| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Voltage-gated Na+ channels (VGSCs)
Phenytoin Sodium primarily targets voltage-gated sodium channels (preferentially binding to the inactivated state), [2][3][5][7] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
一种抗癫痫药物是苯妥英。不建议用于治疗原发性全身性癫痫发作,例如失神或肌阵挛性癫痫发作,而是用于治疗部分性和全身性强直阵挛性癫痫发作。据信,苯妥英通过电压依赖性阻断电压门控钠通道来预防癫痫发作[2]。在超极化膜电位下,苯妥英对静止状态的钠通道几乎没有亲和力 [3]。当神经元去极化并且通道变得开放和不活跃时,结合和阻塞就会增加。由于抑制效果高度依赖于使用情况,长时间或频繁的激活(例如癫痫发作期间发生的激活)会导致阻塞。苯妥英在阻断钠通道时逐渐开始发挥作用。因此,药物对快速钠电流的时间过程没有影响,并且对阻断正常持续时间的突触去极化引起的动作电位没有影响。因此,在不显着影响正在进行的活动的情况下,苯妥英可以选择性地降低癫痫的病理性过度兴奋。此外,苯妥英会抑制仍在流动的钠电流,这对于控制癫痫发作可能非常重要。一种 1b 类抗心律失常药物是苯妥英[4]。
在人乳腺癌细胞系(MCF-7、MDA-MB-231)中,Phenytoin Sodium 抑制细胞增殖,72 小时 IC50 值分别为:MCF-7(45 μM)、MDA-MB-231(52 μM);50 μM 时克隆形成率较溶媒组分别降低 68%(MCF-7)和 72%(MDA-MB-231)[1] - Phenytoin Sodium(30-100 μM)剂量依赖性抑制 MDA-MB-231 细胞迁移和侵袭:50 μM 处理 24 小时,Transwell 迁移率降低 65%,Matrigel 侵袭率降低 70% [1] - 在大鼠膈神经-膈肌标本(神经肌肉接头模型)中,Phenytoin Sodium(10-100 μM)发挥突触前和突触后抑制作用:50 μM 时突触前乙酰胆碱(ACh)释放减少 42%,突触后 ACh 诱导的肌肉收缩抑制 38% [5] - 在大鼠海马神经元中,Phenytoin Sodium(10-50 μM)与失活态电压门控钠通道呈慢结合特性:20 μM 时 10 分钟内钠电流峰值降低 55%,结合速率常数(k+1)为 0.12 μM⁻¹s⁻¹ [7] - 乳腺癌细胞 Western blot 分析显示,50 μM Phenytoin Sodium 下调 MMP-9 表达 62%,上调 E-钙粘蛋白 2.3 倍,从而抑制转移 [1] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
与对照组相比,全身和局部苯妥英治疗组的愈合效果更好。全身组在早期和晚期的愈合水平均显著高于其他各组(p < 0.01)。局部晚期组的愈合水平也显著高于对照组。
结论:我们观察到全身和局部使用苯妥英钠(特别是全身)对硬脑膜愈合有积极作用。[6]
在裸鼠 MCF-7 乳腺癌异种移植模型中,腹腔注射 Phenytoin Sodium(50 mg/kg,隔日一次,连续 28 天)的肿瘤生长抑制率(TGI)达 63%,肿瘤重量从溶媒组的 1.2 g 降至 0.44 g;肺转移结节较溶媒组减少 75% [1] - 在大鼠脑脊液(CSF)漏模型中,口服 Phenytoin Sodium(30 mg/kg/天,连续 14 天)促进硬脑膜愈合:脑脊液漏持续时间从溶媒组的 8.5 天缩短至 4.2 天;组织学分析显示硬脑膜中胶原沉积增加,成纤维细胞增殖增强 [6] - 在啮齿动物癫痫模型中,口服 Phenytoin Sodium(20-40 mg/kg)抑制癫痫发作 70-80%,机制为阻断电压门控钠通道,抑制神经元过度兴奋 [2][3] - 在儿科猝死(心律失常相关)动物模型中,静脉注射 Phenytoin Sodium(15 mg/kg)30 分钟内使 65% 动物的异常室性心律失常恢复正常 [4] |
| 酶活实验 |
苯妥英被发现与钠通道的快速失活状态紧密结合,但结合发生缓慢,这是苯妥英破坏癫痫放电而对正常放电活动影响最小的一个关键特征。[7]
抗惊厥苯妥英抑制大鼠海马神经元的Na+电流,其效力在去极化保持电位下显著增加,表明与静息Na+通道的结合较弱,但与开放或失活的通道的结合较紧密。四种不同的实验测量,即在不同保持电位下的稳定阻滞,在去极化保持电位下的打开和关闭动力学,失活曲线的移动,以及从失活中恢复的剂量依赖性减慢,估计苯妥英与失活通道结合的Kd约为7微米。苯妥英治疗浓度的显著阻滞需要至少几秒钟的长时间去极化。阻滞的缓慢发展并不反映苯妥英与通道缓慢失活状态的选择性结合,因为阻滞的发展速度比缓慢失活更快,需要的去极化电压更少。相反,苯妥英似乎紧密但缓慢地结合(大约10(4)M-1秒-1)到Na+通道的快速失活状态。这种紧密但缓慢的结合可能是苯妥英破坏癫痫放电而对正常放电模式影响最小的能力的基础。[7] 电压门控钠通道结合/阻断实验:培养大鼠海马神经元,采用全细胞膜片钳技术。加入系列浓度的 Phenytoin Sodium(10-50 μM),在电压钳模式下记录钠电流(钳制电位 -70 mV,去极化至 0 mV)。通过双态通道门控模型拟合数据,分析结合动力学和电流抑制率 [7] |
| 细胞实验 |
本研究考察了苯妥英钠对小鼠胸锁乳突神经肌肉组织中e.p.ps量含量的影响。暴露于含有苯妥英钠(10 pg/ml)的溶液时,e.p.ps的平均振幅降低。结果表明,苯妥英钠浓度显著降低了m.e.p.cs的衰减时间常数,但对衰减幅度影响不大。在苯妥英的存在下,m.e.p.cs的衰变似乎缩短了m.e.p.cs的生长时间。在三个实验中,生长时间从对照溶液中的175 + 19 ms下降到苯妥英溶液中的146 + 10 ms。A.结果表明苯妥英在神经肌肉交界处有两种类型的抑制作用。[5]
抗增殖实验:乳腺癌细胞(MCF-7、MDA-MB-231)接种于 96 孔板(3×10³ 个细胞/孔),用系列浓度的 Phenytoin Sodium(10-100 μM)处理 72 小时。MTT 法评估细胞活力,计算 IC50 值 [1] - 克隆形成实验:乳腺癌细胞用 Phenytoin Sodium(20-80 μM)处理 24 小时后,接种于 6 孔板(1×10³ 个细胞/孔),孵育 14 天。结晶紫染色计数菌落,相对于溶媒组计算抑制率 [1] - 迁移侵袭实验:MDA-MB-231 细胞用 Phenytoin Sodium(30-70 μM)处理 24 小时后,接种于 Transwell 小室(无 Matrigel 用于迁移,有 Matrigel 用于侵袭)。染色后在显微镜下计数迁移/侵袭细胞数 [1] - 神经肌肉接头实验:分离大鼠膈神经-膈肌标本,置于器官浴中。加入 Phenytoin Sodium(10-100 μM),放射免疫法定量 ACh 释放;力传感器记录肌肉收缩 [5] |
| 动物实验 |
1. Phenytoin sodium, 10 micrograms/ml (3.6 x 10(-5) M), reduces the amplitude of endplate potentials in mouse sternomastoid neuromuscular junctions. 2. The reduction in amplitude is due to a reduction both in the quantal content of endplate potentials and in the amplitude of the voltage response to quanta of acetylcholine. 3. The reduction caused by phenytoin in the amplitude of spontaneous miniature end plate potentials was due to a reduction in the time constant of decay of miniature endplate currents. 4. It is concluded that phenytoin depresses neuromuscular transmission by reducing both the amount of acetylcholine secreted in response to an action potential and by reducing the lifetime of postsynaptic channels activated by acetylcholine.[5]
Thirty-six male Wistar rats were divided into control, local phenytoin and systemic phenytoin groups with 12 rats in each. For each group, a dura defect was created at thoracic segment. Subjects were sacrificed at following 1st and 6th weeks and damaged segments were isolated. The results were compared histopathologically by Hematoxylin-Eosin and Masson-Trichrome staining. Criteria for the rate of collagen, neovascularization, and granulation formation were assessed semi quantitatively according to the histological assessment scale modified by Ozisik et al.[6] Breast cancer xenograft model: 6-8-week-old nude mice were subcutaneously implanted with 5×10⁶ MCF-7 cells. When tumors reached 100-150 mm³, mice were randomized (n=8/group) and treated with: (1) vehicle (DMSO + sterile saline, DMSO ≤5%) via intraperitoneal injection; (2) Phenytoin Sodium 50 mg/kg via intraperitoneal injection every other day for 28 days. Tumor volume was measured every 3 days, and lung tissues were collected to count metastatic nodules [1] - CSF leakage rat model: Adult Sprague-Dawley rats were subjected to surgical dura mater injury to induce CSF leakage. Rats were randomized (n=10/group) and treated with: (1) vehicle (0.5% carboxymethylcellulose sodium) oral; (2) Phenytoin Sodium 30 mg/kg/day oral for 14 days. CSF leakage time was recorded, and dura mater tissues were collected for histological analysis [6] - Epilepsy rodent model: Adult Wistar rats were induced with pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) to induce seizures. Rats were randomized (n=8/group) and treated with Phenytoin Sodium 20-40 mg/kg oral 1 hour before PTZ administration. Seizure frequency and duration were recorded for 2 hours [2][3] - Phenytoin Sodium was dissolved in 0.5% carboxymethylcellulose sodium for oral administration, and in sterile saline (adjusted to pH 7.4) for intravenous/intraperitoneal administration [1][4][6] |
| 参考文献 |
[1]. The sodium channel-blocking antiepileptic drug phenytoin inhibits breast tumour growth and metastasis. Mol Cancer. 2015 Jan 27;14(1):13.
[2]. The neurobiology of antiepileptic drugs. Nat Rev Neurosci, 2004. 5(7): p. 553-64. [3]. Mechanisms of action of antiseizure drugs. Handb Clin Neurol, 2012. 108: p. 663-81. [4]. Medical therapy for sudden death. Pediatr Clin North Am, 2004. 51(5): p. 1379-87. [5]. Presynaptic and postsynaptic depressant effects of phenytoin sodium at the neuromuscular junction. Br J Pharmacol . 1980 May;69(1):119-21. [6]. Effects of phenytoin sodium on dura mater healing in a rat model of CSF leakage. Turk Neurosurg . 2011;21(4):471-6. [7]. Slow binding of phenytoin to inactivated sodium channels in rat hippocampal neurons. Mol. Pharmacol. 46, 716–725 (1994). |
| 其他信息 |
Diphenylhydantoin (Phenytoin), Sodium Salt can cause cancer according to an independent committee of scientific and health experts.
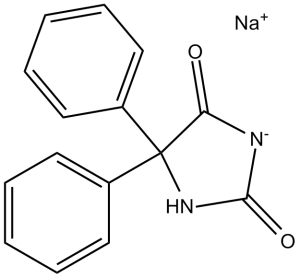
Phenytoin Sodium is the sodium salt form of phenytoin, a hydantoin derivate and non-sedative antiepileptic agent with anticonvulsant activity. Phenytoin sodium promotes sodium efflux from neurons located in the motor cortex, thereby stabilizing the neuron and inhibiting synaptic transmission. This leads to a reduction in posttetanic potentiation at synapses, an inhibition of repetitive firing of action potentials and ultimately inhibits the spread of seizure activity. An anticonvulsant that is used to treat a wide variety of seizures. It is also an anti-arrhythmic and a muscle relaxant. The mechanism of therapeutic action is not clear, although several cellular actions have been described including effects on ion channels, active transport, and general membrane stabilization. The mechanism of its muscle relaxant effect appears to involve a reduction in the sensitivity of muscle spindles to stretch. Phenytoin has been proposed for several other therapeutic uses, but its use has been limited by its many adverse effects and interactions with other drugs. See also: Pentobarbital Sodium; Phenytoin Sodium (component of). Phenytoin Sodium is a classic hydantoin-derived antiepileptic drug with multiple pharmacological activities [2][3] Its core mechanism of action is preferential binding to inactivated voltage-gated sodium channels, blocking sodium ion influx and inhibiting neuronal/axonal hyperexcitability, which underpins its use for epilepsy and arrhythmia [2][3][7] Beyond traditional indications, it exhibits antitumor activity against breast cancer by inhibiting cell proliferation, migration, and invasion (via regulating MMP-9/E-cadherin) and promotes dura mater healing in CSF leakage models [1][6] Clinical indications include generalized tonic-clonic seizures, partial seizures, and ventricular arrhythmias (especially those refractory to other drugs) [2][4] It acts at the neuromuscular junction by inhibiting ACh release and blocking postsynaptic ACh responses, contributing to its anticonvulsant and muscle-relaxant effects [5] |
| 分子式 |
C15H11N2NAO2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
274.25
|
|
| 精确质量 |
274.071
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 65.69; H, 4.04; N, 10.21; Na, 8.38; O, 11.67
|
|
| CAS号 |
630-93-3
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Phenytoin;57-41-0;Phenytoin-d10;65854-97-9; 630-93-3 (sodium)
|
|
| PubChem CID |
657302
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 沸点 |
428.2ºC at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
290-299ºC
|
|
| 闪点 |
212.8ºC
|
|
| LogP |
2.213
|
|
| tPSA |
49.41
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
20
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
356
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| InChi Key |
FJPYVLNWWICYDW-UHFFFAOYSA-M
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C15H12N2O2.Na/c18-13-15(17-14(19)16-13,11-7-3-1-4-8-11)12-9-5-2-6-10-12;/h1-10H,(H2,16,17,18,19);/q;+1/p-1
|
|
| 化学名 |
sodium;5,5-diphenylimidazolidin-3-ide-2,4-dione
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.12 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.12 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.12 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.6463 mL | 18.2315 mL | 36.4631 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7293 mL | 3.6463 mL | 7.2926 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3646 mL | 1.8232 mL | 3.6463 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。