| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
DNA-PK (IC50 = 0.23 μM); PI3K (IC50 = 13 μM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
NU7026 (10 μM) 在呈指数增长的 DNA-PK 熟练但不缺乏的细胞中增强电离辐射 (IR) 细胞毒性 [90% 细胞杀灭时的增强因子 (PF90)=1.51±0.04][1]。 NU7026 协同使 I83 细胞对苯丁酸氮芥 (CLB) 敏感达 3.5 倍[2]。 NU7026,一种全新的DNA依赖性蛋白激酶(DNA-PK)抑制剂。对 CH1 人卵巢癌细胞的显着放射增敏作用需要至少 NU7026 暴露 4 小时以及 10 M 剂量的 3 Gy 辐射,这对细胞本身无毒[3]。体外溶液:NU7026溶解。使用 NU7026 处理细胞,最终 DMSO (v/v) 浓度为 0.25% DMSO (v/v)[4]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
NU7026是一种新型DNA-PK(DNA修复酶DNA依赖性蛋白激酶)抑制剂。以 5 mg/kg 的剂量静脉注射给小鼠后,NU7026 经历了快速的血浆清除(0.108 L/h),这在很大程度上归因于广泛的代谢。通过 ip 或 po 给药 20 mg/kg 后,生物利用度分别为 20% 和 15%[3]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
使用 Q-Sepharose、S-Sepharose 和肝素琼脂糖进行层析后,从 HeLa 细胞核提取物中分离出哺乳动物 DNA-PK (500 ng/μL)。在聚丙烯 96 孔板中,在含有 25 mM HEPES (pH 7.4)、12.5 mM MgCl2、50 mM KCl、1 mM DTT、10% v/v 甘油、0.1% 的缓冲液中评估 DNA-PK (250 ng) 活性w/v NP-40 和 1 mg 底物 GST-p53N66,30°C,最终体积为 40 μL。将不同浓度的 NU7026 添加到测定混合物中(在 DMSO 中,最终浓度为 1% v/v)。孵育 10 分钟后,添加 30 聚体双链 DNA 寡核苷酸(终浓度为 0.5 ng/mL)和 ATP,使终浓度为 50 μM,以开始反应。振荡 1 小时后,向反应液中加入 150 L PBS,然后将 5 µL 转移至每孔含有 45 µl PBS 的 96 孔不透明白色板中。然后给予 GSTp53N66 底物 1 小时以与孔结合。由图形包 Prism 生成的 S 形图绘制了一系列化合物浓度中酶活性与化合物浓度的关系图,用于计算每次酶测定中每种化合物的 IC50。
|
| 细胞实验 |
将 I83 细胞接种于含有 10% FBS (1.5×105 cells/mL) 的 RPMI 1640 培养基中,并用媒介物 (DMSO)、5 μM CLB、CLB IC50、10 μM NU7026 或两种药物的组合处理 0、6、 24 和 48 小时。测定细胞周期分布、细胞凋亡、DNA-PK磷酸化和γH2AX测定,并将它们表示为细胞周期各阶段的百分比。 DNA 含量使用配备 CellQuest 软件的 FACSCalibur 流式细胞仪进行分析[2]。
|
| 动物实验 |
Mice[3]
The BALB/c mice used are female. For i.p. and peroral (p.o.) administration, NU7026 is formulated in 10% DMSO and 5% Tween 20 in saline at 20 and 50 mg/kg, respectively. NU7026 is formulated in 10% ethanol, 25% PEG 200, and 5% Tween 20 in saline for i.v. dosing at 5 mg/kg. The vehicle is given to the control animals alone. Per time point, injections are given to groups of three mice. Following halothane's transient anesthesia, blood is taken by cardiac puncture at time points of 0.083, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 24 hours after administration. Samples are kept at 20°C until analysis after being centrifuged at 1500 g for 2 min to obtain plasma. NU7026 is injected at a rate of 5 mg/kg for studies on urinary excretion. In metabolic cages, urine is collected over a 24-hour period and kept in storage until needed at 20°C. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
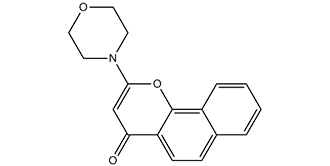
2-(4-morpholinyl)-4-benzo[h][1]benzopyranone is an organooxygen compound and an organic heterotricyclic compound.
Chlorambucil (CLB) treatment is used in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) but resistance to CLB develops in association with accelerated repair of CLB-induced DNA damage. Phosphorylated histone H2AX (gammaH2AX) is located at DNA double-strand break (DSB) sites; furthermore, it recruits and retains damage-responsive proteins. This damage can be repaired by nonhomologous DNA end-joining (NHEJ) and/or homologous recombinational repair (HR) pathways. A key component of NHEJ is the DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) complex. Increased DNA-PK activity is associated with resistance to CLB in CLL. We used the specific DNA-PK inhibitor 2-(morpholin-4-yl)-benzo[h]chomen-4-one (NU7026) to sensitize CLL cells to chlorambucil. Our results indicate that in a CLL cell line (I83) and in primary CLL-lymphocytes, chlorambucil plus NU7026 has synergistic cytotoxic activity at nontoxic doses of NU7026. CLB treatment results in G(2)/M phase arrest, and NU7026 increases this CLB-induced G(2)/M arrest. Moreover, a kinetic time course demonstrates that CLB-induced DNA-PK activity was inhibited by NU7026, providing direct evidence of the ability of NU7026 to inhibit DNA-PK function. DSBs, visualized as gammaH2AX, were enhanced 24 to 48 h after CLB and further increased by CLB plus NU7026, suggesting that the synergy of the combination is mediated by NU7026 inhibition of DNA-PK with subsequent inhibition of DSB repair.[2] In this study we investigated the in vitro time dependence of radiosensitisation, pharmacokinetics and metabolism of NU7026, a novel inhibitor of the DNA repair enzyme DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK). At a dose of 10 muM, which is nontoxic to cells per se, a minimum NU7026 exposure of 4 h in combination with 3 Gy radiation is required for a significant radiosensitisation effect in CH1 human ovarian cancer cells. Following intravenous administration to mice at 5 mg kg(-1), NU7026 underwent rapid plasma clearance (0.108 l h(-1)) and this was largely attributed to extensive metabolism. Bioavailability following interperitoneal (i.p.) and p.o. administration at 20 mg kg(-1) was 20 and 15%, respectively. Investigation of NU7026 metabolism profiles in plasma and urine indicated that the compound undergoes multiple hydroxylations. A glucuronide conjugate of a bis-hydroxylated metabolite represented the major excretion product in urine. Identification of the major oxidation site as C-2 of the morpholine ring was confirmed by the fact that the plasma clearance of NU7107 (an analogue of NU7026 methylated at C-2 and C-6 of the morpholine ring) was four-fold slower than that of NU7026. The pharmacokinetic simulations performed predict that NU7026 will have to be administered four times per day at 100 mg kg(-1) i.p. in order to obtain the drug exposure required for radiosensitisation.[3] |
| 分子式 |
C17H15NO3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
281.3059
|
| 精确质量 |
281.105
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 72.58; H, 5.37; N, 4.98; O, 17.06
|
| CAS号 |
154447-35-5
|
| 相关CAS号 |
503465-21-2 (NU-7107); 79105-88-7 (NU-7031); 842122-14-9 (NU-7200); 69541-04-4 (NU-7199)
|
| PubChem CID |
9860529
|
| 外观&性状 |
Yellow solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
459.9±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
231.9±28.7 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.673
|
| LogP |
3.29
|
| tPSA |
42.68
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
1
|
| 重原子数目 |
21
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
441
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O=C1C2=CC=C3C=CC=CC3=C2OC(N4CCOCC4)=C1
|
| InChi Key |
KKTZALUTXUZPSN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C17H15NO3/c19-15-11-16(18-7-9-20-10-8-18)21-17-13-4-2-1-3-12(13)5-6-14(15)17/h1-6,11H,7-10H2
|
| 化学名 |
2-morpholino-4H-benzo[h]chromen-4-one
|
| 别名 |
DNA-PK Inhibitor II; LY-293646; DNA-PK Inhibitor II; 2-(Morpholin-4-yl)-benzo[h]chromen-4-one; NU-7026; 2-morpholino-4H-benzo[h]chromen-4-one; 2-morpholin-4-ylbenzo[h]chromen-4-one; LY 293646; LY293646; NU7026; NU-7026; NU 7026
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~1 mg/mL (~3.5 mM)
Water: <1 mg/mL Ethanol: <1 mg/mL |
|---|
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5548 mL | 17.7740 mL | 35.5480 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7110 mL | 3.5548 mL | 7.1096 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3555 mL | 1.7774 mL | 3.5548 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
|
|