| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
FAK (IC50 = 1.5 nM); Pyk2 (IC50 = 13 nM); CDK2 (IC50 = 30 nM);CDK3 (IC50 = 47 nM); CDK1 (IC50 = 58 nM); CDK7 (IC50 = 97 nM); FLT3 (IC50 = 97 nM)
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在涉及重组酶的研究中,PF-562271 (VS-6062) 盐酸盐已证明对 CDK2/E、CDK5/p35、CDK1/B 和 CDK3/E 具有 30 至 120 nM 的抑制作用。然而,在涉及细胞的测定中,必须暴露 3.3 μM PF-562271 48 小时才能改变细胞周期的进程。 PF-562271 的 IC50 为 5 nM,在基于诱导细胞的检测磷酸-FAK 的检测中显示出效力。 PF -562271,富含脯氨酸酪氨酸激酶 2 (PYK2) 的选择性抑制剂,FAK 家族成员,也是 FAK 的选择性抑制剂,对尤文肉瘤细胞系中集落的形成和细胞增殖有影响。使用 2 倍连续稀释,用 PF-562271 以不同剂量处理 7 个细胞系五天。治疗三天后,PF-562271 疗法降低了所有细胞系的细胞活力,平均 IC50 为 2.4 μM。两种最敏感的细胞系是 TC32 和 A673,IC50 值分别为 2.1 和 1.7 μM[2]。
癌症细胞的特征是能够以不依赖于凤尾鱼的方式生长。非受体酪氨酸激酶,粘着斑激酶(FAK)的活性被认为是导致这种表型的原因。FAK定位于局灶性粘附斑块,并作为其他粘附分子的支架和信号蛋白发挥作用。最近的研究表明,FAK表达和磷酸化状态的增加与侵袭性人类肿瘤的侵袭表型之间存在很强的相关性PF-562271是一种强效、ATP竞争性、可逆的FAK和Pyk2催化活性抑制剂,IC(50)分别为1.5和14 nmol/L。此外,PF-562271在基于诱导细胞的检测磷酸化FAK的方法中显示出强烈的抑制作用,IC(50)为5 nmol/L。PF-562261对多种激酶进行了评估,对一长串非靶激酶显示出>100倍的选择性。[1] 在这项研究中,我们发现FAK在原发性尤文肉瘤肿瘤样本中高度磷酸化,短发夹RNA下调FAK和用FAK选择性激酶抑制剂PF-562271治疗会损害尤文肉瘤细胞系的生长和集落形成。此外,PF-562271处理尤因肉瘤细胞系诱导细胞凋亡,并导致AKT/mTOR和CAS活性下调。最后,我们发现FAK的小分子抑制可以减轻尤文肉瘤在体内的生长。FAK抑制剂目前正处于成人恶性肿瘤的早期临床试验阶段,这些发现可能与尤文肉瘤患者有直接相关性。[2] |
||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
当腹膜内给予荷瘤动物时,PF-562271 以剂量依赖性方式降低体内 FAK 磷酸化(计算得出的 EC50 为 93 ng/mL,总计)。当给大鼠施用 PF-562271 两周后,肿瘤生长减慢,并出现骨修复迹象,例如在肿瘤受损部位沉积新的皮质骨和松质骨[3]。 [3]。
PF-562271以剂量依赖的方式抑制体内FAK磷酸化(计算EC(50)为93ng/mL,总),口服给药后给荷瘤小鼠。单次口服剂量为33mg/kg时,FAK磷酸化的体内抑制(>50%)持续>4小时。在多种人皮下异种移植物模型中观察到抗肿瘤疗效和消退。在任何体内实验中都没有观察到体重减轻、发病率或死亡率。肿瘤生长抑制呈剂量和药物暴露依赖性。综上所述,这些数据表明,使用ATP竞争性FAK小分子抑制剂抑制激酶可以降低体内的磷酸化状态,从而产生强大的抗肿瘤活性。[1] 研究人员使用2种尤文肉瘤异种移植物模型测试了用PF-562271治疗对FAK活性的抑制是否可以抑制已建立肿瘤的进展。NCr裸小鼠和NSG小鼠分别皮下注射A673和TC32细胞,并使其产生可测量的肿瘤。然后用载体或PF-562271治疗动物,直至处死动物。与对照组相比,PF-562271治疗显著抑制了肿瘤生长,表明FAK活性有助于尤文肉瘤的肿瘤生长。[2] 该化合物耐受性良好。两个化合物治疗组的骨钙素和松质骨参数均显示出显著且相似的增加。对带有肿瘤的胫骨的放射学评估显示,与用PF-562271治疗的大鼠相比,未治疗大鼠的肿瘤扩张,肿瘤生长和骨愈合迹象减少。抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶和荧光原位杂交分析显示,肿瘤部位的大部分骨吸收是由大鼠来源的破骨细胞进行的。 结论:口服5mg/kg剂量的PF-562271抑制了胫骨内肿瘤的生长和局部扩散,并恢复了肿瘤引起的骨丢失。PF-562271抑制肿瘤生长和安全增加骨形成的独特能力可能是许多癌症骨转移和癌症相关骨质疏松症患者的有效治疗[3]。 |
||
| 酶活实验 |
重组激酶测定和酶动力学。[1]
之前已经描述了用于鉴定FAK抑制剂的所有体外试验(31)。简而言之,纯化的活化FAK激酶结构域(氨基酸410-689)与50μmol/L ATP和每孔10μg的Glu和Tyr的随机肽聚合物p(Glu/Tyr)在激酶缓冲液[50 mmol/L HEPES(pH 7.5)、125 mmol/L NaCl和48 mmol/L MgCl2]中反应15分钟。从1μmol/L的最高浓度开始,用1/2-Log浓度的连续稀释化合物挑战p(Glu/Tir)的磷酸化。每种浓度测试三次。用一般的抗磷酸酪氨酸(PY20)抗体检测p(Glu/Tyr)的磷酸化,然后用辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)偶联的山羊抗小鼠IgG抗体检测。加入HRP底物,在加入终止溶液(2mol/L H2SO4)后获得450nm处的吸光度读数。使用Hill Slope模型测定IC50值。宽激酶选择性分析在内部进行,并使用UpState Biotechnology提供的KinaseProfiler选择性筛选服务。2 基于细胞的FAK磷酸化测定。[1] 在米非司酮的诱导调节下,生成了稳定的A431上皮癌克隆,以表达野生型V5标记的FAK蛋白或突变型FAKY397F V5标记的蛋白。稳定的克隆在DMEM 10%胎牛血清、750μg/mL Zeocin和50μg/mL潮霉素中生长。在运行FAK细胞ELISA的前一天,将A431 FAK野生型细胞接种在96孔U形底板的生长培养基中。在37°C、5%CO2下4至6小时后,用0.1 nmol/L米非司酮诱导FAK表达。包括非诱导控制。在室温下,将抗-V5或抗FAK涂层板在3%牛血清白蛋白(BSA)/0.5%吐温中封闭1小时。细胞在37°C、5%CO2下以1μmol/L的最高浓度用1/2-Log系列稀释液处理30分钟。在裂解缓冲液[50 mmol/L Tris-HCl(pH 7.4)、1%NP40、0.25%脱氧胆酸钠、150 mmol/L NaCl、1 mmol/L EDTA、1 mmol/L Na3VO4、1 mmol/L氟化钠和蛋白酶抑制剂]中制备用指定浓度化合物处理的细胞的裂解物,并将其转移到抗V5或抗FAK涂层板上,以捕获总诱导或总FAK蛋白。用抗磷酸特异性FAKY397检测自身磷酸化的FAKY397s,然后检测二级报告抗体。加入HRP底物,在450nmol/L下读取平板读数。使用Hill Slope模型测定IC50值。进行3-(4,5-二甲基噻唑-2-基)-2,5-二苯基溴化四氮唑测定以确定化合物的细胞毒性。 高通量激酶活性分析[1] 如前所述,对6种尤文肉瘤细胞系(EWS502、TC71、TC32、A673、SKNEP和EW8)和293FT细胞进行了Luminex免疫夹心测定。简而言之,对每个细胞系的全细胞裂解物进行定量,并在4°C下将等浓度的蛋白质与87个经验证的抗体偶联的Luminex珠(探针)的混合物一起孵育过夜,这些珠对62种酪氨酸激酶具有特异性。然后洗涤混合物,在室温下用生物素标记的4G10抗体孵育30分钟,洗涤,然后在室温下与4μg/mL的SAPE孵育10分钟。将偶联物再洗涤2次,并在FlexMAP 3D 上用xPONENT软件(版本4.0;Luminez)进行分析,以确定中值荧光强度(MFI)。 |
||
| 细胞实验 |
体外小分子治疗[2]
将尤文肉瘤细胞铺在10cm培养皿中,使其粘附24小时,然后用PF-562271(FAK/PYK2抑制剂、PD0325901或达沙替尼(SRC、BCR/ABL、c-Kit抑制剂)处理。 细胞活力[2] 使用CellTiter Glo发光细胞活力测定法测量ATP含量作为细胞数量的替代指标。使用FLUOstar Omega微孔板读数仪获得发光读数。对于小分子治疗的实验,将1.25×103个尤文氏肉瘤细胞接种在每个孔中,并用不同浓度进行处理。使用GraphPad Prism 5.0中的对数转换归一化数据,从治疗3天后获得的ATP测量值计算IC50值。细胞系也在6-cm培养皿中用化合物处理,胰蛋白酶处理,并使用台盼蓝排斥法通过光学显微镜计数。对于使用shRNA转导细胞的实验,在转导后第3天,每孔将1.25×103个细胞接种到384孔板中。在转导后第3、6和8天测量ATP含量。 甲基纤维素基质中的菌落形成[2] 将约3.75×103个细胞溶解在1.5 mL甲基纤维素基质中,铺在6 cm网格板上,孵育至少10天。使用尼康倒置显微镜对100个正方形的菌落进行计数。 流式细胞术[2] 使用ApoAlert Annexin V-FITC凋亡试剂盒通过流式细胞术鉴定经历凋亡的细胞。对于细胞内磷蛋白染色,使用BD Cytofix/Cytoperm试剂盒固定和渗透细胞,用藻红蛋白(PE)抗磷酸-S6染色,并通过流式细胞术进行分析 PF-562271-01是重组FAK和Pyk2激酶的强效ATP竞争性可逆抑制剂,IC50分别为1.5和14 nMPF-562271使用0.5%甲基纤维素配制用于口服给药。在给药的第一天,大鼠通过经口灌胃接受单剂量PF-562271(10mg/kg)。根据给药后1小时的暴露水平,剂量降至5mg/kg。从第二天开始,大鼠每天口服5mg/kg,持续28天。在肿瘤接种后2周开始给药,并且只有在射线照相证实肿瘤存在后才开始给药。在研究过程中证实了血清中受试化合物的存在[3]。 |
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
The pharmacokinetics, inhibition of phosphorylated FAK, and antitumor efficacy of PF-562,271 was evaluated in the following human s.c. xenograft models: PC-3M (prostate), BT474 (breast), BxPc3 (pancreatic), LoVo (colon), U87MG (glioblastoma), and H125 and H460 (lung; Table 2). Dose-dependent tumor growth inhibition was observed in all models. Maximum tumor inhibition for PC-3M, BT474, BxPc3, and LoVo ranged from 78% to 94% inhibition for the group with regressions in up to 50% of a given dose group (Table 2). Regressions were observed in PC-3M, BT474, BxPc3, and LoVo models at doses of 25 to 50 mg/kg twice daily, corresponding to Cmax (free) ranges of 78 to 885 ng/mL, Cave (free) of 14 to 40 ng/mL, and inhibition of phospho-FAK of 31% to 76% for >4 hours. No weight loss, morbidity, or death was observed in any tumor growth inhibition (TGI) experiment (up to 50 mg/kg twice daily × 29 days or 100 mg/kg daily × 25 days). All data are based on 6 to 10 animals per dose, and experiments were completed at least twice. After dosing, animals were euthanized, blood and tumor were analyzed for drug concentration (PK), and tumors were evaluated for phospho-FAK (PD). [1]
A rigorous in vivo PK/PD evaluation was completed for PF-562,271. The compound is well-absorbed with maximal blood levels occurring between 30 minutes and 2 hours after p.o. administration. Maximal pharmacodynamic modulation occurs simultaneously with maximal pharmacokinetic exposure in the blood regardless of dose or number of repeated doses. Measured PK is accurately modeled using in vitro and in vivo calculation of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, demonstrating a well-behaved and predictable in vivo pharmacology. [1] |
||
| 参考文献 |
|
||
| 其他信息 |
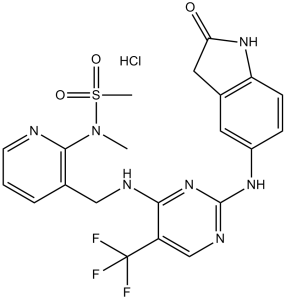
N-methyl-N-[3-[[[2-[(2-oxo-1,3-dihydroindol-5-yl)amino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-4-pyrimidinyl]amino]methyl]-2-pyridinyl]methanesulfonamide is a member of indoles.
Broadly speaking, pharmacologic anticancer therapy consists of cytotoxics and targeted agents (small molecules and biologics). Unfortunately, the majority of patients treated with these agents eventually progress. In addition, toxicities associated with these agents often preclude adequate treatment. In this report, the in vivo pharmacology of a highly selective and potent inhibitor of FAK catalytic activity, PF-562,271, is described. The novel mode of inhibition of FAK, characterized by the inhibitor-induced “DFG helix,” resulted in profound antitumor activity across a wide variety of tumor types while being well-tolerated. PF-562,271 showed well-behaved pharmacology in vivo with a robust PK/PD relationship. PF-562,271 shows the selectivity and pharmacology that has allowed it to be a first in class inhibitor presently in clinical testing for the treatment of cancer.[1] In conclusion, the results of the current study demonstrate that the oral administration of PF-562,271 at a dose of 5 mg/kg suppressed the growth and local spread of intratibial tumors and also restored tumor-induced bone loss. These unique properties of PF-562,271, namely the ability to curb tumor growth and safely increase bone formation, could be effectively used in many cancer patients with bone metastases and cancer-associated osteoporosis. Finally, this class of drugs has the potential to be used effectively in combination with other anticancer therapies as well as with bisphosphonates to prevent and treat bone metastases.[3] |
| 分子式 |
C21H21CLF3N7O3S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
543.95
|
| 精确质量 |
543.106
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 46.37; H, 3.89; Cl, 6.52; F, 10.48; N, 18.03; O, 8.82; S, 5.89
|
| CAS号 |
939791-41-0
|
| 相关CAS号 |
PF-562271;717907-75-0; 939791-38-5 (besylate); 939791-39-6 (mesylate); 939791-41-0 (HCl); 939791-40-9
|
| PubChem CID |
16222312
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| tPSA |
138
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
12
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
36
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
856
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
Cl.O=C1CC2C(=CC=C(NC3N=C(NCC4C(N(S(C)(=O)=O)C)=NC=CC=4)C(C(F)(F)F)=CN=3)C=2)N1
|
| InChi Key |
RQEBZJWSAAWCAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C21H20F3N7O3S.ClH/c1-31(35(2,33)34)19-12(4-3-7-25-19)10-26-18-15(21(22,23)24)11-27-20(30-18)28-14-5-6-16-13(8-14)9-17(32)29-16;/h3-8,11H,9-10H2,1-2H3,(H,29,32)(H2,26,27,28,30);1H
|
| 化学名 |
N-methyl-N-[3-[[[2-[(2-oxo-1,3-dihydroindol-5-yl)amino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidin-4-yl]amino]methyl]pyridin-2-yl]methanesulfonamide;hydrochloride
|
| 别名 |
PF562271 HCl; PF-562271 HCl; 939791-41-0; PF-562,271 (hydrochloride); Methanesulfonamide,N-[3-[[[2-[(2,3-dihydro-2-oxo-1H-indol-5-yl)amino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-4-pyrimidinyl]amino]methyl]-2-pyridinyl]-N-methyl-,hydrochloride(1:1); 939791-41-0 (HCl); PF-00562271; PF562271 hydrochloride; PF 562271; PF562271; PF-562271; PF00562271; PF 00562271; PF00562271 hydrochloride. PF271; PF-271; PF 271;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|---|
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8384 mL | 9.1920 mL | 18.3840 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3677 mL | 1.8384 mL | 3.6768 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1838 mL | 0.9192 mL | 1.8384 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Efficacy of PF-562,271 in PC3M-luc-C6 subcutaneuous local implant xenograft model: PF-562,271 was administered at 25 mg/kg P.O. BID 5x/wk for two weeks.Cancer Biol Ther.2010Jul 1;10(1):38-43. |
(A) Bioluminescent image time course of a subcutaneously inoculated vehicle control mouse. PF-562,271 was administered at 25 mg/kg P.O. BID 5x/wk for two weeks. (B) Bioluminescent image time course of a subcutaneously inoculated mouse treated with PF-562,271. PF-562,271 was administered at 25 mg/kg P.O. BID 5x/wk for two weeks.Cancer Biol Ther.2010Jul 1;10(1):38-43. |
(A) Bioluminescent image time course of an intracardiac inoculated vehicle control mouse. Vehicle was administered P.O. BID 5x/wk for three weeks. (B) Bioluminescent image time course of an intracardiac inoculated treated with PF-562,271. PF-562,271 was administered at 25 mg/kg P.O. BID 5x/wk for three weeks. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010 Jul 1; 10(1): 38–43. |