| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg | |||
| 1g | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
加兰他敏抑制 AChE 和 BChE,IC50 值分别为 0.5 和 8.5 μM[1]。在永久转染的 HEK 293 细胞中,加兰他敏充当人类 α4β2 AChR 表达的正变构调节剂 (PAM)。在极低浓度 (EC50=0.25 nM) 下,加兰他敏可将 (α4β2)2α5 AChR 对 1 μM ACh 的响应增强高达 220%。使用 FLEXstation 检测,仅发现 α4β2 或 (α4β2)2β3 AChR 略有增加 (20%)。当浓度大于 1 μM 时,加兰他敏会抑制三种 AChR 亚型中的每一种 [2]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在海马体中,但在前额皮质中,急性加兰他敏给药(0.3-3 mg/kg,腹腔注射)会以剂量和时间依赖性方式提高 IGF2 mRNA 水平。在海马体中,加兰他敏(3 mg/kg,腹腔注射)暂时升高成纤维细胞生长因子 2 的 mRNA 水平并降低脑源性神经营养因子的 mRNA 水平,但对其他神经营养/生长因子没有影响。 mRNA 浓度。美加明(一种非选择性烟碱乙酰胆碱受体 (nAChR) 拮抗剂)和甲基乌头碱(一种选择性 α7 nAChR 拮抗剂)均可抑制加兰他敏诱导的海马 IGF2 mRNA 水平增加,但替伦西平(一种优先 M1 毒蕈碱性 ACh 受体拮抗剂)则不能。此外,选择性 α7 nAChR 激动剂 PHA-543613 可以升高 IGF2 mRNA 水平,但乙酰胆碱酯酶抑制剂多奈哌齐则不会升高 IGF2 mRNA 水平。此外,甲基乌头碱还可抑制加兰他敏引起的海马IGF2蛋白升高[2]。
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Over a dose range of 8-32 mg/day, galantamine exhibits a dose-linear pharmacokinetic profile. The oral bioavailability of galantamine ranges from 90-100%. Following oral administration, the Tmax is about 1 hour. Following 10 hours of administration, the mean galantamine plasma concentrations were 82–97 µg/L for the 24 mg/day dose and 114–126 µg/L for the 32 mg/day dose. Renal clearance accounts for about 20–25% of total plasma clearance of the drug in healthy individuals: the elimination of galantamine has been shown to be decreased in subjects with renal impairment. Following oral or intravenous administration, approximately 20% of the dose is excreted as unchanged in the urine within 24 h. In a radiolabelled drug study, about 95% and 5% of the total radioactivity was recovered in the urine and feces, respectively. Of the dose recovered in the urine, about 32% was in the unchanged parent compound, and 12% was in the glucuronide form. The mean volume of distribution is 175 L. About 52.7% of galantamine is distributed to blood cells, the blood to plasma concentration ratio of galantamine is 1.2. Galantamine penetrates the blood–brain barrier. The renal clearance is 65 mL/min and the total plasma clearance is about 300 mL/min. Protein binding: Low (18%) Mean volume of distribution is 175 L. The maximum inhibition of acetylcholinesterase activity of about 40% was achieved about one hour after a single oral dose of 8 mg galantamine in healthy male subjects. Galantamine is rapidly and completely absorbed. The absolute oral bioavailability is about 90%. Galantamine shows linear pharmacokinetics with doses ranging from 8 to 32 mg/day. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for GALANTAMINE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites _In vitro_ study findings suggest that about 75% of the drug is metabolized by CYP2D6 and CYP3A4. CYP2D6 promotes O-demethylation of the drug to form O-desmethyl-galantamine and the CYP3A4-mediated pathway forms the galantamine-N-oxide. Important metabolic pathways also include N-demethylation, epimerization, and sulfate conjugation. Other metabolites include norgalantamine, O-desmethyl-galantamine, O-desmethyl-norgalantamine, epigalantamine and galantaminone, which do not retain clinically significant pharmacology activities. Galantamine can also undergo glucuronidation: in one oral radiolabeled drug study in poor and extensive CYP2D6 metabolizers, about 14-24% of the total radioactivity was identified as galantamine glucuronide 8 hours post-dose. O-demethylation by CYP2D6 becomes prominent in patients with who are extensive metabolizers of CYP2D6, but unchanged galatamine (39-77%) and its glucuronide metabolite (14-24%) predominated in the plasma of both poor and extensive metabolizers of CYP2D6 in a radiolabelled drug study. The total plasma clearance, or nonrenal clearnace, accounts for 20–25% of drug elimination. In studies of oral 3(H)-galantamine, unchanged galantamine and its glucuronide, accounted for most plasma radioactivity in poor and extensive CYP2D6 metabolizers. Up to 8 hours post-dose, unchanged galantamine accounted for 39-77% of the total radioactivity in the plasma, and galantamine glucuronide for 14-24%. By 7 days, 93- 99% of the radioactivity had been recovered, with about 95% in urine and about 5% in the feces. Total urinary recovery of unchanged galantamine accounted for, on average, 32% of the dose and that of galantamine glucuronide for another 12% on average. Galantamine is metabolized by hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes, glucuronidated, and excreted unchanged in the urine. In vitro studies indicate that cytochrome CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 were the major cytochrome P450 isoenzymes involved in the metabolism of galantamine, and inhibitors of both pathways increase oral bioavailability of galantamine modestly. O-demethylation, mediated by CYP2D6 was greater in extensive metabolizers of CYP2D6 than in poor metabolizers. In plasma from both poor and extensive metabolizers, however, unchanged galantamine and its glucuronide accounted for most of the sample radioactivity. Galantamine is metabolized by hepatic cytochrome p450 enzymes. Galantamine has known human metabolites that include Galantamine N-oxide, O-Desmethylgalantamine, N-desmethylgalantamine, and [(1S,12S,14R)-14-hydroxy-4-methyl-11-oxa-4-azatetracyclo[8.6.1.01,12.06,17]heptadeca-6(17),7,9,15-tetraen-9-yl] hydrogen sulfate. Biological Half-Life Galantamine has a terminal half-life of about 7 hours. Elimination half-life: 7 hours |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In several large placebo controlled clinical trials, there was no increase in the rate of serum enzyme elevations in patients treated with galantamine compared to those on placebo and no reports of hepatotoxicity. No individual case reports of clinically apparent hepatotoxicity have been published, although cases of liver enzyme elevations and hepatitis attributed to galantamine have been reported to the sponsor. With the exception of tacrine, the acetylcholinesterase inhibitors used for Alzheimer disease have only rarely been linked to instances of clinically apparent, acute liver injury. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Protein Binding The plasma protein binding of galantamine is 18% at therapeutically relevant concentrations. Interactions /Concurrent use of cimetidine or paroxetine with galantamine/ may increase the bioavailability of galantamine. Concurrent use /of anticholinergics with galantamine/ may decrease the effects of these medications. Galantamine is likely to exaggerate the neuromuscular blockade effects of succinylcholine-type and similar neuromuscular blocking agents during anesthesia. Galantamine /used concurrently with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)/ may increase gastric acid secretion, which may contribute to gastrointestinal irritation; patient should be monitored for occult gastrointestinal bleeding. For more Interactions (Complete) data for GALANTAMINE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
Cholinesterase inhibitor Galanatamine is indicated for the treatment of mild to moderate dementia of the Alzheimer's type. / Included in US product labeling/ Drug Warnings In two randomized placebo controlled trials of 2 years duration in subjects with mild cognitive impairment (MCI), a total of 13 subjects on razadyne (n=1026) and 1 subject on placebo (n=1022) died. The deaths were due to various causes which could be expected in an elderly population; about half of the razadyne deaths appeared to result from various vascular causes (myocardial infarction, stroke, and sudden death). Although the difference in mortality between razadyne and placebo-treated groups in these two studies was significant, the results are highly discrepant with other studies of razadyne. Specifically, in these two MCI studies, the mortality rate in the placebo-treated subjects was markedly lower than the rate in placebo-treated patients in trials of razadyne in Alzheimer's disease or other dementias (0.7 per 1000 person years compared to 22-61 per 1000 person years, respectively). Although the mortality rate in the razadyne-treated MCI subjects was also lower than that observed in razadyne -treated patients in Alzheimer's disease and other dementia trials (10.2 per 1000 person years compared to 23-31 per 1000 person years, respectively), the relative difference was much less. When the Alzheimer's disease and other dementia studies were pooled (n=6000), the mortality rate in the placebo group numerically exceeded that in the razadyne group. Furthermore, in the MCI studies, no subjects in the placebo group died after 6 months, a highly unexpected finding in this population. Individuals with mild cognitive impairment demonstrate isolated memory impairment greater than expected for their age and education, but do not meet current diagnostic criteria for Alzheimer's disease. FDA Pregnancy Risk Category: B /NO EVIDENCE OF RISK IN HUMANS. Adequate, well controlled studies in pregnant women have not shown increased risk of fetal abnormalities despite adverse findings in animals, or, in the absence of adequate human studies, animal studies show no fetal risk. The chance of fetal harm is remote but remains a possibility./ Potential for increased risk of seizures secondary to cholinergic activity (seizures also may be a manifestation of Alzheimer's disease). Adverse effects reported in 5% or more of patients receiving galantamine hydrobromide and with an incidence of at least twice that of placebo include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, weight decrease. Most of these adverse effects occurred during the upward titration of dosages. Administration of galantamine with food, use of antiemetic agents, and ensuring adequate fluid intake may reduce the impact of these adverse events. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for GALANTAMINE (14 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Galantamine is a competitive and reversible inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase that works to increase acetylcholine levels. Galantamine acts both centrally and peripherally to inhibit both muscle and brain acetylcholinesterase, thereby increasing cholinergic tone. Galantamine is also a positive allosteric modulator of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. As dementia is a progressive neurodegenerative disease, galatamine has a negligible effect in altering the course of the underlying process of dementia and may exert its therapeutic effectiveness for a short period of time. However, galantamine promoted improvements in cognition, global function, activities of daily living, and behavioural symptoms in clinical studies of Alzheimer’s disease. Galantamine exhibited therapeutic efficacy in studies of vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease with cerebrovascular disease. In one study, galantamine reversed scopolamine-induced acute anticholinergic syndrome that was characterized by drowsiness, disorientation, and delirium. |
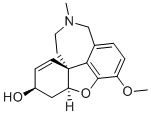
| 分子式 |
C17H21NO3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
287.3535
|
| 精确质量 |
287.152
|
| CAS号 |
357-70-0
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Galanthamine hydrobromide;1953-04-4;Galanthamine-d6;1128109-00-1;Galanthamine-O-methyl-d3;1279031-09-2
|
| PubChem CID |
9651
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
439.3±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
119-121ºC
|
| 闪点 |
219.5±28.7 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.636
|
| LogP |
1.75
|
| tPSA |
41.93
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
1
|
| 重原子数目 |
21
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
440
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
3
|
| SMILES |
CN1CC[C@@]23C=C[C@@H](C[C@@H]2OC4=C(C=CC(=C34)C1)OC)O
|
| InChi Key |
ASUTZQLVASHGKV-JDFRZJQESA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C17H21NO3/c1-18-8-7-17-6-5-12(19)9-14(17)21-16-13(20-2)4-3-11(10-18)15(16)17/h3-6,12,14,19H,7-10H2,1-2H3/t12-,14-,17-/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(1S,12S,14R)-9-methoxy-4-methyl-11-oxa-4-azatetracyclo[8.6.1.01,12.06,17]heptadeca-6(17),7,9,15-tetraen-14-ol
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ≥ 59 mg/mL (~205.32 mM)
1M HCl : 50 mg/mL (~174.00 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.70 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.70 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.70 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4801 mL | 17.4004 mL | 34.8008 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6960 mL | 3.4801 mL | 6.9602 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3480 mL | 1.7400 mL | 3.4801 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。