| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Akt1 (IC₅₀ = 5 nM); Akt2 (IC₅₀ = 18 nM); Akt3 (IC₅₀ = 8 nM); Highly selective against 339 kinases (only ROCK2, PRKGB, and Aurora A showed >50% inhibition at 1 μM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
伊帕他赛替布甲磺酸盐 (10 µM; 12, 24 小时) 在细胞实验中通过 p53 独立的 PUMA 激活抑制结肠癌细胞增殖[1]。伊帕他赛替布甲磺酸盐 (1, 5, 10, 20 μM; 24 小时/10 μM; 3, 6, 12, 24 小时) 以时间和浓度依赖性的方式上调 HCT116 细胞中的 PUMA 表达[1]。伊帕他赛替布甲磺酸盐可增加野生型、p53−/− 和 DLD1(p53 突变体)HCT116 细胞中的 PUMA mRNA 水平[1]。伊帕他赛替布甲磺酸盐 (10 µM; 24 小时) 通过 PUMA/Bax 通路诱导 HCT116 细胞凋亡[1]。
Ipatasertib 以剂量依赖性方式抑制结肠癌细胞增殖(HCT116 IC₅₀≈10 μM),并通过上调PUMA诱导凋亡(不依赖p53状态)。 激活FoxO3a和NF-κB,二者结合PUMA启动子,触发Bax介导的线粒体凋亡。FoxO3a是主要调控因子(ChIP实验结合更强),NF-κB为次要。 与5-FU、顺铂或瑞戈非尼联用具有协同效应,进一步增强PUMA依赖性凋亡。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
伊帕他赛替布甲磺酸盐(30 mg/kg;口服;每天一次,连续 15 天)在野生型和 PUMA−/− HCT116 异种移植小鼠模型中表现出 PUMA 依赖性抗肿瘤活性 [1]。
Ipatasertib(30 mg/kg/天,口服灌胃)显著抑制HCT116 WT小鼠移植瘤生长(肿瘤体积/重量减少),但对PUMA-KO肿瘤效果减弱。 免疫组化显示仅在WT肿瘤中Ki67(增殖标志物)降低、cleaved caspase-3增加。 |
| 酶活实验 |
使用重组Akt酶和生物素化Crosstide底物通过TR-FRET测定法测量Akt抑制。
Western blot检测Akt抑制(↓p-Akt S473)、FoxO3a激活(↓p-FoxO3a S253)、NF-κB激活(↑p-p65 S536)及PUMA/Bax表达。 ChIP实验验证FoxO3a/NF-κB与PUMA启动子结合。 |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定[1]
细胞类型:HCT116 WT、p53−/−、和DLD1 (p53 突变体) 测试浓度:10 µM 孵育时间:12、24 小时 实验结果:三种细胞系活力均降低。 细胞凋亡分析[1] 细胞类型:HCT116 测试浓度:10 µM 孵育时间:24 小时 实验结果:通过 PUMA/Bax 通路诱导细胞凋亡。 Western Blot 分析[1] 细胞类型:HCT116 WT、p53−/− 和 DLD1(p53 突变体) 测试浓度:1、5、10、20 μM,24 小时/10 μM,3、6、12、24 小时 孵育时长:24 小时;3、6、12、24 小时 实验结果:以浓度和时间依赖性方式增加 PUMA 水平。 增殖检测: CCK-8法(24–72h处理);计算HCT116、DLD1及p53-KO细胞的IC₅₀。 凋亡检测: Hoechst 33258染色观察核凝聚;流式细胞术(Annexin V/PI)定量凋亡率。 PUMA依赖性: PUMA/Bax-KO细胞中凋亡消失;克隆形成实验证实生长抑制需PUMA/Bax参与。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: HCT116 WT and PUMA−/− cells xenograft nude mice model[1].
Doses: 30 mg/kg Route of Administration: Oral gavage; single daily for 15 consecutive days. Experimental Results: Inhibited growth of tumors in a PUMA-dependent manner. Xenograft: Nude mice implanted with HCT116 WT or PUMA-KO cells; treated with ipatasertib (30 mg/kg/day oral gavage) for 15 days. Endpoints: Tumor volume/weight measurement; IHC for P-Akt, Ki67, cleaved caspase-3. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Bioavailability: Mouse 31%, Rat 80%, Dog 44%, Human ~60%
Half-life: Mouse 2.3h, Rat 3.1h, Dog 7.8h, Human ~50h Metabolism: Primarily CYP3A4-mediated ketone reduction to alcohol metabolite (inactive); <5% renal excretion. Plasma protein binding: >95% across species; Vd = 1.1-1.7 L/kg. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Reversible ALT/AST elevations in rats/dogs at ≥100 mg/kg/day.
No QTc prolongation in dog telemetry (30 mg/kg). Clinical MTD: 600 mg/day; dose-limiting toxicities include diarrhea and hyperglycemia. Drug interactions: Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors increase AUC by 5.7-fold; inducers decrease exposure 12-fold. Minimal toxicity in normal colon cells (NCM460) at therapeutic doses. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Mechanism: ATP-competitive pan-Akt inhibitor blocking downstream signaling.
Clinical indications: Phase II/III trials for triple-negative breast/prostate cancers (e.g., IPATunity130). Tosylate salt selected for optimal solubility (0.5 mg/mL free base vs 8.7 mg/mL tosylate). Key differentiator: Enables in vivo target engagement studies via pPRAS40 suppression as PD biomarker. Colon cancer is one of the three common malignant tumors, with a lower survival rate. Ipatasertib, a novel highly selective ATP-competitive pan-Akt inhibitor, shows a strong antitumor effect in a variety of carcinoma, including colon cancer. However, there is a lack of knowledge about the precise underlying mechanism of clinical therapy for colon cancer. We conducted this study to determine that ipatasertib prevented colon cancer growth through PUMA-dependent apoptosis. Ipatasertib led to p53-independent PUMA activation by inhibiting Akt, thereby activating both FoxO3a and NF-κB synchronously that will directly bind to PUMA promoter, up-regulating PUMA transcription and Bax-mediated intrinsic mitochondrial apoptosis. Remarkably, Akt/FoxO3a/PUMA is the major pathway while Akt/NF-κB/PUMA is the secondary pathway of PUMA activation induced by ipatasertib in colon cancer. Knocking out PUMA eliminated ipatasertib-induced apoptosis both in vitro and in vivo (xenografts). Furthermore, PUMA is also indispensable in combinational therapies of ipatasertib with some conventional or novel drugs. Collectively, our study demonstrated that PUMA induction by FoxO3a and NF-κB is a critical step to suppress the growth of colon cancer under the therapy with ipatasertib, which provides some theoretical basis for clinical assessment. |
| 分子式 |
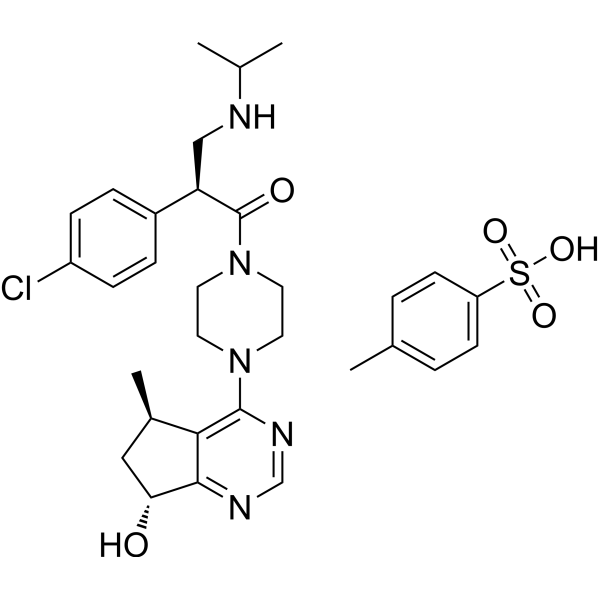
C31H40CLN5O5S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
630.20
|
| CAS号 |
1491138-24-9
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solids at room temperature
|
| SMILES |
C[C@@H]1C[C@H](C2=C1C(=NC=N2)N3CCN(CC3)C(=O)[C@H](CNC(C)C)C4=CC=C(C=C4)Cl)O.CC1=CC=C(C=C1)S(=O)(=O)O
|
| 别名 |
GDC-0068 tosylate; Ipatasertib (tosylate); SCHEMBL16617584; UTUKVTLAXHISRJ-GJYOXNSLSA-N; (S)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(4-((5R,7R)-7-hydroxy-5-methyl-6,7-dihydro-5H-cyclopenta[d]pyrimidin-4-yl)piperazin-1-yl)-3-(isopropylamino)propan-1-one p-toluene Sulfonic Acid Salt; 1491138-24-9; RG7440 tosylate
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.5868 mL | 7.9340 mL | 15.8680 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3174 mL | 1.5868 mL | 3.1736 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1587 mL | 0.7934 mL | 1.5868 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。