| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
VEGFR2 (IC50 = 6.5 nM); VEGFR3 (IC50 = 15 nM); EphB2 (IC50 = 24 nM); VEGFR1 (IC50 = 30 nM); PDGFRα (IC50 = 40 nM)
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 1 (VEGFR1), VEGFR2, and VEGFR3, tyrosine kinases involved in angiogenesis. For Tivozanib (AV951; KRN-951), literature [1] reported: VEGFR1 (IC50 = 0.21 nM), VEGFR2 (IC50 = 0.16 nM), VEGFR3 (IC50 = 0.24 nM) via HTRF kinase assay. It showed weak inhibition of PDGFRβ (IC50 = 4.1 nM) and no activity against EGFR or c-Kit (IC50 > 1 μM) [1] - Consistent with [1], [2] confirmed VEGFR2 (Ki = 0.08 nM) via equilibrium binding assay; VEGFR1 (Ki = 0.12 nM), VEGFR3 (Ki = 0.15 nM) [2] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
AV-951是一种新型的尿素和喹啉衍生物。AV-951可阻止内皮细胞增殖和vegf依赖性的有丝分裂原活化蛋白激酶的激活。[1]
KRN951是一种针对vegfr的新型酪氨酸激酶抑制剂,具有抗肿瘤血管生成和抗生长活性。KRN951在体外亚纳摩尔IC50值(IC50 = 0.16 nmol/L)下有效抑制内皮细胞中vegf诱导的VEGFR-2磷酸化。它还能抑制配体诱导的血小板衍生生长因子受体β (pdgfr - β)和c-Kit的磷酸化(IC50分别为1.72和1.63 nmol/L)。KRN951阻断了vegf依赖性而非非依赖性的丝裂原活化蛋白激酶的激活和内皮细胞的增殖。此外,还能抑制vegf介导的人脐静脉内皮细胞的迁移。[1] VEGFR依赖内皮细胞活性:在HUVECs(VEGFR2依赖)中,Tivozanib(0.001 μM–1 μM)抑制VEGF诱导的增殖,MTT法(72小时)IC50=0.02 μM;0.1 μM处理24小时可抑制管腔形成80%。Western blot显示HUVECs经0.05 μM处理1小时后p-VEGFR2减少90% [1] - 肾细胞癌(RCC)细胞:在786-O(透明细胞RCC,VEGF过表达)和ACHN(RCC)细胞中,Tivozanib(0.01 μM–10 μM)抑制增殖,CCK-8法(72小时)IC50分别为786-O 0.15 μM、ACHN 0.2 μM。0.5 μM处理786-O细胞24小时后,ELISA检测显示VEGF分泌减少65% [2] - 血管生成相关信号:在HUVECs中,Tivozanib(0.01 μM–0.5 μM)剂量依赖性减少p-ERK和p-AKT(VEGFR2下游分子):0.1 μM处理2小时后,两者均减少75%(Western blot) [1] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
体内研究表明,特别是口服剂量为1mg /kg的AV-951,还可以降低肿瘤异种移植物的微血管密度并抑制VEGFR2磷酸化水平。在胸腺发育不全的大鼠中,AV-951几乎完全抑制异种肿瘤的生长(TGI>85%)。[1]另一项使用大鼠腹膜播散性肿瘤模型的研究表明,AV-951可以延长荷瘤大鼠MST后的生存期,最长可达53.5天。当应用于各种人类肿瘤异种移植物,如肺癌、乳腺癌、结肠癌、卵巢癌、胰腺癌和前列腺癌时,AV-951表现出抗肿瘤活性。[2]
给胸大鼠po后,KRN951降低了异种肿瘤移植物内的微血管密度,并减弱了肿瘤内皮中VEGFR-2的磷酸化水平。它也显示抗肿瘤活性,对多种人类肿瘤异种移植物,包括肺癌,乳腺癌,结肠癌,卵巢癌,胰腺癌和前列腺癌。此外,动态对比增强磁共振成像(DCE-MRI)分析显示,肿瘤血管高通透性的显著降低与KRN951的抗肿瘤活性密切相关。这些发现表明,KRN951是一种高效的抗血管生成和抗肿瘤药物,DCE-MRI将有助于在临床环境中检测KRN951的早期反应。KRN951目前处于I期临床开发阶段,用于治疗晚期癌症患者。[1] RCC异种移植模型:6周龄雄性裸鼠接种786-O细胞,随机分为3组(每组n=8):溶媒组(0.5%甲基纤维素+0.1%吐温80)、Tivozanib 0.5 mg/kg组、1 mg/kg组。药物口服每日一次,连续28天。肿瘤体积减少率:0.5 mg/kg组60%、1 mg/kg组85%;肿瘤重量减少率:0.5 mg/kg组55%、1 mg/kg组78%。免疫组化显示1 mg/kg组微血管密度(CD31染色)减少70% [1] - 肝转移模型:7周龄雌性裸鼠建立ACHN肝转移模型后,用Tivozanib 1 mg/kg(口服每日一次)处理35天。转移结节数量较溶媒组减少65%,血清VEGF从450 pg/mL降至180 pg/mL [2] |
| 酶活实验 |
AV-951 针对各种重组受体和非受体酪氨酸激酶(例如 VEGFR1、VEGFR2、VEGFR3、c-Kit、PDGFRβ、Flt-3 和 FGFR1)的 IC50 值通过使用 1 进行四次无细胞激酶测定来确定。 μM ATP。
激酶选择性。[1] 在1 μmol/L ATP条件下进行四次无细胞激酶试验,测定Tivozanib (AV951; KRN-951)的IC50值;Tivozanib (AV951; KRN-951)抗多种重组受体和非受体酪氨酸激酶。重组酶来自ProQinase GmbH。 [1] 以细胞为基础的试验确定Tivozanib (AV951; KRN-951);如前所述,Tivozanib (AV951; KRN-951)抑制受体酪氨酸激酶的配体依赖性磷酸化。简单地说,将细胞在含有0.5%胎牛血清(FBS)的适当基本培养基中饥饿过夜。加入Tivozanib (AV951; KRN-951)或0.1% DMSO后,细胞孵育1小时,然后用同源配体在37℃下刺激。除VEGFR-3(10分钟)、c-Met(10分钟)和c-Kit(15分钟)外,受体磷酸化诱导时间为5分钟。除VEGF-C(一种大鼠重组蛋白)外,实验中使用的所有配体均为人重组蛋白。细胞裂解后,用适当的抗体对受体进行免疫沉淀,并用磷酸酪氨酸进行免疫印迹。印迹的定量和IC50值的计算如前所述进行。 [1] 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶活化。[1] 按照前面的描述对其进行了评估。简单地说,HUVECs在含有0.5% FBS的基本培养基(EBM-2)中饥饿16小时。Tivozanib (AV951; KRN-951)作用1小时,用50 ng/mL VEGF、25 ng/mL碱性成纤维细胞生长因子或20 ng/mL EGF刺激HUVECs。细胞裂解液进行SDS-PAGE,然后用磷酸化的p44/42丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK)抗体对磷酸化的MAPKs进行免疫印迹。[1] 通透性试验和VEGFR‐2磷酸化检测。[2] 恶性腹水对内皮细胞通透性和VEGFR‐2磷酸化的影响,以及Tivozanib (AV951;KRN-951)对这些影响进行了评价。将第25天从经载体处理的腹膜播散性肿瘤模型中采集的腹水样本进行汇总,并将所得上清用于这些实验。我们检查碘化丙啶摄取作为通透性的措施在体外测定。western blotting检测VEGFR‐2磷酸化水平。为了进行渗透性试验,将HUVEC培养在90%的融合度下,在含有0.5%胎牛血清的基本培养基(EBM‐2)中进行血清饥饿过夜。然后用磷酸盐缓冲盐水、恶性腹水和10 nM浓度的Tivozanib (AV951; KRN-951);培养板中加入Tivozanib (AV951; KRN-951)。单独培养基或50 ng/mL无腹水的VEGF作为内部对照。孵育7 h后,收获细胞,碘化丙啶(1µg/mL)处理,进行FACS分析。通过测定HUVEC对碘化丙啶的吸收来评估其通透性。对于western blotting,除了用腹水刺激时间为10分钟外,采用相同的方法处理HUVEC。细胞裂解后,用抗VEGFR - 2抗体免疫沉淀VEGFR蛋白,然后用抗磷酸酪氨酸抗体免疫印迹,如前所述。[2] VEGFR1/2/3 HTRF激酶实验(文献[1]):将重组人VEGFR1(791–1338位氨基酸)、VEGFR2(786–1356位氨基酸)或VEGFR3(803–1363位氨基酸)与生物素化肽底物(Ac-EAIYAAPFAKKK-NH2,20 μM)、Eu标记抗磷酸酪氨酸抗体及ATP(10 μM)共同孵育于激酶缓冲液(25 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5、10 mM MgCl₂、1 mM DTT)中。加入系列稀释的Tivozanib(0.001 nM–10 nM),30°C孵育60分钟。检测时间分辨荧光(激发光340 nm,发射光620 nm),计算IC50 [1] - VEGFR结合实验(文献[2]):重组VEGFR1/2/3与Tivozanib(0.001 nM–10 nM)在结合缓冲液(25 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5、150 mM NaCl)中37°C孵育24小时。平衡透析分离游离/结合药物,HPLC定量游离药物浓度,推导Ki值 [2] |
| 细胞实验 |
使用基于人脐静脉内皮细胞 (HUVEC) 和正常人真皮成纤维细胞的测定来评估 Tivozanib (AV951/KRN-951) 抑制酪氨酸激酶受体配体依赖性磷酸化的能力。在含有 0.5% 胎牛血清 (FBS) 的适当基础培养基中,细胞在第二天处于饥饿状态。将细胞与 Tivozanib (AV951/KRN-951) 或 0.1% DMSO 一起孵育一小时后,在 37 °C 下用同源配体刺激。除了 VEGFR3、c-Met 和 c-Kit 分别诱导 10 分钟和 15 分钟外,受体磷酸化持续 5 分钟。 VEGF-C 是一种大鼠重组蛋白,是检测中使用的唯一非人重组蛋白的配体。细胞裂解后,用适当的抗体进行免疫沉淀后,对受体进行磷酸酪氨酸免疫印迹。印迹定量和IC50值计算均已完成。
内皮细胞增殖。[1] 将HUVECs接种于含5% FBS的M-199中,以4000个细胞/200 μL/孔的密度接种于胶原包被的96孔板中。24小时后,加入Tivozanib (AV951/KRN-951),然后加入20 ng/mL VEGF或10 ng/mL bFGF,培养72小时。加入胸腺嘧啶(1 μCi/mL) [3H],继续培养12小时。然后收集细胞,用液体闪烁计数器测量其放射性。[1] 趋化性分析。[1] 采用96孔微室板评估HUVEC迁移。细胞在含有0.1%牛血清白蛋白(BSA)的EBM-2中饥饿5小时。然后,收集细胞,在含有0.1% BSA的EBM-2中重悬,并置于上腔。将含有10 ng/mL VEGF、0.1% FBS和0.1% BSA的培养基置于底室,开始细胞迁移。当有指示时,在上、下腔均加入Tivozanib (AV951/KRN-951)。孵育22 h后,用4 μg/mL钙黄素AM染色HBSS细胞。在激发/发射波长为485/530 nm的荧光板阅读器中,通过腔室底部直接测量通过荧光阻断膜孔迁移的细胞的荧光。[1] 细胞毒性检测。[1] 这些试验按前面所述进行。简单地说,将细胞接种于96孔板中,并在含有10%胎牛血清的培养基中培养。在开始培养后约24小时加入Tivozanib (AV951/KRN-951),细胞孵育72小时。采用WST-1试剂检测细胞活力[1]。 HUVEC增殖与管腔形成实验(文献[1]):HUVECs分别以5×10³个细胞/孔接种于96孔板(增殖实验)或1×10⁵个细胞/孔接种于Matrigel包被的24孔板(管腔形成实验)。加入Tivozanib(0.001 μM–1 μM)+VEGF(50 ng/mL),37°C、5% CO₂孵育。增殖实验72小时后MTT法检测计算IC50;管腔形成实验24小时后成像并定量总管长 [1] - RCC细胞实验(文献[2]):786-O/ACHN细胞以5×10³个细胞/孔接种于96孔板,用Tivozanib(0.01 μM–10 μM)处理72小时。CCK-8法检测活力;0.5 μM药物处理24小时后ELISA分析VEGF分泌。786-O细胞经0.1 μM处理2小时后,Western blot检测p-VEGFR2/p-ERK [2] |
| 动物实验 |
Mice: The athymic rats receive a subcutaneous injection of cancer cells in their right flank. Tumors up to 1,500 mm3 are surgically removed, and smaller pieces (20–30 mg) are s.c. implanted into the right flank of rats exposed to radiation. Beginning on day zero of randomization, oral administration of KRN951 (0.2 or 1 mg/kg) or the vehicle is administered. Using Vernier calipers, tumor volume is measured and computed twice a week.
\n\nTumor xenograft models. Athymic rats (RH-rnu/rnu) were used. Twenty-four hours after whole body irradiation with a γ-source (7 Gy, Co60), cancer cells were s.c. inoculated into the right flank of the rats. Once established, tumors of ∼1,500 mm3 were surgically excised and smaller tumor fragments (20-30 mg) were s.c. implanted in the right flank of irradiated rats. Oral administration of Tivozanib (AV951/KRN-951) (0.2 or 1 mg/kg) or vehicle was initiated at the day of randomization (day 0). Tumor volume was measured twice weekly with Vernier calipers, and calculated as (length × width2) × 0.5. Relative tumor volume (RTV) was calculated by the formula: RTV at day x = tumor volume at day x / tumor volume at day 0. Percentage tumor growth inhibition (TGI%) was calculated as described previously. Statistical analysis of RTV was done using the unpaired t test.\n\nDCE-MRI. Athymic rats (RH-rnu/rnu) were s.c. implanted with fresh Calu-6 tumor fragments. Rats were randomized when the tumors reached a volume of 274 to 287 mm3 (day −1). Once-daily p.o. administration of Tivozanib (AV951/KRN-951) or vehicle was initiated the day after randomization (day 0) and continued for 2 weeks (days 0-13).\n\nMRI experiments were carried out at 1.5 T on a whole body magnet equipped with a flexible receiver coil (circularly polarized). DCE-MRI acquisitions were done on day −1 (before the start of treatment), day 2, day 13, and day 21. On days 2 and 13, the rats were imaged 4 hours after p.o. administration of Tivozanib (AV951/KRN-951). The rat tail vein was cannulated for contrast agent injection before placing the animals in the magnet. During the experiment, rats were anesthetized by an i.m. injection of a mixture of ketamine and xylazine (2/1, v/v, 70 and 15 mg/kg, respectively). The anesthetized rats were placed in a cradle supine position inside the resonator. The exact position of the rats was assessed by a scout imaging sequence. [1] \n\nMeasurement of tumor vessel diameter. During the MRI study, an additional three groups of Calu-6 tumor-bearing rats (RH-rnu/rnu, three rats per group) were used for measurement of tumor vessel diameter using the fluorescent dye H33342 (24). Rats were treated with Tivozanib (AV951/KRN-951) (0.2 or 1 mg/kg) or vehicle for 14 days (from day 0 to day 13) and were sacrificed 1 minute after the i.v. injection of H33342 (20 mg/kg) at day 13. The tumors were removed and 10 μm cryosections prepared from five levels of each tumor separated by at least 200 μm. Tumor sections were studied under UV illumination using a Nikon epifluorescence microscope to identify blood vessels with a surrounding halo of fluorescent H33342-labeled cells. The lumen enclosed by the halos was measured as the vessel diameter using Win ROOF software. Statistical analysis was done using the Mann-Whitney test.[1] \n\nHistologic analysis of smooth muscle actin–positive pericyte coverage of tumor vessels. Calu-6 tumor xenografts were established in athymic rats by s.c. implantation of cells. Rats were randomized when tumor volumes reached an average of 273 to 275 mm3 and then treated p.o. with Tivozanib (AV951/KRN-951) or vehicle for 2 weeks. Immunofluorescence staining of pericytes in tumors was done with Cy3-conjugated monoclonal anti-α-smooth muscle actin antibody following the staining of endothelial cells with anti-CD31 antibody. Tissue images were captured digitally at ×100 magnification with LSM 510 systems. Six fields per section (0.8489 mm2 each) were randomly analyzed, excluding peripheral surrounding connective tissues and central necrotic tissues. The number of CD31-positive objects and those surrounded by the region positive for α-smooth muscle actin were quantified using Win ROOF software after blind-coding the histology slides to avoid operator bias.[1] \n\nPharmacokinetic analysis of Tivozanib (AV951/KRN-951). Athymic rats (F344/N JcL-rnu, four females per group) received Tivozanib (AV951/KRN-951) p.o. and blood samples were collected from their tail vein at predetermined intervals up to 72 hours postdose. An appropriate amount of internal standard material, KRN633, was added to each serum sample. Serum samples were deproteinated with acetonitrile and supernatants were analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Pharmacokinetic variables were calculated by noncompartmental analysis. The serum concentration of Tivozanib (AV951/KRN-951) at steady state after repeated p.o. administrations of a 0.2 mg/kg dose was simulated as described previously [1] \n\nTivozanib (AV951/KRN-951) was suspended in vehicle (0.5% methyl cellulose in distilled water) and stored at 4°C. Fresh solutions were prepared weekly.[2] \nExperimental design. Rats inoculated with RCN‐9 cells were assigned randomly to three groups and given daily oral doses of Tivozanib (AV951/KRN-951) (1 or 3 mg/kg) or a 0.5% methylcellulose vehicle control. These treatments commenced at 4 or 14 days after tumor transplantation, and continued for 10 or 11 days, respectively. At the end of the treatment periods, the rats were killed and tumor progression was evaluated. Ascites were also collected and their volumes were measured. Each transparent window in the mesentery surrounded by fatty tissue was observed microscopically. The percentages of the mesenteric windows with a vasculature and the number of tumor nodules with or without a vasculature on the mesenteric windows were then counted. [2] \n\nIn a subsequent survival study, rats inoculated with RCN‐9 cells were assigned randomly to vehicle‐treated or 1 mg/kg Tivozanib (AV951/KRN-951)‐treated groups (n = 10 per group). Separate treatments then commenced from the day of tumor inoculation or at 14 days after this transplantation. The results were plotted using Kaplan–Meier methods and the differences in survival were analyzed by log‐rank test. A P‐value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. [2] \n\nTumor vessel imaging. RCN‐9 cell‐inoculated rats with and without Tivozanib (AV951/KRN-951) treatment were anesthetized and injected intravenously with fluorescein isothiocyanate‐labeled dextran (molecular weight 200 000). After the animals had been killed, the mesenteries were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and placed on glass slides. The vasculature associated with each mesenteric window was then photographed microscopically. The number of vessel joints and paths (as vessel bifurcation characteristics), the areas and lengths of vessels (as the angiogenesis density), and the tortuosity of the vasculatures were recorded objectively and evaluated quantitatively using an angiogenesis image analyzer (Kurabo, Osaka, Japan). Four rats were used in these experiments from each group and 12–15 different fields from each animal were analyzed. [2]\n\n 786-O RCC Xenograft Protocol (Literature [1]): Male nude mice (6 weeks old) were subcutaneously implanted with 5×10⁶ 786-O cells. When tumors reached ~100 mm³, Tivozanib was dissolved in 0.5% methylcellulose + 0.1% Tween 80, administered orally once daily (0.5 mg/kg or 1 mg/kg) for 28 days. Tumor volume (length×width²/2) was measured every 3 days; mice were euthanized on day 28, tumors processed for CD31 immunohistochemistry [1] - ACHN Liver Metastasis Protocol (Literature [2]): Female nude mice (7 weeks old) were injected with 2×10⁶ ACHN cells via tail vein to induce liver metastases. Seven days later, Tivozanib (1 mg/kg, dissolved in 0.5% hydroxypropyl methylcellulose) was oral once daily for 35 days. Livers were harvested to count metastatic nodules; serum VEGF was measured via ELISA [2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
The median Tmax of tivozanib is 10 hours, however, can range from 3 to 24 hours. A pharmacokinetic study in 8 healthy subjects revealed a Cmax and AUC for radiolabeled tivozanib of 12.1 ± 5.67 ng/mL and 1084 ± 417.0 ng·h/mL, respectively. Steady-state tivozanib concentrations are achieved at concentrations 6-7 times higher the normal dose. Tivozanib is primarily excreted in the feces. After oral ingestion of a radiolabeled 1.34 mg dose of tivozanib in healthy volunteers, 79% of the administered dose was found in the feces (with 26% unchanged) and 12% was found in the urine solely as metabolites. Tivozanib has an apparent volume of distribution (V/F) of 123 L. The apparent clearance (CL/F) of tivozanib is approximately 0.75 L/h. Metabolism / Metabolites Tivozanib is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4. After oral ingestion of a radiolabeled 1.34 mg dose of tivozanib in healthy volunteers, unchanged tivozanib accounted for 90% of the radioactive drug detected in serum. Biological Half-Life The half-life of tivozanib is about 111 hours according to prescribing information. Information from clinical studies reveals a half-life of 4-5 days. Rat PK (Literature [1]): Male Sprague-Dawley rats (8 weeks old) oral Tivozanib 1 mg/kg: oral bioavailability = 62%, Cmax = 3.5 μM, Tmax = 1.2 h, terminal t₁/₂ = 7.8 h. Intravenous 0.2 mg/kg: CL = 8.3 mL/min/kg, Vss = 1.1 L/kg [1] - Human Plasma Protein Binding: 99% (equilibrium dialysis, [1][2]) - Metabolism (Literature [2]): In human liver microsomes, Tivozanib is metabolized by CYP3A4 (70%) and CYP2D6 (20%); urinary excretion of unchanged drug < 6% [2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In the published preregistration clinical trials of tivozanib, rates of serum ALT or AST elevations ranged from 10% to 29%, with 1% to 4% of treated patients having elevations above 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN). Instances of clinically apparent liver injury including deaths with hepatic failure were reported in some clinical trials, but in all cases were attributed to hepatic metastases or to other underlying liver diseases. Since its approval and more widespread clinical use, there have been no reports of clinically apparent liver injury or hepatic failure attributed to tivozanib, but it has had limited clinical use. Likelihood score: E* (unproven but suspected cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Protein Binding In vitro, the protein binding of tivozanib is mainly bound to albumin at a rate of ≥ 99%. In Vitro Cytotoxicity: In normal human renal proximal tubule cells (RPTECs) and foreskin fibroblasts, Tivozanib (up to 10 μM, 72 h) showed viability > 80%, indicating low non-specific toxicity [1][2] - In Vivo Acute Toxicity: Rats treated with Tivozanib 1 mg/kg (oral, 28 days) had mild hypertension (10% animals, systolic BP increase < 20 mmHg) and no liver/kidney damage (ALT/AST/creatinine normal) [1] - No Severe Toxicity: Mice treated with Tivozanib 1 mg/kg (oral, 35 days) showed no weight loss, lethargy, or organ histopathology changes [2] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Pharmacodynamics
Tivozanib inhibits growth factor receptors, treating renal cell carcinoma. In mice and rats, tivozanib inhibits tumour angiogenesis, tumour growth, and vascular permeability. Tivozanib was shown to frequently cause hypertension in clinical trials; hypertension must be managed before initiating therapy. Cardiac QT segment prolongation was reported in a tivozanib cardiac safety study, however the reactions were not considered clinically serious. In clinical studies, levels of serum soluble VEGFR2 (sVEGFR2) decreased with time and this effect increased with tivozanib exposure, and sVEGFR2 may serve as a pharmacodynamic marker of VEGFR inhibition. Tivozanib (AV951; KRN-951) is a potent, selective oral inhibitor of VEGFR1/2/3, developed for the treatment of angiogenesis-dependent cancers (e.g., renal cell carcinoma, metastatic solid tumors) [1][2] - Its mechanism involves binding to the ATP-binding pocket of VEGFR1/2/3, inhibiting tyrosine kinase activation and downstream ERK/AKT signaling, thereby suppressing angiogenesis and tumor growth [1][2] - It showed robust anti-tumor activity in RCC xenografts and metastasis models, with minimal off-target toxicity due to high VEGFR selectivity [1][2] |
| 分子式 |
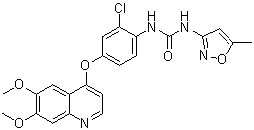
C22H19CLN4O5
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
454.86
|
| 精确质量 |
454.104
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 58.09; H, 4.21; Cl, 7.79; N, 12.32; O, 17.59
|
| CAS号 |
475108-18-0
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Tivozanib hydrochloride hydrate;682745-41-1; Tivozanib;475108-18-0; 682745-40-0 (hydrate)
|
| PubChem CID |
9911830
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light brown to brown solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
550.4±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
220-233
|
| 闪点 |
286.7±30.1 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.680
|
| LogP |
4.31
|
| tPSA |
107.74
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
32
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
631
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
ClC1C([H])=C(C([H])=C([H])C=1N([H])C(N([H])C1C([H])=C(C([H])([H])[H])ON=1)=O)OC1C([H])=C([H])N=C2C([H])=C(C(=C([H])C2=1)OC([H])([H])[H])OC([H])([H])[H]
|
| InChi Key |
SPMVMDHWKHCIDT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C22H19ClN4O5/c1-12-8-21(27-32-12)26-22(28)25-16-5-4-13(9-15(16)23)31-18-6-7-24-17-11-20(30-3)19(29-2)10-14(17)18/h4-11H,1-3H3,(H2,25,26,27,28)
|
| 化学名 |
1-[2-chloro-4-(6,7-dimethoxyquinolin-4-yl)oxyphenyl]-3-(5-methyl-1,2-oxazol-3-yl)urea
|
| 别名 |
Tivozanib; KRN-951, AV-951; AV951; AV 951; KRN951; KRN 951
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.50 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.50 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: 0.5% methylcellulose: 30mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1985 mL | 10.9924 mL | 21.9848 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4397 mL | 2.1985 mL | 4.3970 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2198 mL | 1.0992 mL | 2.1985 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
A Phase 1b/2a, Open-Label, Multi-Center Study of AV-951 in Combination with Paclitaxel in Subjects with Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer
CTID: null
Phase: Phase 2 Status: Completed
Date:
Effects of KRN951 on VEGFR-2 phosphorylation levels on tumor endothelium and tumor microvessel density.Cancer Res.2006 Sep 15;66(18):9134-42. |
DCE-MRI analysis of tumor vascular permeability. Athymic rats bearing Calu-6 tumors were randomized at day −1 and then treated with 0.2 mg/kg KRN951 (○), 1 mg/kg KRN951 (▴), or vehicle (•) once daily for 14 days (days 0-13).Cancer Res.2006 Sep 15;66(18):9134-42. |
Effects of KRN951 on tumor vessel diameter and pericyte coverage.Cancer Res.2006 Sep 15;66(18):9134-42. |