| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
AMPK (EC50 = 0.8 μM)
The primary target of A-769662 is AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key regulator of cellular energy metabolism. - In [1]: It selectively activates AMPK heterotrimers, with an EC50 of ~0.8 μM for recombinant human AMPKα2β1γ1 and ~1.2 μM for AMPKα1β1γ1. It shows no significant activity against other kinases (e.g., PKA, PKCα, mTOR) with IC50/Ki > 10 μM [1] - In [2]: For mouse AMPKα2β2γ3 (predominant in skeletal muscle), the EC50 is ~0.6 μM. It does not activate closely related kinases like SNF1 (yeast AMPK homolog) or inhibit phosphatases targeting AMPK [2] - In [3]: It activates AMPKα1-containing complexes in human colon cancer HCT116 cells with an EC50 of ~1.5 μM, with no cross-reactivity with PI3K-Akt or MAPK pathways [3] - In [4]: In rat liver microsomes, A-769662 does not inhibit cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP3A4) at concentrations up to 10 μM, indicating low drug-drug interaction potential [4] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
A-769662 在激活杆状病毒表达的 AMPK α1,β1,γ1 重组亚型方面同样有效(EC50=0.7 μM)。 A-592107 发挥剂量依赖性 AMPK 激活作用,从不同组织和物种纯化的 AMPK 中观察到的 EC50 仅存在微小变化。使用大鼠心脏、大鼠肌肉或人胚胎肾细胞 (HEK) 测定 A-769662 的 EC50,结果发现它们分别为 2.2 μM、1.9 μM 或 1.1 μM[1]。 A-769662 激活 LKB1 表达 (HEK293) 和 LKB1 缺陷 (CCL13) 细胞中的内源性 AMPK。 A-769662 以变构方式激活包含 1 个和精氨酸 298 (R298G) 取代的 AMPK 复合物。在含有突变体 1 的复合物中,A-769662 抑制 Thr-172 去磷酸化的程度与野生型复合物相似[2]。 A769662 (300 M) 对 MEF 细胞的毒性作用。 A769662 可逆地抑制蛋白酶体活性[3]。
1. 调控肝脏糖代谢(来自[1]): - 原代小鼠肝细胞用A-769662(0.1 μM、0.5 μM、1 μM、5 μM)处理24小时,浓度依赖性抑制胰高血糖素诱导的葡萄糖生成:1 μM时抑制率约45%,5 μM时达68%(葡萄糖氧化酶法检测)。Western blot显示AMPK下游底物ACC(Ser79)磷酸化水平升高,1 μM时p-ACC/ACC比值较对照增加3.2倍[1] 2. 促进骨骼肌脂肪酸氧化(来自[2]): - 小鼠比目鱼肌肌管用A-769662(0.2 μM、1 μM、5 μM)处理16小时,脂肪酸氧化率([14C]-棕榈酸掺入法)较对照增加~35%(1 μM)和~60%(5 μM)。qPCR分析显示,5 μM时脂肪酸转运蛋白1(FATP1)mRNA表达上调2.1倍[2] 3. 抑制结肠癌细胞增殖(来自[3]): - HCT116细胞用A-769662(0.5 μM、2 μM、8 μM)处理72小时,细胞活力(MTT法)呈剂量依赖性降低,IC50约为3.2 μM。流式细胞术显示G1期细胞周期阻滞:G1期细胞比例从对照的52%升至8 μM处理的71%。Western blot显示cyclin D1表达降低,细胞周期抑制剂p21水平升高[3] 4. 体外代谢(来自[4]): - 大鼠肝微粒体与A-769662(1 μM、5 μM)孵育0-120分钟,LC-MS/MS分析代谢产物:5 μM时120分钟仅剩余12%母药,两种主要代谢产物(M1、M2)占总放射性的~65%。人血浆孵育4小时未观察到显著代谢[4] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
A-769662(30 mg/kg,腹腔注射)显着降低 SD 大鼠的呼吸交换比 (RER)。用 30 mg/kg A-769662 (0.905 nmol/g) 或 500 mg/kg 二甲双胍 (0.574 nmol/g) 治疗的动物肝脏中丙二酰辅酶 A 水平分别降低 33% 和 58%。虽然较低剂量的 A-769662(3 和 10 mg/kg)对糖尿病 ob/ob 小鼠没有影响,但较高剂量(30 mg/kg,bid)显着降低饲喂血浆葡萄糖(降低 30%–40%) )[1]。
1. 肥胖小鼠的降糖作用(来自[1]): - 8-10周龄雄性db/db小鼠(高血糖模型)每日口服灌胃A-769662(10 mg/kg、30 mg/kg、100 mg/kg),持续14天。14天时,30 mg/kg组空腹血糖(FBG)较溶剂组(10% DMSO + 90%生理盐水)降低~22%,100 mg/kg组降低~45%。葡萄糖耐量试验(GTT)显示100 mg/kg组曲线下面积(AUC)减少~30%,肝脏甘油三酯含量降低~38%[1] 2. 高脂饮食(HFD)小鼠的胰岛素敏感性改善(来自[2]): - C57BL/6小鼠高脂饮食12周诱导胰岛素抵抗后,每日腹腔注射A-769662(50 mg/kg),持续7天。胰岛素耐量试验(ITT)显示胰岛素敏感性增加2.3倍(葡萄糖清除率评估)。骨骼肌AMPK活性(激酶活性法)较溶剂组高1.8倍,p-ACC(Ser79)水平升高[2] 3. 异种移植模型的抗肿瘤疗效(来自[3]): - 携带HCT116异种移植瘤(体积~100 mm³)的裸鼠,每日两次口服灌胃A-769662(20 mg/kg、60 mg/kg),持续21天。60 mg/kg组肿瘤生长抑制率(TGI)达~58%(肿瘤体积:380±45 mm³ vs 溶剂组900±62 mm³)。肿瘤组织Western blot显示p-AMPK(Thr172)和p21水平升高,cyclin D1降低[3] 4. 大鼠体内药代分布(来自[4]): - 雄性SD大鼠口服(10 mg/kg)或静脉注射(5 mg/kg)A-769662,口服生物利用度约38%。半衰期(t1/2):口服~3.2小时,静脉注射~1.9小时。血药浓度峰值(Cmax):口服1小时达2.1 μg/mL。1小时时肝脏和骨骼肌药物浓度分别为~3.5 μg/g和~1.8 μg/g,高于血浆浓度(1.9 μg/mL)[4] |
| 酶活实验 |
为了测定糖原磷酸化酶 b (GPb) 活性,将 1.5 μg/mL 兔 GPb 添加到含有 20 mM Na2HPO4 (pH 7.2)、2 mM MgSO4、1 mM β-NADP(β-烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸磷酸)的反应混合物中, 1.4 U/mL G-6-PDH(6-磷酸葡萄糖脱氢酶)和 3 U/mL PGM(磷酸葡萄糖变位酶)。添加指定浓度的 AMP 或测试化合物后,将糖原(终浓度 1 mg/mL)添加到测定介质中,开始反应。通过测量 340 nm 处的吸光度,在 25°C 孵育 10 分钟后评估 GPb 活性。
1. AMPK激活实验(来自[1]): - 试剂制备:纯化Sf9细胞表达的重组人AMPKα2β1γ1和α1β1γ1;反应缓冲液含50 mM Tris-HCl(pH7.4)、10 mM MgCl₂、0.2 mM ATP、1 mM DTT、100 μM AMPK底物肽(AMARA肽:AMARAASAAALARRR);加入[γ-³²P]ATP(比活度~2500 cpm/pmol)[1] - 实验设置:A-769662用DMSO系列稀释(0.01 μM~10 μM),加入反应混合物(DMSO终浓度≤1%)。加入AMPK(终浓度20 nM)启动反应,30°C孵育40分钟。设置溶剂(DMSO)和阳性对照(5-氨基咪唑-4-甲酰胺核糖核苷酸AICAR,1 mM)组(n=3)[1] - 检测:取25 μL反应混合物点样到P81滤纸,1%磷酸洗涤3次(每次5分钟),丙酮漂洗后风干。液体闪烁计数测放射性,计算相对于溶剂组的激活倍数,四参数逻辑模型拟合EC50[1] 2. CYP酶抑制实验(来自[4]): - 试剂制备:制备大鼠肝微粒体(0.5 mg/mL)和人CYP酶超微粒体(CYP1A2、CYP2C9、CYP3A4);反应缓冲液含50 mM磷酸钾(pH7.4)、1 mM NADPH、特异性CYP底物(如CYP1A2用非那西丁)[4] - 实验设置:A-769662(0.1 μM、1 μM、10 μM)与微粒体/底物在37°C孵育30分钟,乙腈终止反应。HPLC-UV检测特异性底物的代谢产物[4] - 分析:计算相对于溶剂组的抑制率,所有浓度下抑制率<10%,表明无CYP抑制活性[4] |
| 细胞实验 |
经 A-769662 处理或未经 A-769662 处理的 MEF 细胞的细胞活力测定如下:通过胰蛋白酶消化收获细胞,并在室温下黑暗中与 0.5 mg/mL RNase 和 50 μg/mL 碘化丙啶一起孵育;使用 FACScanto 流式细胞仪,使用 488 nm 激发激光和 600 nm 碘丙啶荧光检测,通过流式细胞术分析细胞活力。通过胰蛋白酶消化收获细胞,通过离心收集,在 PBS 中洗涤,并在 -20°C 下在 80% 乙醇中固定过夜,以确定细胞周期每个阶段的细胞百分比。然后将这些固定的细胞离心以除去固定剂,并将它们在含有 0.5 mg/mL RNase 和 50 μg/mL 碘化丙啶的 PBS 中在室温、黑暗中孵育 20 分钟。如上所述,进行流式细胞术分析。 MODFIT 程序用于计算 G1、S 和 G2 细胞的百分比。在指定时间,使用连接到具有 20 倍物镜的倒置显微镜的相机捕获细胞培养物图像。
1. 肝细胞葡萄糖生成实验(来自[1]): - 细胞制备:胶原酶灌注法分离原代小鼠肝细胞,接种到24孔板(1×10⁵个细胞/孔),DMEM(10% FBS)培养过夜[1] - 药物处理:更换为含A-769662(0.1 μM~5 μM)和胰高血糖素(10 nM)的无糖DMEM,孵育24小时,收集上清[1] - 检测:葡萄糖氧化酶试剂盒测上清葡萄糖浓度;RIPA裂解液提取细胞总蛋白,BCA法测蛋白浓度用于标准化,计算相对于仅胰高血糖素组的葡萄糖生成抑制率[1] 2. 肌管脂肪酸氧化实验(来自[2]): - 细胞制备:小鼠比目鱼肌卫星细胞在含2%马血清的DMEM中分化为肌管(7天),接种到12孔板(5×10⁴个细胞/孔)[2] - 药物处理:A-769662(0.2 μM~5 μM)处理细胞16小时,加入[14C]-棕榈酸(0.5 μCi/孔)孵育2小时,加入CO₂捕获液收集氧化的[14C]-棕榈酸[2] - 检测:液体闪烁计数测捕获液放射性,按蛋白含量标准化脂肪酸氧化率[2] 3. 癌细胞增殖与细胞周期实验(来自[3]): - 增殖实验:HCT116细胞接种到96孔板(5×10³个细胞/孔),A-769662(0.5 μM~8 μM)处理72小时。加入MTT(5 mg/mL)孵育4小时,DMSO溶解甲瓒结晶,测570 nm吸光度,计算IC50[3] - 细胞周期实验:HCT116细胞(2×10⁵个细胞/孔,6孔板)用8 μM A-769662处理48小时,70%乙醇固定,PI(50 μg/mL)+RNase A(100 μg/mL)染色,流式细胞术分析,计算G1、S、G2/M期细胞比例[3] |
| 动物实验 |
After acclimatization, lean and ob/ob mice are distributed randomly to the various treatment groups based on body weight and fed glucose levels (tail snip) at 8 AM. A subset of the animals representing each treatment group (n = 10 lean ob/+ and n = 10 ob/ob littermates) also has baseline plasma insulin samples taken. Ob/ob and lean littermate studies were conducted in two different ways: first, for a short period of time (5 days), and then for a longer period of time (14 days), in order to assess effectiveness and characterize the body weight change seen in the earlier study more thoroughly. Treatment groups for the 5 day study are as follows: ob/ob vehicle (0.2% hydroxypropyl methylcellulose [HPMC], i.p., b.i.d.), A-592107 (10 or 100 mg/kg, i.p., b.i.d.), A-769662 (3 or 30 mg/kg, i.p., b.i.d.), AICAR (375 mg/kg, s.c., b.i.d.), or metformin (450 mg/kg, p.o., q.d., with vehicle in PM), and lean littermates treated with vehicle (i.p., b.i.d.). Treatment groups for the 14 day ob/ob and lean littermate study are as follows: ob/ob vehicle (0.2% HPMC, i.p., b.i.d.), A-769662 (3, 10, or 30 mg/kg, i.p., b.i.d.), or metformin, and lean littermates treated with vehicle or 30 mg/kg of A-769662 (i.p., b.i.d.).
1. db/db mouse antihyperglycemic experiment (from [1]): - Animal model: Male db/db mice (8-10 weeks old, FBG > 16 mmol/L) were housed in 12h light/dark cycle, fed standard chow [1] - Drug formulation: A-769662 was dissolved in 10% DMSO + 90% normal saline to concentrations of 1 mg/mL, 3 mg/mL, 10 mg/mL [1] - Grouping and dosing: Mice were divided into 4 groups (n=6/group): vehicle (10 mL/kg, oral gavage), A-769662 10 mg/kg, 30 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg (oral gavage, once daily) for 14 days [1] - Sample collection: FBG was measured via tail vein blood (glucose meter) every 3 days. At endpoint, mice were euthanized; liver tissue was collected for triglyceride measurement (lipid extraction kit) and Western blot [1] 2. HFD mouse insulin sensitivity experiment (from [2]): - Animal model: C57BL/6 mice (6 weeks old) were fed HFD (60% fat) for 12 weeks to induce insulin resistance [2] - Drug formulation: A-769662 was dissolved in 5% DMSO + 10% Tween 80 + 85% saline to 5 mg/mL [2] - Dosing: Mice were divided into 2 groups (n=5/group): vehicle (10 mL/kg, intraperitoneal injection), A-769662 50 mg/kg (intraperitoneal, once daily) for 7 days [2] - Efficacy assessment: ITT was performed (insulin 0.75 U/kg, intraperitoneal); blood glucose was measured at 0, 15, 30, 60, 90 minutes. Skeletal muscle was collected for AMPK activity assay [2] 3. HCT116 xenograft experiment (from [3]): - Tumor inoculation: HCT116 cells (5×10⁶ cells/mouse) were subcutaneously injected into nude mice (6-8 weeks old) right flank [3] - Dosing: When tumors reached ~100 mm³, mice were divided into 3 groups (n=5/group): vehicle (10% DMSO + 90% saline, 10 mL/kg, oral gavage), A-769662 20 mg/kg, 60 mg/kg (oral gavage, twice daily) for 21 days [3] - Monitoring: Tumor volume (length×width²/2) and body weight were measured every 2 days. At endpoint, tumors were excised for Western blot and histological analysis (H&E staining) [3] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
1. Rat pharmacokinetics (from [4]):
- Study design: Male Sprague-Dawley rats (250-300 g) were divided into 2 groups (n=4/group): oral (10 mg/kg) and intravenous (5 mg/kg) A-769662 [4]
- Sample collection: Blood samples were collected at 0.083, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12 hours post-dosing. Plasma was separated via centrifugation (3000×g, 10 min) [4] - Parameters: Oral bioavailability (F) = ~38%; t1/2 (oral) = ~3.2 hours, t1/2 (intravenous) = ~1.9 hours; Cmax (oral) = ~2.1 μg/mL (1 hour); AUC₀-∞ (oral) = ~15.6 μg·h/mL, AUC₀-∞ (intravenous) = ~20.3 μg·h/mL [4] 2. Tissue distribution (from [4]): - Rats (oral 10 mg/kg) were euthanized at 1, 3, 6 hours post-dosing. Liver, skeletal muscle, kidney, brain were collected. A-769662 concentration was measured via LC-MS/MS: liver (3.5 μg/g at 1 hour), skeletal muscle (1.8 μg/g at 1 hour), kidney (1.2 μg/g at 1 hour), brain (0.3 μg/g at 1 hour) [4] 3. In vitro metabolism (from [4]): - Rat liver microsomes: A-769662 (5 μM) had a half-life of ~45 minutes; two major metabolites (M1: hydroxylated derivative, M2: glucuronide conjugate) were identified [4] - Human plasma: No significant metabolism was observed after 4 hours of incubation (92% parent drug remained) [4] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
1. Acute toxicity in mice (from [1]):
- Female ICR mice were administered A-769662 (50 mg/kg, 150 mg/kg, 300 mg/kg, oral gavage). No mortality was observed at 50 mg/kg or 150 mg/kg; 300 mg/kg caused 20% mortality (1/5 mice). Mild lethargy was observed at 150 mg/kg, resolving within 48 hours [1]
2. Subchronic toxicity in rats (from [4]): - Rats were administered A-769662 (10 mg/kg, 30 mg/kg, 60 mg/kg, oral gavage) once daily for 28 days. No significant changes in body weight, food intake, or organ weight (liver, kidney, heart) were observed. Serum ALT, AST, BUN, Cr were within normal ranges. No histological lesions were found in major organs [4] 3. Plasma protein binding (from [4]): - Measured via ultrafiltration (30 kDa cutoff). Human, rat, mouse plasma were spiked with A-769662 (0.1 μM, 1 μM, 10 μM). Binding rates were ~91% (human), ~88% (rat), ~86% (mouse) across all concentrations [4] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
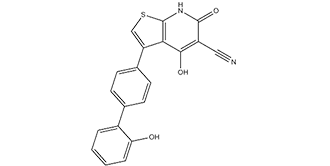
4-hydroxy-3-[4-(2-hydroxyphenyl)phenyl]-6-oxo-7H-thieno[2,3-b]pyridine-5-carbonitrile is a member of biphenyls.
1. Mechanism of action (from [1]): A-769662 activates AMPK by binding to the γ subunit regulatory domain, allosterically enhancing AMPK activity without increasing intracellular AMP levels. It also inhibits AMPK phosphatases, prolonging AMPK phosphorylation (Thr172) and downstream signaling (e.g., ACC inhibition, glucose uptake promotion) [1] 2. Metabolic disease potential (from [1][2]): As a selective AMPK activator, A-769662 improves hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis in preclinical models, supporting its potential for type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). However, it has not advanced to clinical trials due to concerns about off-target effects in long-term use [1][2] 3. Antitumor mechanism (from [3]): In cancer cells, A-769662 activates AMPK to induce G1 cell cycle arrest via upregulating p21 and downregulating cyclin D1. It also suppresses anabolic metabolism (e.g., protein synthesis) required for tumor growth, providing a rationale for combining with other anticancer agents [3] 4. Pharmacokinetic advantages (from [4]): A-769662 has moderate oral bioavailability (~38%) and preferential distribution to metabolic tissues (liver, skeletal muscle), which aligns with its target of action. Low CYP inhibition reduces drug-drug interaction risks, making it a favorable tool compound for preclinical studies [4] |
| 分子式 |
C20H12N2O3S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
360.3859
|
| 精确质量 |
360.056
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 66.65; H, 3.36; N, 7.77; O, 13.32; S, 8.90
|
| CAS号 |
844499-71-4
|
| 相关CAS号 |
844499-71-4
|
| PubChem CID |
54708532
|
| 外观&性状 |
Off-white to yellow solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.6±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
630.1±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
268.39° C
|
| 闪点 |
334.9±31.5 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.9 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.781
|
| LogP |
2.81
|
| tPSA |
125.35
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
| 重原子数目 |
26
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
647
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
N#CC1=C(O)C2=C(SC=C2C2C=CC(C3C(O)=CC=CC=3)=CC=2)NC1=O
|
| InChi Key |
CTESJDQKVOEUOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C20H12N2O3S/c21-9-14-18(24)17-15(10-26-20(17)22-19(14)25)12-7-5-11(6-8-12)13-3-1-2-4-16(13)23/h1-8,10,23H,(H2,22,24,25)
|
| 化学名 |
4-hydroxy-3-[4-(2-hydroxyphenyl)phenyl]-6-oxo-7H-thieno[2,3-b]pyridine-5-carbonitrile
|
| 别名 |
A-769662; A 769662; A-769662; 4-Hydroxy-3-(2'-hydroxy-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-6-oxo-6,7-dihydrothieno[2,3-b]pyridine-5-carbonitrile; A 769662; A769662; 6,7-DIHYDRO-4-HYDROXY-3-(2'-HYDROXY[1,1'-BIPHENYL]-4-YL)-6-OXO-THIENO[2,3-B]PYRIDINE-5-CARBONITRILE; MFCD11977269; UNII-P68477CD2C; A769662
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~72 mg/mL (~199.8 mM)
Water: <1 mg/mL Ethanol: <1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.94 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.94 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.94 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 1% DMSO+30% polyethylene glycol+1% Tween 80: 30mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7748 mL | 13.8739 mL | 27.7477 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5550 mL | 2.7748 mL | 5.5495 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2775 mL | 1.3874 mL | 2.7748 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
A769662 inhibits proteasomal function by an AMPK-independent mechanism.FEBS Lett.2008 Jul 23;582(17):2650-4. |
|---|
Inhibition of proteasomal activity by A769662 is reversible.FEBS Lett.2008 Jul 23;582(17):2650-4. |
A769662 affects the in vitro activity of purified 26S proteasomes but not the in vitro activity of purified 20S proteasomes.FEBS Lett.2008 Jul 23;582(17):2650-4. |
A769662 has toxic effects on MEF cells.FEBS Lett.2008 Jul 23;582(17):2650-4. |
|---|
A-769662 allosterically activates AMPK and protects against dephosphorylation of Thr-172.J Biol Chem.2007 Nov 9;282(45):32539-48 |
A-769662 activates endogenous AMPK in LKB1-expressing (HEK293) and LKB1-deficient (CCL13) cells.J Biol Chem.2007 Nov 9;282(45):32539-48 |