| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
MEK1 (IC50 = 4.2 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Cobimetinib 在多种肿瘤类型中显示出强大的细胞生长抑制活性,特别是在 BRAF 或 KRAS 突变癌细胞系中。与 GDC-0941 联合使用时,GDC-0973 会导致 888MEL 和 A2058 细胞失去活力、抑制某些途径并发生更多细胞凋亡。 [1]在所有 BRAFV600E 系中,GDC-0973 和维莫非尼的共同给药显着增加细胞膜上 GLUT-1 水平的降低。 [2]
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Cobimetinib(10 mg/kg,口服)与 GDC-0973 和 GDC-0941 一起在患有 BRAFV600E 和 KRAS 突变肿瘤的小鼠中表现出更好的抗肿瘤功效。 [1]组合 GDC-0973 和 GDC-0941 可降低耐药 A375 异种移植小鼠体内己糖激酶 II、c-RAF、Ksr 和 p-MEK 蛋白的水平。 [2]
|
| 酶活实验 |
Cobimetinib (GDC-0973, RG7420) 是一种有效的、选择性的口服 MEK1 抑制剂,对 MEK1 的 IC50 为 4.2 nM。
|
| 细胞实验 |
对于888MEL和A2058细胞,cobimetinib (GDC-0973)的EC50浓度分别为0.2 M和10 M。将 EC50 浓度的 MEK 和 PI3K 抑制剂应用于黑色素瘤细胞 24 小时(888MEL:0.05 M GDC-0973、2.5 M GDC-0941;A2058:2.5 M GDC-0973、2.5 M GDC-0941)。在 A375 细胞中,cobimetinib (100 nM) 在具有组成型 MAPK 激活的黑色素瘤中引起的细胞死亡受到线粒体 OXPHOS 的限制。
|
| 动物实验 |
Female NCR nude mice have had 5 million WM-266-4 melanoma cells intradermally implanted into the hind flank. The cells were resuspended in Hank balanced salt solution. Xenograft mice with tumor volumes of roughly 100 to 120 mm3 are randomly assigned to 4 single dose groups and 4 multiple dose groups on days 11 or 13 following the implantation. Mice in the single dose groups receive a single oral dose of the drug Cobimetinib (GDC-0973, expressed as free base equivalents), vehicle (water for injection USP), 1, 3, or 10 mg/kg one day after randomization and group assignment. For 14 days, mice in the multiple dose groups receive daily oral doses of the GDC-0973 1, 3, or 10 mg/kg, vehicle (water for injection USP), or both. On day 1 (single dose groups) or day 14 (multiple dose groups), plasma and tumor samples (n=3 per time point) are taken from euthanized mice predose and at 2, 4, 8, 16, 24, 72, and 168 hours postdose. Samples are kept until analysis at 80°C. Liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS-MS) is used to assess the concentrations of GDC-0973 in tumor lysates and plasma. The assay's dynamic range is 0.004 to 35 μM.
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Following oral dosing of 60 mg once daily in cancer patients, the median time to achieve peak plasma levels (Tmax) was 2.4 (range:1–24) hours, geometric mean steady-state AUC0-24h was 4340 ng∙h/mL (61% CV) and Cmax was 273 ng/mL (60% CV). The absolute bioavailability of COTELLIC was 46% (90% CI: 40%, 53%) in healthy subjects. A high‐fat meal (comprised of approximately 150 calories from protein, 250 calories from carbohydrate, and 500–600 calories from fat) had no effect on cobimetinib AUC and Cmax after a single 20 mg COTELLIC was administered to healthy subjects. Following oral administration of a single 20 mg radiolabeled cobimetinib dose, 76% of the dose was recovered in the feces (with 6.6% as unchanged drug) and 17.8% of the dose was recovered in the urine (with 1.6% as unchanged drug). The estimated apparent volume of distribution was 806 L in cancer patients based on a population PK analysis. Following oral administration of COTELLIC 60 mg once daily in cancer patients, the mean apparent clearance (CL/F) was 13.8 L/h (61% CV). Metabolism / Metabolites Cobimetinib is mainly metabolized via CYP3A oxidation and UGT2B7 glucuronidation with no major metabolites formed. Biological Half-Life Following oral administration of COTELLIC 60 mg once daily in cancer patients, the mean elimination half-life (t1/2) was 44 (range: 23–70) hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Elevations in serum aminotransferase and alkaline phosphatase levels are common during vemurafenib therapy and are even more common when it is combined with cobimetinib, abnormal liver tests occurring in 26% to 70% of treated patients and ALT values rising above 5 times the upper limit of the normal range (ULN) in 6% to 12%. Instances of clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice have also been reported during the clinical trials of cobimetinib and vemurafenib therapy, but the clinical features, course and outcomes of these episodes have not been described in detail. At least one instance of hepatocellular injury with jaundice was included in the initial safety review of cobimetinib. The MAPK pathway inhibitors as a class are often associated with transient serum enzyme elevations and more rarely with instances of clinically apparent liver injury, but the clinical features have not been described and the association with cobimetinib not clearly defined. The rate of clinically significant liver injury and hepatic failure associated with protein kinase inhibitors is increased in patients with preexisting cirrhosis or hepatic impairment due to liver tumor burden. Likelihood score: D (possible cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the clinical use of cobimetinib during breastfeeding. Because cobimetinib is 90% bound to plasma proteins, the amount in milk is likely to be low. However, its half-life is about 44 hours and it might accumulate in the infant. The manufacturer recommends that breastfeeding be discontinued during cobimetinib therapy and for 2 weeks after the last dose. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Cobimetinib is 95% bound to human plasma proteins in vitro, independent of drug concentration. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Pharmacodynamics
Cobimetinib is a reversible inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (MAPK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 (MEK1) and MEK2. Preclinical studies have demonstrated that this agent is effective in inhibiting the growth of tumor cells bearing a BRAF mutation, which has been found to be associated with many tumor types. A threonine-tyrosine kinase and a key component of the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway that is frequently activated in human tumors, MEK1 is required for the transmission of growth-promoting signals from numerous receptor tyrosine kinases. Cobimetinib is used in combination with vemurafenib because the clinical benefit of a BRAF inhibitor is limited by intrinsic and acquired resistance. Reactivation of the MAPK pathway is a major contributor to treatment failure in BRAF-mutant melanomas, approximately ~80% of melanoma tumors become BRAF-inhibitor resistant due to reactivation of MAPK signaling. BRAF-inhibitor-resistant tumor cells are sensitive to MEK inhibition, therefore cobimetinib and vemurafenib will result in dual inhibition of BRAF and its downstream target, MEK. |
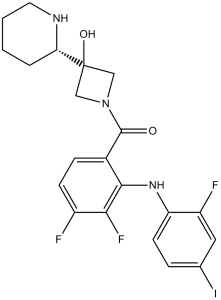
| 分子式 |
C21H21F3IN3O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
531.318
|
| 精确质量 |
531.063
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 47.47; H, 3.98; F, 10.73; I, 23.88; N, 7.91; O, 6.02
|
| CAS号 |
934660-93-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Cobimetinib hemifumarate;1369665-02-0;Cobimetinib racemate;934662-91-6;Cobimetinib (R-enantiomer);934660-94-3
|
| PubChem CID |
16222096
|
| 外观&性状 |
white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.7±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
565.9±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
296.1±30.1 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.662
|
| LogP |
5.96
|
| tPSA |
64.6
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
30
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
624
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
C(N1CC([C@H]2NCCCC2)(O)C1)(C1=CC=C(F)C(F)=C1NC1C=CC(I)=CC=1F)=O
|
| InChi Key |
BSMCAPRUBJMWDF-KRWDZBQOSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C21H21F3IN3O2/c22-14-6-5-13(19(18(14)24)27-16-7-4-12(25)9-15(16)23)20(29)28-10-21(30,11-28)17-3-1-2-8-26-17/h4-7,9,17,26-27,30H,1-3,8,10-11H2/t17-/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
[3,4-difluoro-2-(2-fluoro-4-iodoanilino)phenyl]-[3-hydroxy-3-[(2S)-piperidin-2-yl]azetidin-1-yl]methanone
|
| 别名 |
cobimetinib; Cotellic; XL518; XL 518; XL-518; GDC0973; GDC-0973; GDC 0973;RG 7420; RG-7420; RG7420
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.71 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.71 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.71 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.71 mM) (饱和度未知) in 5% DMSO + 95% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 5 中的溶解度: 5% DMSO+30% PEG 300+5% Tween 80+ddH2O: 5mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8821 mL | 9.4105 mL | 18.8210 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3764 mL | 1.8821 mL | 3.7642 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1882 mL | 0.9411 mL | 1.8821 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
XL888 + Vemurafenib + Cobimetinib for Unresectable BRAF Mutated Stage III/IV Melanoma
CTID: NCT02721459
Phase: Phase 1 Status: Active, not recruiting
Date: 2024-11-20
FDG-PET imaging. FDG-PET imaging is effective for monitoring vemurafenib and GDC-0973 combination drug action in BRAFV600E mutant and resistant xenografts. EJNMMI Res. 2012; 2: 22. |
GDC-0973 is a selective, potent MEK inhibitor with efficacy in BRAF and RAS mutant cell lines. A, chemical structure of GDC-0973. B, GDC-0973 was tested in a panel of cell lines in 96-hour viability assays.Cancer Res.2012 Jan 1;72(1):210-9. |
GDC-0973 single-agent efficacy and pharmacodynamic (PD) studies in BRAFV600Eand KRAS mutant tumor models. Dose-ranging efficacy studies were carried out in the (A) A375.X1 and (B) NCI-H2122 tumor xenograft models.Cancer Res.2012 Jan 1;72(1):210-9. |
Combination of GDC-0973 + GDC-0941 results in reduced viability, pathway inhibition, and increased apoptosis. A, the 888MEL and A2058 BRAF mutant melanoma cell lines were treated with increasing concentrations of GDC-0973 and GDC-0941 as single agents and in combination and assayed in a 96-hour viability assay.Cancer Res.2012 Jan 1;72(1):210-9. |
GDC-0973 and GDC-0941 combination results in TGI when dosed daily.Cancer Res.2012 Jan 1;72(1):210-9. |
GDC-0973 and GDC-0941 combination results in TGI when dosed intermittently.
Transient treatment of GDC-0973 + GDC-0941 results in apoptosis and prolonged accumulation of Bim. |