| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Akt1 (IC50 = 5 nM); Akt3 (IC50 = 8 nM); Akt2 (IC50 = 18 nM); PKA (IC50 = 3100 nM)
Selective ATP-competitive inhibitor of Akt isoforms, including Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440). It exhibits potent inhibitory activity against Akt1 with an IC50 of approximately 5 nM, Akt2 with an IC50 of approximately 18 nM, and Akt3 with an IC50 of approximately 12 nM. It shows high selectivity over other kinases (e.g., >100-fold selectivity against PKA, PKC, and other AGC kinases) [1] - Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) maintains selective inhibition of Akt1 (IC50: 5 nM), Akt2 (IC50: 18 nM), and Akt3 (IC50: 12 nM) in kinase panels, with minimal activity against non-Akt kinases, confirming its specificity for the Akt family [2] - In cellular assays, Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) inhibits phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt) at Ser473 and Thr308, downstream of Akt isoforms, without affecting the total Akt protein level; no new IC50 values for Akt isoforms are provided beyond those reported in [1] [3] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
当针对大量 230 种激酶(PRKG1α、PRKG1β 和 p70S6K,IC50 值分别为 98 nM、69 nM 和 860 nM)进行测试时,GDC-0068 在 1 μM 浓度下仅抑制 3 种激酶 >70%。 GDC-0068 的 IC50 为 3.1 μM,对 Akt 的选择性是 PKA 的 100 倍以上。 GDC-0068 处理可抑制 LNCaP、PC3 和 BT474M1 细胞中 Akt 底物 PRAS40 的磷酸化,IC50 值分别为 157 nM、197 nM 和 208 nM。此外,GDC-0068 选择性抑制肿瘤抑制因子 PTEN 缺陷、PIK3CA 致癌突变和 HER2 扩增的 Akt 信号驱动癌细胞系,其中 HER2+ 和 Luminal 亚型的效果最强。 [1-3]
Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) 对多种Akt信号激活的人肿瘤细胞系具有增殖抑制作用。例如,对PC-3前列腺癌细胞的抗增殖IC50约为0.8 μM;对LNCaP前列腺癌细胞的IC50约为1.2 μM;对MDA-MB-468乳腺癌细胞的IC50约为0.6 μM。Western blot结果显示,用1-5 μM Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) 处理细胞4小时,可使p-Akt(Ser473和Thr308)水平降低>70%,同时使下游底物(如p-FOXO1 Ser256、p-GSK3β Ser9)的磷酸化水平降低60%-80%[1] - 在24种人肿瘤细胞系组成的筛选面板中,Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) 的抗增殖IC50范围为0.3 μM-3.5 μM,其中对PTEN缺失或PI3K突变的细胞系(如BT-474乳腺癌细胞)活性最强,IC50为0.3 μM。Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440)(0.5 μM)与紫杉醇(10 nM)联合处理MDA-MB-231乳腺癌细胞,较单药处理细胞活力额外降低40%。克隆形成实验显示,0.5 μM Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) 处理PC-3细胞14天后,克隆形成率降低>60%[2] - Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) 可诱导HCT116结直肠癌细胞和MCF-7乳腺癌细胞凋亡。2 μM浓度处理24小时后,凋亡细胞比例(Annexin V阳性)较对照组增加30%-40%。Western blot显示,1-3 μM Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) 可使促凋亡蛋白PUMA表达上调2-3倍,并激活Caspase-3/7(切割型Caspase-3水平增加>2倍)。实时定量PCR结果显示,2 μM Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) 处理HCT116细胞后,PUMA mRNA表达上调3.5倍。此外,敲低FoxO3a或NF-κB p65可消除Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) 诱导的PUMA上调,表明FoxO3a和NF-κB介导该效应[3] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
GDC-0068 口服给药会导致 PC3 前列腺肿瘤异种移植模型中 p-PRAS40 下调。 BT474-Tr 异种移植物中的 GDC-0068 治疗可降低 pS6 和 peIF4G 水平,将 FOXO3a 重新定位到细胞核,并导致 HER3 和 pERK 的反馈上调。在许多异种移植肿瘤模型中,包括 PTEN 缺陷型前列腺癌模型 LNCaP 和 PC3、PIK3CA H1047R 突变乳腺癌模型 KPL-4 和 MCF7-neo/HER2 肿瘤模型,GDC-0068 的给药表现出强大的抗肿瘤功效。 [1-3]
在PC-3前列腺癌裸鼠异种移植模型中,口服给予Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440)(30 mg/kg/天、100 mg/kg/天)21天,肿瘤生长抑制率(TGI)分别为45%和72%(vs 溶媒对照组)。处理组小鼠无明显体重下降(≤5%)。肿瘤组织Western blot显示,100 mg/kg/天Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) 可使p-Akt(Ser473)水平降低>80%,p-GSK3β(Ser9)水平降低70%[1] - 在MDA-MB-468乳腺癌裸鼠异种移植模型中,Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) 单药(100 mg/kg/天,口服)处理28天,TGI为65%;与多西他赛(10 mg/kg/周,腹腔注射)联合处理,TGI达90%,且显著延长小鼠中位生存期(溶媒组42天 vs 联合组68天)。肿瘤组织免疫组化(IHC)显示,Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) 处理使p-Akt(Ser473)染色强度降低>70%[2] - 在HCT116结直肠癌裸鼠异种移植模型中,口服Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440)(100 mg/kg/天)14天,肿瘤组织中PUMA蛋白表达(IHC检测)较对照组增加2.5倍,凋亡细胞数(TUNEL阳性)增加3倍。处理组小鼠无明显毒性(如体重下降、器官损伤)[3] |
| 酶活实验 |
Enzymatic Assays/酶实验[1]
用于测定Akt1/2/3和PKA激酶活性的测定采用IMAP荧光偏振(FP)磷酸化检测试剂来检测已被相应激酶磷酸化的荧光标记肽底物。这些研究中使用的Akt酶由重组杆状病毒表达、氨基末端、聚组氨酸标记、全长、野生型人类形式组成,并从商业上获得。这些研究中使用的PKA酶由商业上获得的大肠杆菌中表达的重组未标记的PKA人分离催化亚基组成。在环境温度下,将抑制剂、酶(9 nM Akt1或100 pM PKA)和底物(100 nM Crosstide)与5μM ATP在测定缓冲液(10 mM Tris-HCl(pH 7.2)、10 mM MgCl2、0.1%BSA(w/v)、最终DMSO 2%(v/v))中在5μL反应体积中孵育60分钟。通过向ATP溶液中加入酶+肽底物引发反应。加入IMAP结合试剂(15μL)终止反应,并将停止的反应在室温下孵育至少30分钟。 Akt激酶活性实验(基于HTRF技术):将重组人Akt亚型(Akt1、Akt2、Akt3)用实验缓冲液(含Tris-HCl、MgCl2、DTT和BSA)稀释至终浓度1 nM;向反应体系中加入底物(生物素化GSK3β肽段,终浓度2 μM)、ATP(终浓度10 μM,接近Akt的Km值)及不同浓度的Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440)(0.1 nM-10 μM);30°C孵育60分钟后,加入检测混合物(链霉亲和素偶联Eu3+与抗磷酸化GSK3β抗体偶联XL665);检测665 nm和620 nm处的荧光共振能量转移(FRET)信号,以665/620比值计算激酶活性抑制率;采用四参数逻辑模型拟合抑制曲线,计算IC50[1] - 激酶选择性实验:使用包含130种重组人激酶(含AGC家族激酶、酪氨酸激酶、丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶)的筛选面板;每种激酶与特异性底物、ATP(Km浓度)及1 μM Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) 共同孵育;采用放射性法(33P-ATP掺入底物)检测激酶活性;以溶媒对照组为参照,计算剩余激酶活性百分比,活性剩余<10%的激酶视为潜在脱靶;结果显示仅Akt1、Akt2、Akt3活性剩余<10%,证实Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) 的选择性[1] - 细胞裂解液中p-Akt抑制实验:用Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) 处理肿瘤细胞(如PC-3)4小时后,用含蛋白酶和磷酸酶抑制剂的RIPA缓冲液裂解细胞;离心收集上清液,取20 μg蛋白进行SDS-PAGE电泳,转印至PVDF膜;用5%脱脂牛奶封闭膜后,4°C孵育抗p-Akt(Ser473)、p-Akt(Thr308)或总Akt一抗过夜;洗涤后,室温孵育HRP偶联二抗1小时;ECL底物显影,ImageJ软件定量条带强度;以溶媒对照组为参照,计算p-Akt抑制率[2] |
| 细胞实验 |
在以5000个细胞/孔的密度镀在黑色透明底96孔板上的LNCaP细胞中测量细胞存活率的抑制,随后在37°C和5%CO2下用0-10μM 28(ipatasertib)处理72小时。细胞增殖的程度是通过使用560nm的激发波长和590nm的发射波长测量制造商方案中所述的刃天青还原为再硫酸镁来确定的。使用四参数逻辑斯蒂模型生成剂量-反应曲线,并根据这些曲线拟合确定50%抑制浓度(IC50)值。[1]
简而言之,在ipatasertib处理后,HCT116 WT或p53-/-用1%甲醛固定,并在温SDS裂解缓冲液中裂解。获得基因组DNA,并通过在冰上超声处理将其剪切至200-1000bp。样品用蛋白A-琼脂糖/鲑鱼精子DNA(50%浆液)在4°C下搅拌预清洗1小时。然后加入抗FoxO3a抗体或抗p65抗体,在4°C的摇床上孵育过夜。正常兔IgG用作阴性对照。然后加入蛋白质琼脂糖/鲑鱼精子DNA(50%浆液)珠,以沉淀抗体/蛋白质/DNA复合物。用连续洗涤缓冲液洗涤后,用洗脱缓冲液(1%SDS,0.1 M NaHCO3)从珠粒中洗脱DNA-蛋白质免疫复合物30分钟。最后,通过在65°C下与0.2 M NaCl孵育4小时,逆转蛋白质-DNA交联以释放DNA[3]。 抗增殖实验(MTT法):将人肿瘤细胞以2×10^3个/孔的密度接种于96孔板,过夜培养;向各孔加入不同浓度的Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440)(0.01 μM-10 μM),每个浓度设3个复孔;37°C、5% CO2培养箱中孵育72小时;每孔加入20 μL MTT溶液(5 mg/mL),继续孵育4小时;弃去上清液,加入150 μL DMSO溶解甲瓒结晶;酶标仪检测570 nm处吸光度;以溶媒对照组为参照计算细胞活力,GraphPad Prism软件计算IC50[1] - 克隆形成实验:PC-3细胞以5×10^2个/孔的密度接种于6孔板,过夜培养;加入终浓度为0.1 μM、0.5 μM、1 μM的Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440),设溶媒对照组;37°C、5% CO2培养箱中培养14天,每3天更换培养基和药物;培养结束后,4%多聚甲醛固定细胞15分钟,0.1%结晶紫染色30分钟,水洗;显微镜下计数含>50个细胞的克隆;克隆形成率=(药物组克隆数/对照组克隆数)×100%[2] - 凋亡实验(Annexin V-FITC/PI双染法):HCT116细胞以2×10^5个/孔接种于6孔板,过夜培养;加入终浓度2 μM的Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440),孵育24小时;胰酶消化收集细胞,冷PBS洗涤2次,用1×结合缓冲液重悬;向细胞悬液中加入5 μL Annexin V-FITC和10 μL PI,室温避光孵育15分钟;流式细胞仪检测凋亡率,FlowJo软件分析数据[3] - PUMA mRNA实时定量PCR检测:2 μM Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) 处理HCT116细胞12小时;RNA提取试剂盒提取总RNA,NanoDrop分光光度计测定RNA浓度和纯度;逆转录试剂盒合成cDNA;使用SYBR Green PCR预混液进行实时定量PCR,以PUMA特异性引物和GAPDH特异性引物(内参)扩增;反应条件:95°C 10分钟,随后40个循环(95°C 15秒、60°C 1分钟);采用2^(-ΔΔCt)法计算PUMA mRNA相对表达量[3] |
| 动物实验 |
Female nude mice bearing LNCaP, PC3, KPL-4, or MCF7 tumor xenografts
\n~100 mg/kg/day \nOrally \n\nFor in vivo tumor xenograft studies, female nu/nu (nude) mice were inoculated subcutaneously in the right hind flank with PC3 cells suspended in Hank’s balanced salt solution (HBSS). When tumors reached a mean volume of 150 mm3, the animals were size matched and distributed into treatment groups consisting of 10 animals/group. Tumor volume was calculated as follows: tumor size (mm3) = (longer measurement × (shorter measurement)2) × 0.5. Following data analysis, p values were determined using Dunnett’s t test with JMP statistical software, version 7.0 (SAS Institute). Mouse body weights were recorded twice weekly using an Adventura Pro AV812 scale (Ohaus Corp.). Mice were promptly euthanized when the tumor volume exceeded 2000 mm3 or if body weight loss was ≥20% of the starting weight per IACUC protocol guidelines.[1] \n\nFor PK/PD studies, blood and tumor samples were collected at 1, 3, 8, and 24 h after a single dose of ipatasertib from PC3 tumor bearing mice. Blood samples (approximately 800 μL) were collected from each animal at the scheduled sample collection time by terminal cardiac puncture into tubes containing K2EDTA as an anticoagulant and centrifuged at 1500–2000g to isolate plasma. The concentration of ipatasertib in each plasma sample was determined by a nonvalidated LC/MS/MS assay in the DMPK Bioanalytical Department at Genentech. The assay lower limit of quantitation (LLOQ) was 0.005 μM. Tumor samples were dissociated in Tris lysis buffer containing 150 mM NaCl, 20 mM Tris (pH 7.5), 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM EGTA, and 1% Triton X-100. Protein concentrations were determined using the BCA Protein Assay Kit. The human enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits were used to determine the levels of total PRAS40 and PRAS40 phosphorylated at Thr246 (p-PRAS40). The assay quantifies protein levels on the basis of measurements of absorbance. The colored product is directly proportional to the concentration of p-PRAS40 and tPRAS40 present in the specimen. The Meso Scale Discovery Multi-Spot Biomarker Detection System was used to determine the levels of total S6RP and S6RP phosphorylated at Ser235/236 (pS6RP). These assays quantify protein levels on the basis of measurements of electrochemiluminescence intensity. Levels of phosphorylated protein were normalized to total protein levels in ipatasertib-treated tumors and compared to the vehicle control.[1] \n\nIn vivo efficacy was evaluated in multiple tumor cell line- and patient-derived xenograft models. Cells or tumor fragments were implanted subcutaneously into the flank of immunocompromised mice. Female or male nude (nu/nu) or severe combined immunodeficient mice (SCID)/beige mice were used. For the MCF7-neo/HER2 model, 17β-estradiol pellets (0.36 mg/pellet, 60-day release, no. SE-121) were implanted into the dorsal shoulder before cell inoculation. Male mice were castrated before implantation of tumor fragments. After implantation of tumor cells or fragments into mice, tumors were monitored until they reached mean tumor volumes of 180 to 350 mm3 and distributed into groups of 8 to 10 animals/group. ipatasertib/GDC-0068 was formulated in 0.5% methylcellulose/0.2% Tween-80 (MCT) and administered daily (QD), via oral (per os; PO) gavage.[2] \n\nHCT116 WT and PUMA−/− were harvested, and 1 × 10~6 cells in 0.2 ml of medium were implanted subcutaneously into the back of athymic nude female mice. Female 5-week-old nude mice were housed in a sterile environment with microisolator cages and allowed access to water and chow ad libitum. Mice were treated daily with ipatasertib/GDC-0068 at 40 mg/kg by oral gavage for 21 days treatment after 7 days. Calipers were used to monitor the tumor growth, volume was calculated by the formula: 0.5 × length × width2. Mice were euthanized when tumors reached ~1.0 cm3 in size. Tumors were dissected and fixed in 10% formalin and embedded in paraffin.[3] PC-3 prostate cancer xenograft model in nude mice: Male nude mice (6-8 weeks old) are used. Logarithmically growing PC-3 cells (1×10^6 cells in 0.1 mL of PBS/matrigel mixture, 1:1) are subcutaneously injected into the right dorsal flank of each mouse. When the tumor volume reaches 100-200 mm³, the mice are randomly divided into 3 groups (n=6 per group): vehicle control group, Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) 30 mg/kg group, and Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) 100 mg/kg group. Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) is dissolved in a vehicle consisting of 0.5% methylcellulose and 0.1% Tween 80, and administered orally once daily. The vehicle control group receives the same volume of vehicle. Tumor volume (calculated as length × width² × 0.5) and mouse body weight are measured twice a week. After 21 days of treatment, the mice are euthanized, and tumor tissues are collected for western blot analysis [1] - MDA-MB-468 breast cancer xenograft combination model: Female nude mice (6-8 weeks old) are subcutaneously injected with MDA-MB-468 cells (2×10^6 cells in 0.1 mL of PBS/matrigel, 1:1) into the right dorsal flank. When tumors reach 150-200 mm³, mice are divided into 4 groups (n=8 per group): vehicle control, Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) alone (100 mg/kg, oral, once daily), docetaxel alone (10 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection, once weekly), and combination of Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) and docetaxel. The treatment lasts for 28 days. Tumor volume and body weight are measured twice a week. Mouse survival is recorded daily, and the median survival time is calculated. After treatment, tumor tissues are collected for immunohistochemistry (IHC) analysis of p-Akt [2] - HCT116 colorectal cancer xenograft mechanism model: Nude mice (6-8 weeks old) are subcutaneously injected with HCT116 cells (1.5×10^6 cells in 0.1 mL of PBS/matrigel, 1:1). When tumors reach 100-150 mm³, mice are divided into 2 groups (n=6 per group): vehicle control and Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) 100 mg/kg (oral, once daily). Treatment continues for 14 days. Tumor volume and body weight are measured every 3 days. After euthanasia, tumor tissues are fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, embedded in paraffin, and sectioned. IHC is performed to detect PUMA protein expression (using anti-PUMA antibody), and TUNEL staining is used to detect apoptotic cells. The number of PUMA-positive cells and TUNEL-positive cells is counted under a microscope [3] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
In vitro metabolism: Human liver microsomes (0.5 mg/mL) are incubated with Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) (1 μM) and NADPH (1 mM) at 37°C for 0-60 minutes. The reaction is stopped by adding acetonitrile containing an internal standard. The samples are centrifuged, and the supernatant is analyzed by LC-MS/MS to detect metabolites. Results show that Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4, producing three major oxidative metabolites (M1, M2, M3). The half-life of Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) in human liver microsomes is approximately 45 minutes [1]
- Plasma protein binding: Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) (1 μM) is incubated with human, rat, and dog plasma (0.5 mL) at 37°C for 1 hour. The samples are then subjected to ultrafiltration using centrifugal ultrafiltration tubes. The concentration of Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) in the filtrate (free drug) and plasma (total drug) is measured by LC-MS/MS. The plasma protein binding rate is calculated as [(total drug concentration - free drug concentration) / total drug concentration] × 100%. Results show that the plasma protein binding rate is >95% in human, rat, and dog plasma [1] - In vivo pharmacokinetics in rats: Male Sprague-Dawley rats (n=3 per time point) receive a single oral dose of Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) (10 mg/kg, dissolved in 0.5% methylcellulose/0.1% Tween 80) or intravenous dose (2 mg/kg, dissolved in DMSO/saline, 1:9). Blood samples are collected at 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, and 24 hours after administration. Plasma is separated by centrifugation, and Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) concentration is measured by LC-MS/MS. Pharmacokinetic parameters are calculated using non-compartmental analysis: oral bioavailability (F) is 35%, Tmax (oral) is 1.5 hours, Cmax (oral) is 1.2 μg/mL, and terminal half-life (t1/2) is 5.2 hours [1] - In vivo pharmacokinetics in mice: Female nude mice (n=3 per time point) receive a single oral dose of Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) (100 mg/kg). Blood samples are collected at 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 12 hours. Plasma concentration analysis shows Tmax is 1 hour, Cmax is 5.1 μg/mL, and t1/2 is 3.1 hours [2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Acute toxicity in mice: Female ICR mice (n=5 per group) receive a single oral dose of Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) at 500, 1000, or 2000 mg/kg. The mice are observed for 14 days for mortality, clinical signs, and body weight changes. No mortality is observed in any group. Mild and transient body weight loss (≤5%) is observed in the 1000 and 2000 mg/kg groups within the first 3 days, but body weight returns to normal by day 7. No other clinical signs of toxicity (e.g., lethargy, diarrhea) are noted [1]
- Repeat-dose toxicity in rats: Male Sprague-Dawley rats (n=6 per group) receive oral Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) at 10, 30, or 100 mg/kg/day for 28 days. The vehicle control group receives 0.5% methylcellulose/0.1% Tween 80. Body weight is measured weekly, and blood samples are collected at the end of treatment for clinical chemistry analysis. At 100 mg/kg/day, a slight increase in serum ALT (1.5-fold vs. control) and AST (1.3-fold vs. control) is observed, but no histopathological changes in the liver are detected. No significant changes in body weight, hematology parameters, or other clinical chemistry markers are observed in the 10 and 30 mg/kg/day groups. No toxicity-related mortality occurs [1] - Toxicokinetics in dogs: Beagle dogs (n=4 per group) receive oral Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) at 5, 20, or 50 mg/kg/day for 90 days. Plasma samples are collected on day 1 and day 90 to measure Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) concentration. The Cmax and AUC0-24h increase in a dose-proportional manner, with no evidence of accumulation (accumulation ratio <1.2). No significant changes in body weight, clinical signs, or laboratory parameters are observed in any group, indicating good tolerability at doses up to 50 mg/kg/day [2] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
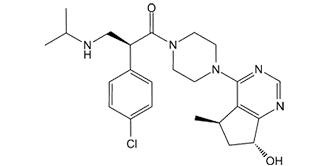
(2S)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-[4-[(5R,7R)-7-hydroxy-5-methyl-6,7-dihydro-5H-cyclopenta[d]pyrimidin-4-yl]-1-piperazinyl]-3-(propan-2-ylamino)-1-propanone is a N-arylpiperazine.
Ipatasertib has been used in trials studying the treatment of Cancer, Neoplasms, Solid Cancers, Breast Cancer, and Gastric Cancer, among others. Ipatasertib is an orally bioavailable inhibitor of the serine/threonine protein kinase Akt (protein kinase B) with potential antineoplastic activity. Ipatasertib binds to and inhibits the activity of Akt in a non-ATP-competitive manner, which may result in the inhibition of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and tumor cell proliferation and the induction of tumor cell apoptosis. Activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway is frequently associated with tumorigenesis and dysregulated PI3K/Akt signaling may contribute to tumor resistance to a variety of antineoplastic agents. Drug Indication Treatment of breast cancer , Treatment of prostate cancer Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) was developed as a targeted therapy for tumors with aberrant Akt activation, which is frequently caused by genetic alterations such as PTEN loss, PI3K mutation, or Akt amplification. These alterations lead to uncontrolled cell proliferation and survival, making Akt a key therapeutic target in oncology [1] - In preclinical studies, Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) shows efficacy in multiple tumor types with activated Akt, including prostate, breast, colorectal, and lung cancers, supporting its potential for broad application in cancer treatment [2] - The mechanism by which Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) induces apoptosis involves dual regulation of PUMA: inhibition of Akt releases FoxO3a from cytoplasmic sequestration, allowing it to translocate to the nucleus and transactivate PUMA; simultaneously, Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) activates NF-κB, which directly binds to the PUMA promoter and enhances PUMA transcription. This dual mechanism contributes to the potent apoptotic effect of Ipatasertib (GDC0068; RG7440) in tumor cells [3] |
| 分子式 |
C24H32CLN5O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
457.9962
|
| 精确质量 |
457.224
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 62.94; H, 7.04; Cl, 7.74; N, 15.29; O, 6.99
|
| CAS号 |
1001264-89-6
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Ipatasertib dihydrochloride;1396257-94-5; Ipatasertib;1001264-89-6; 1489263-16-2 (HCl); 1491138-24-9; 1491138-23-8 (besylate)
|
| PubChem CID |
24788740
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to light yellow solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
669.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
358.7±31.5 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.1 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.603
|
| LogP |
1.71
|
| tPSA |
81.59
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
32
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
622
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
3
|
| SMILES |
ClC1C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=1[H])[C@@]([H])(C([H])([H])N([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])C(N1C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N(C([H])([H])C1([H])[H])C1C2=C([C@@]([H])(C([H])([H])[C@@]2([H])C([H])([H])[H])O[H])N=C([H])N=1)=O
|
| InChi Key |
GRZXWCHAXNAUHY-NSISKUIASA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C24H32ClN5O2/c1-15(2)26-13-19(17-4-6-18(25)7-5-17)24(32)30-10-8-29(9-11-30)23-21-16(3)12-20(31)22(21)27-14-28-23/h4-7,14-16,19-20,26,31H,8-13H2,1-3H3/t16-,19-,20-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(2S)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-[4-[(5R,7R)-7-hydroxy-5-methyl-6,7-dihydro-5H-cyclopenta[d]pyrimidin-4-yl]piperazin-1-yl]-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propan-1-one
|
| 别名 |
GDC0068; GDC 0068; GDC-0068; RG-7440; 1001264-89-6; Ipatasertib (GDC-0068); RG7440; (S)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(4-((5R,7R)-7-hydroxy-5-methyl-6,7-dihydro-5H-cyclopenta[d]pyrimidin-4-yl)piperazin-1-yl)-3-(isopropylamino)propan-1-one; RG-7440; GDC0068; RG 7440; RG7440; Ipatasertib
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~92 mg/mL (~200.9 mM)
Water: <1 mg/mL Ethanol: ~92 mg/mL (~200.9 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.54 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.54 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.54 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 5% DMSO+40% PEG 300+5%Tween80+ 50%ddH2O: 92mg/ml 配方 5 中的溶解度: 10 mg/mL (21.83 mM) in 0.5% MC 0.5% Tween-80 (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1834 mL | 10.9170 mL | 21.8341 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4367 mL | 2.1834 mL | 4.3668 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2183 mL | 1.0917 mL | 2.1834 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Targeted Therapy Directed by Genetic Testing in Treating Patients With Advanced Refractory Solid Tumors, Lymphomas, or Multiple Myeloma (The MATCH Screening Trial)
CTID: NCT02465060
Phase: Phase 2 Status: Active, not recruiting
Date: 2024-11-18
Dose-dependent effect of GDC-0068 on Akt pathway biomarkers. Clin Canc Res 2013, 19:1760–1772. |
Single agent efficacy of GDC-0068 in human tumor xenograft models. |
Pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) relationship of GDC-0068 in xenograft models. |