| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g | |||
| 2g | |||
| 5g | |||
| Other Sizes |

| 靶点 |
ROS1 (Ki < 0.025 nM); c-Met (IC50 = 11 nM); NPM-ALK (IC50 = 24 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:PF-2341066 在 mIMCD3 小鼠或 MDCK 犬上皮细胞中表现出类似的抗 c-Met 磷酸化功效,IC50 分别为 5 nM 和 20 nM。与 NIH3T3 细胞相比,PF-2341066 对工程表达 c-Met ATP 结合位点突变体 V1092I 或 H1094R 或 P 环突变体 M1250T 的 NIH3T3 细胞表现出改善或相似的活性,IC50 分别为 19 nM、2 nM 和 15 nM表达野生型受体,IC50 为 13 nM。相反,与野生型受体相比,观察到 PF-2341066 针对表达 c-Met 激活环突变体 Y1230C 和 Y1235D 的细胞的效力发生显着变化,IC50 分别为 127 nM 和 92 nM。 PF-2341066 还可有效防止 NCI-H69 和 HOP92 细胞中 c-Met 的磷酸化,IC50 分别为 13 nM 和 16 nM,这些细胞分别表达内源性 c-Met 变体 R988C 和 T1010I。与 c-Met 相比,PF-2341066 对 VEGFR2 和 PDGFRβ RTK 的选择性 > 1,000 倍,对 IRK 和 Lck 的选择性 > 250 倍,对 Tie2、TrkA 和 TrkB 的选择性大约 40 至 60 倍。 PF-2341066 对 RON 和 Axl RTK 的选择性是 20 至 30 倍。相比之下,PF-2341066 对 KARPAS299 人间变性大细胞淋巴瘤 (ALCL) 细胞系表达的 ALK RTK 的核磷蛋白 (NPM)-间变性淋巴瘤激酶 (ALK) 致癌融合变体显示出近乎等效的 IC50 为 24 nM。 PF-2341066 抑制癌细胞的 c-Met 依赖性肿瘤表型和内皮细胞的血管生成表型。 PF-2341066 抑制人 GTL-16 胃癌细胞生长,IC50 为 9.7 nM。 PF-2341066 诱导 GTL-16 细胞凋亡,IC50 为 8.4 nM。 PF-2341066 抑制 HGF 刺激的人 NCI-H441 肺癌细胞迁移和侵袭,IC50 分别为 11 nM 和 6.1 nM。 PF-2341066 抑制 MDCK 细胞散射,IC50 为 16 nM。 PF-2341066 可防止 HGF 刺激的 c-Met 磷酸化、细胞存活和基质胶侵袭,IC50 分别为 11 nM、14 nM 和 35 nM。此外,PF-2341066 还可防止纤维蛋白凝胶中血清刺激的 HMVEC 分支管生成(血管形成)。 PF-2341066 还可有效抑制 Karpas299 或 SU-DHL-1 ALCL 细胞中的 NPM-ALK 磷酸化,IC50 为 24 nM。 PF-2341066 有效防止细胞增殖,这与 G(1)-S 期细胞周期停滞和诱导 ALK 阳性 ALCL 细胞凋亡相关,IC50 为 30 nM,但与 ALK 阴性淋巴瘤细胞无关。此外,PF-2341066 还可预防与原发肿瘤生长(即增殖和存活)以及转移(例如侵袭和克隆性)相关的骨肉瘤行为。激酶测定:将细胞接种在 96 孔板中补充有 10% 胎牛血清 (FBS) 的培养基中,24 小时后转移至无血清培养基 [含 0.04% 牛血清白蛋白 (BSA)]。在研究配体依赖性 RTK 磷酸化的实验中,添加相应的生长因子长达 20 分钟。将细胞与 PF-2341066 和/或适当的配体孵育指定时间后,用补充有 1 mM Na3VO4 的 HBSS 洗涤细胞一次,并从细胞中产生蛋白质裂解物。随后,使用用于包被 96 孔板的特异性捕获抗体和对磷酸化酪氨酸残基具有特异性的检测抗体,通过夹心 ELISA 方法评估所选蛋白激酶的磷酸化。抗体包被板 (a) 在蛋白质裂解物存在下于 4°C 孵育过夜; (b) 用含 1% Tween 20 的 PBS 洗涤七次; (c) 在辣根过氧化物酶缀合的抗总磷酸酪氨酸 (PY-20) 抗体 (1:500) 中孵育 30 分钟; (d)再清洗七次; (e) 在 3,3',5,5'-四甲基联苯胺过氧化物酶底物中孵育以启动比色反应,通过添加 0.09 N H2SO4 来终止该反应; (f) 使用分光光度计测量 450 nm 处的吸光度。细胞测定:将包括GTL-16胃癌细胞和T47D乳腺癌细胞的细胞(GTL-16胃癌细胞和T47D乳腺癌细胞)接种到96孔板中补充有10%胎牛血清(FBS)的培养基中并转移24 小时后转移至无血清培养基 [含 0.04% 牛血清白蛋白 (BSA)]。在研究配体依赖性 RTK 磷酸化的实验中,添加相应的生长因子长达 20 分钟。将细胞与 PF-2341066 和/或适当的配体孵育指定时间后,用补充有 1 mM Na3VO4 的 HBSS 洗涤细胞一次,并从细胞中产生蛋白质裂解物。随后,使用用于包被 96 孔板的特异性捕获抗体和对磷酸化酪氨酸残基具有特异性的检测抗体,通过夹心 ELISA 方法评估所选蛋白激酶的磷酸化。抗体包被板 (a) 在蛋白质裂解物存在下于 4 °C 孵育过夜; (b) 用含 1% Tween 20 的 PBS 洗涤七次; (c) 在辣根过氧化物酶缀合的抗总磷酸酪氨酸 (PY-20) 抗体 (1:500) 中孵育 30 分钟; (d)再清洗七次; (e) 在 3,3',5,5'-四甲基联苯胺过氧化物酶底物中孵育以启动比色反应,通过添加 0.09 N H2SO4 来终止该反应; (f) 使用分光光度计测量 450 nm 处的吸光度。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在 GTL-16 模型中,PF-2341066 揭示了在 50 mg/kg/天和 75 mg/kg/天治疗组中,能够使已形成的大肿瘤 (>600 mm3) 显着消退,减少 60% 43 天给药方案的平均肿瘤体积。在另一项研究中,PF-2341066 显示出完全抑制 GTL-16 肿瘤生长超过 3 个月的能力,在 50 mg/kg/ 的 3 个月治疗方案中,12 只小鼠中只有 1 只表现出肿瘤生长显着增加。天。在 NCI-H441 NSCLC 模型中,在 38 天的 PF-2341066 给药周期中,每天 50 mg/kg 时观察到平均肿瘤体积减少 43%。在 Caki-1 RCC 模型中,在 33 天的 PF-2341066 给药周期中,观察到平均肿瘤体积减少 53%,与每天 50 mg/kg/天的每个肿瘤体积减少至少 30% 相关。 PF-2341066 还显示,在 U87MG 胶质母细胞瘤或 PC-3 前列腺癌异种移植模型中,每天 50 mg/kg 剂量时,PF-2341066 几乎完全预防已形成肿瘤的生长,在最后研究日分别抑制 97% 或 84%。相比之下,以 50 mg/kg/天口服给予 PF-2341066 不会显着抑制 MDA-MB-231 乳腺癌模型或 DLD-1 结肠癌模型中的肿瘤生长。在 GTL-16 肿瘤中,在 12.5 mg/kg/天、25 mg/kg/天和 50 mg/kg/天时观察到 CD31 阳性内皮细胞的显着剂量依赖性减少,表明 MVD 的抑制显示出剂量与抗肿瘤功效的依赖性相关性。 PF-2341066 在 GTL-16 和 U87MG 模型中均显示出人 VEGFA 和 IL-8 血浆水平的显着剂量依赖性降低。口服 PF-2341066 后,在 GTL-16 肿瘤中观察到磷酸化 c-Met、Akt、Erk、PLCλ1 和 STAT5 水平的显着抑制。对携带 Karpas299 ALCL 肿瘤异种移植物的严重联合免疫缺陷米色小鼠口服 PF-2341066 会产生剂量依赖性抗肿瘤功效,在初始化合物给药 15 天内,100 mg/kg/d 剂量下所有肿瘤完全消退。此外,在浓度或剂量水平下观察到 PF-2341066 对关键 NPM-ALK 信号传导介质(包括磷脂酶 C-gamma、信号转导器和转录激活剂 3、细胞外信号调节激酶和 Akt)的抑制作用,这与抑制作用相关NPM-ALK 磷酸化和功能。 PF-2341066 可预防与原发肿瘤生长(例如增殖和存活)以及转移(例如侵袭和克隆性)相关的骨肉瘤行为。在通过口服强饲法用 PF-2341066 治疗的裸鼠中,PF-2341066 阻止了骨肉瘤异种移植物的生长以及相关的骨质溶解和皮质外骨基质形成。用 50 mg/kg PF-2341066 处理 c-MET 扩增的 GTL-16 异种移植物可引起肿瘤消退,这与 18F-FDG 摄取缓慢减少有关,并降低葡萄糖转运蛋白 1 (GLUT-1) 的表达。
|
| 酶活实验 |
将细胞接种在含有 10% 胎牛血清 (FBS) 补充培养基的 96 孔板中,然后在 24 小时后切换至含有 0.04% 牛血清白蛋白 (BSA) 的无血清培养基。在检查配体依赖性 RTK 磷酸化的实验中添加相应的生长因子最多 20 分钟。与 PF-2341066 和/或适当的配体孵育指定时间一小时后,再次用补充有 1 毫克 Na3VO4 的 HBSS 洗涤细胞,并且蛋白质裂解物是从细胞中产生的。然后使用夹心 ELISA 技术测量特定蛋白激酶的磷酸化,该技术采用对磷酸化酪氨酸残基具有特异性的检测抗体和用于包被 96 孔板的特定捕获抗体。抗体包被的板经历以下步骤:(a)在蛋白质裂解物存在下过夜孵育; (b) 用 1% Tween 20 进行 7 次 PBS 洗涤; (c) 在辣根过氧化物酶缀合的抗总磷酸酪氨酸 (PY-20) 抗体 (1:500) 中孵育 30 分钟; (d) 再用 PBS 洗涤七次; (e) 在3,3',5,5'-四甲基联苯胺过氧化物酶底物中孵育以启动比色反应,通过添加0.09 N H2SO4来停止该反应; (f) 用分光光度计测量 450 nm 处的吸光度。
|
| 细胞实验 |
将细胞(包括 GTL-16 胃癌细胞和 T47D 乳腺癌细胞)接种到含有 10% 胎牛血清 (FBS) 和 0.04% 牛血清白蛋白 (BSA) 的培养基的 96 孔板中 24 小时后,移动至无血清培养基。在检查配体依赖性 RTK 磷酸化的实验中添加相应的生长因子最多 20 分钟。 PF-2341066 孵育一小时或在指定时间内应用合适的配体后,再次用补充有 1 mM Na3VO4 的 HBSS 洗涤细胞,然后从细胞中提取蛋白质裂解物。然后,使用夹心 ELISA 技术,采用磷酸化酪氨酸残基的磷酸化特异性检测抗体和特异性捕获抗体来包被 96 孔板,评估特定蛋白激酶的磷酸化。抗体包被的板经历以下步骤:(a)在蛋白质裂解物存在下过夜孵育; (b) 用 1% Tween 20 进行 7 次 PBS 洗涤; (c) 在辣根过氧化物酶缀合的抗总磷酸酪氨酸 (PY-20) 抗体 (1:500) 中孵育 30 分钟; (d) 再用 PBS 洗涤七次; (e) 在3,3',5,5'-四甲基联苯胺过氧化物酶底物中温育以启动比色反应,用0.09 N H2SO4终止该反应; (f) 用分光光度计测量 450 nm 处的吸光度。
|
| 动物实验 |
PF-2341066 is administered orally by gavage to athymic mice carrying xenografts (300-800 mm3) at predetermined dose levels. Mice are humanely put to sleep at predetermined intervals after PF-2341066 administration, and tumors are removed. Using a liquid nitrogen-cooled cryomortar and pestle, tumors are snap frozen, ground into a paste, protein lysates are produced, and protein concentrations are measured with a BSA assay. Through the use of immunoprecipitation-immunoblotting or capture ELISA, the amount of total and phosphorylated protein is measured.
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption
In patients with pancreatic, colorectal, sarcoma, anaplastic large-cell lymphoma and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with crizotinib doses ranging from 100 mg once a day to 300 mg twice a day, the mean AUC and Cmax increased in a dose-proportional manner. A single crizotinib dose of crizotinib is absorbed with a median tmax 4 to 6 hours. In patients receiving multiple doses of crizotinib 250 mg twice daily (n=167), the mean AUC was is 2321.00 ng⋅hr/mL, the mean Cmax was 99.60 ng/mL, and the median tmax was 5.0 hours. The mean absolute bioavailability of crizotinib is 43%, ranging from 32% to 66%. High-fat meals reduce the AUC0-INF and Cmax of crizotinib by approximately 14%. Age, sex at birth, and ethnicity (Asian vs non-Asian patients) did not have a clinically significant effect on crizotinib pharmacokinetics. In patients less than 18 years old, higher body weight was associated with a lower crizotinib exposure. Route of Elimination After administering a single 250 mg radiolabeled crizotinib dose to healthy subjects, 63% and 22% of the administered dose were recovered in feces and urine. Unchanged crizotinib represented approximately 53% and 2.3% of the administered dose in feces and urine, respectively. Volume of Distribution Following a single intravenous dose, the mean volume of distribution (Vss) of crizotinib was 1772 L. Clearance At steady-state (250 mg twice daily), crizotinib has a mean apparent clearance (CL/F) of 60 L/hr. This value is lower than the one detected after a single 250 mg oral dose (100 L/hr),, possibly due to CYP3A auto-inhibition. Metabolism / Metabolites Crizotinib is mainly metabolized in the liver by CYP3A4 and CYP3A5, and undergoes an O-dealkylation, with subsequent phase 2 conjugation. Non-metabolic elimination, such as biliary excretion, can not be excluded. PF-06260182 (with two constituent diastereomers, PF-06270079 and PF-06270080) is the only active metabolite of crizotinib that has been identified. _In vitro_ studies suggest that, compared to crizotinib, PF-06270079 and PF-06270080 are approximately 3- to 8-fold less potent against anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and 2.5- to 4-fold less potent against Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (HGFR, c-Met). Biological Half-Life Following single doses of crizotinib, the plasma terminal half-life was 42 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In large early clinical trials, elevations in serum aminotransferase levels occurred in up to 57% of patients treated with standard doses of crizotinib, were greater than 5 times ULN in 6% of patients, and led to early discontinuation of therapy in 2% to 4% of patients. Serum aminotransferase elevations typically arose after 4 to 12 weeks of treatment, but usually without jaundice or alkaline phosphatase elevations. Restarting crizotinib after resolution of the aminotransferase abnormalities can be done starting with a reduced dose. Most cases of liver injury due to crizotinib have been minimally or not symptomatic, and the injury resolved within 1 to 2 months of stopping the drug (Case 1). However, cases with jaundice and symptoms during crizotinib therapy have been reported which were fatal in 0.1% of treated patients (Case 2). The severe cases of liver injury due to crizotinib typically arose within 2 to 6 weeks of starting therapy and presented with marked elevations in serum aminotransferase levels followed by jaundice, progressive hepatic dysfunction, coagulopathy, encephalopathy and death. For these reasons, routine periodic monitoring of liver tests at 2 to 4 week intervals during therapy is recommended. Likelihood score: C (probable cause of clinically apparent acute liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the clinical use of crizotinib during breastfeeding. Because crizotinib is 91% bound to plasma proteins, the amount in milk is likely to be low. However, its half-life is about 42 hours and it might accumulate in the infant. The manufacturer recommends that breastfeeding be discontinued during crizotinib therapy and for 45 days after the last dose. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Crizotinib is 91% bound to plasma protein. _In vitro_ studies suggest that this is not affected by drug concentration. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
The c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase and its ligand, hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), have been implicated in the progression of several human cancers and are attractive therapeutic targets. PF-2341066 was identified as a potent, orally bioavailable, ATP-competitive small-molecule inhibitor of the catalytic activity of c-Met kinase. PF-2341066 was selective for c-Met (and anaplastic lymphoma kinase) compared with a panel of >120 diverse tyrosine and serine-threonine kinases. PF-2341066 potently inhibited c-Met phosphorylation and c-Met-dependent proliferation, migration, or invasion of human tumor cells in vitro (IC(50) values, 5-20 nmol/L). In addition, PF-2341066 potently inhibited HGF-stimulated endothelial cell survival or invasion and serum-stimulated tubulogenesis in vitro, suggesting that this agent also exhibits antiangiogenic properties. PF-2341066 showed efficacy at well-tolerated doses, including marked cytoreductive antitumor activity, in several tumor models that expressed activated c-Met. The antitumor efficacy of PF-2341066 was dose dependent and showed a strong correlation to inhibition of c-Met phosphorylation in vivo. Near-maximal inhibition of c-Met activity for the full dosing interval was necessary to maximize the efficacy of PF-2341066. Additional mechanism-of-action studies showed dose-dependent inhibition of c-Met-dependent signal transduction, tumor cell proliferation (Ki67), induction of apoptosis (caspase-3), and reduction of microvessel density (CD31). These results indicated that the antitumor activity of PF-2341066 may be mediated by direct effects on tumor cell growth or survival as well as antiangiogenic mechanisms. Collectively, these results show the therapeutic potential of targeting c-Met with selective small-molecule inhibitors for the treatment of human cancers.[1]
|
| 分子式 |
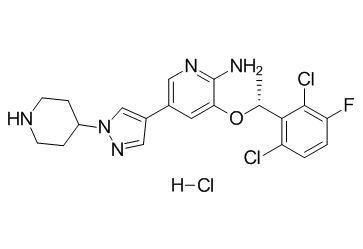
C₂₁H₂₃CL₃FN₅O
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
486.80
|
| 精确质量 |
485.095
|
| CAS号 |
1415560-69-8
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Crizotinib;877399-52-5;Crizotinib-d5;1395950-84-1; 877399-53-6 (acetate)
|
| PubChem CID |
71576688
|
| 外观&性状 |
Yellow to brown solid
|
| LogP |
6.749
|
| tPSA |
77.99
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
31
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
558
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
ClC1=C(C([H])=C([H])C(=C1[C@@]([H])(C([H])([H])[H])OC1=C(N([H])[H])N=C([H])C(=C1[H])C1C([H])=NN(C=1[H])C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N([H])C([H])([H])C1([H])[H])Cl)F.Cl[H]
|
| InChi Key |
BTDNHKQCPIBABF-UTONKHPSSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C21H22Cl2FN5O.ClH/c1-12(19-16(22)2-3-17(24)20(19)23)30-18-8-13(9-27-21(18)25)14-10-28-29(11-14)15-4-6-26-7-5-15;/h2-3,8-12,15,26H,4-7H2,1H3,(H2,25,27);1H/t12-;/m1./s1
|
| 化学名 |
3-[(1R)-1-(2,6-dichloro-3-fluorophenyl)ethoxy]-5-(1-piperidin-4-ylpyrazol-4-yl)pyridin-2-amine;hydrochloride
|
| 别名 |
PF-02341066 hydrochloride; PF2341066; PF-2341066; PF-02341066; PF02341066; PF 02341066; PF 2341066; Crizotinib; US trade name: Xalkori
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~97 mg/mL (~199.3 mM)
Ethanol: ~97 mg/mL (~199.3 mM) Water: ~97 mg/mL (~199.3 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 55 mg/mL (112.98 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶。
请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0542 mL | 10.2712 mL | 20.5423 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4108 mL | 2.0542 mL | 4.1085 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2054 mL | 1.0271 mL | 2.0542 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT02034981 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Crizotinib | Hematologic Cancers Solid Tumors |
UNICANCER | August 2013 | Phase 2 |
| NCT02223819 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Crizotinib | Uveal Melanoma | Columbia University | March 2015 | Phase 2 |
| NCT04439266 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Crizotinib | Advanced Lymphoma Refractory Lymphoma |
National Cancer Institute (NCI) |
August 12, 2015 | Phase 2 |
| NCT04439253 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Crizotinib | Advanced Lymphoma Refractory Lymphoma |
National Cancer Institute (NCI) |
August 12, 2015 | Phase 2 |
| NCT01121588 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Crizotinib | Neoplasms Malignant | Pfizer | March 22, 2011 | Phase 1 |