| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |

| 靶点 |
Influenza virus neuraminidase (IC50 = 2 nM) ; influenza A/H3N2, A/H1N2, A/H1N1, and B viruses
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
奥司他韦似乎对 B 型和 A/H1N1 流感病毒有效(平均 B IC50 值:13 nM;平均 H1N1 IC50 值:1.34 nM),但对 A/H1N2 和 A/H3N2 病毒更有效(平均 H3N2 IC50 值) :0.67 nM;平均 H1N2 IC50 值:0.9 nM)[3]。 RWJ-270201在甲型流感病毒神经氨酸酶抑制实验中的IC50(约0.34 nM)与奥司他韦酸(0.45 nM)相似。 B 病毒分离株 RWJ-270201 的 IC50 为 1.36 nM,低于羧酸奥司他韦 (8.5 nM),与扎那米韦 (2.7 nM) 相似[4]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
奥司他韦酸(0.1、1 或 10 mg/kg/天)对 Vietnam/1203/04 (VN1203/04) 病毒的抗病毒活性呈剂量依赖性。通过边缘管饲法每天两次施用。 50% 的小鼠受到 10 毫克/公斤/天的 5 天治疗方案的保护;治疗组的延迟死亡表明治疗停止后病毒仍在复制。理由:1 毫克/公斤/天和 10 毫克/公斤/天的剂量分别导致 60% 和 80% 的发病率,并显着降低器官中的病毒滴度 [5]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
RWJ-270201是一种新型的甲型和乙型流感病毒神经氨酸酶(NA)环戊烷抑制剂。我们比较了RWJ-270201与扎那米韦奥司他韦羧酸盐抑制临床流感分离株和具有明确耐药性突变的病毒NA活性的能力。在用甲型流感病毒进行的NA抑制试验中,RWJ-270201(约0.34 nM)的50%抑制浓度中值(IC(50))与羧酸奥司他韦(0.45 nM)相当,但低于扎那米韦(0.95 nM)。对于乙型流感病毒分离株,RWJ-270201的IC(50)(1.36 nM)与扎那米韦(2.7 nM)相当,低于奥司他韦羧酸盐(8.5 nM)。在NA(N2)中带有Glu119->Gly或Glu119->Ala取代的扎那米韦抗性变体仍然对RWJ-270201和奥司他韦羧酸盐敏感。然而,在NA(N2)中具有Arg292-->Lys替代的扎那米韦选择性变体对RWJ-270201(IC(50)=30 nM)和扎那米维尔(IC(50中)=20 nM。携带Arg152-->Lys替代的扎那米韦抗性乙型流感病毒变体对每种NA抑制剂都有抗性(IC(50)=100至750 nM)。具有His274-->Tyr取代的奥司他韦选择变体(N1)对奥司他韦羧酸盐(IC(50)=400 nM)和RWJ-270201(IC(50=40 nM)表现出抗性,但对扎那米韦(IC(50-=1.5 nM)保持完全敏感性。因此,在框架残基119或274中具有置换的耐药变体可以保持对其他NA抑制剂的敏感性,而功能残基152或292的置换会导致不同水平的交叉耐药性。我们得出结论,RWJ-270201是野生型和一些耐扎那米韦或耐奥司他韦的甲型和乙型流感病毒变体NA的强效抑制剂[4]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
GS 4071(oseltamivir carboxylate)是一种有效的流感病毒神经氨酸酶碳环过渡态模拟抑制剂,在体外对甲型和乙型流感病毒都有活性。GS 4116是GS 4071的胍类类似物,在组织培养中对流感病毒复制的抑制作用比GS 4071强10倍。测定了GS 4071、GS 4116及其乙酯前药在大鼠体内的口服生物利用度。胍类嘌呤类似物的母体化合物和前药均表现出较差的口服生物利用度(2 - 4%)和较低的血浆峰浓度(cmax;Cmax <0.06 μ g/ml)。相比之下,GS 4071的乙酯前药GS 4104具有良好的口服生物利用度(35%)和较高的Cmax (0.47 μ g/ml),是抑制流感病毒神经氨酸酶活性所需浓度的150倍(90%)。测定了GS 4104与GS 4071在小鼠(30%)、雪貂(11%)和犬(73%)中的生物利用度。所有四种动物的血浆中GS 4071的浓度都持续较高,在给药后12小时,血浆中GS 4071的浓度超过了抑制流感病毒神经氨酸酶活性所需的浓度90%。这些结果表明,GS 4104是GS 4071在动物体内的口服生物可利用前药,它有可能成为预防和治疗人类甲型和乙型流感病毒感染的口服药物。[1]
|
| 动物实验 |
Distribution of oseltamivir and oseltamivir carboxylate (OC) to the CNS and brain of rats.[6]
Several studies were performed to characterize the pharmacokinetics of oseltamivir and OC in the plasma, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and brain of Sprague-Dawley rats following single-dose bolus administration of oseltamivir (intravenous [i.v.] and oral) and OC (i.v.). In the i.v. studies, nonfasted adult rats (two groups of 35 animals for each test substance) received a dose of 30 mg/kg body weight of either oseltamivir or OC in aqueous solution with sodium chloride (0.9%; pH 4.0) via slow injection into the tail vein over 20 to 30 s. In both i.v. studies, pharmacokinetic sampling took place at 5 min and at 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, and 8 h postdose (four or five rats/time point). In the oral study, rats received oseltamivir phosphate by oral gavage at a dose of 1,000 mg/kg free base, and sampling was performed at 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8 h postdose (four rats/time point). Rats were terminally anesthetized using isoflurane (5% in oxygen) at each scheduled time point (at 5 min and at 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, and 8 h postdose for i.v. studies and at 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8 h postdose for oral studies), and approximately 0.5 ml of blood and as much CSF as possible were collected via puncture of the heart and cysterna magna, respectively. To investigate the effect of residual blood in brain tissue on the observed oseltamivir and OC concentrations in the i.v. studies, brain samples were obtained by whole-brain removal and homogenization in one group per test substance, while in the other group, brain tissue was perfused transcardially with physiological sodium chloride solution (0.9%; ca. 30 ml) before tissue collection and homogenization. Brain tissue perfusion was also performed in the oral study before collection and homogenization. All samples were stored at −20°C. Female 6-week-old BALB/c mice are anesthetized with isofluorane and intranasally inoculated with 50 μL of 10-fold serial dilutions of VN1203/04 virus in PBS. The mouse lethal dose (MLD50) is calculated after a 16-day observation period. Oseltamivir is administered by oral gavage twice daily for 5 or 8 days to groups of 10 mice at dosages of 0.1, 1, and 10 mg/kg/day. Control (infected but untreated) mice received sterile PBS (placebo) on the same schedule. Four hours after the first dose of Oseltamivir, the mice are inoculated intranasally with 5 MLD50 of VN1203/04 virus in 50 μL of PBS. Survival and weight change are observed for 24 days. Virus titers in the mouse organs are determined on days 3, 6, and 9 after inoculation. Three mice from each experimental and placebo group are killed, and the lungs and brains are removed. The organs are homogenized and suspended in 1 mL of PBS. The cellular debris is cleared by centrifugation at 2000 g for 5 min. The limit of virus detection is 0.75 log10 EID50. For calculation of the mean, samples with a virus titer <0.75 log10 EID50/mL are assigned a value of 0. Virus titers in each organ are calculated by use of the method of Reed and Muench and are expressed as mean log10 EID50/mL±SE.[3] Several studies are performed to characterize the pharmacokinetics of Oseltamivir and OC in the plasma, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and brain of Sprague-Dawley rats following single-dose bolus administration of Oseltamivir (intravenous [i.v.] and oral) and OC (i.v.). In the i.v. studies, nonfasted adult rats (two groups of 35 animals for each test substance) received a dose of 30 mg/kg body weight of either Oseltamivir or Oseltamivir carboxylate (OC) in aqueous solution with sodium chloride (0.9%; pH 4.0) via slow injection into the tail vein over 20 to 30 s. In both i.v. studies, pharmacokinetic sampling took place at 5 min and at 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, and 8 h postdose (four or five rats/time point).[4] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Oseltamivir, a potent and selective inhibitor of influenza A and B virus neuraminidases, is a prodrug that is systemically converted into the active metabolite oseltamivir carboxylate. In light of reported neuropsychiatric events in influenza patients, including some taking oseltamivir, and as part of a full assessment to determine whether oseltamivir could contribute to, or exacerbate, such events, we undertook a series of nonclinical studies. In particular, we investigated (i) the distribution of oseltamivir and oseltamivir carboxylate in the central nervous system of rats after single intravenous doses of oseltamivir and oseltamivir carboxylate and oral doses of oseltamivir, (ii) the active transport of oseltamivir and oseltamivir carboxylate in vitro by transporters located in the blood-brain barrier, and (iii) the extent of local conversion of oseltamivir to oseltamivir carboxylate in brain fractions. In all experiments, results showed that the extent of partitioning of oseltamivir and especially oseltamivir carboxylate to the central nervous system was low. Brain-to-plasma exposure ratios were approximately 0.2 for oseltamivir and 0.01 for oseltamivir carboxylate. Apart from oseltamivir being a good substrate for the P-glycoprotein transporter, no other active transport processes were observed. The conversion of the prodrug to the active metabolite was slow and limited in human and rat brain S9 fractions. Overall, these studies indicate that the potential for oseltamivir and oseltamivir carboxylate to reach the central nervous system in high quantities is low and, together with other analyses and studies, that their involvement in neuropsychiatric events in influenza patients is unlikely.[6]
|
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Oseltamivir acid is a cyclohexenecarboxylic acid that is cyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylic acid which is substituted at positions 3, 4, and 5 by pentan-3-yloxy, acetamido, and amino groups, respectively (the 3R,4R,5S enantiomer). An antiviral drug, it is used as the corresponding ethyl ester prodrug, oseltamivir, to slow the spread of influenza. It has a role as an antiviral drug, an EC 3.2.1.18 (exo-alpha-sialidase) inhibitor and a marine xenobiotic metabolite. It is a cyclohexenecarboxylic acid, an acetate ester, an amino acid and a primary amino compound.
Oseltamivir acid is a Neuraminidase Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of oseltamivir acid is as a Neuraminidase Inhibitor. See also: Oseltamivir (is active moiety of); Oseltamivir Phosphate (active moiety of); Oseltamivir carboxylate (annotation moved to). |
| 分子式 |
C14H24N2O4
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
284.356
|
| 精确质量 |
284.173
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 59.14; H, 8.51; N, 9.85; O, 22.51
|
| CAS号 |
187227-45-8
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Oseltamivir;196618-13-0;Oseltamivir acid hydrochloride;1415963-60-8;Oseltamivir acid-d3;1242184-43-5;Oseltamivir phosphate;204255-11-8
|
| PubChem CID |
449381
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
508.7±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
183-185°C
|
| 闪点 |
261.5±30.1 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.8 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.525
|
| LogP |
0.45
|
| tPSA |
101.65
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
20
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
391
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
3
|
| SMILES |
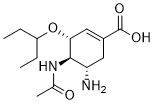
CCC(CC)O[C@@H]1C=C(C[C@@H]([C@H]1NC(=O)C)N)C(=O)O
|
| InChi Key |
(3R,4R,5S)-4-Acetamido-5-amino-3-pentan-3-yloxycyclohexene-1-carboxylic acid
|
| InChi Code |
NENPYTRHICXVCS-YNEHKIRRSA-N
|
| 化学名 |
Oseltamivir carboxylate
|
| 别名 |
GS-4071; Ro 64-0802; GS 4071; Ro-64-0802; GS4071; Ro64-0802; Oseltamivir acid; 187227-45-8; Oseltamivir carboxylate; GS4071; Oseltamivir free acid; (-)-;Oseltamivir acid
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ≥ 230 mg/mL (~808.86 mM)
H2O : ~125 mg/mL (~439.60 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 5.75 mg/mL (20.22 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 57.5 mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;再向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;然后加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 5.75 mg/mL (20.22 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 57.5mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入到900μL 20%SBE-β-CD生理盐水中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 5.75 mg/mL (20.22 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 100 mg/mL (351.68 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5167 mL | 17.5833 mL | 35.1667 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7033 mL | 3.5167 mL | 7.0333 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3517 mL | 1.7583 mL | 3.5167 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。