| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
The primary target of U-104 is the tumor-associated carbonic anhydrase IX (CA IX), a zinc-dependent enzyme highly expressed in hypoxic tumor cells. For recombinant human CA IX, the IC50 in the carbonic anhydrase activity assay was 1.2 nM [1]
; It exhibited high selectivity for CA IX over other CA isoforms: the IC50 for human recombinant CA II (a ubiquitous isoform) was >1000 nM (≈833-fold lower affinity than CA IX), and no significant inhibition of CA I/IV was observed (IC50 > 1000 nM) [1] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
U-104 (SLC-0111) 是一种强效外泌体抑制剂[3]。对于 CA I (Ki=5080 nM) 和 CA II (Ki=9640 nM),U-104 表现出适度的抑制作用[1]。在缺氧条件下,U-104 (50 μM) 抑制 4T1 细胞中癌症干细胞群的间充质表型。该效果持续72小时。在转移性 MDA-MB-231 LM2 -4Luc+ 细胞中,U-104 (<50 μM) 显着且剂量依赖性地减少迁移,导致细胞发育为类似于亲代 MDA-MB-231 细胞的紧凑集落[2] 。
1. 抑制缺氧乳腺癌细胞中CA IX活性:在缺氧条件(1% O₂,48小时)培养的MDA-MB-231(三阴性乳腺癌,TNBC)细胞中,U-104以剂量依赖性方式抑制CA IX活性。10 nM时,CA IX活性较缺氧溶媒对照组降低58%;20 nM(≈2×IC50)时,抑制率达82%。该抑制作用可逆转肿瘤细胞微环境酸化(20 nM U-104处理后,细胞外pH从6.5升至7.2)[1] 。 2. 对缺氧乳腺癌细胞的抗增殖活性:U-104选择性抑制缺氧乳腺癌细胞增殖。72小时MTS实验显示: - 缺氧MDA-MB-231细胞:IC50=15 nM [1] - 缺氧MCF-7(雌激素受体阳性乳腺癌)细胞:IC50=18 nM [1] - 常氧(21% O₂)MDA-MB-231/MCF-7细胞:IC50>200 nM(无显著抗增殖作用)[1] 。 3. 耗竭乳腺癌干细胞(BCSC):在MDA-MB-231细胞中,U-104降低缺氧条件下BCSC(CD44⁺/CD24⁻表型)比例。10 nM时,BCSC比例从缺氧对照组的35%降至18%;20 nM时进一步降至8%(流式细胞术分析)[2] 。U-104(20 nM)还可抑制BCSC自我更新:超低吸附板中形成的肿瘤球数量较对照组减少70%,干性相关蛋白(Sox2、Oct4、Nanog)表达下调55-65%(Western blot)[2] 。 4. 抑制肿瘤细胞迁移与侵袭:U-104(20 nM)使缺氧MDA-MB-231细胞迁移能力降低60%(划痕实验),侵袭能力降低55%(Matrigel Transwell实验)[1] 。Western blot显示,U-104(20 nM)下调血管生成与转移关键介质VEGF(65%)和MMP-9(70%)[1] 。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在原位植入 MDA-MB-231 LM2-4Luc+ 细胞的小鼠中,U-104(19、38 mg/kg;每天;持续 27 天)抑制原发性肿瘤的形成。 4T1 实验性转移小鼠模型表现出 U-104(19 毫克/千克;每天;持续 27 天;5 天)对转移形成的抑制作用[1]。当 MDA-MB-231 LM2-4Luc+ 细胞原位植入 NOD/SCID 小鼠时,U-104(38 mg/kg;腹腔注射;11-27 天)可显着抑制癌症干细胞的数量并减缓原代细胞的形成。肿瘤[2]。 ?原位植入 4T1 细胞的 Balb/c 小鼠在给予 U-104(50 mg/kg;口服强饲;连续 4 天,暂停 1 天;10 至 30 天)时,肿瘤形成明显延迟[2 ]。
1. 抑制异种移植模型中乳腺癌生长:6-8周龄雌性裸鼠皮下注射5×10⁶个缺氧预处理的MDA-MB-231细胞(0.1 mL PBS与基质胶1:1混合)。待肿瘤体积达~100 mm³时,小鼠随机分为3组: - 溶媒对照组:0.5%甲基纤维素PBS溶液(口服,每日1次,连续21天); - U-104 25 mg/kg组:口服,每日1次,连续21天; - U-104 50 mg/kg组:口服,每日1次,连续21天。 25 mg/kg组肿瘤生长抑制率(TGI)为65%,50 mg/kg组TGI达80% [1] 。50 mg/kg组肿瘤重量仅为对照组的20%,免疫组化(IHC)染色显示肿瘤组织中CA IX阳性细胞减少75% [1] 。 2. 抑制乳腺癌转移:在MDA-MB-231肺转移模型(尾静脉注射2×10⁶个细胞)中,U-104(25 mg/kg,口服,每日1次,连续28天)处理组小鼠肺转移结节数较对照组减少70%(对照组平均17个/鼠,处理组平均5个/鼠)[1] 。 3. 体内耗竭BCSC:在携带MDA-MB-231异种移植瘤的裸鼠中,口服U-104(25 mg/kg/天,连续14天)可使肿瘤中CD44⁺/CD24⁻ BCSC比例从对照组的32%降至9%(肿瘤单细胞悬液流式分析)[2] 。这种耗竭与停药后肿瘤复发潜伏期延长2.5倍(从20天延长至50天)相关 [2] 。 |
| 酶活实验 |
1. 重组人CA IX活性测定(pH-stat法):实验在37°C下通过pH电极进行。反应缓冲液含25 mM Tris-HCl(pH 7.5)、10 mM NaCl及10 nM重组人CA IX蛋白。U-104在反应缓冲液中系列稀释(0.1-50 nM),与CA IX预孵育10分钟。加入37°C CO₂饱和水启动反应(CO₂水合为H₂CO₃,导致溶液pH下降),记录2分钟内的pH下降速率。CA IX活性以相对于溶媒对照组的pH变化速率百分比计算,IC50通过四参数逻辑模型拟合抑制曲线得到 [1]
。 2. CA II选择性实验:实验流程与CA IX测定一致,但以10 nM重组人CA II为酶源,且U-104测试浓度最高达1000 nM。结果显示1000 nM时CA II活性抑制率<10%,证实U-104对CA IX的选择性 [1] 。 |
| 细胞实验 |
1. 缺氧细胞培养与抗增殖(MTS)实验:MDA-MB-231/MCF-7细胞以5×10³个细胞/孔接种于96孔板,常氧(21% O₂,5% CO₂)孵育过夜。随后转移至低氧培养箱(1% O₂,5% CO₂,94% N₂)培养48小时以诱导CA IX表达,加入U-104(0.5-200 nM),继续缺氧培养72小时。每孔加入20 μL MTS试剂,孵育2小时后读取490 nm处吸光度,定义抑制增殖50%的U-104浓度为IC50 [1]
。 2. 乳腺癌干细胞(BCSC)检测(流式细胞术):MDA-MB-231细胞缺氧培养48小时后,用U-104(10-30 nM)处理72小时。胰酶消化收集细胞,冷PBS洗涤,加入荧光标记抗体(CD44-PE、CD24-FITC)4°C避光染色30分钟,流式细胞术分析,计算CD44⁺/CD24⁻细胞比例 [2] 。 3. 肿瘤球形成实验:缺氧MDA-MB-231细胞经U-104(10-30 nM)处理72小时后,以1×10³个细胞/孔接种于超低吸附6孔板,培养基为干细胞培养基(DMEM/F12添加B27、EGF、bFGF)。培养10天后,计数直径>50 μm的肿瘤球,计算相对于对照组的球形成率 [2] 。 4. Western blot分析:缺氧MDA-MB-231/MCF-7细胞经U-104(10-30 nM)处理24小时后,用含蛋白酶抑制剂的RIPA缓冲液裂解,4°C、12,000×g离心15分钟。取30 μg蛋白进行10% SDS-PAGE电泳,转移至PVDF膜,5%脱脂牛奶TBST溶液室温封闭1小时。膜与一抗(抗CA IX、抗HIF-1α、抗VEGF、抗Sox2)4°C孵育过夜,再与HRP标记二抗孵育1小时,ECL显影,ImageJ定量条带强度 [1, 2] 。 |
| 动物实验 |
Dissolved in 55.6% PEG 400, 11.1% ethanol and 33% water; 5 mg/kg; oral gavage
Balb/c mice orthotopically implanted with 4T1 cells. 1. Nude mouse breast cancer subcutaneous xenograft model: Female nude mice (6-8 weeks old, n=6 per group) were anesthetized with isoflurane. A total of 5×10⁶ MDA-MB-231 cells (pre-cultured under hypoxia for 48 hours) were suspended in 0.1 mL of a 1:1 mixture of PBS and Matrigel, then subcutaneously injected into the right flank of each mouse. When tumors reached an average volume of ~100 mm³ (7 days after cell injection), mice were randomly assigned to three groups: - Vehicle control group: 0.5% methylcellulose in PBS, administered orally via gavage once daily for 21 days; - U-104 25 mg/kg group: U-104 was suspended in 0.5% methylcellulose to a concentration of 5 mg/mL, administered orally once daily for 21 days; - U-104 50 mg/kg group: U-104 was suspended in 0.5% methylcellulose to a concentration of 10 mg/mL, administered orally once daily for 21 days. Tumor volume was measured every 2 days using a digital caliper (volume = length × width² / 2), and body weight was recorded weekly. At the end of treatment, mice were euthanized, tumors were excised and weighed, and tumor tissues were collected for IHC staining (anti-CA IX) [1] . 2. Nude mouse breast cancer lung metastasis model: Female nude mice (6-8 weeks old, n=6 per group) were injected with 2×10⁶ hypoxic preconditioned MDA-MB-231 cells via the tail vein (0.2 mL PBS). One day after cell injection, mice were treated with U-104 (25 mg/kg, oral, once daily) or vehicle for 28 days. At the end of treatment, mice were euthanized, lungs were removed and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, and metastatic nodules on the lung surface were counted under a stereomicroscope [1] . 3. BCSC depletion in vivo assay: Female nude mice (6-8 weeks old, n=5 per group) were subcutaneously injected with 5×10⁶ CD44⁺/CD24⁻ MDA-MB-231 cells (purified by flow cytometry). When tumors reached ~100 mm³, mice were treated with U-104 (25 mg/kg, oral, once daily) or vehicle for 14 days. Tumors were excised, dissociated into single cells, and the proportion of CD44⁺/CD24⁻ cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. For recurrence latency analysis, remaining mice were monitored for tumor regrowth after drug withdrawal [2] . |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
1. Acute toxicity in mice: Female CD-1 mice (6-8 weeks old, n=6 per dose) were administered U-104 orally at doses of 50, 100, 200 mg/kg. At 50 and 100 mg/kg, no mortality or significant toxicity was observed (body weight loss <4%, and normal serum levels of ALT, AST, and creatinine). At 200 mg/kg, 1 out of 6 mice died within 7 days, and surviving mice showed transient weight loss (6%) with no significant changes in liver/kidney function markers [1]
. 2. Chronic toxicity in nude mice: In the 21-day xenograft study, U-104 (25-50 mg/kg, oral, once daily) did not cause significant body weight loss (<5% change from baseline) or abnormal serum biochemistry (ALT, AST, creatinine) [1] . In the 14-day BCSC depletion study, no adverse effects on mouse behavior or organ morphology (liver, kidney, spleen) were observed [2] . |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
CAIX Inhibitor SLC-0111 is a sulfonamide carbonic anhydrase inhibitor with potential antineoplastic activity. Upon administration, CAIX inhibitor SLC-0111 inhibits tumor-associated carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX), an hypoxia-inducible transmembrane glycoprotein that catalyzes the reversible reaction and rapid interconversion of carbon dioxide and water to carbonic acid, protons, and bicarbonate ions. This prevents both the acidification of the tumor's extracellular microenvironment and cytoplasmic alkalization. This increases cell death in CAIX-expressing, hypoxic tumors. CAIX is overexpressed in various tumors and plays a key role in intra- and extracellular pH regulation, cancer cell progression, survival, migration and invasion; it is also involved in resistance to both chemo- and radiotherapy.
1. Chemical class and design background: U-104 is a synthetic, sulfonamide-derived selective carbonic anhydrase IX (CA IX) inhibitor. It was designed to target the unique active site of CA IX (overexpressed in hypoxic tumors) and avoid inhibiting ubiquitous CA isoforms (e.g., CA II), thereby reducing off-target toxicity [1] . 2. Mechanism of antitumor action: U-104 exerts its effects through three key pathways: (1) Inhibiting CA IX activity to reverse tumor microenvironment acidification, which suppresses tumor cell proliferation and migration; (2) Downregulating HIF-1α/VEGF signaling to inhibit angiogenesis and metastasis; (3) Depleting CD44⁺/CD24⁻ breast cancer stem cells to reduce tumor recurrence potential [1, 2] . 3. Therapeutic potential: U-104 shows preclinical potential for the treatment of hypoxic breast cancer, especially triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) — a subtype with high CA IX expression, high metastasis rate, and poor prognosis. Its ability to inhibit both primary tumor growth and metastasis, as well as deplete BCSCs, addresses unmet needs in TNBC treatment [1, 2] . |
| 分子式 |
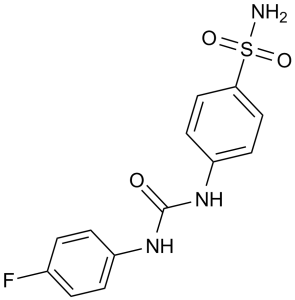
C13H12FN3O3S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
309.32
|
|
| 精确质量 |
309.058
|
|
| CAS号 |
178606-66-1
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
310360
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.5±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 熔点 |
242-243℃
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.673
|
|
| LogP |
2.12
|
|
| tPSA |
109.67
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
21
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
450
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| InChi Key |
YJQZNWPYLCNRLP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C13H12FN3O3S/c14-9-1-3-10(4-2-9)16-13(18)17-11-5-7-12(8-6-11)21(15,19)20/h1-8H,(H2,15,19,20)(H2,16,17,18)
|
|
| 化学名 |
1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)urea
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (6.72 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (6.72 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (6.72 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 30% PEG400+0.5% Tween80+5% propylene glycol:30mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2329 mL | 16.1645 mL | 32.3290 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6466 mL | 3.2329 mL | 6.4658 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3233 mL | 1.6164 mL | 3.2329 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT05025722 | Completed | Other: Non Interventional | Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum | Daiichi Sankyo | August 30, 2021 | |
| NCT04459585 | Completed Has Results | Drug: Dabigatran Etexilate Mesylate Drug: Quizartinib |
Healthy Subjects Drug-drug Interaction |
Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd. | August 28, 2020 | Early Phase 1 |
|
|---|
|
|
|
|---|
|
|