| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:Etretinate(Ro 10-9359)是第二代类维生素A,用于治疗严重银屑病;已被阿维A取代,阿维A是阿维A酯的更安全的代谢物。细胞测定:将HSC-5细胞以1.5×103/100μL的密度接种于96孔板中并用于实验。进行初步实验以确定阿维A酯的有效剂量和细胞毒性。将细胞与浓度为 5、10、25 和 50 nmol/L 的阿维A酯一起孵育 72 小时 [溶解在含有 0.0001% 二甲基亚砜 (DMSO) 的盐水中]。然后将细胞在有或没有 200 μmol/L ALA (Sigma) 的情况下再孵育 2 小时。然后使用金属卤化物灯以 10、20、40 和 80 J/cm2 的剂量照射每个板。
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
与对照组相比,28 天的阿维A酯治疗组小鼠的平均真皮厚度显着降低(P < 0.05),胶原束也发生变化。 TUNEL检测显示,阿维A酯治疗小鼠真皮中TUNEL阳性细胞密度14天显着增加(P < 0.05)。与对照小鼠相比,阿维A酯治疗1天的小鼠的前胶原α1(I)链与β肌动蛋白mRNA的比率显着下降,但阿维A酯治疗14天的小鼠的比率显着增加( P<0.05)。 Etretinate 通过诱导细胞凋亡并可能调节 MRL/lpr 小鼠的细胞因子表达来减少真皮厚度并抑制皮肤病变的出现。
|
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Absorbed in the small intestine. Studies in normal volunteers indicate that the absorption of etretinate is greater in patients consuming whole milk or a high-fat diet than in patients in a fasting state. Concentrations of etretinate and its active metabolite in epidermal specimens obtained after 1 to 36 months of therapy were a function of location; subcutis much greater than serum greater than epidermis greater than dermis. Etretinate accumulates in high concentrations in adipose tissue, especially in the liver and in subcutaneous fat. Liver concentrations of etretinate in patients who had received therapy for six months were generally higher than accompanying plasma concentrations and tended to be higher still in livers with a higher degree of fatty infiltration. Studies in normal volunteers indicate that the absorption of etretinate is greater in patients consuming whole milk or a high-fat diet than in patients in a fasting state. Etretinate is absorbed in the small intestine. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for ETRETINATE (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Extensively metabolized, with significant first-pass metabolism to the pharmacologically active acid form. Subsequent metabolism results in the inactive 13-cis acid form, chain-shortened breakdown products, and conjugates that are ultimately excreted. The aromatic retinoid acitretin is the primary active metabolite of etretinate, and in this study the ethyl esterification of acitretin to etretinate using [(14)C]acitretin and human liver microsomes /was investigated/. ... This study demonstrated that in the presence of ethanol the ethyl esterification of acitretin to etretinate proceeds via formation of acitretinoyl-CoA. Predicting clearance of acitretin in vivo via this unique metabolic pathway will be a challenge, as the intracellular concentration of ethanol could never be predicted with any degree of accuracy in humans. Biological Half-Life In one study, the apparent terminal half-life of etretinate after 6 months of therapy was approximately 120 days. In another study of 47 patients who had undergone chronic therapy with etretinate, 5 patients had detectable serum drug concentrations (0.5 to 12 ng/mL) 2.1 to 2.9 years after therapy was completed. In one study, the apparent terminal half life of etretinate after 6 months of therapy was approximately 120 days. |
||
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding
More than 99% bound to plasma proteins, predominantly lipoproteins, whereas its active metabolite, acetretin (etretin), is predominantly bound to albumin. Interactions /Concurrent use of etretinate with tetracyclines/ may increase the potential for pseudotumor cerebri. Concurrent use /with other photosensitizing medications/ may cause additive photosensitizing effects. Concurrent use with other hepatotoxic medications, especially methotrexate, may increase the potential for hepatotoxicity. /Concurrent use of etretinate with isotretinoin, tretinoin, or vitamin A/ may result in additive toxic effects. For more Interactions (Complete) data for ETRETINATE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Mouse ip 1176 mg/kg (20 days) LD50 Rat ip >2000 mg/kg (20 days) LD50 Mouse oral >2000 mg/kg (20 days) LD50 Rat oral >4000 mg/kg (20 days) |
||
| 参考文献 |
Clin Exp Dermatol.2009 Apr;34(3):385-9;Lupus.2005;14(7):510-6.
|
||
| 其他信息 |
Etretinate can cause developmental toxicity according to an independent committee of scientific and health experts.
Etretinate is a retinoid, an enoate ester and an ethyl ester. It has a role as a keratolytic drug. Etretinate is a medication used to treat severe psoriasis. It is a synthetic aromatic retinoid. The mechanism of action of etretinate is still incompletely understood although, like retinoic acid, it is thought to interfere with the terminal differentiation of keratinocytes. It is thought to bind to the retinoic acid receptors. Etretinate is also believed to enhance the binding of cAMP to the regulatory RI subunit of cAMP dependent protein kinases. Etretinate was taken off the market in Canada in 1996 and America in 1998 due to the risk of birth defects. Etretinate is now used to treat T-cell lymphomas. It also appears to inhibit NADH oxidase activity. Etretinate is a synthetic oral retinoid that is a prodrug of acitretin. Etretinate activates retinoid receptors, causing an induction of cell differentiation, inhibition of cell proliferation, and inhibition of tissue infiltration by inflammatory cells. Etretinate is no longer commercially available in the U.S. due to the extended potential for teratogenic effects related to its long half-life. (NCI04) An oral retinoid used in the treatment of keratotic genodermatosis, lichen planus, and psoriasis. Beneficial effects have also been claimed in the prophylaxis of epithelial neoplasia. The compound may be teratogenic. Drug Indication For the treatment of severe psoriasis in adults. Mechanism of Action The mechanism of action of the active metabolite, acitretin, is unknown, however it is believed to work by targeting specific receptors (retinoid receptors) in the skin which help normalize the growth cycle of skin cells. Therapeutic Uses Antipsoriatic Etretinate is indicated for the treatment of severe recalcitrant psoriasis, including the erythrodermic and generalized pustular types, in patients who are unresponsive to or intolerant of the standard therapies. /Included in US product labeling/ Etretinate is used for the treatment of severe, intractable oral lichen planus. /NOT included in use product labeling/ Etretinate is also used in correcting severe intractable forms of keratinization disorders, such as: dermatoses, ichthyosiform; erythroderma, congenital ichthyosiform; ichthyosis, lamellar, and other ichthyoses; keratosis follicularis (Darier's disease); keratosis palmaris et plantaris; pityriasis rubra pilaris (PRP); pustulosis, palmoplanter. /NOT included in US product labeling/ Drug Warnings Pregnancy risk category: X /CONTRAINDICATED IN PREGNANCY. Studies in animals or humans, or investigational or post-marketing reports, have demonstrated positive evidence of fetal abnormalities or risk which clearly outweights any possible benefit to the patient./ Etretinate is contraindicated during pregnancy, since it has caused major human fetal abnormalities, including meningomyelocele; meningoencephalocoele; multiple synostoses; facial dysmorphia; syndactyly; absence of terminal phalanges; malformations of hip, ankle, and forearm; abnormalities of the heart and thymus; low set ears; high palate; decreased cranial volume; and alterations of the skull and cervical vertebrae. ... It has not been determined how long pregnancy should be avoided after discontinuation of treatment; patients have been followed for a long as 2 years after treatment was discontinued, and fetal abnormalities associated with etretinate have occurred during this 2 year period. Therefore, etretinate should not be used in women who plan to have children in the future. In women of childbearing potential, etretinate should not be used until the possibility of pregnancy is ruled out. In addition, etretinate should not be used in women who, while undergoing treatment and for an indefinite period of time thereafter, are deemed unreliable in their use of contraception or who may not use reliable contraception. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for ETRETINATE (13 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics The active metabolite responsible for etretinate's effects, acitretin, is a retinoid. Retinoids have a structure similar to vitamin A and are involved in the normal growth of skin cells. Acitretin works by inhibiting the excessive cell growth and keratinisation (process by which skin cells become thickened due to the deposition of a protein within them) seen in psoriasis. It therefore reduces the thickening of the skin, plaque formation and scaling. |
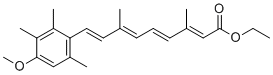
| 分子式 |
C23H30O3
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
354.48
|
|
| 精确质量 |
354.219
|
|
| CAS号 |
54350-48-0
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Etretinate-d3;1185237-13-1
|
|
| PubChem CID |
5282375
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Crystals
|
|
| 密度 |
1.0±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
506.4±38.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
104-105ºC
|
|
| 闪点 |
219.4±21.4 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.544
|
|
| LogP |
6.77
|
|
| tPSA |
35.53
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
26
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
568
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
O(C([H])([H])[H])C1C([H])=C(C([H])([H])[H])C(/C(/[H])=C(\[H])/C(=C(\[H])/C(/[H])=C(\[H])/C(=C(\[H])/C(=O)OC([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])/C([H])([H])[H])/C([H])([H])[H])=C(C([H])([H])[H])C=1C([H])([H])[H]
|
|
| InChi Key |
HQMNCQVAMBCHCO-DJRRULDNSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C23H30O3/c1-8-26-23(24)14-17(3)11-9-10-16(2)12-13-21-18(4)15-22(25-7)20(6)19(21)5/h9-15H,8H2,1-7H3/b11-9+,13-12+,16-10+,17-14+
|
|
| 化学名 |
ethyl (2E,4E,6E,8E)-9-(4-methoxy-2,3,6-trimethylphenyl)-3,7-dimethylnona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoate
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.05 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入900 μL 玉米油中,混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8210 mL | 14.1052 mL | 28.2103 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5642 mL | 2.8210 mL | 5.6421 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2821 mL | 1.4105 mL | 2.8210 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。