| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Topoisomerase I
Topoisomerase I (Topo I) [2] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
伊立替康被羧酸酯酶激活为 SN-38,从而能够与其靶标拓扑异构酶 I 相互作用。伊立替康在 LoVo 细胞和 HT-29 细胞系中以 IC50 诱导相似数量的可裂解复合物。 SN-38 诱导可裂解复合物的浓度依赖性形成,这在 LoVo 细胞和 HT-29 细胞系中没有显着差异。伊立替康的细胞积累明显不同,在 HT-29 细胞中达到的水平始终高于 LoVo 细胞中的水平。伊立替康和 SN-38 的内酯 E 环在水溶液中可逆水解,内酯和羧酸盐形式之间的相互转化取决于 pH 值和温度。肝脏主要负责将伊立替康激活为 SN-38。在伊立替康和 SN-38 葡萄糖醛酸浓度相同的情况下,在肿瘤和正常组织中,β-葡萄糖醛酸酶介导的 SN-38 产生率高于伊立替康形成的 SN-38 产生率。伊立替康还在肠道、血浆和肿瘤组织中转化为 SN-38。伊立替康在 SCLC 细胞系中的活性显着高于 NSCLC 细胞系,而在 SN-38 中未观察到组织学类型之间存在显着差异。细胞测定:将指数生长的细胞(LoVo 和 HT-29 细胞)接种在 20 cm2 培养皿中,每个细胞系具有最佳细胞数(LoVo 细胞为 2 × 104,HT-29 细胞为 105)。 2 天后,用增加浓度的伊立替康或 SN-38 处理细胞一个细胞倍增时间(LoVo 细胞为 24 小时,HT-29 细胞为 40 小时)。用0.15 M NaCl洗涤后,细胞在正常培养基中进一步生长两次倍增,用胰蛋白酶-EDTA从支持物上分离并在血细胞计数器中计数。然后将 IC50 值估计为与没有伊立替康或 SN-38 孵育的细胞相比造成 50% 生长抑制的伊立替康或 SN-38 浓度。
伊立替康(CPT-11) 对两种人结直肠肿瘤细胞系(HT29和SW620)具有细胞毒性作用。HT29和SW620细胞的IC50值分别为0.65 μM和0.82 μM。该细胞毒性与DNA单链断裂形成增加及凋亡诱导相关[2] - 伊立替康(CPT-11) 以剂量依赖方式诱导小鼠腹膜驻留巨噬细胞(PRMs)凋亡。在10 μM、25 μM和50 μM浓度下,PRMs的凋亡率分别为18.3%、35.7%和62.1%。Western blot分析显示切割型caspase-3、切割型caspase-9和Bax表达上调,Bcl-2表达下调[5] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在 COLO 320 异种移植物中,伊立替康可诱导最大 92% 的生长抑制。单剂量的伊立替康显着增加胃、十二指肠、结肠和肝脏中与 DNA 共价结合的拓扑异构酶 I 的量。与此同时,与对照组相比,伊立替康治疗组在结肠粘膜细胞中显示出显着更高数量的 DNA 链断裂。
向携带实验性恶性神经外胚层肿瘤的小鼠腹腔内给予 伊立替康(CPT-11),剂量为100 mg/kg,每周1次,持续3周。该药物显著抑制肿瘤生长,与对照组相比,肿瘤体积缩小率为58.6%。治疗期间未观察到明显的全身毒性[1] - 在携带晚期人结肠癌异种移植物的小鼠中测试了凝血酶敏感蛋白1(TSP-1)与 伊立替康(CPT-11) 的联合治疗效果。伊立替康(CPT-11) 以60 mg/kg剂量静脉注射,每4天1次,共3个周期;TSP-1以2 μg/只剂量皮下注射,隔天1次。联合治疗对肿瘤生长的抑制率达72.3%,显著高于 伊立替康(CPT-11) 单药治疗的41.5%[3] |
| 酶活实验 |
拓扑异构酶I活性测定采用纯化的人Topo I和超螺旋质粒DNA。反应体系包含不同浓度的 伊立替康(CPT-11)、Topo I和质粒DNA,在37°C下孵育30分钟。加入SDS终止反应后,通过琼脂糖凝胶电泳分离DNA产物,根据松弛型DNA条带的减少程度评估 伊立替康(CPT-11) 对Topo I的抑制作用[2]
|
| 细胞实验 |
在 20 cm 2 培养皿中,按指数生长的细胞接种每个细胞系理想数量的细胞(LoVo 细胞为 20,000 个,HT-29 细胞为 100,000 个)。两天后,他们接受浓度递增的伊立替康或 SN-38 治疗,进行单细胞倍增期(LoVo 细胞为 24 小时,HT-29 细胞为 40 小时)。 0.15 M NaCl 洗涤后,将细胞在正常培养基中再培养两次倍增,然后使用胰蛋白酶-EDTA 将其与支持物分离并使用血细胞计数器进行计数。随后,对经药物处理的细胞产生 50% 生长抑制的药物浓度估计为 IC50 值 [2]。
结直肠肿瘤细胞毒性测定:将HT29和SW620细胞以5×10³个细胞/孔的密度接种到96孔板中,过夜孵育。用系列浓度的 伊立替康(CPT-11)(0.1-10 μM)处理细胞72小时,采用基于线粒体脱氢酶活性的比色法检测细胞活力。通过碱性彗星实验检测DNA单链断裂, Annexin V-FITC/PI染色后流式细胞术评估凋亡情况[2] - 腹膜驻留巨噬细胞凋亡测定:分离小鼠PRMs并以2×10⁵个细胞/孔接种到6孔板中。用10 μM、25 μM和50 μM浓度的 伊立替康(CPT-11) 处理细胞24小时,通过Hoechst 33342染色和流式细胞术鉴定凋亡细胞。Western blot分析检测caspase-3、caspase-9、Bax和Bcl-2蛋白的表达水平[5] |
| 动物实验 |
One cycle of therapy consists of injecting 0.1 cc of the suitable solution intraperitoneally (IV) with irinotecan at a dose of 5 mg/kg per day for 5 days on two consecutive weeks, separated by a 7-day rest period. Over the course of eight weeks, rats receive three cycles. By intratumoral injection, control animals are given 0.1 cc of sterile 0.9% sodium chloride solution according to the same protocol as group II animals[1].
Malignant neuroectodermal tumor model: Mice were inoculated subcutaneously with tumor cells (1×10⁶ cells/mouse) to establish xenografts. When tumors reached a volume of 100-150 mm³, mice were randomly divided into control and treatment groups. Irinotecan (CPT-11) was dissolved in normal saline and administered intraperitoneally at 100 mg/kg once a week for 3 consecutive weeks. Tumor volume was measured every 3 days using a caliper, and body weight was recorded to monitor toxicity [1] - Human colon tumor xenograft model: Nude mice were implanted subcutaneously with human colon tumor cells (2×10⁶ cells/mouse). When tumors grew to 200-250 mm³, mice were assigned to three groups: control, Irinotecan (CPT-11) alone, and Irinotecan (CPT-11) + TSP-1. Irinotecan (CPT-11) was dissolved in 5% dextrose solution and administered intravenously at 60 mg/kg every 4 days for 3 cycles. TSP-1 was dissolved in phosphate-buffered saline and injected subcutaneously at 2 μg/mouse every other day. Tumor size and body weight were measured twice a week [3] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
The maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) when a dose of 125 mg/m^2 is given to patients with solid tumours is 1660 ng/mL. The AUC (0-24) is 10,200 ng·h/mL. The Cmax when a dose of 340 mg/m^2 is given to patients with solid tumours is 3392 ng/mL. The AUC (0-24) is 20,604 ng·h/mL. The cumulative biliary and urinary excretion of irinotecan and its metabolites (SN-38 and SN-38 glucuronide) over a period of 48 hours following administration of irinotecan in two patients ranged from approximately 25% (100 mg/m2) to 50% (300 mg/m2). The volume of distribution of terminal elimination phase is 110 L/m^2 when a dose of 125 mg/m^2 is given to patients with solid tumours. The volume of distribution of terminal elimination phase is 234 L/m^2 when a dose of 340 mg/m^2 is given to patients with solid tumours. 13.3 L/h/m^2 [Dose of 125 mg/m^2, patients with solid tumours] 13.9 L/h/m^2 [Dose of 340 mg/m^2, patients with solid tumours] Pharmacokinetic parameters for irinotecan and SN-38 were determined in 2 pediatric solid-tumor trials at dose levels of 50 mg/sq m (60-min infusion, n=48) and 125 mg/sq m (90-min infusion, n=6). Irinotecan clearance (mean + or - S.D.) was 17.3 + or - 6.7 L/h/sq m for the 50 mg/sq m dose and 16.2 + or - 4.6 L/h/sq m for the 125 mg/sq m dose, which is comparable to that in adults. Dose-normalized SN-38 AUC values were comparable between adults and children. Minimal accumulation of irinotecan and SN-38 was observed in children on daily dosing regimens (daily X 5 every 3 weeks or (daily X 5) X 2 weeks every 3 weeks). The clinical pharmacokinetics of irinotecan (CPT11) can be described by a 2 or 3 compartment model, a mean terminal half-life of 12 hours, a volume of distribution at steady state of 168 L/sq m and a total body clearance of 15 L/sq m/hr. Irinotecan is 65% bound to plasma proteins. The areas under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) of both irinotecan and active metabolite SN38 increase proportionally to the administered dose, although interpatient variability is important. ... The mean 24 hr irinotecan urinary excretion represents 17-25% of the administered dose, whereas SN38 and its glucuronide recovery in urine is minimal (0.5 and 6%, respectively). Irinotecan and SN38 pharmacokinetics are not influenced by prior exposure to the parent drug. Irinotecan and SN38 AUCs correlate significantly with leuko-neutropenia and sometimes with the intensity of diarrhea. Increased bilirubin levels appear to influence irinotecan total body clearance. Metabolism / Metabolites Hepatic. The metabolic conversion of irinotecan to the active metabolite SN-38 is mediated by carboxylesterase enzymes and primarily occurs in the liver. SN-38 is subsequently conjugated predominantly by the enzyme UDP-glucuronosyl transferase 1A1 (UGT1A1) to form a glucuronide metabolite. ... SN38 levels achieved in humans are about 100-fold lower than corresponding irinotecan levels, but these concentrations are important since SN38 is 100- to 1,000-fold more cytotoxic than the parent compound. SN38 is 95% bound to plasma proteins. SN38 plasma decay follows closely that of the parent compound. Irinotecan is extensively metabolized in the liver. The bipiperidinocarbonyloxy group of irinotecan is first removed by a carboxyesterase to yield the corresponding carboxylic acid and SN38. This metabolite can be converted into SN38 glucuronide by UDP-glucuronyltransferase (1.1 isoform). A recently identified metabolite is the 7-ethyl-10-[4-N-(5-aminopentanoic acid)-1-piperidino]-carbonyloxy-camptothecin (APC), which is formed by the action of cytochrome P450 3A4. Numerous other unidentified metabolites are detected in bile and urine. ... Irinotecan, a camptothecin analogue, is a prodrug which requires bioactivation to form the active metabolite SN-38. SN-38 acts as a DNA topoisomerase I poison. ... Irinotecan is subjected to be shunted between CYP3A4 mediated oxidative metabolism to form two inactive metabolites APC or NPC and tissue carboxylesterase mediated hydrolysis to form SN-38 which is eventually detoxified via glucuronidation by UGT1A1 to form SN-38G. The pharmacology of this compound is further complicated by the existence of genetic inter-individual differences in activation and deactivation enzymes of irinotecan (e.g., CYP3A4, CYP3A5, UGT1A1) and sharing competitive elimination pathways with many concomitant medications, such as anticonvulsants, St. John's Wort, and ketoconazole. Efflux of the parent compound and metabolites out of cells by several drug transporters (e.g., Pgp, BCRP, MRP1, MRP2) also occurs. This review highlights the latest findings in drug activation, transport mechanisms, glucuronidation, and CYP3A-mediated drug-drug interactions of irinotecan in order to unlock some of its complicated pharmacology and to provide ideas for relevant future studies into optimization of this promising agent. Irinotecan serves as a water-soluble precursor of the lipophilic metabolite SN-38. SN-38 is formed from irinotecan by carboxylesterase-mediated cleavage of the carbamate bond between the camptothecin moiety and the dipiperidino side chain. SN-38 is approximately 1000 times as potent as irinotecan as an inhibitor of topoisomerase I purified from human and rodent tumor cell lines. In vitro cytotoxicity assays show that the potency of SN-38 relative to irinotecan varies from 2- to 2000-fold. However, the plasma area under the concentration versus time curve (AUC) values for SN-38 are 2% to 8% of irinotecan and SN-38 is 95% bound to plasma proteins compared to approximately 50% bound to plasma proteins for irinotecan. The precise contribution of SN-38 to the activity of Camptosar is thus unknown. Both irinotecan and SN-38 exist in an active lactone form and an inactive hydroxy acid anion form. A pH-dependent equilibrium exists between the two forms such that an acid pH promotes the formation of the lactone, while a more basic pH favors the hydroxy acid anion form. The metabolic conversion of irinotecan to the active metabolite SN-38 is mediated by carboxylesterase enzymes and primarily occurs in the liver. SN-38 is subsequently conjugated predominantly by the enzyme UDP-glucuronosyl transferase 1A1 (UGT1A1) to form a glucuronide metabolite. UGT1A1 activity is reduced in individuals with genetic polymorphisms that lead to reduced enzyme activity such as the UGT1A128 polymorphism. Approximately 10% of the North American population is homozygous for the UGT1A128 allele. In a prospective study, in which irinotecan was administered as a single-agent on a once-every-3-week schedule, patients who were homozygous for UGT1A128 had a higher exposure to SN-38 than patients with the wild-type UGT1A1 allele. SN-38 glucuronide had 1/50 to 1/100 the activity of SN-38 in cytotoxicity assays using two cell lines in vitro. The disposition of irinotecan has not been fully elucidated in humans. The urinary excretion of irinotecan is 11% to 20%; SN-38, <1%; and SN-38 glucuronide, 3%. The cumulative biliary and urinary excretion of irinotecan and its metabolites (SN-38 and SN-38 glucuronide) over a period of 48 hours following administration of irinotecan in two patients ranged from approximately 25% (100 mg/sq m) to 50% (300 mg/sq m). Irinotecan has known human metabolites that include (2S,3S,4S,5R)-6-[[(19S)-10,19-diethyl-14,18-dioxo-7-(4-piperidin-1-ylpiperidine-1-carbonyl)oxy-17-oxa-3,13-diazapentacyclo[11.8.0.02,11.04,9.015,20]henicosa-1(21),2,4(9),5,7,10,15(20)-heptaen-19-yl]oxy]-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid and 7-ethyl-10-[4-N-(5-aminopentanoic acid)-1-piperidino] carbonyloxycamptothecin. Biological Half-Life The half life of irinotecan is about 6 - 12 hours. The terminal elimination half-life of the active metabolite, SN-38 is 10 - 20 hours. After intravenous infusion of irinotecan in humans, irinotecan plasma concentrations decline in a multiexponential manner, with a mean terminal elimination half-life of about 6 to 12 hours. The mean terminal elimination half-life of the active metabolite SN-38 is about 10 to 20 hours. The half-lives of the lactone (active) forms of irinotecan and SN-38 are similar to those of total irinotecan and SN-38, as the lactone and hydroxy acid forms are in equilibrium. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding
30%-68% protein bound, mainly to albumin. Interactions A total of 190 patients (49 smokers, 141 nonsmokers) treated with irinotecan (90-minute intravenous administration on a 3-week schedule) were evaluated for pharmacokinetics. Complete toxicity data were available in a subset of 134 patients receiving 350 mg/sq m or 600 mg flat-fixed dose irinotecan. In smokers, the dose-normalized area under the plasma concentration-time curve of irinotecan was significantly lower (median, 28.7 v 33.9 ng x hr/mL/mg; P = .001) compared with nonsmokers. In addition, smokers showed an almost 40% lower exposure to SN-38 (median, 0.54 v 0.87 ng x h/mL/mg; P < .001) and a higher relative extent of glucuronidation of SN-38 into SN-38G (median, 6.6 v 4.5; P = .006). Smokers experienced considerably less hematologic toxicity. In particular, the incidence of grade 3 to 4 neutropenia was 6% in smokers versus 38% in nonsmokers (odds ratio [OR], 0.10; 95% CI, 0.02 to 0.43; P < .001). There was no significant difference in incidence of delayed-onset diarrhea (6% v 15%; OR, 0.34; 95% CI, 0.07 to 1.57; P = .149). This study indicates that smoking significantly lowers both the exposure to irinotecan and treatment-induced neutropenia, indicating a potential risk of treatment failure. Although the underlying mechanism is not entirely clear, modulation of CYP3A and uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase isoform 1A1 may be part of the explanation. The data suggest that additional investigation is warranted to determine whether smokers are at increased risk for treatment failure. The coadministration of protease inhibitors with anticancer drugs in the management of human immunodeficiency virus-related malignancies can cause potential drug-drug interactions. The effect of lopinavir/ritonavir (LPV/RTV) on the pharmacokinetics of irinotecan (CPT11) has been investigated in seven patients with Kaposi's sarcoma. Coadministration of LPV/RTV reduces the clearance of CPT11 by 47% (11.3+/-3.5 vs 21.3+/-6.3 l/h/m(2), P=0.0008). This effect was associated with an 81% reduction (P=0.02) of the AUC (area under the curve) of the oxidized metabolite APC (7-ethyl-10-[4-N-(5-aminopentanoic-acid)-1-piperidino]-carbonyloxycamptothecin). The LPV/RTV treatment also inhibited the formation of SN38 glucuronide (SN38G), as shown by the 36% decrease in the SN38G/SN38 AUCs ratio (5.9+/-1.6 vs 9.2+/-2.6, P=0.002) consistent with UGT1A1 inhibition by LPV/RTV. This dual effect resulted in increased availability of CPT11 for SN38 conversion and reduced inactivation on SN38, leading to a 204% increase (P=0.0001) in SN38 AUC in the presence of LPV/RTV. The clinical consequences of these substantial pharmacokinetic changes should be investigated. Irinotecan or CPT-11 [7-ethyl-10-[4-(1-piperidino)-1-piperidino]carbonyloxycamptothecine] is a derivative of camptothecine used in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer. It requires activation to SN-38 (7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecine) by carboxylesterase. Irinotecan and SN-38 are detoxified through two major metabolic pathways: the first one leads to oxidative degradation compounds, APC (7-ethyl-10-[4-N-(5-aminopentanoic acid)-1-piperidino)carbonyloxycamptothecine] and NPC [7-ethyl-10-(4-amino-1-piperidino)carbonyloxycamptothecine], and involves cytochrome P450 (3A4 isoform); the second one leads to SN-38 glucuronide (SN-38G) and involves UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT). Using human hepatic microsomes, ... the interactions of 15 drugs of common use in colorectal cancer patients on these metabolic pathways /were studied/. Only nifedipine had a significant effect on SN-38 formation, decreasing carboxylesterase activity by 50% at 100 microM and 35% at 10 microM. Three drugs had a significant effect on SN-38G formation: clonazepam increased UGT activity by 50% at 100 uM and 30% at 10 microM, and nifedipine and vinorelbine inhibited the activity by 65 and 55% at 100 uM, respectively, with no effect at 10 microM. Five drugs exerted a significant inhibition on SN-38 formation at 100 microM: clonazepam (70%), methylprednisolone (50%), nifedipine (80%), omeprazole (85%), and vinorelbine (100%). Only omeprazole and vinorelbine still exerted a significant inhibition at 10 microM (30 and 90%, respectively), whereas only vinorelbine had a significant effect at 2 and 0.5 microM (70 and 40%, respectively). In conclusion, potential clinical interactions with the metabolism of irinotecan are likely to be important for vinorelbine, which strongly inhibits irinotecan catabolism by CYP3A4 at clinically relevant concentrations, but not for the other drugs, which exert an effect at concentrations not achievable in patients. Coadministration of atazanavir sulfate, a CYP3A4 and UGT1A1 inhibitor has the potential to increase systemic exposure to SN-38, the active metabolite of irinotecan. Physicians should take this into consideration when co-administering these drugs. For more Interactions (Complete) data for IRINOTECAN (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page. In the murine malignant neuroectodermal tumor model, Irinotecan (CPT-11) at 100 mg/kg (intraperitoneal, weekly for 3 weeks) did not cause significant changes in body weight, hematological parameters (white blood cell count, red blood cell count, platelet count), or liver and kidney function indices (ALT, AST, BUN, creatinine) compared to the control group [1] - Irinotecan (CPT-11) induced apoptosis of murine peritoneal resident macrophages in vitro, which may be a potential off-target toxicity related to peritoneal immune function [5] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
Irinotecan is used in combination with cisplatin for the initial treatment of extensive small cell lung cancer. Irinotecan hydrochloride is used as a single agent for the treatment of metastatic carcinoma of the colon or rectum in patients whose disease has recurred or progressed following initial therapy with fluorouracil-based antineoplastic regimens. /Irinotecan hydrochloride/ Irinotecan is being investigated as an active agent in the treatment of metastatic or recurrent cervical cancer. Objective response rates of 13-21% have been reported with use of irinotecan as a single agent for advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix. Although no responses to irinotecan were observed in one small uncontrolled phase II study of patients with platinum-resistant advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix, responses to the drug have been reported in similar patients in another phase II study. The benefit of combination chemotherapy regimens vs single-agent therapy (e.g., cisplatin alone) has not been fully established, and further study is needed to determine the role of irinotecan in the treatment of advanced cervical cancer. /Use is not currently included in the labeling approved by the US FDA/ Irinotecan hydrochloride is used as a component of first-line therapy in combination with fluorouracil and leucovorin for the treatment of metastatic carcinoma of the colon or rectum. /Irinotecan hydrochloride/ The effectiveness of irinotecan in pediatric patients has not been established. Results from two open-label, single arm studies were evaluated. One hundred and seventy children with refractory solid tumors were enrolled in one phase 2 trial in which 50 mg/ sq m of irinotecan was infused for 5 consecutive days every 3 weeks. Grade 3-4 neutropenia was experienced by 54 (31.8%) patients. Neutropenia was complicated by fever in 15 (8.8%) patients. Grade 3-4 diarrhea was observed in 35 (20.6%) patients. This adverse event profile was comparable to that observed in adults. In the second phase 2 trial of 21 children with previously untreated rhabdomyosarcoma, 20 mg/sq m of irinotecan was infused for 5 consecutive days on weeks 0, 1, 3 and 4. This single agent therapy was followed by multimodal therapy. Accrual to the single agent irinotecan phase was halted due to the high rate (28.6%) of progressive disease and the early deaths (14%). The adverse event profile was different in this study from that observed in adults; the most significant grade 3 or 4 adverse events were dehydration experienced by 6 patients (28.6%) associated with severe hypokalemia in 5 patients (23.8%) and hyponatremia in 3 patients (14.3%); in addition Grade 3-4 infection was reported in 5 patients (23.8%) (across all courses of therapy and irrespective of causal relationship). Drug Warnings Camptosar injection should be administered only under the supervision of a physician who is experienced in the use of cancer chemotherapeutic agents. Appropriate management of complications is possible only when adequate diagnostic and treatment facilities are readily available. Camptosar can induce both early and late forms of diarrhea that appear to be mediated by different mechanisms. Both forms of diarrhea may be severe. Early diarrhea (occurring during or shortly after infusion of Camptosar) may be accompanied by cholinergic symptoms of rhinitis, increased salivation, miosis, lacrimation, diaphoresis, flushing, and intestinal hyperperistalsis that can cause abdominal cramping. Early diarrhea and other cholinergic symptoms may be prevented or ameliorated by atropine. Late diarrhea (generally occurring more than 24 hours after administration of Camptosar) can be life threatening since it may be prolonged and may lead to dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, or sepsis. Late diarrhea should be treated promptly with loperamide. Patients with diarrhea should be carefully monitored and given fluid and electrolyte replacement if they become dehydrated or antibiotic therapy if they develop ileus, fever, or severe neutropenia. Administration of Camptosar should be interrupted and subsequent doses reduced if severe diarrhea occurs. Severe myelosuppression may occur. Close monitoring is advised in patients older than 65 years of age because of increased risk of treatment-related toxicity, such as late diarrhea, during irinotecan therapy. Patients receiving irinotecan/fluorouracil/leucovorin therapy should be monitored closely (e.g., weekly assessment), particularly during the first cycle of treatment, since most of the treatment-related toxicities leading to early death occurred within the first 3-4 weeks. Changes in serum electrolytes and/or acid-base balance, including hyponatremia or hypernatremia, hypokalemia, and/or metabolic acidosis, may be an early indication of treatment-related toxicity; patients with abnormalities in serum sodium, potassium, and/or bicarbonate concentrations, with or without concomitant elevations in serum BUN or creatinine concentrations, should be evaluated carefully for dehydration and receive aggressive medical management, including fluid and electrolyte replacement. Deaths due to sepsis following severe neutropenia have been reported in patients treated with Camptosar. In addition to GI and hematologic toxicity, other severe adverse effects have occurred in patients receiving irinotecan. Hypersensitivity reactions, including severe anaphylactic or anaphylactoid reactions, have been reported. Renal impairment and acute renal failure have occurred rarely, usually in patients who became volume-depleted from severe vomiting and/or diarrhea. Cardiovascular and thromboembolic events also have been reported. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for IRINOTECAN (19 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Irinotecan is an antineoplastic enzyme inhibitor primarily used in the treatment of colorectal cancer. Irinotecan is a semisynthetic derivative of camptothecin. Camptothecins interact specifically with topoisomerase I, an enzyme in the cell nucleus that regulates DNA topology and facilitates nuclear processes such as DNA replication, recombination, and repair. During these processes, topoisomerase I relieves torsional strain in DNA by inducing reversible single-strand breaks, allowing single DNA strands to pass through the break. The 3'-DNA terminus of the broken DNA strands bind covalently with the topoisomerase enzyme to form a catalytic intermediate called a cleavable complex. After the DNA is sufficiently relaxed and the strand passage reaction is complete, DNA topoisomerase reattaches the broken DNA strands to form the chemically unaltered topoisomers that allow transcription to proceed. Irinotecan and its active metabolite SN-38 bind to the topoisomerase I-DNA complex and prevent religation of these single-strand breaks. Current research suggests that the cytotoxicity of irinotecan is due to double-strand DNA damage produced during DNA synthesis when replication enzymes interact with the ternary complex formed by topoisomerase I, DNA, and either Irinotecan or SN-38. Mammalian cells cannot efficiently repair these double-strand breaks. The precise contribution of SN-38 to the activity of irinotecan in humans is not known. Irinotecan is cell cycle phase-specific (S-phase). Irinotecan (CPT-11) exerts its antitumor effect primarily by inhibiting Topoisomerase I, which leads to the accumulation of DNA single-strand breaks and subsequent induction of apoptosis in tumor cells [2] - The combination of Irinotecan (CPT-11) with antiangiogenic agent TSP-1 showed synergistic antitumor activity against advanced human colon tumor xenografts, suggesting a potential clinical application of this combination strategy [3] |
| 分子式 |
C33H38N4O6
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
586.68
|
|
| 精确质量 |
586.279
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 67.56; H, 6.53; N, 9.55; O, 16.36
|
|
| CAS号 |
97682-44-5
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
100286-90-6 (HCl); 136572-09-3 (HCl trihydrate); 143490-53-3 (Lactone Impurity) ; 97682-44-5; 1329502-92-2 (Carboxylate Sodium Salt)
|
|
| PubChem CID |
60838
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to yellow solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
873.4±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
222-223 °C
222-223 °C 222 - 223 °C |
|
| 闪点 |
482.0±34.3 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.689
|
|
| LogP |
4.35
|
|
| tPSA |
114.2
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
43
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1200
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
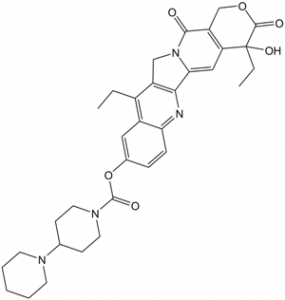
C(C1C2C=C(C=CC=2N=C2C3=CC4[C@@](C(OCC=4C(=O)N3CC=12)=O)(O)CC)OC(N1CCC(N2CCCCC2)CC1)=O)C
|
|
| InChi Key |
UWKQSNNFCGGAFS-XIFFEERXSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C33H38N4O6/c1-3-22-23-16-21(43-32(40)36-14-10-20(11-15-36)35-12-6-5-7-13-35)8-9-27(23)34-29-24(22)18-37-28(29)17-26-25(30(37)38)19-42-31(39)33(26,41)4-2/h8-9,16-17,20,41H,3-7,10-15,18-19H2,1-2H3/t33-/m0/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
[(19S)-10,19-diethyl-19-hydroxy-14,18-dioxo-17-oxa-3,13-diazapentacyclo[11.8.0.02,11.04,9.015,20]henicosa-1(21),2,4(9),5,7,10,15(20)-heptaen-7-yl] 4-piperidin-1-ylpiperidine-1-carboxylate
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.55 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.55 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.55 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 30% Propylene glycol , 5% Tween 80 , 65% D5W: 30 mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7045 mL | 8.5225 mL | 17.0451 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3409 mL | 1.7045 mL | 3.4090 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1705 mL | 0.8523 mL | 1.7045 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Dinutuximab With Chemotherapy, Surgery and Stem Cell Transplantation for the Treatment of Children With Newly Diagnosed High Risk Neuroblastoma
CTID: NCT06172296
Phase: Phase 3 Status: Recruiting
Date: 2024-12-02
|