| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
The target of Prasugrel [2]
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
普拉格雷是一种新型口服活性噻吩并吡啶,比氯吡格雷具有更快、更强和更可靠的血小板聚集抑制作用,反映了其在体内代谢为具有选择性 P2Y(12) 拮抗活性的活性代谢物。
体外实验中,Prasugrel 需经代谢激活生成活性代谢产物(R-138727),该活性代谢产物可抑制 ADP 诱导的血小板聚集,其抗血小板活性与氯吡格雷的活性代谢产物(R-130964)相似 [2] - 人体肝脏微粒体孵育实验显示,Prasugrel 转化为活性代谢产物的效率显著高于氯吡格雷 [2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
普拉格雷的活性代谢物的 IC50 值为 1.8 μM,在体外抑制大鼠血小板中腺苷 ADP (10 μM) 产生的血小板聚集 [2]。与氯吡格雷相比,普拉格雷在体内发挥作用更快、更有效。身体必须对无活性的前药普拉格雷进行代谢加工,才能产生活性的抗血小板代谢物。肠道很快吸收普拉格雷。口服常规负荷剂量60 mg后,活性代谢物的血浆浓度在1小时内达到最大,1-2小时内生效,并最大限度地抑制血小板聚集[1]。
犬体内实验中,口服给予 Prasugrel(0.3、1、3 mg/kg)后,呈剂量依赖性抑制 ADP 诱导的血小板聚集,3 mg/kg 剂量下最大聚集抑制率可达 80% 以上,且抑制作用持续时间超过 24 小时 [2] - 大鼠体内实验中,Prasugrel 口服后快速吸收并代谢为活性产物,其活性产物的血浆浓度峰值高于氯吡格雷活性产物,且达峰时间更短 [2] - 对比实验显示,相同口服剂量下,Prasugrel 体内抗血小板聚集效果显著强于氯吡格雷 [2] |
| 酶活实验 |
血小板聚集抑制实验:分离动物或人体富血小板血浆,加入不同浓度的 Prasugrel 或其活性代谢产物,孵育一定时间后,加入 ADP 作为诱导剂,通过血小板聚集仪检测血小板聚集率,计算抑制效果 [2]
- 肝脏代谢转化实验:将 Prasugrel 与肝脏微粒体及辅酶体系共同孵育,采用高效液相色谱法分离并定量检测活性代谢产物的生成量,对比其与氯吡格雷的代谢转化效率 [2] |
| 细胞实验 |
血小板分离与聚集实验:采集动物或人体静脉血,经离心分离获得富血小板血浆,调整血小板浓度后,加入 Prasugrel 预处理,再加入 ADP 诱导聚集,连续记录血小板聚集曲线,以聚集率作为评价指标 [2]
|
| 动物实验 |
0.03-3 mg/kg/day; p.o.
Mice and rats Canine antiplatelet activity experiment: Healthy dogs were selected and randomly divided into groups. They were orally administered Prasugrel or clopidogrel at doses of 0.3, 1, or 3 mg/kg. Venous blood was collected before administration and at different time points after administration. PRP was isolated to detect ADP-induced platelet aggregation rate, so as to evaluate the drug potency and duration [2] - Rat pharmacokinetic experiment: After oral or intravenous administration of Prasugrel to rats, blood samples were collected at different time points. The concentrations of the parent drug and active metabolite in plasma were detected by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) to analyze the pharmacokinetic parameters [2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption: Prasugrel is rapidly absorbed after oral administration with high bioavailability, and the time to peak (tmax) is approximately 1-2 hours [2]
- Metabolism: Prasugrel is a prodrug, mainly metabolized by the cytochrome P450 enzyme system in the liver to rapidly form the active metabolite R-138727. Its metabolic conversion efficiency is significantly higher than that of clopidogrel [2] - Distribution: The active metabolite is widely distributed in tissues throughout the body [2] - Excretion: The drug metabolites are mainly excreted through the kidneys, with a half-life (t1/2) of approximately 7-10 hours [2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
The main toxicity-related risk of Prasugrel is bleeding tendency. Slight increase in bleeding was observed in the high-dose group in in vivo experiments, but no obvious hepatotoxicity or nephrotoxicity was found [2]
- No definite median lethal dose (LD50) data is reported. Compared with clopidogrel, Prasugrel does not significantly increase the bleeding risk at similar antiplatelet effects [2] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Epothilone B is an epithilone that is epithilone D in which the double bond in the macrocyclic ring has been oxidised to the corresponding epoxide (the S,S stereoisomer). It has a role as an apoptosis inducer, an antineoplastic agent and a microtubule-stabilising agent. It is an epothilone and an epoxide.
Epothilone B is a 16-membered macrolide that mimics the biological effects of taxol. Epothilone B has been reported in Sorangium cellulosum and Apis cerana with data available. Patupilone is a compound isolated from the myxobacterium Sorangium cellulosum. Similar to paclitaxel, patupilone induces microtubule polymerization and stabilizes microtubules against depolymerization conditions. In addition to promoting tubulin polymerization and stabilization of microtubules, this agent is cytotoxic for cells overexpressing P-glycoprotein, a characteristic that distinguishes it from the taxanes. Patupilone may cause complete cell-cycle arrest. Drug Indication Investigated for use/treatment in ovarian cancer, lung cancer, brain cancer, breast cancer, and gastric cancer. Malignant neoplasm of other and unspecified genital organs - Fallopian tube (oviduct, uterine tube), Malignant neoplasm of the retroperitoneum and peritoneum - Peritoneum, unspecified Mechanism of Action The principal mechanism of the epothilone class is inhibition of microtubule function. Microtubules are essential to cell division, and epothilones therefore stop cells from properly dividing. Epothilone B possess the same biological effects as taxol both in vitro and in cultured cells. This is because they share the same binding site, as well as binding affinity to the microtubule. Like taxol, epothilone B binds to the αβ-tubulin heterodimer subunit. Once bound, the rate of αβ-tubulin dissociation decreases, thus stabilizing the microtubules. Furthermore, epothilone B has also been shown to induce tubulin polymerization into microtubules without the presence of GTP. This is caused by formation of microtubule bundles throughout the cytoplasm. Finally, epothilone B also causes cell cycle arrest at the G2-M transition phase, thus leading to cytotoxicity and eventually cell apoptosis. Prasugrel is an antiplatelet drug belonging to the ADP receptor antagonist class. It inhibits ADP-mediated platelet activation and aggregation by irreversibly binding to the platelet P2Y12 receptor, thereby preventing thrombosis [1][2] - Its mechanism of action is similar to that of clopidogrel, but due to the higher efficiency of active metabolite formation, it has stronger and faster-onset antiplatelet effects in vivo [2] - It is clinically indicated for the treatment of thrombotic diseases such as acute coronary syndrome, aiming to reduce the risk of cardiovascular events [1] |
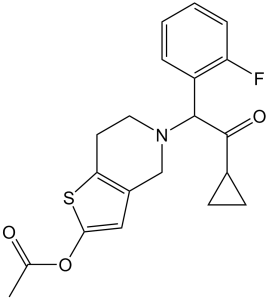
| 分子式 |
C20H20FNO3S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
373.44
|
| 精确质量 |
373.115
|
| CAS号 |
150322-43-3
|
| 相关CAS号 |
389574-19-0; 389574-20-3
|
| PubChem CID |
448013
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to light yellow solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.347
|
| 沸点 |
493.5ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
122 °C
|
| 闪点 |
252.3ºC
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.619
|
| LogP |
3.828
|
| tPSA |
74.85
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
| 重原子数目 |
35
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
816
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
7
|
| SMILES |
C[C@H]1CCC[C@@]2([C@@H](O2)C[C@H](OC(=O)C[C@@H](C(C(=O)[C@@H]([C@H]1O)C)(C)C)O)/C(=C/C3=CSC(=N3)C)/C)C
|
| InChi Key |
DTGLZDAWLRGWQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C20H20FNO3S/c1-12(23)25-18-10-14-11-22(9-8-17(14)26-18)19(20(24)13-6-7-13)15-4-2-3-5-16(15)21/h2-5,10,13,19H,6-9,11H2,1H3
|
| 化学名 |
5-(2-cyclopropyl-1-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridin-2-yl acetate
|
| 别名 |
CS-747; LY-640315; PCR-4099; CS747; LY640315; PCR4099; CS 747; LY 640315; PCR 4099; trade name Effient; Prasita
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.69 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.69 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.69 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6778 mL | 13.3890 mL | 26.7781 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5356 mL | 2.6778 mL | 5.3556 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2678 mL | 1.3389 mL | 2.6778 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
 |
|---|
|