BML-275,Compound C; BML275; BML-275; dorsomorphin; 866405-64-3; 6-(4-(2-(Piperidin-1-yl)ethoxy)phenyl)-3-(pyridin-4-yl)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine; Compound C; AMPK Inhibitor, Compound C; 6-[4-(2-Piperidin-1-ylethoxy)phenyl]-3-pyridin-4-ylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine; Dorsomorphin free base; BML 275; CpdC;Dorsomorphin
6-[4-(2-哌啶-1-基乙氧基)苯基]-3-吡啶-4-基吡唑并[1,5-A]嘧啶; 6-[4-[2-(1-哌啶基)乙氧基]苯基]-3-(4-吡啶基)吡唑并[1,5-A]嘧啶; BML-275 ;Dorsomorphin(化合物C)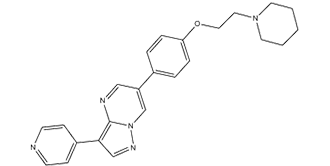
| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
AMPK (Ki = 109 nM); ACVR1; BMPR1A; ALK6; Autophagy
- AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) (IC50 = 10 μM) [1] - Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) type I receptors (ALK2, ALK3, ALK6) (IC50 values: ALK2 = 178 nM, ALK3 = 187 nM, ALK6 = 131 nM) [2] - Type II TGF-β receptor (TβRII) (IC50 = 1.1 μM) [3] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Dorsomorphin 降低 AICAR 和二甲双胍增加脂肪酸氧化或抑制肝细胞中脂肪生成基因的能力,以及它们灭活 ACC 的能力。 [1] 在 HT-29 细胞中,Dorsomorphin 通过抑制 AMPK 活性几乎完全阻止自噬蛋白水解。 [2] Dorsomorphin 通过选择性抑制 BMP I 型受体 ALK2、ALK3 和 ALK6 来另外阻断 BMP 介导的 SMAD1/5/8 磷酸化、靶基因转录和成骨分化。 [3]
Dorsomorphin抑制SMAD依赖性BMP信号[3] 在体外测试了dorsomorphin对BMP信号传导的影响。培养的小鼠肺动脉平滑肌细胞(PASMCs)表达BMP受体的补体。为了应对不同的BMP配体,PASMC显示SMAD1/5/8激活、MAPK p38激活和分化抑制剂(Id)基因的转录,Id是一组显性负作用的基本螺旋-环-螺旋转录因子,通常用于促进增殖和抑制分化。Dorsomorphin以剂量依赖的方式抑制BMP4诱导的BMP反应性SMAD的磷酸化(半数最大抑制浓度(IC50)=0.47µM),而不影响MAPK p38的激活(图2a,b)。dorsomorphin在功能上分离SMAD1/5/8和MAPK p38激活的独特能力表明,BMPs通过不同的机制激活这些效应器。与dorsomorphin相反,noggin抑制了BMP4诱导的SMAD1/5/8和MAPK p38的磷酸化(图2c),这与BMP配体隔离对SMAD依赖性和SMAD非依赖性信号传导的抑制是一致的。Dorsomorphin(4µM)抑制结构多样的BMPs的活性,阻断BMP2、BMP4、BMP6和BMP7对BMP反应的SMAD激活(图2d),并将未处理细胞中的磷酸化SMAD水平降低到基础水平以下。Dorsomorphin在浓度等于或大于抑制BMP信号传导的浓度时,不会抑制TGF-β1对SMAD2的激活,并且仅在浓度≥10µM时适度抑制激活素A对SMAD2激活(图2e,f)。这些结果在补充图3a-e中进行了定量描述。 Dorsomorphin抑制BMP I型受体功能[3] 为了测试dorsomorphin是否抑制BMP II型受体的功能,我们在缺乏BMP II型接收器(BMPR-II)的PASMC中测试了dorsomorphn。BMPR-II缺陷细胞使用激活素IIa型受体(ActR-IIa)而不是BMPR-II来激活I型BMP受体。Dorsomorphin抑制BMPR-II缺陷细胞中BMP2、BMP4、BMP6和BMP7的信号传导(补充图3f),这表明Dorsomorphin在BMPR-II存在或不存在的情况下抑制BMP信号。这一发现表明,dorsomorphin可能抑制II型受体下游BMP I型受体的信号传导。为了验证这一假设,用BMP I型受体ALK2、ALK3和ALK6的组成型活性(ca)形式转染细胞。转染这些组成型活性受体增加了细胞提取物中SMAD1/5/8的磷酸化,这种作用被dorsomorphin预孵育所抑制(图2g)。同样,在没有配体的情况下,用caALK2、caALK3或caALK6转染Id1启动子(BRE-Luc)的活性增加了5到12倍。Dorsomorphin抑制了caALK2、caALK3和caALK6的活性,对caALK2和caALK3的选择性明显高于caALK6.(图2h)。在相似的浓度下,dorsomorphin不会抑制组成型活性ALK4、ALK5或ALK7、TGF-β和激活素I型受体的功能(在线补充图4)。dorsomorphin具有以下能力:(i)阻断BMP介导的SMAD1/5/8磷酸化,(ii)抑制活化的BMP i型受体磷酸化SMAD1/5/8并诱导下游转录,这强烈表明dorsomorphn抑制BMP i型接收器激酶功能。 Dorsomorphin抑制成骨细胞分化[3] dorsomorphin阻断BMP介导的信号传导和转录活性的能力表明,dorsomorphing可能阻断BMP诱导的成骨细胞分化。BMP4有效地诱导了肌成纤维细胞C2C12细胞中的碱性磷酸酶活性(成骨分化的标志物),在培养5天后,BMP6的诱导程度较低(图3a)。添加4µM的dorsomorphin几乎完全消除了这种活性,在该浓度下,没有观察到对细胞计数的显著影响(图3b)。这些发现表明,与抑制BMP功能一致,dorsomorphin抑制BMP诱导的多能间充质衍生细胞的成骨分化,而没有细胞毒性。 化合物C/Dorsomorphin阻断AICAR诱导的AMPK激活[4] 最近人们认识到,AMPK信号控制着免疫疾病模型的炎症反应。为了研究AICAR(其激活剂之一)诱导的AMPK激活和磷酸化,我们用AICAR刺激小鼠巨噬细胞,并观察到AICAR以时间依赖的方式诱导AMPK激活(图1A),以及剂量依赖性反应。 同时,我们用AICAR和不同剂量的化合物C(一种常用的AMPK药理学抑制剂)同时处理RAW 264.7细胞,发现化合物C可以以剂量依赖的方式阻断AICAR诱导的AMPK激活,并在最高剂量下几乎消除AMPK激活(图1B)。数据表明AICAR是AMPK的激活剂,化合物C是AMPK抑制剂。此外,化合物C可以有效阻断AICAR诱导的AMPK激活。 化合物C/Dorsomorphin可降低LPS诱导的AMPK激活[4] LPS是革兰氏阴性菌的主要外膜,通过立即触发多种细胞信号来促进免疫反应。我们研究了LPS诱导的AMPK激活,并注意到LPS启动了AMPK及其下游蛋白ACC的磷酸化(图2A)。上述数据与之前的研究一致。然而,化合物C对巨噬细胞的预处理减少了LPS诱导的AMPK和ACC的磷酸化(图2A)。 接下来,我们评估了AICAR和化合物C对LPS诱导的AMPK活化的影响。AICAR处理增强了LPS诱导的AMPK信号传导,特别是ACC的磷酸化,而化合物C处理抑制了上述试剂诱导的AMPK激活(图2B)。结果表明,化合物C作为AMPK抑制剂,可以在各种条件下消除AMPK的激活,例如AICAR治疗和LPS攻击。 化合物C/Dorsomorphin阻断LPS诱导的活性氧(ROS)-NFκB信号传导[4] 我们研究了NFκB信号激活,包括依次磷酸化IKK、IκB和NFκB,发现LPS对巨噬细胞的刺激以NFκB的信号级联激活为特征(图3A)。之前有报道称,AMPK激动剂如AICAR下调了LPS诱导的免疫反应。在这里,我们进一步研究了化合物C在LPS攻击后不同时间点对AMPK抑制对NFκB信号传导的影响。化合物C的预处理抑制了由LPS刺激驱动的IKK、IκB和NFκB p65的磷酸化(图3A)。 为了评估AICAR和化合物C调节的ROS诱导,我们在AICAR或/和化合物C存在的情况下用LPS刺激巨噬细胞。AICAR和复合物C都抑制了ROS的产生(图3D)、NFκB信号的激活(数据未显示)和TNF的生成(图3E)。然而,与单独使用LPS相比,AICAR和化合物C治疗的组合降低了每种单一治疗的抑制作用,包括抑制ROS的产生和TNF的产生(图3D和E)。 - 抑制AMPK活性:10 μM的Dorsomorphin(BML-275)在大鼠肝脏AMPK制剂中抑制AMPK活性,阻断AMPK下游靶标(如乙酰辅酶A羧化酶,ACC)的磷酸化。这种抑制具有可逆性,且对AMPK的选择性高于其他激酶[1] - 拮抗BMP信号通路:在0.1-10 μM浓度范围内,Dorsomorphin(BML-275)抑制C2C12成肌细胞和原代成骨细胞中BMP诱导的Smad1/5/8磷酸化。它降低BMP依赖性转录活性(通过BRE-荧光素酶报告基因检测),并抑制BMP诱导的成骨细胞分化(通过碱性磷酸酶活性评估)[2] - 抑制TGF-β信号通路:在HEK293细胞中,Dorsomorphin(BML-275)(1-10 μM)阻断TGF-β诱导的Smad2磷酸化和TGF-β依赖性转录活性(通过CAGA-荧光素酶报告基因)。它还抑制NMuMG细胞中TGF-β介导的上皮-间质转化[3] - 影响细胞增殖:在人脐静脉内皮细胞(HUVECs)中,Dorsomorphin(BML-275)(5-20 μM)抑制VEGF诱导的增殖和管腔形成,这与VEGFR2和ERK1/2的磷酸化减少相关[4] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Dorsomorphin (10 mg/kg) 会增加成年小鼠的血清铁水平并降低铁调素表达的基础水平。 [3] Dorsomorphin (0.2 mg/kg, iv) 显着降低 LPS 治疗大鼠胸主动脉中的 VCAM-1 和 ICAM-1 表达。 [4]
Dorsomorphin诱导小鼠出现高铁血症[3] 喂食标准铁补充饮食的野生型(WT)C57BL/6成年小鼠表达高水平的hepcidin15,这可能是由于铁的大量供应引起的。dorsomorphin阻断斑马鱼铁诱导的hepcidin表达的能力导致了这样一种假设,即dorsomorphing可以抑制基础hepcidin的表达,并增加铁充足小鼠的血清铁水平。静脉注射dorsomorphin 6小时后,肝hepcidin mRNA水平降至载体注射小鼠的三分之一(P<0.01)(图5e)。hepcidin水平的改变通过改变ferroportin33对细胞内铁的动员来影响24小时内的血清铁浓度。在24小时内服用dorsomorphin导致血清总铁浓度增加60%(图5f)。因此,Dorsomorphin治疗可有效降低hepcidin表达的基础水平,并增加成年小鼠的血清铁浓度。 Dorsomorphin诱导斑马鱼胚胎背侧化[3] 基于BMP拮抗剂会使发育中的斑马鱼胚胎背侧化的前提,使用体内筛选试验寻找BMP信号传导的小分子抑制剂。从我们的小分子收藏中测试了7500多种化合物,其中包括已知的生物活性分子、美国食品和药物管理局批准的药物和商业分子多样性库。斑马鱼胚胎排列在96孔板中,从受精后4小时(h.p.f.)开始与化合物一起孵育,并在24和48小时进行视觉评估。我们称之为dorsomorphin的一种化合物(1,图1a)会使斑马鱼胚产生实质性和可重复的背化。Dorsomorphin处理的胚胎显示出球形胚胎背极结构的扩张,而腹极结构的扩展是代价。 AICAR和化合物C均能减轻LPS诱导的肝损伤[4] 基于上述发现,AICAR和化合物C都阻断了LPS诱导的体外巨噬细胞活化,我们假设AMPK调节因子可以抑制LPS诱导的体内免疫反应。接下来,我们研究了这些AMPK信号调节剂是否可以保护动物免受内毒素血症诱导的肝损伤和死亡,内毒素血症是一种典型的疾病,其特征是LPS诱导的过度免疫反应[21]。腹腔注射LPS导致肝损伤,血清丙氨酸转氨酶(ALT)和天冬氨酸转氨酶(AST)水平升高。然而,与LPS组相比,AICAR(LPS+AICAR)或化合物C(LPS+CC)预处理降低了小鼠血清中ALT和AST的水平(图4A和B)。 化合物C/Dorsomorphin抑制肝脏的免疫反应[4] 免疫反应,包括过度的免疫细胞活化和浸润到肝组织中,会导致内毒素诱导的肝损伤[21]。如图5A所示,在正常小鼠中,肝脏局部组织中分布着少量巨噬细胞(库普弗细胞)。小鼠腹腔注射LPS可诱导快速炎症反应,包括巨噬细胞和中性粒细胞浸润,其特征是肝组织中CD68的高水平表达(图5A)和MPO活性(图5B),以及血清中TNF的产生(图5C)。AICAR或化合物C的治疗抑制了单核细胞/巨噬细胞向肝组织的浸润,有证据表明肝组织中CD68的表达降低(图5A)。根据体外TNF产生的抑制(图3E),AICAR或化合物C治疗降低了肝组织中的MPO活性(图5B)和血清TNF产生(图5C),这意味着这两种治疗也可能抑制中性粒细胞功能和肝组织的浸润。上述数据表明,单一AICAR和化合物C治疗对内毒素血症期间肝脏免疫反应的负面影响。 化合物C/Dorsomorphin提高内毒素血症小鼠的存活率[4] 抑制免疫反应已被证明可以提高实验动物的存活率,并防止内毒素血症诱导的致死[22],[23]。然后,我们研究了AICAR或化合物C是否可以保护小鼠免受LPS诱导的内毒素休克和致死。如图6所示,与仅用LPS攻击治疗的动物相比,在注射LPS之前用AICAR(LPS+AICAR)或化合物C(LPS+CC)治疗小鼠显著降低了致死率(与LPS组相比,LPS+AICA和LPS+CC的P<0.01和P<0.001)。同时,与AICAR或化合物C的单一治疗相比,AICAR和化合物C的联合治疗(LPS+AICAR+CC)显示出更高的死亡率(图6)。 Fisetin可降低大鼠体重并改善动情周期[6] 从实验开始到结束,定期监测大鼠的体重变化。研究中包括的大鼠显示出大致相等的初始体重。服用米非司酮后,PCOS组在实验后的体重(279.5±4.105 g,p<0.05)明显高于正常对照组(228.8±3.877 g,p<0.05)(图1)。相反,与PCOS组相比,不同剂量的非瑟酮(LD:267±2.543 g和HD:250.3±3.232 g,p<0.05)和盐酸二甲双胍(245.5±2.232 g,p<0.05)组逆转了体重的增加(图1)。相反,与非瑟酮(HD)治疗的PCOS大鼠相比,Dorsomorphin(270.8±2.638 g,p<0.05)抑制了非瑟酮的作用。 Fisetin改善PCOS大鼠的HOMA-IR[6] 测量血清FBG和FINS水平以计算PCOS大鼠的胰岛素抵抗。与正常对照组相比,PCOS组的FBG(138.7±3.313 mg/dL,p<0.05)和FINS(3.267±0.166µU/mL,p<0.05)的血清水平更高(FBG:81.5±2.872和FINS:1.233±0.095µU/mL,p<0.05)。不同剂量的非瑟酮(LD和HD)和盐酸二甲双胍的给药显著降低了PCOS组的FBG(非瑟酮LD:117±3.0 mg/dL和非瑟酮HD:97.33±2.813 mg/dL,盐酸二甲双胍:86.5±4.006 mg/dL)和FINS(非瑟汀LD:2.51±0.163µU/mL和非瑟汀HD:1.41±0.065µU/mL,盐酸二甲双胍:1.242±0.108µU/mL,p<0.05)的血清水平(图3a和b)。与非瑟汀(HD)治疗的PCOS大鼠相比,Dorsomorphin(FBG:133.5±2.766 mg/dL和FINS:2.823±0.189µU/mL,p<0.05)分别显著抑制了非瑟汀对FBG和FINS血清水平的影响(图3a和b)。相应地,与正常大鼠(0.24±0.022,p<0.05)相比,PCOS组的HOMA-IR相对升高(1.115±0.049,p<0.05)。非瑟汀暴露(LD:0.651±0.026和HD:0.339±0.20,p<0.05)和盐酸二甲双胍(0.265±0.028,p<0.05)显著降低了这一激增。然而,与非瑟酮(HD)治疗的PCOS大鼠相比,dorsomorphin显著抑制了非瑟酮的这种作用(0.932±0.068,p<0.05)(图3c)。这些发现证实了非瑟酮对多囊卵巢综合征大鼠胰岛素抵抗的保护作用。 本研究探讨了PI3K和AMPK信号通路抑制剂对瘦素诱导的大鼠精子不良反应的影响。将14-16周龄的Sprague-Dawley大鼠随机分为对照组、瘦素组、瘦素+Dorsomorphin(AMPK抑制剂)组和瘦素+LY294002(PI3K抑制剂)治疗组,每组6只。瘦素通过腹腔注射(i.p.)途径每天一次,持续14天,剂量为60 ug kg-1体重。瘦素和抑制剂治疗组的大鼠同时接受dorsomorphin(5 mg kg-1 day-1)或LY294002(1.2 mg kg-1 day-1)腹腔注射,持续14天。对照组接受0.1ml生理盐水。完成后,估计精子计数、精子形态、生精小管上皮高度(STEH)、生精管直径(STD)、8-羟基-2-脱氧鸟苷(8-OHdG)和磷酸化Akt/总Akt比值。使用方差分析对数据进行分析。与对照组和LY294002治疗组相比,瘦素和瘦素+dorsomorphin治疗组的大鼠精子计数、STEH和STD显著降低,而形态异常的精子百分比和8-OHdG水平显著升高。瘦素和瘦素+LY294002治疗的大鼠睾丸磷酸化Akt/总Akt比值显著升高。总之,LY294002可以防止瘦素诱导的大鼠精子参数变化,这表明PI3K信号通路在瘦素对精子参数的不利影响中可能起作用[7]。 - 抑制骨形成:以Dorsomorphin(BML-275)(25 mg/kg/天,腹腔注射)处理小鼠14天,结果显示骨矿物质密度降低且骨形成受损,骨切片中 osteoblast数量和碱性磷酸酶活性减少可证明这一点。这归因于体内BMP信号通路的抑制[2] - 影响糖代谢:在肥胖糖尿病小鼠中,Dorsomorphin(BML-275)(10 mg/kg,腹腔注射)可急性升高血糖水平,并降低胰岛素诱导的骨骼肌中ACC磷酸化,与AMPK抑制一致[1] - 抗血管生成活性:在小鼠Matrigel栓测定中,Dorsomorphin(BML-275)(20 mg/kg/天,皮下注射)减少VEGF诱导的血管生成,表现为栓中血红蛋白含量和CD31阳性血管密度降低[4] |
| 酶活实验 |
AMPK激酶检测(ELISA检测)[5]
将HT1080细胞接种在24孔板中(每孔2×104个细胞),在有或没有葡萄糖或10 mM 2DG的情况下用化合物C(Dorsomorphin)处理2小时。通过将质粒DNA(pAMPKα1-wt、pAMPKβ1-D168A和pcFlag作为对照)转染在6孔板中,接种在24孔板中并用UPR抑制剂处理,制备过表达野生型和显性阴性AMPKα1的HT1080细胞。用细胞裂解缓冲液(20 mM Tris-HCl,pH 7.5,250 mM NaCl,10%甘油,0.5%NP-40,1 mM EDTA,1 mM EGTA,0.2 mM PMSF,1µg/mL pepstatin,0.5µg/mL亮肽,5 mM NaF,2 mM Na3Vo4,2 mMβ-甘油磷酸,1 mM DTT)裂解细胞。根据制造商的说明,使用CycLex AMPK激酶测定试剂盒测定对照样品(正常生长条件下的载体或pcFlag)的相对AMPK激酶活性(重复测定的平均值±标准差)。[5] 碱性磷酸酶活性[3] 将C2C12细胞接种到96孔板中,每孔2000个细胞,在添加了2%FBS的DMEM中。用BMP配体和Dorsomorphin或载体对孔进行四次处理。在用50µl Tris缓冲盐水、1%Triton X-100培养5天后收获细胞。将裂解物加入96孔板中的对硝基苯基磷酸盐试剂中1小时,碱性磷酸酶活性以405 nM的吸光度表示。使用与碱性磷酸酶测量相同的重复孔,分别通过细胞滴度Glo和核染料CyQuant的结合来测量细胞存活率和数量。 Dorsomorphin diHCl (BML-275 二盐酸盐;化合物 C 二盐酸盐) 是一种有效的、选择性的 ATP 竞争性 AMK 抑制剂,Kiof 109 nM。 Dorsomorphin diHCl 通过靶向 I 型受体 ALK2、ALK3 和 ALK6 抑制 BMP 通路。 - AMPK激酶活性测定:将纯化的大鼠肝脏AMPK与Dorsomorphin(BML-275)(0-100 μM)在ATP和合成肽底物存在下孵育。使用放射测定法测量底物的磷酸化。基于剂量-反应曲线计算IC50[1] - BMP受体激酶测定:将重组ALK2、ALK3或ALK6激酶结构域与Dorsomorphin(BML-275)(0-1 μM)和ATP孵育。使用时间分辨荧光共振能量转移(TR-FRET)测定法定量Smad1衍生肽底物的磷酸化。通过非线性回归确定IC50值[2] |
| 细胞实验 |
在体外研究中,将约1×106/mL RAW264.7细胞接种在48孔板中。细胞用AICAR或/和Dorsomorphin(化合物C)处理不同的时间点。或者,在100ng/mL或1µg/mL脂多糖(LPS,来自大肠杆菌0111:B4)攻击之前,用AICAR或/和Dorsomorphin(化合物C)预处理细胞15分钟至1小时。[4]
活性氧(ROS)检测[4] 在10µM二苯碘鎓氯化物(DPI)、AICAR或Dorsomorphin(化合物C)存在或不存在的情况下,用2µM羧基-2′,7′-二氯二氢荧光素二乙酸酯(H2DCFDA)预处理细胞15分钟,然后用LPS(1µg/mL)刺激。15分钟后,通过流式细胞术分析确定ROS的产生。未经H2DCFDA处理的细胞被定义为阴性对照。 Dorsomorphin (compound C)(0-10 μM,18 h)以剂量依赖性方式抑制人纤维肉瘤 HT1080 细胞中 2DG 诱导的 GRP78 启动子活性,但对 tunicamycin 诱导的 GRP78 启动子活性几乎没有影响。 Dorsomorphin(化合物 C) 还可抑制葡萄糖戒断诱导的 GRP78 启动子活性。 Dorsomorphin(化合物 C)对 2DG 诱导的 PERK 激活没有影响,并降低 HT1080 细胞中基础和 2DG 诱导的 AMPK 磷酸化水平。 BMP反应元件和hepcidin启动子萤光素酶报告基因检测[3] 使用Fugene6用0.3µg Id1启动子萤光素酶报告构建体(BRE-Luc)与0.6µg表达BMP I型受体组成型活性形式(caALK2、caALK3或caALK6)的质粒组合瞬时转染在6孔板中生长至50%融合的小鼠PASMC。为了评估激活素和TGF-βI型受体的功能,用0.3µg PAI-1启动子萤光素酶报告构建体(CAGA-Luc)与0.6µg表达I型受体组成型活性形式(caALK4、caALK5和caALK7)的质粒组合瞬时转染PASMC。对于这两种报告质粒,使用0.2µg pRL-TK-Renilla萤光素酶(Promega)来控制转染效率。转染后1小时,PASMC与Dorsomorphin(4-10µM)或载体一起孵育。收获细胞提取物,并使用双荧光素酶检测试剂盒通过萤火虫与海肾荧光素酶活性的比率来定量相对启动子活性。将2.5µg hepcidin启动子萤光素酶报告基因与0.25µg pRL-TK联合瞬时转染HepG2或Hep3B细胞,以控制转染效率,有或没有编码FLAG标记的人HJV的20ng cDNA。转染后2天,将HepG2和Hep3B细胞在1%FBSα-MEM中孵育6小时,用Dorsomorphin(10µM)或载体处理30分钟,然后在BMP2(25 ng ml-1)存在或不存在的情况下孵育16小时。如上所述,通过萤光素酶测定法测量Hepcidin启动子活性。 - BMP响应报告基因测定:转染BRE-荧光素酶报告质粒的C2C12细胞用Dorsomorphin(BML-275)(0.1-10 μM)预处理1小时,然后用BMP2(100 ng/ml)刺激24小时。测量荧光素酶活性并归一化为蛋白质浓度[2] - TGF-β信号测定:转染CAGA-荧光素酶报告基因的HEK293细胞在TGF-β1(5 ng/ml)刺激前30分钟用Dorsomorphin(BML-275)(1-10 μM)处理。24小时后,测定荧光素酶活性。通过蛋白质印迹分析检测Smad2磷酸化[3] - 内皮细胞管形成测定:将HUVECs接种在Matrigel包被的孔中,并用Dorsomorphin(BML-275)(5-20 μM)和VEGF(50 ng/ml)处理。6小时后,通过显微镜观察管形成,并量化管的数量和分支点[4] |
| 动物实验 |
Iron-replete mice; Wild-type (WT) C57BL/6 adult mice that are fed a standard iron-replete diet express high levels of hepcidin.
10 mg/kg. Intravenously once. Zebrafish bone mineralization[3] WT zebrafish embryos were raised in E3 buffer containing phenylthiourea. At 1 day post fertilization (d.p.f.), embryos were treated with dorsomorphin (1–4 µM) or DMSO vehicle. At 5 d.p.f. and onward, larvae were fed for 1 h every other day. Following each feeding, residual food was washed out and medium was replaced with E3 containing dorsomorphin or vehicle. At 10 d.p.f., larvae were immersed in 0.2% calcein for 30 min. Embryos were washed repeatedly in E3 buffer for 3 h to remove unbound calcein and anesthetized with tricaine. Calcified skeletal structures were visualized by green fluorescence, and the number of vertebral bodies were counted. Iron-dextran injections[3] Adult fish were anesthetized with tricaine and injected with 10 µl of iron-dextran solution (100 mg ml−1, average dextranMW= 5,000) into the abdominal cavity with dorsomorphin (23 µg/g) or vehicle (DMSO). Control fish were injected with 10 µl of dextran (average MW = 5,000, Sigma). Fish were revived in water. 1 h after injection, fish were anesthetized on ice, and livers were collected into 200 µl SDS-lysis buffer and homogenized mechanically. 15 µl of protein extract was fractionated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted, as described above. 3 h after injection, total RNA was extracted from mechanically homogenized zebrafish livers using Trizol reagent.[3] 12-week-old C57BL/6 mice raised on a standard diet are injected via the tail vein with 0.2 g/kg of Dextran or 0.2 g/kg of iron-dextran USP. Dextran is injected with vehicle only, whereas iron-dextran is injected with either vehicle or Dorsomorphin (10 mg/kg). 1 h after injection, mice are killed and liver segments are collected in 500 µL of SDS-lysis buffer and mechanically homogenized. 20 µL of liver extracts are resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted. Total RNA is harvested using Trizol from mechanically homogenized mouse livers (6 h after injection with a single intraperitoneal dose of Dorsomorphin (10 mg/kg) or DMSO).[3] Animal Studies[4] Male BALB/c mice at 6–7 weeks of age weighing 20–22 g were fed with food and water ad libitum, and housed in a standard animal facility with 12 h light/dark cycle and 50%–70% humidity) for 3 days before the study. BALB/c mice were randomly divided into five experimental groups: Control (intraperitoneally (i.p.) injection of PBS), LPS (i.p. injection of 2 mg/kg body weight), LPS+AICAR (i.p. injection, 500 mg/kg body weight 60 min before LPS injection), LPS+Compound C (CC or Dorsomorphin) (i.p. injection, 25 mg/kg body weight 60 min before LPS challenge), and LPS+AICAR+Compound C (CC or Dorsomorphin) (i.p. injection of 500 mg of AICAR and 25 mg of Compound C (CC or Dorsomorphin) per kilogram of body weight 60 min before i.p. injection of LPS). Six or twelve hours after injection of LPS, the mice were anesthetized with pentobarbital and euthanized thereafter by cervical dislocation, and blood and tissues were collected for analysis. For survival experiment, the grouped mice as mentioned above were injected i.p. with LPS (20 mg/kg body weight). To investigate the effect of AICAR or compound C/Dorsomorphin, the mice received injection (i.p.) of 500 mg of AICAR or/and 25 mg of compound C per kilogram of body weight 60 min before administration of LPS. Survival of animals was monitored every 2 hours for up to 24 hours. Severity of sepsis was monitored according to general appearance, breathing frequency, and provoked behavior. The mice were euthanized by cervical dislocation under deep anaesthesia, if the mice exhibited a disease point of no return. After 24 hours, the number of the survival mice of each group was recorded: 8 mice survived in total 8 Control mice (8/8), 0/20, 8/19, 12/19, and 3/19 surviving mice in LPS, LPS+AICAR, LPS+CC, LPS+AICAR+CC respectively. All surviving mice were anesthetized and euthanized with the same protocol described above. Sprague-Dawley (SD) of 9–12 weeks old female rats (220–270 g) were used in this research. The mechanistic group was given Dorsomorphin (0.2 mg/kg, i.p dissolved in 1% DMSO solution, for the next 21 days) 30 min prior to fisetin HD (40 mg/kg, p.o.). Dorsomorphin was employed as an inhibitor of the activity of AMPK and SIRT1. [6] The rats were randomised into four groups, that is control, leptin-, leptin + dorsomorphin (AMPK inhibitor)- and leptin + LY294002 (PI3K inhibitor)-treated groups, with each group consisting of six rats. Leptin was given once daily for 14 days via the intraperitoneal (i.p.) route at a dose of 60 µg/kg body weight (Recombinant Rat Leptin; Purity >95%, Biovision, USA). In the leptin- and inhibitor-treated groups, the animals were given either Dorsomorphin (5 mg kg−1 day−1) or LY294002 (PI3K inhibitor; 1.2 mg kg−1 day−1) i.p. together with leptin for 14 days. Control rats received 0.1 ml of normal saline i.p. for 14 days. Body weight of both the control and experimental animals was recorded weekly. The doses of leptin and dorsomorphin used in this study were according to Almabhouh et al., 2015, and Pachori et al., 2010, respectively. The dose of LY294002 used was according to Shan et al., 2008. The duration of treatment was based on Haron et al., 2010.[7] - Bone formation study: C57BL/6 mice were administered Dorsomorphin (BML-275) (25 mg/kg/day) via intraperitoneal injection for 14 days. Control mice received vehicle (dimethyl sulfoxide in saline). Femurs were harvested for micro-CT analysis and histomorphometric assessment of osteoblast parameters [2] - Glucose metabolism study: Obese diabetic mice were fasted overnight, then injected intraperitoneally with Dorsomorphin (BML-275) (10 mg/kg) or vehicle. Blood glucose levels were measured at 0, 1, and 2 hours. Skeletal muscle was collected for Western blot analysis of ACC phosphorylation [1] - Matrigel plug assay: Mice were subcutaneously implanted with Matrigel containing VEGF (500 ng/plug) and Dorsomorphin (BML-275) (100 μM) or vehicle. After 7 days, plugs were removed, and hemoglobin content was measured. Sections were stained for CD31 to quantify vessel density [4] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
- Acute toxicity: Mice treated with Dorsomorphin (BML-275) at 50 mg/kg (i.p.) showed transient lethargy and reduced food intake within 24 hours, but no mortality. At 100 mg/kg, 30% mortality was observed within 3 days [6]
- Hepatotoxicity: Rats treated with Dorsomorphin (BML-275) (30 mg/kg/day, i.p.) for 14 days showed elevated serum ALT and AST levels, along with histopathological changes in the liver (vacuolar degeneration of hepatocytes) [6] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Dorsomorphin is a pyrazolopyrimidine that is pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine which is substituted at positions 3 and 6 by pyridin-4-yl and p-[2-(piperidin-1-yl)ethoxy]phenyl groups, respectively. It is a potent, selective, reversible, and ATP-competitive inhibitor of AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase, EC 2.7.11.31) and a selective inhibitor of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling. It has a role as an EC 2.7.11.31 {[hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase (NADPH)] kinase} inhibitor and a bone morphogenetic protein receptor antagonist. It is a pyrazolopyrimidine, a member of piperidines, an aromatic ether and a member of pyridines.
Dorsomorphin has been reported in Trigonella foenum-graecum with data available. Dorsomorphin has been reported in Trigonella foenum-graecum. Activation of the NF-κB and mitogen activated protein (MAP) kinases plays an important role in the expression of inflammatory genes such as adhesion molecules. Although compound C (Dorsomorphin) is known as an AMPK inhibitor, AMPK-independent action of it has been recognized. Effects on the expression of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 by compound C (Dorsomorphin) were investigated in TNF-α-activated human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) in vitro and in thoracic aorta of rats treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in vivo. Compound C inhibited ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression at the transcriptional as well as translational level in TNF-α-activated HUVECs. In both DN-AMPK- and AMPKα(1)-siRNA-transfected HUVECs, compound C still inhibited TNF-α-induced VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 expression, indicating that this is AMPK-independent action. Interestingly, compound C significantly inhibited NF-κB activity and translocation of p65 to nucleus in HUVECs when activated with TNF-α. Importantly, administration of compound C (0.2 mg/kg) significantly reduced expression of both ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 in LPS-treated rat thoracic aortas. In addition, compound C significantly inhibited iNOS and production of NO in both TNF-α- and LPS-activated RAW 264.7 cells. Finally, compound C significantly inhibited phosphorylation of Akt and p-38MAPK but not protein kinase c or ERK1/2 in HUVECs. Taken together, we conclude that adhesion molecules (ICAM-1, VCAM-1) are to be the novel targets of compound C in preventing inflammatory insult to endothelial cells independent of AMPK inhibition via inhibition of NF-κB activity along with inhibition of phosphorylation of PI3K and P38 MAPK.[Atherosclerosis. 2011 Nov;219(1):57-64. ] Inhibiting the unfolded protein response (UPR) can be a therapeutic approach, especially for targeting the tumor microenvironment. Here, we show that compound C (Dorsomorphin) (also known as dorsomorphin), a small-molecule inhibitor of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling, inhibit the UPR-induced transcription program depending on the glucose deprivation conditions. We found that compound C prevented UPR marker glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78) accumulation and exerted enhanced cytotoxicity during glucose deprivation. Gene expression profiling, together with biochemical analysis, revealed that compound C (Dorsomorphin) had a unique mode of action to suppress the transcriptional activation of UPR-targeted genes, as compared with the classic UPR inhibitors versipelostatin and biguanides. Surprisingly, the UPR-inhibiting activity of compound C was not associated with either AMPK or BMP signaling inhibition. We further found that combination treatments of compound C and the classic UPR inhibitors resulted in synergistic cell death with UPR suppression during glucose deprivation. Our findings demonstrate that compound C could be a unique tool for developing a UPR-targeted antitumor therapy.[PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45845.] Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signals coordinate developmental patterning and have essential physiological roles in mature organisms. Here we describe the first known small-molecule inhibitor of BMP signaling-Dorsomorphin, which we identified in a screen for compounds that perturb dorsoventral axis formation in zebrafish. We found that dorsomorphin selectively inhibits the BMP type I receptors ALK2, ALK3 and ALK6 and thus blocks BMP-mediated SMAD1/5/8 phosphorylation, target gene transcription and osteogenic differentiation. Using dorsomorphin, we examined the role of BMP signaling in iron homeostasis. In vitro, dorsomorphin inhibited BMP-, hemojuvelin- and interleukin 6-stimulated expression of the systemic iron regulator hepcidin, which suggests that BMP receptors regulate hepcidin induction by all of these stimuli. In vivo, systemic challenge with iron rapidly induced SMAD1/5/8 phosphorylation and hepcidin expression in the liver, whereas treatment with dorsomorphin blocked SMAD1/5/8 phosphorylation, normalized hepcidin expression and increased serum iron levels. These findings suggest an essential physiological role for hepatic BMP signaling in iron-hepcidin homeostasis.[3] - Dorsomorphin (BML-275) was initially identified as an AMPK inhibitor but later found to potently block BMP and TGF-β signaling pathways. It is widely used as a tool compound in preclinical studies to investigate the roles of these pathways in development, cancer, and metabolic diseases [1][2][3] - The compound exhibits off-target effects on several kinases, limiting its use as a specific inhibitor. Structural analogs with improved selectivity have been developed based on its scaffold [3] |
| 分子式 |
C24H25N5O
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
399.49
|
|
| 精确质量 |
399.205
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 72.16; H, 6.31; N, 17.53; O, 4.00
|
|
| CAS号 |
866405-64-3
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Dorsomorphin dihydrochloride;1219168-18-9;Dorsomorphin dihydrochloride;1219168-18-9
|
|
| PubChem CID |
11524144
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to yellow solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.670
|
|
| LogP |
2.39
|
|
| tPSA |
55.55
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
30
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
514
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
N1C=CC(C2=C3N(C=C(C4C=CC(OCCN5CCCCC5)=CC=4)C=N3)N=C2)=CC=1
|
|
| InChi Key |
XHBVYDAKJHETMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C24H25N5O/c1-2-12-28(13-3-1)14-15-30-22-6-4-19(5-7-22)21-16-26-24-23(17-27-29(24)18-21)20-8-10-25-11-9-20/h4-11,16-18H,1-3,12-15H2
|
|
| 化学名 |
6-(4-(2-(piperidin-1-yl)ethoxy)phenyl)-3-(pyridin-4-yl)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~3 mg/mL (7.5 mM)
Water: <1 mg/mL Ethanol: 2 mg/mL (5.0 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 10 mg/mL (25.03 mM) in 50% PEG300 + 50% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浮液。
*生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 10 mg/mL (25.03 mM) in 0.5% CMC/saline water (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5032 mL | 12.5160 mL | 25.0319 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5006 mL | 2.5032 mL | 5.0064 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2503 mL | 1.2516 mL | 2.5032 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。