| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Bexarotene (LGD-1069) is a selective agonist of retinoid X receptors (RXRs), including RXRα, RXRβ, and RXRγ. It exhibits EC50 values of 23 nM for human RXRα, 15 nM for RXRβ, and 27 nM in a RXR-responsive luciferase reporter assay, with no significant activity on retinoic acid receptors (RARs, EC50 > 1000 nM) [1]
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Bexarotene 优先结合并激活 RXR 同工型,对于 RXRα、RXRβ 和 RXRγ 同工型,Kd=14±2 nM、21±4 nM 和 29±7 nM [1]。 Bexarotene 可有效减少白血病 (HL-60) 细胞的增殖。 Bexarotene 在 1 μM 时可抑制 HL-60 细胞增殖 37% [1]。 Bexarotene 作为单药处理细胞,在高剂量下显示出抗增殖作用,IC50 为 40.62±0.45 μM (PC3) 和 50.20±4.10 μM (DU145) [2]。 Bexarotene(20 和 40 μM)和多西紫杉醇(5 和 10 μM)在抑制 PC3 和 DU145 细胞生长方面表现出协同作用 [2]。 Bexarotene(20 和 40 μM)抑制 PC3 和 DU145 细胞中细胞周期蛋白 D1 和细胞周期蛋白 D3 的表达 [2]。
RXR激活实验:在转染RXRα/β/γ表达质粒和RXR响应性荧光素酶报告基因的HEK293细胞中,贝沙罗汀(Bexarotene,LGD-1069)(1-1000 nM)呈剂量依赖性诱导荧光素酶活性。100 nM浓度下,较溶媒对照组,RXRα介导的荧光素酶活性升高8.2倍,RXRβ升高7.5倍,RXRγ升高6.8倍,证实其RXR特异性激动作用[1] - 前列腺癌细胞抗增殖实验:在人前列腺癌细胞系(PC-3、LNCaP、DU145)中,贝沙罗汀(Bexarotene,LGD-1069)(0.1-10 μM)单药处理72小时(MTT法),IC50分别为1.2 μM(PC-3)、0.8 μM(LNCaP)和1.5 μM(DU145)。与多西他赛(1 nM)联合使用时,协同增强抗增殖效应:联合组PC-3细胞活力降至22%(单药贝沙罗汀组为48%,单药多西他赛组为55%),胱天蛋白酶-3/7活性(凋亡标志物,荧光法检测)升高3.1倍[2] - 肺癌细胞实验:在小鼠Lewis肺癌(3LL)细胞和人非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)A549细胞中,贝沙罗汀(Bexarotene,LGD-1069)(0.5-20 μM)抑制集落形成(克隆形成实验):5 μM浓度下,3LL细胞集落数减少65%,A549细胞集落数减少58%。Western blot显示,5 μM贝沙罗汀处理的3LL细胞中,细胞周期抑制剂p21表达升高2.4倍,细胞周期促进因子Cyclin D1表达降低42%[3] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在帕金森病 (PD) 大鼠模型中,贝沙罗汀(1 mg/kg/天)可有效预防行为缺陷和多巴胺神经元变性的发生,从而显着降低血清 T4 和甘油三酯的变化 [1]。贝沙罗汀是一种能有效阻止肺部肿瘤发展和扩散的药物。在所有三种基因型(p53wt/wtK-raswt/wt、p53val135/wtK-raswt/wt 或 p53wt/wtK-rasko/wt)的小鼠中,贝沙罗汀(灌胃法 100mg/kg)抑制肿瘤多样性和肿瘤体积。贝沙罗汀使 p53wt/wtK-rasko/wt 中腺瘤进展为腺癌的速度降低了约 50%。以及 p53wt/wtK-raswt/wt 的小鼠 [3]。
前列腺癌异种移植模型:雄性裸鼠(BALB/c nu/nu,6-8周龄)皮下注射5×10⁶个PC-3细胞,待肿瘤达100-150 mm³时,随机分为4组(每组n=6):溶媒组(0.1% DMSO+生理盐水)、贝沙罗汀(Bexarotene,LGD-1069)单药组(100 mg/kg/天,口服灌胃)、多西他赛单药组(5 mg/kg/周,腹腔注射)、联合组(贝沙罗汀+多西他赛)。治疗21天后,联合组肿瘤体积减少最显著(78%,从850 mm³降至187 mm³),单药贝沙罗汀组减少42%,单药多西他赛组减少38%。肿瘤组织TUNEL实验显示,联合组凋亡细胞数增加5.2倍[2] - 小鼠肺癌模型: 1. A/J小鼠(雌性,6-8周龄)腹腔注射100 mg/kg乌拉坦诱导肺肿瘤,4周后分为2组(每组n=10):对照组(标准啮齿类饲料)、贝沙罗汀(Bexarotene,LGD-1069)组(饲料中掺入贝沙罗汀,按100 mg/kg体重/天给药,根据日均进食量计算)。喂养16周后安乐死小鼠,取肺组织用10%福尔马林固定,解剖显微镜下计数表面肿瘤数量和大小:贝沙罗汀组肺肿瘤数量减少52%(从18.3个/鼠降至8.8个/鼠),肿瘤体积减少45%(平均直径从1.2 mm降至0.66 mm)[3] 2. 携带皮下3LL肿瘤(200-250 mm³)的C57BL/6小鼠,口服贝沙罗汀(Bexarotene,LGD-1069)(50 mg/kg/天)持续14天,肿瘤体积减少48%(从920 mm³降至478 mm³),中位生存期延长30%(从26天延长至33.8天)[3] |
| 酶活实验 |
RXR响应性荧光素酶报告基因实验:HEK293细胞以5×10⁴细胞/孔接种于24孔板,含10% FBS的DMEM培养24小时。用转染试剂共转染0.5 μg人RXRα/β/γ表达质粒、0.5 μg RXR响应性荧光素酶报告质粒(含DR1型RXR结合元件)和0.1 μg β-半乳糖苷酶质粒(内参)。转染24小时后,更换为含贝沙罗汀(Bexarotene,LGD-1069)(1、10、100、1000 nM)或溶媒(0.1% DMSO)的无血清DMEM,继续孵育24小时。用报告基因裂解缓冲液裂解细胞, luminometer检测荧光素酶活性,比色法检测β-半乳糖苷酶活性以校正转染效率,非线性回归计算EC50[1]
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞增殖测定[2]
细胞类型:人 PCa 雄激素非依赖性细胞系 PC3 和 DU145 测试浓度:5、10、20、30 , PC3 细胞为 40 μM; DU145 细胞为 1、5、10、20、40 μM。 孵育持续时间:24和48小时 实验结果:证明具有抗增殖作用,IC50分别为40.62±0.45 µM (PC3)和50.20 ±4.10 µM (DU145)。 细胞活力测定[2] 细胞类型: PC3 和 DU145 细胞 测试浓度: 20 和 40 µM <孵化持续时间:24或48小时 实验结果:24小时处理后细胞周期蛋白D1和细胞周期蛋白E2减少。治疗 48 小时后,不仅减少了细胞周期蛋白 D1 和细胞周期蛋白 E2 的表达,而且抑制了细胞周期蛋白 B1 和 CDK1 的表达。 前列腺癌细胞增殖与凋亡实验: 1. PC-3、LNCaP、DU145细胞分别以2×10³细胞/孔(PC-3/DU145)或3×10³细胞/孔(LNCaP)接种于96孔板,含10% FBS的RPMI 1640培养24小时。加入贝沙罗汀(Bexarotene,LGD-1069)(0.1-10 μM)单药或与多西他赛(1 nM)联合处理,孵育72小时。加入20 μL MTT(5 mg/mL),4小时后用DMSO溶解甲瓒结晶,570 nm处测吸光度计算细胞活力[2] 2. 凋亡检测:PC-3细胞以2×10⁵细胞/孔接种于6孔板,用贝沙罗汀(5 μM)+多西他赛(1 nM)处理48小时后裂解,使用荧光底物(Ac-DEVD-AMC)检测胱天蛋白酶-3/7活性,酶标仪检测荧光强度(激发380 nm,发射460 nm)[2] - 肺癌细胞克隆形成实验:3LL和A549细胞以500细胞/孔接种于6孔板,培养24小时后加入贝沙罗汀(Bexarotene,LGD-1069)(0.5-20 μM),孵育14天(3LL)或18天(A549)形成集落。4%多聚甲醛固定,0.1%结晶紫染色,计数>50个细胞的集落,以溶媒对照组为基准计算抑制率[3] - 细胞周期蛋白Western blot检测:3LL细胞(10 cm培养皿中2×10⁶细胞/皿)用5 μM 贝沙罗汀(Bexarotene,LGD-1069)处理48小时,含蛋白酶抑制剂的RIPA缓冲液裂解,BCA法测蛋白浓度。30 μg蛋白经10% SDS-PAGE电泳后转移至PVDF膜,一抗孵育p21、Cyclin D1和β-肌动蛋白(内参),HRP标记二抗结合后ECL显色,ImageJ定量条带灰度[3] |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: UL53-3 mice (p53wt/wtK-raswt/wt, p53val135/wtK-raswt/wt, or p53wt/wtK-rasko/wt)[3]
Doses: 100 mg/kg Route of Administration: Gavage with 18 gage of gavage -needle, 0.1 mL per mouse per day, 5 times a week, continued for 12 weeks Experimental Results: Inhibited both tumor multiplicity and tumor volume in mice of all three genotypes. Prostate Cancer Xenograft Model (PC-3): Male BALB/c nu/nu mice (6-8 weeks old, 20-22 g) were housed under SPF conditions (22±2°C, 12-hour light/dark cycle, free access to food/water). Mice were subcutaneously injected with 5×10⁶ PC-3 cells (suspended in 100 μL PBS + 50 μL Matrigel) into the right flank. When tumors reached 100-150 mm³, mice were randomized into 4 groups (n=6/group): - Vehicle: 0.1% DMSO + normal saline, oral gavage once daily; - Bexarotene (LGD-1069) alone: 100 mg/kg/day, dissolved in 0.1% DMSO + normal saline, oral gavage once daily; - Docetaxel alone: 5 mg/kg/week, dissolved in normal saline, intraperitoneal injection once weekly; - Combination: Bexarotene (100 mg/kg/day, oral) + docetaxel (5 mg/kg/week, ip). Treatment lasted 21 days. Tumor volume was measured every 3 days (volume = length × width² / 2). On day 21, mice were euthanized, tumors were harvested for TUNEL assay, and serum was collected for cytokine analysis [2] - Murine Lung Cancer Models: 1. A/J mouse urethane-induced lung tumor model: Female A/J mice (6-8 weeks old, 18-20 g) were intraperitoneally injected with 100 mg/kg urethane (dissolved in saline). Four weeks later, mice were divided into 2 groups (n=10/group): control (standard rodent diet) and Bexarotene (LGD-1069) (diet containing bexarotene at 100 mg/kg body weight/day, calculated based on average daily food intake). Mice were fed the respective diets for 16 weeks, then euthanized. Lungs were removed, fixed in 10% formalin, and the number and size of surface tumors were counted under a dissecting microscope [3] 2. C57BL/6 mouse 3LL xenograft model: Female C57BL/6 mice (6-8 weeks old) were subcutaneously injected with 1×10⁶ 3LL cells into the right flank. When tumors reached 200-250 mm³, mice were randomized into 2 groups (n=8/group): vehicle (0.5% carboxymethylcellulose sodium, CMC-Na, 10 mL/kg/day, oral gavage) and Bexarotene (LGD-1069) (50 mg/kg/day, dissolved in 0.5% CMC-Na, oral gavage). Treatment continued until mice met euthanasia criteria (tumor volume > 2000 mm³ or >15% weight loss). Survival time was recorded daily, and tumor volume was measured every 2 days [3] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Urinary elimination of bexarotene and its known metabolites is a minor excretory pathway (<1% of administered dose). After oral administration, bexarotene is absorbed with a Tmax of about two hours. ...Studies in patients with advanced malignancies show approximate single dose linearity within the therapeutic range and low accumulation with multiple doses. Plasma bexarotene AUC and Cmax values resulting from a 75 to 300 mg dose were 35% and 48% higher, respectively, after a fat-containing meal than after a glucose solution. Bexarotene is highly bound (>99%) to plasma proteins. The plasma proteins to which bexarotene binds have not been elucidated, and the ability of bexarotene to displace drugs bound to plasma proteins and the ability of drugs to displace bexarotene binding have not been studied. The renal elimination of bexarotene and its metabolites was examined in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Neither bexarotene nor its metabolites were excreted in urine in appreciable amounts. Bexarotene is thought to be eliminated primarily through the hepatobiliary system. Metabolism / Metabolites Four bexarotene metabolites have been identified in plasma: 6- and 7-hydroxy-bexarotene and 6- and 7-oxo-bexarotene. In vitro studies suggest that cytochrome P450 3A4 is the major cytochrome P450 responsible for formation of the oxidative metabolites and that the oxidative metabolites may be glucuronidated. The oxidative metabolites are active in in vitro assays of retinoid receptor activation, but the relative contribution of the parent and any metabolites to the efficacy and safety of /bexarotene/ is unknown. Bexarotene has known human metabolites that include 6-hydroxy-bexarotene, 7-hydroxy-bexarotene, and 7-oxo-bexarotene. Biological Half-Life 7 hours Terminal half-life of bexarotene is about seven hours. Bexarotene (LGD-1069) exhibits oral bioavailability of ~40% in rats and ~35% in humans. After oral administration of 100 mg/kg in rats, plasma Cmax (peak concentration) is 2.8 μg/mL, Tmax (time to peak) is 2 hours, and elimination half-life (t1/2) is 7.5 hours. It is highly bound to plasma proteins (>99%) and distributed to various tissues, with highest concentrations in the liver, adipose tissue, and skin (target tissue for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma) [1] - Metabolism: Bexarotene (LGD-1069) is primarily metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP3A4 and CYP2C8) in the liver, producing inactive metabolites that are excreted mainly via feces (≈60%) and urine (≈30%) within 72 hours [1] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Serum aminotransferase elevations occur in 5% of patients treated with bexarotene, but the abnormalities are generally mild, transient and not associated with symptoms or jaundice. However, cases of clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice have been reported with bexarotene therapy, some of which were severe and even fatal. Hepatotoxicity appears to be more common with higher doses. The clinical features of the hepatic injury with bexarotene have not been described in any detail and case reports of hepatotoxicity have yet to be published. Nevertheless, the product label mentions hepatotoxicity and recommends prospective monitoring of routine liver tests. Likelihood score: D (possible but uncommon cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Protein Binding >99% Interactions Because bexarotene is metabolized by cytochrome P450 3A4, ketoconazole, itraconazole, erythromycin, gemfibrozil, grapefruit juice, and other inhibitors of cytochrome P450 3A4 would be expected to lead to an increase in plasma bexarotene concentrations. Furthermore, rifampin, phenytoin, phenobarbital and other inducers of cytochrome P450 3A4 may cause a reduction in plasma bexarotene concentrations. Concomitant administration of /bexarotene/ capsules and gemfibrozil resulted in substantial increases in plasma concentrations of bexarotene, probably at least partially related to cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibition by gemfibrozil. Under similar conditions, bexarotene concentrations were not affected by concomitant atorvastatin administration. Concomitant administration of gemfibrozil with /bexarotene/ capsules is not recommended. Based on interim data, concomitant administration of /bexarotene/ capsules and tamoxifen resulted in approximately a 35% decrease in plasma concentrations of tamoxifen, possibly through an induction of cytochrome P450 3A4. Based on this known interaction, bexarotene may theoretically increase the rate of metabolism and reduce plasma concentrations of other substrates metabolized by cytochrome P450 3A4, including oral or other systemic hormonal contraceptives. Leukopenic and/or thrombocytopenic effects of bexarotene may be increased with concurrent or recent therapy /with blood dycrasia-causing medications/ if these medications cause the same effects; dosage adjustment of the bone marrow depressant, if necessary, should be based on blood counts. For more Interactions (Complete) data for BEXAROTENE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Preclinical toxicity in mice/rats: - Daily oral administration of Bexarotene (LGD-1069) (50-200 mg/kg) for 4 weeks caused dose-dependent adverse effects: skin dryness (80% of mice at 100 mg/kg), hyperlipidemia (increased triglycerides by 2.3-fold and cholesterol by 1.8-fold at 150 mg/kg), and mild hepatomegaly (10% increase in liver weight at 200 mg/kg). No significant renal toxicity (serum BUN/creatinine unchanged) or myelosuppression (peripheral blood cell counts normal) was observed [1] - In the 3LL xenograft model [3], mice treated with 50 mg/kg/day bexarotene for 14 days showed mild weight loss (<5% of baseline) and transient skin scaling, which resolved after treatment cessation; no histopathological changes in liver/kidney were detected [3] - Clinical toxicity (summarized in Literature [1]): Common adverse events in patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) include cutaneous reactions (dry skin, pruritus, rash, 65-75%), dyslipidemia (hypertriglyceridemia, 50-60%; hypercholesterolemia, 30-40%), and headache (20-25%). Grade 3/4 toxicities (occurring in <10% of patients) include severe hypertriglyceridemia (requiring lipid-lowering agents) and hepatotoxicity (transient ALT/AST elevation) [1] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
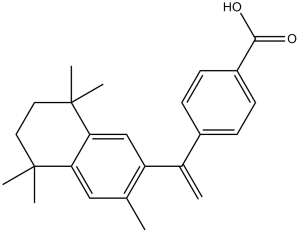
Bexarotene is a retinoid, a member of benzoic acids and a member of naphthalenes. It has a role as an antineoplastic agent.
Bexarotene (Targretin) is an antineoplastic agent indicated by the FDA for Cutaneous T cell lymphoma. It has been used off-label for lung cancer, breast cancer, and Kaposi's sarcoma. Bexarotene is a Retinoid. Bexarotene is a retinoid analogue that is used to treat the skin manifestations of cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL). Bexarotene therapy is associated with a high rate of serum enzyme elevations and rare instances of clinically apparent acute liver injury. Bexarotene is a synthetic retinoic acid agent with potential antineoplastic, chemopreventive, teratogenic and embryotoxic properties. Bexarotene selectively binds to and activates retinoid X receptors (RXRs), thereby inducing changes in gene expression that lead to cell differentiation, decreased cell proliferation, apoptosis of some cancer cell types, and tumor regression. (NCI04) A rexinoid (an RXR-binding ligand), tetrahydronaphthalene derivative and RETINOID X RECEPTOR antagonist that is used in the treatment of CUTANEOUS T-CELL LYMPHOMA. Drug Indication Used orally for the treatment of skin manifestations of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) in patients who are refractory to at least one prior systemic therapy. Also used topically for the treatment of skin lesions in early (stage IA and IB) CTCL in patients who experience refractory or persistent disease with the use of other therapies or are intolerant of other therapies. FDA Label Targretin capsules are indicated for the treatment of skin manifestations of advanced stage cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) patients refractory to at least one systemic treatment. Mechanism of Action Bexarotene selectively binds with and activates retinoid X receptor subtypes. There are three subtypes in total: RXRα, RXRβ, RXRγ. The exact mechanism of action of bexarotene in the treatment of CTCL is unknown but the drug has activity in all clinical stages of CTCL. Bexarotene selectively binds and activates retinoid X receptor subtypes (RXR(alpha), RXR(beta), RXR(gamma)). RXRs can form heterodimers with various receptor partners such as retinoic acid receptors (RARs), vitamin D receptor, thyroid receptor, and peroxisome proliferator activator receptors (PPARs). Once activated, these receptors function as transcription factors that regulate the expression of genes that control cellular differentiation and proliferation. Bexarotene inhibits the growth in vitro of some tumor cell lines of hematopoietic and squamous cell origin. It also induces tumor regression in vivo in some animal models. The exact mechanism of action of bexarotene in the treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) is unknown. Therapeutic Uses THERAP CAT: Antineoplastic Bexarotene is indicated for the treatment of cutaneous manifestations of cutaneous T-cell lyphoma in patients who are refractory to at least one other prior systemic therapy. /Included in US product label/ Drug Warnings May cause fetal harm; teratogenicity and embryolethality demonstrated in animals. No adequate and well-controlled studies to date in humans. Pregnancy should be avoided during therapy. If used during pregnancy, apprise of potential fetal hazard. ... Male patients receiving the drug should use condoms during sexual intercourse with women who are or may become pregnant. Effective contraception must be used for one month prior to the initiation of therapy, during therapy and for at least one month following discontinuation of therapy; it is recommended that two reliable forms of contraception be used simultaneously unless abstinence is the chosen method. Bexarotene can potentially induce metabolic enzymes and thereby theoretically reduce the plasma concentrations of oral or other systemic hormonal contraceptives. Hyperlipidemia occurred in 79% of patients receiving oral bexarotene in phase II-III clinical studies. Elevations in fasting triglycerides and cholesterol and decreases in HDL-cholesterol were observed in more than half of patients receiving 300 mg/sq m or more. Lipid abnormalities usually developed within 2-4 weeks and were reversible with cessation of therapy. If fasting triglycerides are elevated or become elevated during treatment, antilipemic therapy should be instituted, and the dosage of bexarotene reduced or suspended. Acute pancreatitis has been reported in several patients treated with bexarotene and has been fatal in at least one patient. The manufacturer states that patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) who have risk factors for pancreatitis (eg, prior pancreatitis, uncontrolled hyperlipidemia, excessive alcohol consumption, uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, biliary tract disease, or drugs associated with pancreatic toxicity or known to increase triglyceride concentrations) generally should not be treated with bexarotene. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for BEXAROTENE (15 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Bexarotene is a member of a subclass of retinoids that selectively activate retinoid X receptors (RXRs). These retinoid receptors have biologic activity distinct from that of retinoic acid receptors (RARs). Bexarotene is indicated for the treatment of cutaneous manifestations of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma in patients who are refractory to at least one prior systemic therapy. Bexarotene selectively binds and activates retinoid X receptor subtypes (RXRα, RXRβ, RXRγ). RXRs can form heterodimers with various receptor partners such as retinoic acid receptors (RARs), vitamin D receptor, thyroid receptor, and peroxisome proliferator activator receptors (PPARs). Once activated, these receptors function as transcription factors that regulate the expression of genes that control cellular differentiation and proliferation. Bexarotene inhibits the growth in vitro of some tumor cell lines of hematopoietic and squamous cell origin. It also induces tumor regression in vivo in some animal models. Mechanism of action: Bexarotene (LGD-1069) activates RXRs, which form homodimers or heterodimers with other nuclear receptors (e.g., PPARγ, LXRα). Activated RXR dimers bind to specific DNA response elements (e.g., DR1, DR5) in target gene promoters, regulating transcription of genes involved in cell cycle arrest (e.g., p21), apoptosis (e.g., Bax), and lipid metabolism (e.g., ABCA1) [1,3] - Therapeutic applications: Bexarotene (LGD-1069) is FDA-approved for the treatment of refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) in patients with stage IIB-IV disease. Preclinical studies [2,3] support its potential in other cancers (prostate cancer, lung cancer) when combined with chemotherapeutics (e.g., docetaxel) or as a chemopreventive agent [1,2,3] - Synergistic mechanism with docetaxel [2]: Bexarotene (LGD-1069) downregulates expression of ABCB1 (a multidrug resistance pump) by 45% in PC-3 cells, reducing docetaxel efflux and increasing intracellular drug accumulation. It also enhances docetaxel-induced G2/M cell cycle arrest (from 32% to 58% in PC-3 cells) via upregulating p21 [2] - Lung cancer chemoprevention [3]: Bexarotene (LGD-1069) inhibits lung tumor progression by reducing cancer stem cell (CSC) enrichment: it decreases the percentage of CD133⁺ CSCs in 3LL tumors from 12% to 4% and downregulates CSC-related genes (e.g., SOX2, Nanog) by 50-60% [3] |
| 分子式 |
C24H28O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
348
|
| 精确质量 |
348.208
|
| CAS号 |
153559-49-0
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Bexarotene-d4;2182068-00-2
|
| PubChem CID |
82146
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.0±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
489.7±44.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
230-231ºC
|
| 闪点 |
229.5±23.1 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.556
|
| LogP |
8.55
|
| tPSA |
37.3
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
2
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
| 重原子数目 |
26
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
551
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
NAVMQTYZDKMPEU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C24H28O2/c1-15-13-20-21(24(5,6)12-11-23(20,3)4)14-19(15)16(2)17-7-9-18(10-8-17)22(25)26/h7-10,13-14H,2,11-12H2,1,3-6H3,(H,25,26)
|
| 化学名 |
4-[1-(3,5,5,8,8-pentamethyl-6,7-dihydronaphthalen-2-yl)ethenyl]benzoic acid
|
| 别名 |
LGD1069; LGD 1069; LG 100069; Ro26-445; LGD-1069; SR-11247; Ro 26 445; Targretin Ro 26-445; SR 11247; SR11247; 3-methyl TTNEB. Bexarotene; US trade name: Targretin.
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 2.62 mg/mL (7.52 mM) in 5% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 50% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浮液;超声助溶。
*生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 2.62 mg/mL (7.52 mM) in 5% DMSO + 95% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.97 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.97 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100μL 20.8mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入到900μL 20%SBE-β-CD生理盐水中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 5 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.97 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8736 mL | 14.3678 mL | 28.7356 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5747 mL | 2.8736 mL | 5.7471 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2874 mL | 1.4368 mL | 2.8736 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT05296304 | Recruiting | Drug: Bexarotene Radiation: Total Skin Electron Beam (TSEB) |
Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma | Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center |
March 16, 2022 | Phase 1 |
| NCT03323658 | Completed Has Results | Drug: Bexarotene Other: Questionnaire Administration |
Breast Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia Breast Atypical Lobular Hyperplasia |
National Cancer Institute (NCI) | June 15, 2018 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00153842 | Terminated Has Results | Drug: Bexarotene (targretin) | Carcinoma, Non-small-cell Lung | Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center | August 2001 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
| NCT01782742 | Completed Has Results | Drug: Bexarotene Drug: Placebo |
Alzheimer's Disease | The Cleveland Clinic | February 2013 | Phase 2 |