| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Epothilone B (EPO 906; Patupilone) specifically targets β-tubulin, binding to the taxane-binding site to stabilize microtubules, with IC50 values of 0.3 nM (human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells), 0.5 nM (human breast cancer MCF-7 cells), and 0.8 nM for inhibiting microtubule depolymerization [1][2]
It exhibits no significant binding to other cytoskeletal proteins (e.g., actin) or kinases at therapeutic concentrations [2][3] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在HCT-116细胞系细胞毒性实验中,埃坡霉素B抑制HCT116细胞,IC50为0.8 nM[1]。一种针对微管 (MT) 的药物称为埃坡霉素 B 或帕妥匹隆。 MTT 细胞增殖实验证明,Epothilone B 有效抑制细胞生长,治疗 72 小时后 IC50 为 6 nM,但值≤1 nM 没有细胞毒性。在 1 nM 的非细胞毒性浓度下,埃坡霉素 B 显着抑制 Transwell 细胞迁移;在 10 nM 时,影响更加明显[2]。在人髓母细胞瘤细胞系中,埃坡霉素 B (Patupilone) 是一种新型、非紫杉烷相关且无神经毒性的微管稳定药物。埃坡霉素 B 在 D341 细胞系中的 IC50 为 0.53 nM,在 D425Med 细胞系中为 0.37 nM,在 DAOY 细胞系中为 0.19 nM,可降低这三种细胞系的增殖活性。在与增殖活性和活力程度相当的剂量(IC50,0.50-0.75 nM)下观察到埃坡霉素 B 对 D341Med 细胞系中克隆形成存活的影响。然而,在埃坡霉素 B 浓度降低 10 倍(IC50,30 pM)时,D425Med 和 DAOY 细胞的克隆形成性已显着降低。总体而言,这些研究结果表明埃坡霉素 B 具有很强的抗髓母细胞瘤细胞系作用[3]。
在人类癌细胞系(A549、MCF-7、HeLa)中,Epothilone B 抑制细胞增殖,IC50 值范围为 0.3 nM 至 0.7 nM,2 nM 浓度处理 24 小时后 75%-80% 的细胞发生 G2/M 期阻滞 [1] - 在人类胶质母细胞瘤细胞系(U87MG、LN229)中,Epothilone B(0.5-5 nM)剂量依赖性抑制细胞迁移和侵袭,2 nM 浓度下使 U87MG 细胞迁移减少 82%、LN229 细胞迁移减少 78%,机制为诱导微管灾难并使 EB1 在微管正极的积累减少 65% [2] - 在人类髓母细胞瘤细胞系(DAOY、D283MED)中,Epothilone B(0.1-1 nM)是强效放射增敏剂:与 2 Gy 电离辐射(IR)联用时,使 DAOY 细胞活力降低 85%、D283MED 细胞活力降低 80%(辐射单独处理仅降低 40%-45%),同时使 γH2AX 灶(DNA 损伤标志物)增加 2.3 倍 [3] - 0.5-1 nM Epothilone B 诱导 D283MED 细胞凋亡,48 小时后膜联蛋白 V 阳性细胞比例从 5% 升至 55%,伴随半胱天冬酶 -3 激活和 PARP 切割 [3] - 0.5-2 nM Epothilone B 破坏 U87MG 细胞的微管动力学,增加微管成束现象,使微管更新速率降低 70% [2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
相比之下,联合治疗发挥了强大的超加性肿瘤生长控制作用,在随访期间肿瘤完全消退(P<0.005,单独电离辐射或埃坡霉素 B 与联合治疗相比)。单独使用埃坡霉素 B (Patupilone) 或电离辐射治疗可在 10 天内部分抑制肿瘤生长[3]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
微管解聚抑制实验:纯化微管蛋白(10 μM)与系列浓度的 Epothilone B(0.1 nM 至 20 nM)在解聚缓冲液中 37°C 孵育。90 分钟内通过检测 340 nm 吸光度监测微管解聚,从解聚抑制的剂量 - 反应曲线计算 IC50 值 [2]
- β- 微管蛋白结合实验:荧光标记的紫杉醇(紫杉ane 类似物)与重组 β- 微管蛋白(5 μM)及系列浓度的 Epothilone B(0.2 nM 至 15 nM)25°C 孵育 40 分钟。荧光偏振法检测竞争性结合,推导 Epothilone B 与 β- 微管蛋白的解离常数(Kd)为 0.4 nM [1] |
| 细胞实验 |
抗增殖实验:癌细胞(A549、MCF-7、HeLa)接种于 96 孔板(3×103 个细胞 / 孔),用系列浓度的 Epothilone B(0.01 nM 至 10 nM)处理 72 小时。基于四唑盐还原的比色法评估细胞活力,计算 IC50 值 [1]
- 迁移和侵袭实验:U87MG/LN229 细胞接种于 Transwell 小室(迁移实验)或基质胶包被的 Transwell 小室(侵袭实验),并加入 Epothilone B(0.5-5 nM)。24 小时后对迁移或侵袭的细胞进行染色计数,相对于溶媒对照组计算抑制率 [2] - 放射增敏实验:DAOY/D283MED 细胞用 Epothilone B(0.1-1 nM)预处理 12 小时,随后暴露于电离辐射(0-8 Gy)。7 天后通过克隆形成实验评估克隆生长,计算存活分数。免疫荧光染色检测并定量 γH2AX 灶 [3] - 细胞周期分析:U87MG/DAOY 细胞用 Epothilone B(0.5-2 nM)处理 24 小时,70% 乙醇固定,碘化丙啶染色,流式细胞术定量 G2/M 期比例 [2][3] - 凋亡实验:D283MED 细胞用 Epothilone B(0.5-1 nM)处理 48 小时后,用膜联蛋白 V-FITC 和碘化丙啶染色,流式细胞术分析。Western blot 检测半胱天冬酶 -3/PARP 切割 [3] - 微管动力学及 EB1 定位实验:U87MG 细胞用 Epothilone B(0.5-2 nM)处理 16 小时,固定后用抗 β- 微管蛋白和抗 EB1 抗体染色。共聚焦显微镜观察微管形态和 EB1 在微管正极的积累情况并定量 [2] |
| 动物实验 |
Dissolved in30% PEG-300; 2.5 mg/kg–4 mg/kg; i.v. injection
Mice xenograft model of RPMI 8226 cells |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Epothilone B is an epithilone that is epithilone D in which the double bond in the macrocyclic ring has been oxidised to the corresponding epoxide (the S,S stereoisomer). It has a role as an apoptosis inducer, an antineoplastic agent and a microtubule-stabilising agent. It is an epothilone and an epoxide.
Epothilone B is a 16-membered macrolide that mimics the biological effects of taxol. Epothilone B has been reported in Sorangium cellulosum and Apis cerana with data available. Patupilone is a compound isolated from the myxobacterium Sorangium cellulosum. Similar to paclitaxel, patupilone induces microtubule polymerization and stabilizes microtubules against depolymerization conditions. In addition to promoting tubulin polymerization and stabilization of microtubules, this agent is cytotoxic for cells overexpressing P-glycoprotein, a characteristic that distinguishes it from the taxanes. Patupilone may cause complete cell-cycle arrest. Drug Indication Investigated for use/treatment in ovarian cancer, lung cancer, brain cancer, breast cancer, and gastric cancer. Malignant neoplasm of other and unspecified genital organs - Fallopian tube (oviduct, uterine tube), Malignant neoplasm of the retroperitoneum and peritoneum - Peritoneum, unspecified Mechanism of Action The principal mechanism of the epothilone class is inhibition of microtubule function. Microtubules are essential to cell division, and epothilones therefore stop cells from properly dividing. Epothilone B possess the same biological effects as taxol both in vitro and in cultured cells. This is because they share the same binding site, as well as binding affinity to the microtubule. Like taxol, epothilone B binds to the αβ-tubulin heterodimer subunit. Once bound, the rate of αβ-tubulin dissociation decreases, thus stabilizing the microtubules. Furthermore, epothilone B has also been shown to induce tubulin polymerization into microtubules without the presence of GTP. This is caused by formation of microtubule bundles throughout the cytoplasm. Finally, epothilone B also causes cell cycle arrest at the G2-M transition phase, thus leading to cytotoxicity and eventually cell apoptosis. Epothilone B is a natural microtubule-stabilizing agent isolated from the myxobacterium Sorangium cellulosum, with structural and functional similarity to taxanes but higher potency against taxane-resistant tumors [1][2] Its mechanism of action involves binding to the taxane-binding site of β-tubulin, stabilizing microtubules, inhibiting microtubule depolymerization and turnover, inducing G2/M cell cycle arrest, and ultimately leading to cancer cell apoptosis [1][2][3] Epothilone B inhibits glioblastoma cell migration by inducing microtubule catastrophes and disrupting EB1-mediated microtubule plus-end tracking, which is critical for cell polarization and movement [2] It enhances the efficacy of ionizing radiation in medulloblastoma cells by increasing DNA double-strand breaks (via γH2AX upregulation) and suppressing DNA repair, acting as a potent radiosensitizer [3] Epothilone B has potential clinical applications in the treatment of solid tumors such as non-small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, glioblastoma, and medulloblastoma, particularly in taxane-refractory cases [1][2][3] |
| 分子式 |
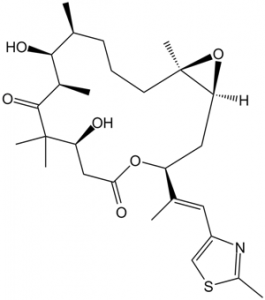
C27H41NO6S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
507.68
|
|
| 精确质量 |
507.265
|
|
| CAS号 |
152044-54-7
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
448013
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.1±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
680.2±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
95-97ºC
|
|
| 闪点 |
365.2±31.5 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.2 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.532
|
|
| LogP |
2.29
|
|
| tPSA |
137.49
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
35
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
816
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
7
|
|
| SMILES |
C[C@H]1CCC[C@@]2([C@@H](O2)C[C@H](OC(=O)C[C@@H](C(C(=O)[C@@H]([C@H]1O)C)(C)C)O)/C(=C/C3=CSC(=N3)C)/C)C
|
|
| InChi Key |
QXRSDHAAWVKZLJ-PVYNADRNSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C27H41NO6S/c1-15-9-8-10-27(7)22(34-27)12-20(16(2)11-19-14-35-18(4)28-19)33-23(30)13-21(29)26(5,6)25(32)17(3)24(15)31/h11,14-15,17,20-22,24,29,31H,8-10,12-13H2,1-7H3/b16-11+/t15-,17+,20-,21-,22-,24-,27+/m0/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
(1S,3S,7S,10R,11S,12S,16R)-7,11-dihydroxy-8,8,10,12,16-pentamethyl-3-[(E)-1-(2-methyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)prop-1-en-2-yl]-4,17-dioxabicyclo[14.1.0]heptadecane-5,9-dione
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.10 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.10 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: 2.08 mg/mL (4.10 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 30% PEG400+0.5% Tween80+5% Propylene glycol :5 mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9697 mL | 9.8487 mL | 19.6974 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3939 mL | 1.9697 mL | 3.9395 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1970 mL | 0.9849 mL | 1.9697 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。