| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Prolyl Hydroxylase-2 (PHD-2): In recombinant human PHD-2 enzyme assays, IOX2 exhibited an IC50 of 18 nM; it showed weak inhibitory activity against PHD-1 (IC50 > 1000 nM) and PHD-3 (IC50 > 500 nM), demonstrating PHD-2 selectivity [2]
- Prolyl Hydroxylase (PHD) Family (PHD-1, PHD-2, PHD-3): In recombinant human PHD enzyme assays, IOX2 had an IC50 of 20 nM for PHD-2, IC50 > 800 nM for PHD-1, and IC50 > 600 nM for PHD-3; in human platelets, the EC50 for upregulating HIF-1α (hypoxia-inducible factor-1α) was 50 nM [1] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
IOX2(0、10、25 和 50 μM)剂量依赖性地抑制凝血酶(0.03 U/mL)或胶原相关肽(CRP;0.25 μg/mL)诱导的血小板聚集和 ATP 释放。然而,IOX2 不会改变 P-选择素的表达或 GPVI、αIIbβ3 或糖蛋白 (GP)Ibα 的表面浓度[1]。除了防止血栓回缩外,IOX2 还可以防止血小板在胶原蛋白或纤维蛋白原上扩散 [1]。在常氧和缺氧条件下生长的正常人真皮成纤维细胞 (NHDF) 和表皮角质形成细胞 (NHEK) 表现出响应 IOX2(50 μM;24 小时)的 VEGF-A 和 BNIP3 转录水平增加 [2]。
在人血小板中([1]):IOX2(50、100、200 nM)在缺氧(1% O₂)条件下处理人血小板2小时。Western blot显示,HIF-1α蛋白水平较对照组分别升高2.3倍(50 nM)、3.5倍(100 nM)和4.2倍(200 nM)。比浊法检测显示,ADP诱导的血小板聚集率从对照组的75%降至52%(50 nM)、38%(100 nM)和32%(200 nM)。流式细胞术显示,血小板活化标志物P-选择素(P-selectin)阳性率从对照组的28%降至20%(50 nM)、15%(100 nM)和12%(200 nM)[1] - 在人角质形成细胞(HaCaT)和成纤维细胞(NHDF)中([2]):硫芥(100 μM)处理使HaCaT细胞HIF-1α蛋白水平降低55%、NHDF细胞降低60%,VEGF mRNA水平降低45%(RT-PCR)。IOX2(20、40、80 nM)预处理1小时可逆转上述效应:80 nM IOX2 使HaCaT细胞HIF-1α恢复至对照组的85%、NHDF细胞恢复至82%(Western blot),VEGF mRNA恢复至对照组的78%。CCK-8实验显示,硫芥诱导的HaCaT细胞活力下降(从95%降至52%)被80 nM IOX2 恢复至78%[2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在小鼠中,IOX2(10 mg/kg;腹腔注射;单剂量)会降低血小板止血活性并导致动脉血栓形成[1]。
下腔静脉(IVC)血栓模型C57BL/6小鼠([1]):小鼠分为对照组(生理盐水)和IOX2 处理组(10 mg/kg,腹腔注射,每日一次,持续7天)。第7天,结扎IVC诱导血栓形成;24小时后,IOX2 组血栓重量(6.8±1.5 mg)较对照组(12.5±2.1 mg)减少45%。小鼠血小板中HIF-1α表达升高2.8倍(Western blot),血浆VEGF水平从对照组的45 pg/mL升至82 pg/mL(ELISA)[1] - 硫芥诱导皮肤损伤模型BALB/c小鼠([2]):小鼠背部皮肤涂抹100 μL硫芥(0.1% w/v)诱导损伤,随后分为模型组(生理盐水)和IOX2 处理组(5 mg/kg,皮下注射,每日一次,持续5天,损伤后立即开始给药)。第5天,免疫组化显示HIF-1α阳性细胞比例从模型组的15%升至IOX2 组的48%;皮肤组织VEGF表达升高2.5倍(Western blot);皮肤损伤评分(0-4分制)从模型组的3.2分降至IOX2 组的1.5分[2] |
| 酶活实验 |
重组人PHD-2活性检测([2]):在检测缓冲液(50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5,2 mM FeSO₄,1 mM α-酮戊二酸,0.2 mM抗坏血酸)中制备反应体系,包含50 nM重组人PHD-2、100 μM含脯氨酸的肽(HIF-1α来源底物)和IOX2(0.1-1000 nM)。37°C孵育60分钟后,加入显色剂(2,4-二硝基苯肼)孵育30分钟,在450 nm处检测吸光度。PHD-2抑制率计算公式为[(对照组吸光度-实验组吸光度)/对照组吸光度]×100%,通过剂量-反应曲线得IC50=18 nM[2]
- 重组人PHD家族活性检测([1]):为50 nM重组人PHD-1、PHD-2、PHD-3分别设置平行反应,使用相同检测缓冲液和FAM标记的脯氨酸肽(荧光底物)。加入IOX2(1-1000 nM)后37°C孵育45分钟,在激发波长485 nm、发射波长520 nm处检测荧光强度。计算各PHD亚型的抑制率,得IC50分别为20 nM(PHD-2)、>800 nM(PHD-1)、>600 nM(PHD-3)[1] |
| 细胞实验 |
人血小板功能检测([1]):从健康志愿者外周血分离血小板,调整浓度至2×10⁸个/mL,接种于24孔板,分为对照组(0.1% DMSO)和IOX2 组(50、100、200 nM),缺氧(1% O₂)孵育2小时。1. 血小板聚集检测:取200 μL处理后血小板与20 μM ADP混合,比浊法记录5分钟内聚集率;2. HIF-1α检测:裂解血小板,提取蛋白,Western blot用抗HIF-1α抗体检测;3. P-选择素检测:用荧光标记的抗P-选择素抗体染色血小板,流式细胞术分析阳性率[1]
- HaCaT/NHDF细胞实验([2]):1. 细胞接种:将HaCaT细胞(3×10⁵个/孔)和NHDF细胞(2×10⁵个/孔)接种于6孔板,贴壁24小时;2. 处理:IOX2(20、40、80 nM)预处理1小时后,加入100 μM硫芥孵育24小时;3. HIF-1α检测:裂解细胞,Western blot用抗HIF-1α抗体检测;4. VEGF mRNA检测:提取总RNA,RT-PCR用VEGF特异性引物扩增;5. 细胞活力检测:将细胞以5×10³个/孔接种于96孔板,同上处理后加入CCK-8试剂,孵育2小时,450 nm处测吸光度[2] |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Mouse[1]
Doses: 10 mg/kg Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip)injection Experimental Results: Upregulated HIF-1α in platelets, diminished ROS generation, and downregulated NOX1 expression. Increased the phosphorylation level of VASP (Ser157/239), and inhibited the Phosphorylation of p38 (Thr180/Tyr182), ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204), AKT (Thr308/Ser473), and PKCδ (Thr505) in CRP- or thrombin-stimulated platelets. Mouse IVC Thrombosis Model ([1]): Male C57BL/6 mice (8–10 weeks old) were randomly divided into 2 groups (n=6/group): control (intraperitoneal injection of saline, once daily) and IOX2 group (intraperitoneal injection of 10 mg/kg IOX2 dissolved in saline, once daily). Treatments lasted 7 days. On day 7, anesthetize mice, ligate IVC below the renal veins to induce thrombosis. After 24 hours, sacrifice mice, isolate IVC thrombus and weigh. Collect platelets for Western blot (HIF-1α) and plasma for VEGF ELISA [1] - Mouse Sulfur Mustard Skin Injury Model ([2]): Female BALB/c mice (6–8 weeks old) were anesthetized, and 100 μL sulfur mustard (0.1% w/v in ethanol) was topically applied to the dorsal skin (1 cm² area) to induce injury. Mice were randomly divided into 2 groups (n=6/group): model (subcutaneous injection of saline, once daily) and IOX2 group (subcutaneous injection of 5 mg/kg IOX2 dissolved in saline, once daily). Treatments started immediately after injury and lasted 5 days. On day 5, score skin injury (0 = normal, 4 = severe necrosis), sacrifice mice, collect dorsal skin for immunohistochemistry (HIF-1α) and Western blot (VEGF) [2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
In C57BL/6 mice treated with 10 mg/kg IOX2 (intraperitoneal, 7 days) ([1]): No significant weight loss (body weight change: -2.1% vs. control: +2.5%, P > 0.05) or overt toxic signs (lethargy, diarrhea) were observed. Serum biochemistry: ALT (25.8 U/L vs. control 24.5 U/L), AST (41.2 U/L vs. control 39.8 U/L), BUN (14.2 mg/dL vs. control 13.8 mg/dL), and creatinine (0.75 mg/dL vs. control 0.73 mg/dL) were normal. Plasma protein binding rate (measured by ultrafiltration) was 82.5% [1]
- In BALB/c mice treated with 5 mg/kg IOX2 (subcutaneous, 5 days) ([2]): No redness, swelling, or necrosis at the injection site. Liver and kidney histopathology showed no obvious inflammation or necrosis. In HaCaT cells, IOX2 at concentrations up to 200 nM showed no significant cytotoxicity (cell viability > 85% vs. control) [2] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
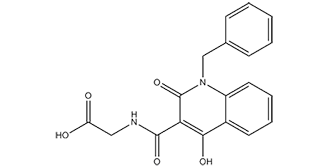
2-[[[4-hydroxy-2-oxo-1-(phenylmethyl)-3-quinolinyl]-oxomethyl]amino]acetic acid is a member of quinolines.
IOX2 is a selective prolyl hydroxylase (PHD) inhibitor with preferential activity against PHD-2. Its core mechanism involves inhibiting PHD-mediated hydroxylation of HIF-1α, thereby stabilizing HIF-1α protein and activating HIF-dependent transcriptional programs (e.g., VEGF expression) [1,2] - In thrombotic diseases, IOX2 modulates platelet function by stabilizing HIF-1α, reducing platelet aggregation and thrombus formation, showing potential as an anti-thrombotic agent [1] - In sulfur mustard-induced tissue injury, IOX2 counteracts impaired HIF-1α signaling in keratinocytes and fibroblasts, promotes VEGF expression, and enhances cell viability and tissue repair, suggesting utility in treating chemical-induced tissue damage [2] |
| 分子式 |
C19H16N2O5
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
352.3407
|
| 精确质量 |
352.105
|
| CAS号 |
931398-72-0
|
| 相关CAS号 |
IOX2 sodium;2377239-85-3
|
| PubChem CID |
54685215
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.5±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
642.8±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
342.5±31.5 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.689
|
| LogP |
1.02
|
| tPSA |
108.63
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
26
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
609
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
CAOSCCRYLYQBES-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C19H16N2O5/c22-15(23)10-20-18(25)16-17(24)13-8-4-5-9-14(13)21(19(16)26)11-12-6-2-1-3-7-12/h1-9,24H,10-11H2,(H,20,25)(H,22,23)
|
| 化学名 |
2-[(1-benzyl-4-hydroxy-2-oxoquinoline-3-carbonyl)amino]acetic acid
|
| 别名 |
IOX-2; IOX2; IOX 2
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: 7 mg/mL (19.9 mM)
Water:<1 mg/mL
Ethanol:<1 mg/mL
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.10 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 +5% Tween-80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80+,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8382 mL | 14.1908 mL | 28.3817 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5676 mL | 2.8382 mL | 5.6763 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2838 mL | 1.4191 mL | 2.8382 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
J Biol Chem. 2011 Apr 15;286(15):13041-51. |
Levels of HIF asparaginyl hydroxylation in hypoxic cells and in rat and human tissues. J Biol Chem. 2011 Apr 15;286(15):13041-51. |
Differential inhibition of HIF prolyl and asparaginyl hydroxylation by HIF hydroxylase inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 2011 Apr 15;286(15):13041-51. |