| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 靶点 |
β-adrenergic receptor (β-AR)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
普萘洛尔(10-9 M-10-3 M;24 和 48 小时):使用 10-4 M 普萘洛尔 24 小时和使用 10-9 M 普萘洛尔 48 小时后,可显着降低 HemSC 细胞增殖 [4]。普萘洛尔(10-7 M-10-3 M;24 和 48 小时)以剂量依赖性方式增加总 ERK1/2 水平,并在 10-5 M 浓度下振动激活 HemSC 中的 ERK1/2。 (50 μM–200 μM;24 小时)激活 caspase-3,增加由膜联蛋白 V 激活的 HemSC 活性,并快速引起 HemSC 炎症 [4]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
相对于媒介物处理的入口,普萘洛尔(粉剂;40 mg/kg;每日)显着减小血管直径并增加 IH Matrigel 入口中表达磷酸化 ERK1/2 的细胞数量 [4]。
心得安对IH异种移植小鼠模型血管发育的影响 [4] 为了评估心得安对体内造血干细胞和IH发育的影响,我们采用了先前描述的小鼠模型[20]。在IH小鼠模型中,将在Matrigel中重悬的HemSCs植入免疫功能低下的小鼠皮下,IH血管的发育进展超过3周。小鼠每日给予心得安或对照药40 mg/kg。使用1/12的表面积转换因子[37-39],小鼠每天接受3.3-4.8 mg/kg的人体等效剂量。通过多普勒超声测量,心得安处理小鼠的IH Matrigel植入物在植入后14天和21天的血流量与对照组相比有所减少(数据未显示;图7 a)。21天IH Matrigel植入物的组织学分析(图7B)表明,与载体处理的植入物相比,普pranolol不影响血管密度(图7C),但确实显著降低了血管直径(图7D)。心得安治疗组血管直径减小与多普勒可检测血流损失相关。心得安还显著增加了IH Matrigel植入物中表达磷酸化ERK1/2的细胞数量(图7E),这与我们的体外研究结果一致。因此,心得安改善了与MAPK通路激活相关的IH小鼠模型中的血管发育。[4] |
| 酶活实验 |
Caspase-3检测[4]
将HemSCs接种于含20% FBS培养基的EGM-2中,静置4小时。在0.1% FBS的SFM中,浓度递增的propranolol/普萘洛尔处理HemSCs 24小时。收集蛋白裂解物,使用caspase-3人酶联免疫吸附测定试剂盒(caspase-3 Human ELISA Kit)定量caspase-3的活化。 cAMP测定[4] 使用LANCE Ultra cAMP试剂盒测定HemSCs中的cAMP水平。将HemSCs洗涤并在提供的刺激缓冲液(Hanks平衡盐水溶液、牛血清白蛋白、异丁基甲基黄嘌呤、HEPES缓冲盐水溶液)中重悬,并在96孔板上播种(每孔1000粒)。然后用药物治疗这些细胞30分钟。加入示踪剂和抗光camp工作液,室温孵育1小时。时间分辨荧光共振能量转移信号使用EnVision多标签平板阅读器进行测定。使用标准曲线确定cAMP水平,并使用综合曲线拟合(非线性回归)和Prism对数据进行插值。每种条件一组三次,实验至少进行两次。图中给出了一个有代表性的实验。 为了确定βARs在HemSCs中是否与Gαs或Gαi偶联,我们用异丙肾上腺素(含或不含10 μM福斯可林)在6倍剂量范围内连续用水稀释30分钟。接下来,按照描述测量cAMP水平,以确定HemSCs中βARs是否与Gαs或Gαi偶联。 ERK1/2 Western Blotting [4] 细胞在纤维连接蛋白包被的板上培养,用不同浓度的βAR拮抗剂处理,孵育30分钟。细胞在TENT缓冲液(50 mM Tris [pH 8.0], 2 mM EDTA, 150 mM NaCl, 1% Triton-X-100)中裂解,其中含有1% Halt蛋白酶抑制剂,1%磷酸酶抑制剂和0.5%正钒酸钠。对ERK1/2 (p44/42, 1:10 00)和pERK1/2 (P-p44/42, 1:50 00)进行Western blotting。将印迹剥离,然后检测α-微管蛋白(1:10 000),使蛋白负载正常化。实验至少进行了三次,并在图中给出了一个有代表性的实验。 |
| 细胞实验 |
蛋白质印迹分析[4]
细胞类型: HemSC 细胞 测试浓度: 10-7 M-10- 3 M 孵育持续时间:24 和 48 小时 实验结果:总 ERK1/2 水平以剂量依赖性方式增加。 细胞增殖测定[4] 细胞类型: HemSC 细胞 测试浓度: 10-9 M-10-3 M 孵育持续时间:24和48小时 实验结果:HemSC增殖受到抑制。 细胞凋亡分析 [4] 细胞类型: HemSC 细胞 测试浓度: 50 μM、100 μM 或 200 μM 孵育持续时间:24小时 实验结果:HemSC细胞死亡是通过凋亡途径诱导的。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: IH (infant hemangioma) xenograft mouse model of HemSC cells [4]
Doses: 40 mg/kg Route of Administration: Oral administration; 40 mg/kg; daily Experimental Results: IH mouse model with MAPK Vascular development associated with pathway activation is improved. IH Mouse Model [4] To study the effects of propranolol on HemSCs in vivo, a xenograft mouse model of IH was used as previously described. In brief, 1.5 × 106 HemSCs (n = 2) suspended in 200 µL of Corning Matrigel Matrix was implanted subcutaneously into the flanks of female 6–8-week-old NCrNude immunodeficient mice. Propranolol, which was provided in drinking solution, was initiated the day of IH xenografting. Propranolol was diluted to 270 µM in 5% dextrose water (vehicle), and daily consumption was measured to calculate the treatment dosage, which averaged 40 mg/kg daily. Blood flow within the IH Matrigel implant was analyzed using a VEVO 2100 Ultrasound Imaging System on a Doppler setting on days 14 and 21 of IH development. The mice were anesthetized with isoflurane and restrained in a supine position. The region of interest was fully scanned, with the transducer positioned at its largest longitudinal section over the implant to optimize the spatial resolution of the image, maximizing the detail. Next, two-dimensional images were captured in uniform steps of 0.05 mm. The images of blood flow were analyzed using software provided by VisualSonics. The mice were sacrificed after 21 days. The Matrigel implants were collected and fixed overnight at 4°C in 10% formalin. The implants were dehydrated and embedded in paraffin for histological analysis. Vessel density and caliber were counted in 3–4 HPFs per implant (n = 4 for each group). Vessel density was determined as the number of vessels (whether longitudinally or axially oriented) per HPF. The vessel diameter was measured according to the orientation. For longitudinally oriented vessels, the width was measured at three points and averaged, and the cross-section (axial) vessels were measured once. Vessels were identified as tubular structures with erythrocytes within. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Patients taking doses of 40mg, 80mg, 160mg, and 320mg daily experienced Cmax values of 18±15ng/mL, 52±51ng/mL, 121±98ng/mL, and 245±110ng/mL respectively. Propranolol has a Tmax of approximately 2 hours, though this can range from 1 to 4 hours in fasting patients. Taking propranolol with food does not increase Tmax but does increase bioavailability. 91% of an oral dose of propranolol is recovered as 12 metabolites in the urine. The volume of distribution of propranolol is approximately 4L/kg or 320L. The clearance of propranolol is 2.7±0.03L/h/kg in infants <90 days and 3.3±0.35L/h/kg in infants >90 days. Propranolol clearance increases linearly with hepatic blood flow. Propranolol has a clearance in hypertensive adults of 810mL/min. Metabolism / Metabolites Propranolol undergoes side chain oxidation to α-naphthoxylactic acid, ring oxidation to 4’-hydroxypropranolol, or glucuronidation to propranolol glucuronide. It can also be N-desisopropylated to become N-desisopropyl propranolol. 17% of a dose undergoes glucuronidation and 42% undergoes ring oxidation. Propranolol has known human metabolites that include (2S,3S,4S,5R)-3,4,5-Trihydroxy-6-[1-naphthalen-1-yloxy-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propan-2-yl]oxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid. Biological Half-Life The elimination half-life of propranolol is approximately 8 hours. The plasma half-life of propranolol is 3 to 6 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Mild-to-moderate elevations in serum aminotransferase levels occur in less than 2% of patients on propranolol and are usually transient and asymptomatic, resolving even with continuation of therapy. Despite its widespread use, propranolol has not been convincingly linked to instances of clinically apparent liver injury; the few cases reported have generally occurred in patients who were receiving other well known hepatotoxic agents or were associated with elevations in serum enzymes only without jaundice. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Because of the low levels of propranolol in breastmilk, amounts ingested by the infant are small and would not be expected to cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants. Studies during breastfeeding have found no adverse reactions in breastfed infants clearly attributable to propranolol. No special precautions are required. Propranolol has been used successfully in cases of persistent pain of the breast during breastfeeding. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants A study of mothers taking beta-blockers during nursing found a numerically, but not statistically significant increased number of adverse reactions in those taking any beta-blocker. Although the ages of infants were matched to control infants, the ages of the affected infants were not stated. Of 8 mothers taking propranolol, one reported sleepiness in her breastfed infant, but she was also taking other unspecified drugs for hypertension. A case of bradycardia in a 2-day-old breastfed infant was reported to the French pharmacovigilance system. However it is not clear from the report whether the mother had been taking propranolol near term and might have transmitted the drug to the infant transplacentally. A prospective study of pregnant patients taking a beta-blocker asked mothers to complete a questionnaire about postpartum breastfeeding and any side effects in their breastfed infants. Sixteen mothers reported taking propranolol in unreported dosages while breastfeeding. Three women reported hypoglycemia in their infant with “a favorable outcome” and one reported bradycardia in her child with discontinuation of propranolol after 3 weeks of breastfeeding. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information on the effects of beta-blockade or propranolol during normal lactation was not found as of the revision date. A study in 6 patients with hyperprolactinemia and galactorrhea found no changes in serum prolactin levels following beta-adrenergic blockade with propranolol. ◈ What is propranolol? Propranolol is a medication that has been used to treat high blood pressure, some heart conditions, overactive thyroid, tremors, glaucoma, and migraines. It belongs to the class of medications called beta-blockers. Some brand names for propranolol are Inderal®, InnoPran XL®, Detensol®, Novo-Pranol®, Deralin®, and Cardinol®.Sometimes when people find out they are pregnant, they think about changing how they take their medication, or stopping their medication altogether. However, it is important to talk with your healthcare providers before making any changes to how you take this medication. Your healthcare providers can talk with you about the benefits of treating your condition and the risks of untreated illness during pregnancy. ◈ I take propranolol. Can it make it harder for me to get pregnant? It is not known if propranolol can make it harder to get pregnant. ◈ Does taking propranolol increase the chance for miscarriage? Miscarriage can occur in any pregnancy for many different reasons. Studies have not been done to see if propranolol increases the chance for miscarriage. ◈ Does taking propranolol increase the chance of birth defects? Every pregnancy starts out with a 3-5% chance of having a birth defect. This is called the background risk. It is not known if propranolol increases the chance for birth defects above the background risk. Studies on the use of beta-blockers in general during pregnancy have not reported an increased chance of birth defects. ◈ Does taking propranolol in pregnancy increase the chance of other pregnancy-related problems? Propranolol has been linked with reduced growth of the baby. However, it is not clear if this happens because of the medication, the condition being treated, or other factors. Studies have not shown an increased chance for other pregnancy-related problems, like preterm delivery (birth before week 37).The use of propranolol in late pregnancy may cause the baby to have symptoms of the drug acting on its heart, blood vessels, and metabolism. These symptoms could include a slowed heart rate and low blood sugar. Not all babies exposed to propranolol will have these symptoms. It is important that your healthcare providers know you are taking propranolol so that if symptoms occur your baby can get the care that is best for them. ◈ Does taking propranolol in pregnancy affect future behavior or learning for the child? Studies have not been done to see if propranolol can cause behavior or learning issues for the child. ◈ Breastfeeding while taking propranolol: Propranolol passes into breastmilk in small amounts. Studies on propranolol have not found adverse health reactions in infants fed breastmilk from someone exposed to propranolol. If you suspect that the baby has symptoms such as being too sleepy or having trouble with feeding, contact the child’s healthcare provider. Be sure to talk to your healthcare provider about all your breastfeeding questions. ◈ If a male takes propranolol, could it affect fertility or increase the chance of birth defects? Propranolol may cause some males to develop erectile dysfunction (ED), which could make it harder to conceive a pregnancy. In general, exposures that fathers or sperm donors have are unlikely to increase the risks to a pregnancy. For more information, please see the MotherToBaby fact sheet Paternal Exposures at https://mothertobaby.org/fact-sheets/paternal-exposures-pregnancy/. Protein Binding Approximately 90% of propranolol is protein bound in plasma. Other studies have reported ranges of 85-96%. 4946 women TDLo oral 3200 ug/kg/2D- ENDOCRINE: HYPOGLYCEMIA Israel Journal of Medical Sciences., 18(725), 1982 [PMID:7107213] 4946 human TDLo oral 2300 ug/kg/D BEHAVIORAL: HALLUCINATIONS, DISTORTED PERCEPTIONS British Medical Journal., 1(1182), 1978 [PMID:638680] 4946 child LDLo oral 800 ug/kg/12H CARDIAC: PULSE RATE INCREASE WITHOUT FALL IN BP; VASCULAR: BP LOWERING NOT CHARACTERIZED IN AUTONOMIC SECTION; LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: ACUTE PULMONARY EDEMA British Medical Journal., 2(254), 1978 4946 child TDLo oral 400 mg/kg BEHAVIORAL: CONVULSIONS OR EFFECT ON SEIZURE THRESHOLD; CARDIAC: ARRHYTHMIAS (INCLUDING CHANGES IN CONDUCTION) Medical Journal of Australia., 1(82), 1981 [PMID:7231257] 4946 man TDLo oral 8343 mg/kg/4Y- ENDOCRINE: EVIDENCE OF THYROID HYPERFUNCTION Archives of Internal Medicine., 143(2193), 1983 [PMID:6639243] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
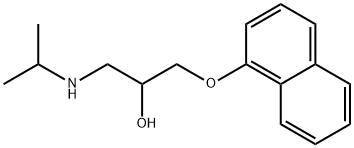
Propranolol is a propanolamine that is propan-2-ol substituted by a propan-2-ylamino group at position 1 and a naphthalen-1-yloxy group at position 3. It has a role as a beta-adrenergic antagonist, an anxiolytic drug, an anti-arrhythmia drug, a vasodilator agent, an antihypertensive agent, a xenobiotic, an environmental contaminant and a human blood serum metabolite. It is a secondary amine, a propanolamine and a member of naphthalenes. It is functionally related to a 1-naphthol.
Propranolol is a racemic mixture of 2 enantiomers where the S(-)-enantiomer has approximately 100 times the binding affinity for beta adrenergic receptors. Propranolol is used to treat a number of conditions but most commonly is used for hypertension. Propranolol was granted FDA approval on 13 November 1967. Propranolol is a beta-Adrenergic Blocker. The mechanism of action of propranolol is as an Adrenergic beta-Antagonist. Propranolol is a nonselective beta-adrenergic receptor blocker (beta-blocker) that is widely used for the therapy of hypertension, cardiac arrhythmias, angina pectoris and hyperthyroidism. Propranolol has yet to be convincingly associated with clinically apparent liver injury and is often used in patients with liver disease and cirrhosis. Propranolol has been reported in Asimina triloba with data available. Propranolol is a synthetic, nonselective beta-adrenergic receptor blocker with antianginal, antiarrhythmic, antihypertensive properties. Propranolol competitively antagonizes beta-adrenergic receptors, thereby causing negative chronotropic and inotropic effects leading to a reduction in cardiac output. A widely used non-cardioselective beta-adrenergic antagonist. Propranolol has been used for MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION; ARRHYTHMIA; ANGINA PECTORIS; HYPERTENSION; HYPERTHYROIDISM; MIGRAINE; PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA; and ANXIETY but adverse effects instigate replacement by newer drugs. See also: Propranolol Hydrochloride (has salt form). Drug Indication Propranolol is indicated to treat hypertension. Propranolol is also indicated to treat angina pectoris due to coronary atherosclerosis, atrial fibrillation, myocardial infarction, migraine, essential tremor, hypertrophic subaortic stenosis, pheochromocytoma, and proliferating infantile hemangioma. FDA Label Hemangiol is indicated in the treatment of proliferating infantile haemangioma requiring systemic therapy: , , , Life- or function-threatening haemangioma,, Ulcerated haemangioma with pain and/or lack of response to simple wound care measures,, Haemangioma with a risk of permanent scars or disfigurement. , , , It is to be initiated in infants aged 5 weeks to 5 months. , Mechanism of Action Propranolol is a nonselective β-adrenergic receptor antagonist. Blocking of these receptors leads to vasoconstriction, inhibition of angiogenic factors like vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and basic growth factor of fibroblasts (bFGF), induction of apoptosis of endothelial cells, as well as down regulation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. |
| 分子式 |
C16H21NO2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
259.3434445858
|
| 精确质量 |
259.157
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 74.10; H, 8.16; N, 5.40; O, 12.34
|
| CAS号 |
525-66-6
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Propranolol hydrochloride;318-98-9;Propranolol-d7;98897-23-5; 525-66-6
|
| PubChem CID |
4946
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.093 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
434.9ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
163-164ºC
|
| 闪点 |
216.8ºC
|
| 折射率 |
1.5500 (estimate)
|
| LogP |
2.968
|
| tPSA |
41.49
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
19
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
257
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
CC(C)NCC(COC1=CC=CC2=CC=CC=C21)O
|
| InChi Key |
AQHHHDLHHXJYJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C16H21NO2/c1-12(2)17-10-14(18)11-19-16-9-5-7-13-6-3-4-8-15(13)16/h3-9,12,14,17-18H,10-11H2,1-2H3
|
| 化学名 |
1-naphthalen-1-yloxy-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propan-2-ol
|
| 别名 |
propranolol; 525-66-6; Propanolol; beta-Propranolol; Betalong; Euprovasin; Proprasylyt; Reducor;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~385.59 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.64 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.64 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.64 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.8559 mL | 19.2797 mL | 38.5594 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7712 mL | 3.8559 mL | 7.7119 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3856 mL | 1.9280 mL | 3.8559 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。