| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
CDK9 (IC50 = 34 nM); CDK2 (IC50 = 240 nM); CDK1 (IC50 = 250 nM); CDK5 (IC50 = 460 nM); GSK3-β (IC50 = 220 nM); Mk2 (IC50 = 470 nM); Plk1 (IC50 = 980 nM); Chk2 (IC50 = 1100 nM)
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:PHA-767491 对 Cdk1、Cdk2 和 GSK3-β 的选择性约为 20 倍,对 MK2 和 Cdk5 的选择性约为 50 倍,对 PLK1 和 CHK2 的选择性约为 100 倍。 PHA-767491 可抑制多种人类细胞系的细胞增殖,SF-268 的 IC50 为 0.86 μM,K562 的 IC50 为 5.87 μM,并且与 5-FU 或吉西他滨仅在少数细胞系中起作用。与目前的 DNA 合成抑制剂不同,5 μM 的 PHA-767491 处理会阻止 DNA 复制的启动,但不会阻止复制叉的进展,因为它对 Cdc7 激酶和 Cdc7 依赖性 Ser40 位点的 Mcm2 磷酸化有特异性抑制。 3 μM 的 PHA-767491 处理可显着降低 ABT-737 耐药性 OCI-LY1 和 SU-DHL-4 细胞中上调的 Mcl-1 水平,这可能是由于 Cdk9 的抑制,从而恢复对 ABT-737 敏感。当以 1 μM 浓度应用于静态慢性淋巴细胞白血病 (CLL) 细胞时,通过类似的机制也观察到 PHA-767491 的直接线粒体依赖性促凋亡作用,EC50 为 0.34-0.97 μM。在 CD154 和 IL-4 刺激的 CLL 细胞增殖中,5 μM 的 PHA-767491 处理通过抑制 Cdc7 来消除 DNA 合成,而不是触发细胞死亡。激酶测定:PHA-767491 对 Cdc7 和 Cdk9 的抑制 (IC50) 使用基于强阴离子交换剂(Dowex 1-X8 树脂,甲酸盐形式)的测定来确定。对于每种酶,首先确定 ATP 和特定底物的绝对 Km 值,然后以优化的 ATP/33P-γ-ATP 混合物 (2Km) 和底物 (5Km) 浓度运行每次测定。 Cdc7 激酶测定在含有 50 mM Hepes pH 7.9、15 mM MgCl2、2 mM β-磷酸甘油、0.2 mg/mL BSA、1 mM DTT、3 μM Na3VO4、2Km ATP/33P-γ-ATP 混合物、5Km 的缓冲液中进行Mcm2 (aa 10-294)、37 nM 重组 Cdc7/Dbf4 和浓度不断增加的 PHA-767491,最终体积为 30 μL,并在 25 °C 下孵育 1 小时。使用 50 mM HEPES pH 7.5、10 mM MgCl2、1 mM DTT、3 μM Na3VO4、2Km ATP/33P-γ-ATP 混合物、5Km RNA 聚合酶 CDT 肽和增量溶液中的 50 nM 重组 Cdk9/cyclin T 进行 Cdk9 激酶测定。将 PHA-767491 浓缩至最终体积 30 μL,并在 25 °C 下孵育 1 小时。孵育后,加入 150 μL 树脂/甲酸盐 (pH 3.0) 以停止反应并捕获未反应的 33P-γ-ATP,将其与溶液中的磷酸化底物分离。静置 1 小时后,将 50 μL 上清液转移至 Optiplate 96 孔板中。添加 150 μL Microscint 40 后,在 TopCount 中对放射性进行计数。细胞测定:将细胞(HeLa、MCF7、HCT-116、U2OS、A2780、K562、SF-539、SF-268、Ovcar8、SW480、COLO205、HCT-15、Jurkat、PC3 和 NHDF)暴露于 PHA-767491 24 或 72 小时。将细胞裂解,并使用基于热稳定性萤火虫荧光素酶的测定法测定孔中的 ATP 含量(用作活细胞的测量值)。 caspase-3 和 caspase-7 的激活通过基于荧光素酶的测定(包含特定的发光底物)以处理的样品与未处理的对照之间的比率来测量。 DNA 复制是通过流式细胞术将核苷酸类似物 BrdU 掺入 DNA 来测量的。
|
||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
PHA-767491 每天两次,持续 5 天,以剂量依赖性方式显着抑制 HL60 异种移植物的生长,剂量为 20 mg/kg 和 30 mg/kg 时,TGI 分别为 50% 和 92%。这也在 A2780、Mx-1 和 HCT-116 异种移植模型以及 DMBA 诱导的乳腺癌中被标记,并且与 Cdc7 抑制以及随后 Cdc7 依赖位点 Ser40 处 Mcm2 磷酸化的降低相关。
PHA-767491对肿瘤模型具有抗肿瘤活性[4] PHA-767491作为一种抗癌药物的潜力首次在裸鼠身上进行了评估,裸鼠携带来自急性髓性白血病(AML) HL60人细胞系的皮下植入肿瘤。在静脉注射20和30 mg kg−1两种剂量水平,每天两次,连续5天后,观察到相对于药物治疗的动物,肿瘤体积呈剂量依赖性减少(图4a)。在治疗结束后的第二天计算,肿瘤生长抑制在低剂量下为50%,在高剂量下为92%,其中8只动物中有5只观察到肿瘤消退的证据。在此条件下,化合物达到微摩尔血浆水平,浓度-时间曲线下面积(AUC)分别为47 μM h−1和71 μM h−1,与基于细胞的活性水平一致。PHA-767491在组织中表现出良好的体积分布(约为体内总含水量的两倍),并能迅速从血浆中清除(在线补充图7)。在这些剂量下,这种化合物似乎具有良好的耐受性,并且没有引起明显的体重减轻;然而,进一步的剂量增加是不能容忍的。在一项毒理学研究中,PHA-767491每天两次,剂量为30 mg kg−1,持续5天,未观察到临床症状或大体病变。从治疗动物身上移植的36个不同器官的组织病理学分析表明,睾丸萎缩,骨髓骨髓中度增生,脾脏淋巴细胞减少,这与报道的Cdc7在睾丸中的高水平表达和Cdc7在高增殖组织中的作用一致。在A2780卵巢癌、Mx-1乳腺腺癌和HCT-116结肠癌异种移植模型中,给药PHA-767491也导致肿瘤生长抑制,治疗5天后,肿瘤生长抑制率约为50%(图4b和在线补充图8)。 然后,我们给患有7,12-二甲基苯(a)蒽(DMBA, 12)诱导的乳腺癌的大鼠注射PHA-767491 10天。在这个实验中,肿瘤生长在治疗期间受到抑制,并在接下来的两周内显著降低(图4c)。为了将抗肿瘤活性与Cdc7抑制作用联系起来,用western blot方法分析了从对照或动物外植的HCT-116肿瘤,并对其进行了5 d周期的PHA-767491处理。在治疗动物的肿瘤中,cdc7依赖位点Ser40的Mcm2磷酸化显著降低(图5a)。肿瘤切片的免疫组织化学(IHC)证实,在处理过的肿瘤活区,大多数细胞的Ser40 Mcm2磷酸化水平较低(图5b),而Ser807/811的Rb磷酸化水平和cyclin a阳性细胞的数量没有减少。PHA-767491处理导致ki67阳性细胞显著增加,原因尚不清楚。 总之,这些结果表明(i) PHA-767491可以在体内抑制Cdc7激酶,(ii) Mcm2磷酸化的丧失是该化合物对活的循环细胞的直接影响,而不是由治疗肿瘤细胞的增殖指数下降或坏死区域的差异引起的-坏死区域是hct -116来源的异种移植肿瘤的特征38。 我们得出结论,PHA-767491在多种临床前癌症模型和至少两种不同物种体内具有抗肿瘤活性。 |
||
| 酶活实验 |
将浓度逐渐增加的每种 DDK 抑制剂与 20 ng 纯化的人 DDK 预孵育 5 分钟。添加 1.5 µM 冷 ATP 和 10 µCi (γ)-32P ATP 后,将混合物与 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5)、10 mM MgCl2 混合和 1 mM DTT。然后在 30°C 下孵育 30 分钟。蛋白质在 1X Laemmli 缓冲液中于 100°C 变性后,进行 SDS-PAGE 和 HyBlot CL 胶片上的放射自显影。测量 DDK 激酶活性的一种方法是寻找自磷酸化。 ImageJ 用于量化 32P 标记条带,GraphPad 用于确定 IC50 值。
体外激酶测定。[4] 该化合物对Cdc7和属于我们激酶选择性筛选(KSS)面板的37种其他激酶的效力是通过基于强阴离子交换剂(Dowex 1-X8树脂,甲酸酯形式)的测定或闪烁接近测定来确定的,如前所述25,26。用50 nM重组Cdk9/cyclin T在50 mM HEPES pH 7.5、10 mM MgCl2、1 mM DTT、3 μM Na3VO4、150 μM RNA聚合酶CDT肽和80 μM ATP中测定Cdk9活性。Cdk7实验在相同的缓冲液中进行,使用37 nM纯化激酶,存在200 μM ATP和10 μM髓鞘结合蛋白作为底物。 对于每种酶,首先确定ATP和特定底物的绝对Km值,然后在优化的ATP (2Km)和底物(5Km)浓度下运行每个实验。因为在这些条件下IC50 = 3βKi,这个设置可以直接比较整个KSS面板上PHA-767491的IC50值,以评估其生化选择性。 |
||
| 细胞实验 |
用于测定的96孔板的每个孔中铺有2500个细胞。 24小时后,细胞接受小分子抑制剂处理,然后在37°C下孵育72小时。接下来,细胞进行裂解,并采用 CellTiter-Glo 测定来量化 ATP 含量,作为代谢活跃细胞的标记。利用GraphPad软件确定IC50值。用于测定的六孔板中每孔铺有 100,000 个细胞。一天后将小分子抑制剂应用于细胞,然后培养不同的时间长度。将胰蛋白酶处理的细胞悬浮于 5 毫升磷酸盐缓冲盐水中。将 30 µL 该悬浮液与 30 µL CellTiter-Glo 试剂混合后,在室温下孵育 10 分钟。 EnVision 2104 多标签读板机和 BioTek Synergy Neo 酶标仪用于测量光度。
细胞活力测定[3] 5×103 U87-MG和U251-MG细胞于处理前24 h接种于96孔板。第二天,用抑制剂(终浓度为10µM)、溶剂对照(水)或不处理细胞。72h后,细胞上加入10µl PrestoBlue细胞活力试剂,测定细胞活力。将溶剂控制的活力设为100%,计算相对细胞活力。实验至少重复了三次。 细胞增殖试验[3] 将U87-MG和U251-MG细胞在添加1% FBS的培养基中保持24 h,然后将1 × 104个U87-MG和U251-MG细胞接种于96孔板中。第二天,用抑制剂(终浓度2.5或10µM)、溶剂对照(水)或不处理细胞。治疗72小时后,按照制造商的说明使用溴脱氧尿苷(BrdU)细胞增殖ELISA试剂盒。将溶剂对照处理的细胞增殖率设为100%,计算细胞的相对增殖率。 |
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
In a toxicology study in which PHA-767491 was administered for 5 d at 30 mg kg−1 twice a day, no clinical signs or gross lesions were observed. Histopathological analysis of 36 different organs explanted from the treated animals indicated signs of atrophy of the testes, moderate myeloid hyperplasia in the bone marrow and minimal lymphoid depletion in the spleen, which is consistent with the reported high levels of Cdc7 expression in testis10 and with Cdc7's role in highly proliferating tissues. [4]
|
||
| 参考文献 |
|
||
| 其他信息 |
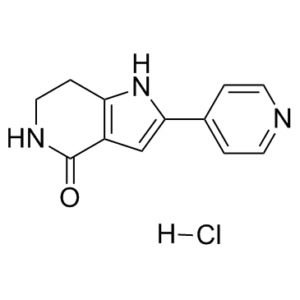
2-pyridin-4-yl-1,5,6,7-tetrahydropyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-4-one is a pyrrolopyridine.
PHA-767491 is a Cdc7/CDK9 inhibitor. Cdc7-Dbf4 kinase or DDK (Dbf4-dependent kinase) is required to initiate DNA replication by phosphorylating and activating the replicative Mcm2-7 DNA helicase. DDK is overexpressed in many tumor cells and is an emerging chemotherapeutic target since DDK inhibition causes apoptosis of diverse cancer cell types but not of normal cells. PHA-767491 and XL413 are among a number of potent DDK inhibitors with low nanomolar IC50 values against the purified kinase. Although XL413 is highly selective for DDK, its activity has not been extensively characterized on cell lines. We measured anti-proliferative and apoptotic effects of XL413 on a panel of tumor cell lines compared to PHA-767491, whose activity is well characterized. Both compounds were effective biochemical DDK inhibitors but surprisingly, their activities in cell lines were highly divergent. Unlike PHA-767491, XL413 had significant anti-proliferative activity against only one of the ten cell lines tested. Since XL413 did not effectively inhibit DDK in multiple cell lines, this compound likely has limited bioavailability. To identify potential leads for additional DDK inhibitors, we also tested the cross-reactivity of ∼400 known kinase inhibitors against DDK using a DDK thermal stability shift assay (TSA). We identified 11 compounds that significantly stabilized DDK. Several inhibited DDK with comparable potency to PHA-767491, including Chk1 and PKR kinase inhibitors, but had divergent chemical scaffolds from known DDK inhibitors. Taken together, these data show that several well-known kinase inhibitors cross-react with DDK and also highlight the opportunity to design additional specific, biologically active DDK inhibitors for use as chemotherapeutic agents.[1] Activation of checkpoint kinase 1 (Chk1) is essential in chemoresistance of hepatocarcinoma (HCC) to 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and other antimetabolite family of drugs. In this study, we demonstrated that PHA-767491, a dual inhibitor of two cell cycle checkpoint kinases, cell division cycle kinase 7 (Cdc7) and cyclin-dependent kinase 9 (Cdk9), has synergistic antitumor effect with 5-FU to suppress human HCC cells both in vitro and in vivo. Compared with the sole use of each agent, PHA-767491 in combination with 5-FU exhibited much stronger cytotoxicity and induced significant apoptosis manifested by remarkably increased caspase 3 activation and poly(ADP-Ribose) polymerase fragmentation in HCC cells. PHA-767491 directly counteracted the 5-FU-induced phosphorylation of Chk1, a substrate of Cdc7; and decreased the expression of the anti-apoptotic protein myeloid leukemia cell 1, a downstream target of Cdk9. In tumor tissues sectioned from nude mice HCC xenografts, administration of PHA-767491 also decreased Chk1 phosphorylation and increased in situ cell apoptosis. Our study suggests that PHA- 767491 could enhance the efficacy of 5-FU by inhibiting Chk1 phosphorylation and down-regulating Mcl1 expression through inhibition of Cdc7 and Cdk9, thus combinational administration of PHA-767491 with 5-FU could be potentially beneficial to patients with advanced and resistant HCC. [2] Background: Genomic instability is a hallmark of cancer cells, and this cellular phenomenon can emerge as a result of replicative stress. It is possible to take advantage of replicative stress, and enhance it in a targeted way to fight cancer cells. One of such strategies involves targeting the cell division cycle 7-related protein kinase (CDC7), a protein with key roles in regulation of initiation of DNA replication. CDC7 overexpression is present in different cancers, and small molecule inhibitors of the CDC7 have well-documented anti-tumor effects. Here, we aimed to test the potential of CDC7 inhibition as a new strategy for glioblastoma treatment. Methods: PHA-767491 hydrochloride was used as the CDC7 inhibitor. Two glioblastoma cell lines (U87-MG and U251-MG) and a control cell line (3T3) were used to characterize the effects of CDC7 inhibition. The effect of CDC7 inhibition on cell viability, cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion were analyzed. In addition, real-time PCR arrays were used to identify the differentially expressed genes in response to CDC7 inhibition. Results: Our results showed that CDC7 inhibition reduces glioblastoma cell viability, suppresses cell proliferation, and triggers apoptosis in glioblastoma cell lines. In addition, we determined that CDC7 inhibition also suppresses glioblastoma cell migration and invasion. To identify molecular targets of CDC7 inhibition, we used real-time PCR arrays, which showed dysregulation of several mRNAs and miRNAs. Conclusions: Taken together, our findings suggest that CDC7 inhibition is a promising strategy for treatment of glioblastoma.[3] Cdc7 is an essential kinase that promotes DNA replication by activating origins of replication. Here, we characterized the potent Cdc7 inhibitor PHA-767491 (1) in biochemical and cell-based assays, and we tested its antitumor activity in rodents. We found that the compound blocks DNA synthesis and affects the phosphorylation of the replicative DNA helicase at Cdc7-dependent phosphorylation sites. Unlike current DNA synthesis inhibitors, PHA-767491 prevents the activation of replication origins but does not impede replication fork progression, and it does not trigger a sustained DNA damage response. Treatment with PHA-767491 results in apoptotic cell death in multiple cancer cell types and tumor growth inhibition in preclinical cancer models. To our knowledge, PHA-767491 is the first molecule that directly affects the mechanisms controlling initiation as opposed to elongation in DNA replication, and its activities suggest that Cdc7 kinase inhibition could be a new strategy for the development of anticancer therapeutics. [4] |
| 分子式 |
C12H11N3O.HCL
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
249.7
|
|
| 精确质量 |
249.067
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 57.72; H, 4.84; Cl, 14.20; N, 16.83; O, 6.41.
|
|
| CAS号 |
942425-68-5
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
PHA-767491;845714-00-3; PHA-767491 hydrochloride;942425-68-5; 845538-12-7 (2HCl)
|
|
| PubChem CID |
11715766
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to yellow solid powder
|
|
| LogP |
2.493
|
|
| tPSA |
57.78
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
2
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
1
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
17
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
275
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
Cl.O=C1C2=C(NC(C3C=CN=CC=3)=C2)CCN1
|
|
| InChi Key |
IMVNFURYBZMFDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C12H11N3O.ClH/c16-12-9-7-11(8-1-4-13-5-2-8)15-10(9)3-6-14-12;/h1-2,4-5,7,15H,3,6H2,(H,14,16);1H
|
|
| 化学名 |
2-pyridin-4-yl-1,5,6,7-tetrahydropyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-4-one;hydrochloride
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 1 mg/mL (4.00 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 10.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 1 mg/mL (4.00 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 10.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: 5% DMSO+30% PEG 300+2% Tween 80+ddH2O: 1mg/mL 配方 4 中的溶解度: 50 mg/mL (200.24 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.0048 mL | 20.0240 mL | 40.0481 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8010 mL | 4.0048 mL | 8.0096 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4005 mL | 2.0024 mL | 4.0048 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
|
|---|
|
|