只雄性和60只雌性大鼠随机分为单性别组,接受每日剂量的帕瑞肽(0.3mg/kg/天,皮下注射)、奥司罗他(20mg/kg/天,口服)、奥司罗他/帕瑞肽组合(低剂量,1.5/0.03mg/kg/天;中剂量,5/0.1mg/kg/天;或高剂量,20/0.3mg/kg/日)或赋形剂治疗13周。与对照组相比,帕瑞肽单独治疗组和联合治疗组从基线到第13周的平均体重增加明显较低,而接受奥司他单药治疗的雌性大鼠的平均体重增长明显较高。Osilodrostat和帕瑞肽单药治疗与垂体和肾上腺、肝脏和卵巢/输卵管的组织学和平均重量的显著变化有关。单独使用Osilodrostat与肾上腺皮质肥大和肝细胞肥大有关。联合使用,奥司他/帕瑞肽不会加剧任何靶器官的变化,并改善了单一疗法观察到的肝脏和肾上腺的变化。奥司他和帕瑞肽的Cmax和AUC0-24h以近似剂量成比例的方式增加。总之,与单一疗法相比,帕瑞肽和奥司他联合用药不会加剧靶器官重量或毒性的变化,并且具有可接受的安全性;在osilodrostat方案中加入帕瑞肽可能会减轻潜在的肾上腺过度活化和肝细胞肥大,这是osilodrosat单一疗法的潜在副作用[3]。 |
| 酶活实验 |
体外酶抑制[1]
实验设计[1] 细胞系和组织样本[1] 重组人细胞色素P450(CYP)11B2和CYP11B1酶分别由细胞系V79-4 CYP11B2肾上腺毒素-肾上腺毒素还原酶(AAR)#317和V79-4 CYP11B1-AAR#618制备。类似地制备重组大鼠CYP11B2和CYP11B1酶。所有细胞系均保存在添加了10%胎牛血清、0.5倍抗生素、800μg/mL遗传霉素和250μg/mL潮霉素的Dulbecco改良Eagle培养基中。 如前所述,从雄性Sprague-Dawley(S-D)大鼠的肾上腺制备大鼠肾上腺匀浆。从雌性食蟹猴的肾上腺制备猴CYB11B2和CYB11B1匀浆。将猴肾上腺组织在玻璃组织研磨机中在冰上切碎并均质化,每100mg组织加入1mL冰冷的均质缓冲液(每50mL缓冲液加入2.7mmol/L CaCl2和一片无乙二胺四乙酸(EDTA)的蛋白酶抑制剂片)。将均质材料在450℃下离心 g在4°C下放置5分钟,使上清液的最终甘油浓度达到5%,在液氮中快速冷冻,并在-80°C下储存直至分析。使用96孔板测定法定量醛固酮、皮质醇和皮质酮浓度(见附加文件1)。 CYP11B2和CYP11B1酶测定[1] 人CYP11B2和CYP11B1测定如前所述。使用11-DOC作为底物,对大鼠和猴子进行了类似的检测。 |
| 细胞实验 |
根据制造商的说明,将Osilodrostat、Metrapon和酮康唑的储备溶液分别溶解在0.01N盐酸、蒸馏水和无水乙醇中,并在-20°C下以10-2M的储备浓度储存。在每次实验开始时,将Osilodrostat、Metrapone和酮康唑在溶解的相同溶液中稀释至正确浓度。Synacten的储备浓度在4°C下储存,并在使用当天在培养基中稀释。血管紧张素II储备浓度储存在-20°C下,并在使用当天用蒸馏水稀释。使用的ACTH和血管紧张素II的浓度分别基于HAC15细胞中皮质醇和醛固酮产生的剂量反应曲线,并根据先前报道的研究。接种细胞一天后,开始孵育。对照细胞经过载体处理。对于HAC15,细胞以每孔100000个细胞的密度在0.5mL培养基中铺板。加入Osilodrostat、美曲普龙或酮康唑(0.01至5µM)3天,加入或不加入10 nM ACTH或100 nM血管紧张素II,分别评估对类固醇谱和醛固酮产生的影响。为了评估osilodrostat对小鼠促肾上腺皮质激素垂体细胞的影响,将AtT20细胞与osilodrosta一起孵育1、3和7天(0.01至10µM),以评估该药物在多种条件下(不同孵育时间和更高浓度)的潜在影响。对于7天的实验,培养基和化合物在3天后被刷新[2]。
原发性人类肾上腺和垂体腺瘤培养实验与HAC15和AtT20细胞的实验相似,但略有调整:ACTH的浓度为85 pM,血管紧张素II的浓度为10 nM,在细胞接种后3至4天开始治疗,然后进行培养基更新,在原发性促肾上腺皮质激素垂体腺瘤培养中,Osilodrostat的浓度仅为1µM。原代培养中使用的ACTH和血管紧张素II的浓度低于HAC15细胞中的浓度,因为原代培养对这些化合物的敏感性通常更高。由于从某些标本中获得的细胞数量有限,并非所有实验都可以在每个原代培养物中进行[2]。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Male Ang-II- and ACTH-stimulated Sprague Dawley rats[1]
Doses: 0.1, 0.3, 1 and 3 mg/kg (Ang-II-stimulated rats) and 1, 3, 10, 30 and 100 mg/ kg (ACTH-stimulated rats) Route of Administration: Oral administration; once Experimental Results: Inhibited the increase in plasma aldosterone concentrations stimulated by Ang II or ACTH in a dose-dependent manner. Animal/Disease Models: dTG rats[1] Doses: 3, 10, 30 and 100 mg/kg Route of Administration: Oral administration; daily, for 52 weeks Experimental Results: Increased fractional LV (systolic and diastolic) shortening, normalized LV isovolumic relaxation time to RR (IVRT/RR) ratio and myocardial cell size and decreased LV weight in a dose-dependent manner. LCI699/Osilodrostat formulation [1] LCI699/Osilodrostat solution was freshly prepared (from powder) before each experiment. In the rat models, Osilodrostat/LCI699 (free base) was first dissolved in 1.5 molar equivalents of 1 N HCl plus 10 parts of water and then diluted in 3% cornstarch (1 mL/kg volume). In the monkey model, LCI699 (phosphate salt) was dissolved in water (1 mL/kg volume). LCI699 was administered by oral (rat and monkey) or nasogastric gavage (monkey). Compound doses in the monkey model are quoted as free base equivalents. Experimental protocol for rat models [1] Study protocols for the rat models of Ang-II- and ACTH-stimulated aldosterone synthesis followed a published protocol. For the Ang-II-infusion model, an initial loading dose of 300 ng/kg angiotensin II (Ang II) was followed by 100 ng/kg/min intravenous (i.v.) infusion for 9 h. For the ACTH-infusion model, the loading and infusion doses of ACTH were 100 ng/kg and 30 ng/kg/min, respectively. After 1 h of Ang II or ACTH infusion, a blood sample was collected for determining the post-Ang II or ACTH ‘baseline’ (i.e., secretagogue-elevated) plasma aldosterone and corticosterone concentrations. Osilodrostat/LCI699 was administered at doses of 0.1, 0.3, 1 and 3 mg/kg in the Ang-II-infusion model, and 1, 3, 10, 30 and 100 mg/kg in the ACTH-infusion model. In both models, infusion continued for a further 8 h. Blood samples were withdrawn in heparin (final concentration 15 U/mL) from the arterial cannula at 15 and 30 min, and 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 24 h post-dosing. Plasma aldosterone and cortisol were determined by radioimmunoassay and LCI699 by liquid chromatography separation coupled with tandem mass spectrometric detection (LC-MS/MS) (see Additional file 1). Experimental protocol for monkey model [1] Six monkeys (4.9–8.8 kg) were selected and were divided into two groups of three animals. Experiments were not initiated until after at least 2 weeks of recovery from the catheter/vascular access port (VAP) surgeries. Thirty minutes before the start of the experiment, a Huber needle was inserted transdermally into the VAP for the collection of blood samples and injection of ACTH. Between samplings, catheters/VAPs were flushed with saline and kept patent with 10 U/mL heparin. In all cases, the total blood withdrawn did not exceed 1% of body weight per week, and at least 1 week of recovery was allowed between sequential experiments. Blood samples (0.3 mL in 15 U/mL heparin) for baseline pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic assessments were collected at 0.5 h, 0.25 h and immediately before dosing. Osilodrostat/LCI699 (5, 15, 50 or 150 μg/kg) or vehicle (water) was administered followed 3 h later by ACTH(1–24) 3000 ng/kg i.v. in 0.1 mL/kg (over ~2 min). The 3000 ng/kg dose of ACTH was determined from a pilot dose–response experiment, which showed a consistent and maximal stimulation of plasma aldosterone and cortisol. Blood samples were collected at 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75 and 1 h after ACTH injection to assess the time course of plasma aldosterone and cortisol stimulation. Further blood samples were collected up to 8 h and at 23.5 and 24 h after LCI699/vehicle administration. Between the 8 h and 23.5 h collections, the Huber needles were removed and the monkeys were returned to their home cages. All instrumentation was removed after the last sample at 24 h. Plasma aldosterone and cortisol were determined by radioimmunoassay and LCI699 by LC-MS/MS (see Additional file 1). Sixty male and 60 female rats were randomized into single-sex groups to receive daily doses of vehicle, low-dose Osilodrostat/pasireotide, mid-dose osilodrostat/pasireotide, high-dose osilodrostat/pasireotide, high-dose osilodrostat monotherapy, or high-dose pasireotide monotherapy (Table 1). Prior to initiation of dosing, all animals were weighed, and randomization was stratified by body weight. Rats received their specified treatment regimen daily for 13 weeks; the 13-week treatment period was chosen according to current European Medicines Agency recommendations (ICH M3 [R2]). Three female sentinel rats were used for health screening procedures. Osilodrostat was administered orally using a plastic gavage tube, followed by, where applicable, sc injection of pasireotide into the interscapular area within 5 min of osilodrostat administration. Animals were dosed at approximately the same time each day, except during designated procedures. Oral and sc routes of administration were selected for osilodrostat and pasireotide, respectively, as they represent the intended routes of administration in humans. The low, mid, and high doses of Osilodrostat (1.5, 5, and 20 mg/kg/day) and pasireotide (0.03, 0.1, and 0.3 mg/kg/day) were considered appropriate based on the results of previous monotherapy studies in rats (osilodrostat dose range: 0.2–50 mg/kg/day, orally; pasireotide dose range: 0.08–0.24 mg/kg/day, sc; Novartis Pharma AG, unpublished data); these doses were expected to provide sufficient exposure multiples against human systemic exposure at therapeutic doses. Osilodrostat and pasireotide doses of up to 20 and 0.24 mg/kg/day, respectively, were tolerated during two 6-month monotherapy studies; the no-observed-adverse-effect levels (NOAELs) for osilodrostat and pasireotide were 2 and 0.024 mg/kg/day, respectively. Compounds and formulation [2] Osilodrostat was formulated in ultrapure water for administration by oral gavage. Pasireotide was formulated with acetate-buffered solution (pH 4.5), acetic acid, and d-mannitol in sterile water for sc injection. Vehicle control consisted of ultrapure water for oral gavage and acetate-buffered solution (pH 4.5), acetic acid, and d-mannitol in sterile water for sc injection. Dosing volumes were 5 mL/kg for oral gavage (osilodrostat and vehicle) and 1 mL/kg for sc injection (pasireotide and vehicle). Agents were stored at 4 °C and protected from light. For administration of osilodrostat, dosing solutions were removed from the refrigerator and stirred for at least 10 min at room temperature prior to initiation of dosing. Dosing solutions of pasireotide were removed from the refrigerator and allowed to warm to room temperature for at least 30 min prior to initiation of dosing. Endpoints and assessments [2] This study sought to determine the effects of daily Osilodrostat and pasireotide, alone and in combination, on the pituitary–adrenal axis and to report any other treatment-related toxicities. The toxicokinetic characteristics of osilodrostat and pasireotide were also determined. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
The oral absorption of osilodrostat is rapid, with a Tmax of approximately 1 hour, and assumed to be essentially complete. Exposure (i.e. AUC and Cmax) increases slightly more than dose-proportionately over the standard dosing range. Coadministration of osilodrostat with food does not affect its pharmacokinetics to a clinically significant extent. Age and gender do not affect pharmacokinetics, but bioavailability and total exposure is higher (though not clinically significant) in patients of Asian descent. Exposure to osilodrostat is greater in patients with moderate-severe hepatic impairment - prescribing information recommends a starting dose of 1mg twice daily in patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B) and a starting dose of 1mg each evening in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C). Following oral administration of radiolabeled osilodrostat, 90.6% of the radioactivity was eliminated in the urine with only 1.58% in the feces. Only 5.2% of the administered dose was eliminated in the urine as unchanged parent drug, suggesting that metabolism followed by urinary elimination is osildrostat's primary means of clearance. The median apparent volume of distribution of osilodrostat is 100 L. Data regarding the oral clearance of osilodrostat are not currently available. Metabolism / Metabolites Osilodrostat is extensively metabolized - approximately 80% of an orally administered dose is excreted as metabolites, and this is the predominant means of drug clearance. The most abundant metabolites in plasma are M35.4 (di-oxygenated osilodrostat), M16.5, and M24.9 at 51%, 9%, and 7% of the administered dose, respectively. The M34.5 and M24.9 metabolites have longer half-lives than the parent drug which may lead to accumulation with twice-daily dosing. Of the thirteen metabolites observed in the urine, the most abundant are M16.5 (osilodrostat glucuronide), M22 (a glucuronide conjugate of M34.5), and M24.9 at 17%, 13%, and 11% of the administered dose, respectively. The M34.5 metabolite accounts for less than 1% of the dose excreted in urine, but its glucuronide conjugate (M22) accounts for approximately 13%. The biotransformation of osilodrostat is mediated by multiple cytochrome P450 (CYP) and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) enzymes, though no single enzyme appears to contribute >25% to the total clearance. Of the total clearance, approximately 26% is CYP-mediated, 19% is UGT-mediated, and 50% is mediated by other enzymes. The formation of M34.5, the major metabolite of osilodrostat, is likely non-CYP-mediated. The formation of osilodrostat glucuronide (M16.5), its major urinary metabolite, is catalyzed by UGT1A4, UGT2B7, and UGT2B10. _In vitro_ data suggest that none of the metabolites contribute to the therapeutic efficacy of osilodrostat, but the M34.5 metabolite has been implicated in the inhibition and/or induction of multiple enzymes and transporters. Biological Half-Life The elimination half-life of osilodrostat is approximately 4 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In preregistration trials, mild, transient serum aminotransferase elevations occurred in 37 of 137 (27%) patients receiving Osilodrostat for Cushing disease, but in only 8 (6%) patients were values above 3 times the upper limit of normal (ULN), and only 1 was above 5 times ULN ( Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the use of osilodrostat during breastfeeding. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions, such as adrenal insufficiency, in the breastfed infant, breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with osilodrostat and should be avoided until 1 week after the final dose. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Both osilodrostat and its M34.5 metabolite are minimally protein-bound in plasma at less than 40%. The extent of protein-binding is independent of drug concentration. The specific plasma proteins to which osilodrostat binds have not been elucidated. Toxicokinetics [3] On Day 1, an increase in Osilodrostat dose from 0.5 to 20 mg/kg/day in combination with pasireotide (dose range, 0.03–0.3 mg/kg/day) was accompanied by approximately dose-proportional increases in maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) and area under the concentration–time curve from 0 to 24 h (AUC0–24h) for osilodrostat in male and female rats (Table 4). For each dose group, the osilodrostat AUC0–24h and Cmax were similar after multiple doses (Day 77) compared with those after a single dose (Day 1) and were, in general, similar between sexes. An increase in pasireotide dose from 0.03 to 0.3 mg/kg/day in combination with Osilodrostat (dose range, 0.5–20 mg/kg/day) on Day 1 led to dose-proportional increases in Cmax and AUC0–24h for pasireotide in male and female rats (Table 4); the Cmax and AUC0–24h of pasireotide increased slightly after multiple doses compared with those after a single dose. A slight gender difference was observed in pasireotide exposure at all doses tested (male/female AUC0–24h ratio, 1.4–1.8). Toxicokinetic parameters were not assessed for rats administered osilodrostat or pasireotide alone. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Osilodrostat is an inhibitor of 11β-hydroxylase (also referred to as CYP11B1), the enzyme that catalyzes the final step in the biosynthesis of endogenous cortisol. It is used to lower circulating cortisol levels in the treatment of Cushing's disease, a disorder in which cortisol levels are chronically and supraphysiologically elevated. Cushing's disease is often the result of ACTH hypersecretion secondary to a pituitary tumor, and surgical resection of the tumour is generally the treatment of choice. As an orally bioavailable drug therapy, osilodrostat provides a novel treatment option for patients in whom removal of the causative tumor is not an option or for whom previous pituitary surgery has not been curative. Osilodrostat is manufactured by Novartis under the brand name Isturisa. It has undergone phase II clinical trials for the treatment of solid tumours, hypertension, and heart failure, but development for these indications was discontinued by Novartis in January 2013. Osilodrostat was approved for use in the EU in January 2020 for the treatment of endogenous Cushing's syndrome (i.e. Cushing's disease), and was granted FDA approval and Orphan Drug designation in the US in March 2020 for the same indication.
Osilodrostat is a Cortisol Synthesis Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of osilodrostat is as a Cytochrome P450 11B1 Inhibitor, and Cytochrome P450 1A2 Inhibitor, and Cytochrome P450 2C19 Inhibitor, and Cytochrome P450 2D6 Inhibitor, and Cytochrome P450 3A4 Inhibitor, and Cytochrome P450 3A5 Inhibitor. Osilodrostat is an inhibitor of cortisol synthesis that is used in the treatment of Cushing disease not controlled by standard therapy. Osilodrostat therapy has not been linked to serum aminotransferase elevations during therapy or with instances of clinically apparent liver injury. Osilodrostat is an orally bioavailable inhibitor of both steroid 11beta-hydroxylase (cytochrome P450 (CYP) 11B1) and aldosterone synthase (CYP11B2; steroid 18-hydroxylase), with potential anti-adrenal activity and ability to treat Cushing disease (CD). Upon administration, osilodrostat binds to and inhibits the activity of CYP11B1, the enzyme that catalyzes the final step of cortisol synthesis from the precursor 11-deoxycortisol, and CYP11B2, the enzyme that catalyzes aldosterone synthesis from corticosterone and 11-deoxycorticosterone in the adrenal gland. The inhibition of CYP11B1 prevents the production of excess cortisol, thereby decreasing and normalizing the levels of cortisol. CD is most often caused by an adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)-secreting pituitary tumor. See also: Osilodrostat Phosphate (active moiety of). Drug Indication Osilodrostat is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with Cushing's disease for whom pituitary surgery is not an option or has not been curative. FDA Label Isturisa is indicated for the treatment of endogenous Cushing's syndrome in adults. Treatment of adrenal cortical hyperfunction Mechanism of Action Cushing’s syndrome is an endocrine disorder resulting from chronic and excessive exposure to glucocorticoids, the symptoms of which may include thinning of the skin and hair, weight gain, muscle weakness, and osteoporosis, as well a constellation of psychiatric, cardiovascular, and immunological deficiencies. Cushing’s syndrome is most commonly precipitated by exogenous treatment with supraphysiological doses of glucocorticoids such as those found in nasal sprays, skin creams, and inhalers. Cushing’s disease - another less common cause of Cushing’s syndrome - is generally the result of increased endogenous cortisol exposure due to excessive secretion of adrenocroticotrophic hormone (ACTH) from a pituitary adenoma. Osilodrostat is an inhibitor of 11β-hydroxylase (CYP11B1) and, to a lesser extent, aldosterone synthase (CYP11B2). The CYP11B1 enzyme is responsible for catalyzing the final step of cortisol synthesis - by inhibiting this enzyme, osilodrostat helps to normalize endogenous cortisol levels and alleviate symptoms of Cushing’s disease. In conclusion, we show that osilodrostat in pharmacological concentrations is a potent inhibitor of in vitro cortisol and aldosterone secretion in human adrenocortical cells. We demonstrate highly variable sensitivity to steroidogenesis inhibitors with respect to cortisol production between adrenal tissues of patients, which together with differences in pharmacokinetics, potentially explain clinically observed differences between patients treated with the same compound. Under the conditions of our study, effects of osilodrostat and metyrapone on the steroid profile are highly comparable, where osilodrostat seems to block CYP11B1 and CYP11B2, in some conditions to a lesser extent CYP17A1 lyase activity, and a proximal step in the steroidogenesis pathway. Differences between osilodrostat and metyrapone in vivo are potentially the result of pharmacokinetic differences rather than the pharmacodynamic effects on the adrenal cortex. These data indicate that osilodrostat is a promising treatment option for patients with CS. Additional information from phase 3 trials will provide important further data on efficacy and safety of osilodrostat.[2] The combination of pasireotide and osilodrostat in rats did not change the toxicity profile and plasma exposure seen during administration of either agent alone, whereas the addition of pasireotide to the osilodrostat regimen may attenuate potential adrenal gland hypertrophy and hepatocellular hypertrophy. As such, this study suggests that the combination of pasireotide and osilodrostat has an acceptable safety profile. However, other safety concerns, in particular effects on QT interval, should also be considered prior to using the pasireotide and osilodrostat drug combination in humans.[3] |
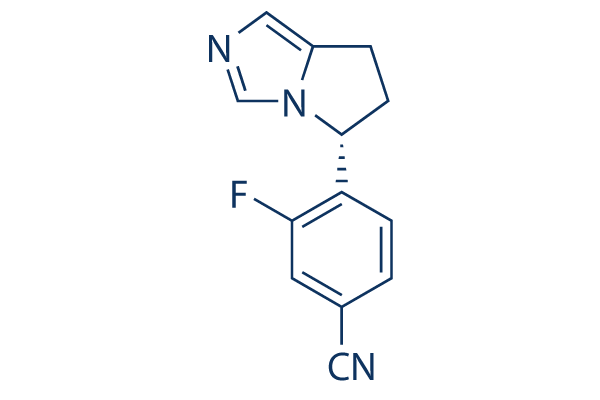
| 分子式 |
C13H10FN3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
227.24
|
| 精确质量 |
227.085
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 68.71; H, 4.44; F, 8.36; N, 18.49
|
| CAS号 |
928134-65-0
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Osilodrostat phosphate;1315449-72-9
|
| PubChem CID |
44139752
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to yellow solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
433.8±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
216.2±28.7 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.664
|
| LogP |
1.13
|
| tPSA |
41.61
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
1
|
| 重原子数目 |
17
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
337
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
C1CC2=CN=CN2[C@H]1C3=C(C=C(C=C3)C#N)F
|
| InChi Key |
USUZGMWDZDXMDG-CYBMUJFWSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C13H10FN3/c14-12-5-9(6-15)1-3-11(12)13-4-2-10-7-16-8-17(10)13/h1,3,5,7-8,13H,2,4H2/t13-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
4-[(5R)-6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo[1,2-c]imidazol-5-yl]-3-fluorobenzonitrile
|
| 别名 |
Osilodrostat;LCI699; Isturisa; LCI 699; osilodrostat; (+)-Osilodrostat; LCI699-NX; LCI-699-NX; 5YL4IQ1078; UNII-5YL4IQ1078; ...; 928134-65-0; LCI-699
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (11.00 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (11.00 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (11.00 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (11.00 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% EtOH + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 EtOH 储备液加入400 μL PEG300 中,混匀;再向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;然后加入450 μL 生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 5 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (11.00 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% EtOH + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100μL 25.0mg/mL澄清EtOH储备液加入到900μL 20%SBE-β-CD生理盐水中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 6 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (11.00 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% EtOH + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清乙醇储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.4006 mL | 22.0032 mL | 44.0063 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8801 mL | 4.4006 mL | 8.8013 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4401 mL | 2.2003 mL | 4.4006 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。