| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 靶点 |
BRD4 (1/2) (IC50= 77/33 nM)
BET family bromodomains (BRD2 BD1: IC₅₀ ≈ 0.13 μM; BRD2 BD2: IC₅₀ ≈ 0.45 μM; BRD3 BD1: IC₅₀ ≈ 0.11 μM; BRD3 BD2: IC₅₀ ≈ 0.39 μM; BRD4 BD1: IC₅₀ ≈ 0.07 μM; BRD4 BD2: IC₅₀ ≈ 0.32 μM; no significant inhibition of non-BET bromodomains (e.g., CREBBP) with IC₅₀ > 10 μM) [1] - BRDT (BET family bromodomain testis-specific) (BRDT BD1: IC₅₀ ≈ 0.08 μM; BRDT BD2: IC₅₀ ≈ 0.29 μM) [3] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
(+)-JQ-1 是 Bromodomain BET 家族的一种强效、高选择性和 Kac 竞争性抑制剂。 (+)-JQ-1(100 nM,48 小时)可促进鳞状细胞发育,细胞纺锤体形成、变平和角蛋白表达增强即可证明这一点。通过定量免疫组织化学评估,与 (-)-JQ1 (250 nM) 和载体对照相比,(+)-JQ-1 (250 nM) 刺激处理的 NMC 797 细胞中角蛋白的快速表达。 (+)-JQ-1(相对于 (-)-JQ1 (250 nM))在处理的 NMC 797 细胞中引起时间依赖性强 (3+) 角蛋白染色 [1]。添加 (+)-JQ-1 后几乎立即观察到自噬基因的去抑制[2]。 (+)-JQ-1 是 BET 家族共激活蛋白 BRD4 的强效噻吩二氮卓抑制剂 (Kd=90 nM),该蛋白通过 MYC 癌基因的转录调节参与癌症的发展。 (+)-JQ-1 的剂量范围实验表明可有效抑制 H4Kac4 结合,小鼠 BRDT (1) 的 IC50 值为 10 nM,人 BRDT (1) 的 IC50 值为 11 nM [3]。
1. 癌细胞抗增殖活性:(+)-JQ1 对血液系统及实体瘤细胞均有强效杀伤作用。急性髓系白血病(AML)细胞系MOLM-13的72小时MTT实验IC₅₀≈0.12 μM;多发性骨髓瘤细胞系MM.1S的IC₅₀≈0.15 μM;肺癌细胞系NCI-H460的IC₅₀≈0.21 μM。在0.5 μM浓度下,MOLM-13细胞的克隆形成能力(甲基纤维素克隆实验,14天)下降>80%[1] 2. MYC转录抑制:MOLM-13细胞经0.5 μM (+)-JQ1 处理24小时后,qRT-PCR显示MYC mRNA水平下降2.8倍,Western blot显示MYC蛋白减少3.2倍。ChIP-qPCR证实,(+)-JQ1 使BRD4与MYC启动子的结合量较溶媒组减少约70%[1] 3. 自噬与溶酶体功能激活:HeLa细胞经0.5 μM (+)-JQ1 处理48小时后,Western blot显示自噬标志物LC3B-II蛋白增加2.5倍,自噬底物p62蛋白减少1.8倍。qRT-PCR显示自噬相关基因ATG5(+2.1倍)、ATG7(+1.9倍)上调。免疫荧光显示LC3B斑点数从约5个/细胞增至25个/细胞,溶酶体标志物LAMP1蛋白增加1.7倍[2] 4. 精原细胞分化抑制:原代小鼠精原细胞经0.2 μM (+)-JQ1 培养72小时后,减数分裂标志物SYCP3的免疫荧光显示,SYCP3阳性细胞比例从35%降至8%。Western blot(染色质分级分离实验)证实BRD4与染色质的结合量减少90%[3] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
将与已形成肿瘤相匹配的小鼠队列随机每天接受载体或 (+)-JQ1 (50 mg/kg) 腹膜内注射。 FDG-PET 成像用于在治疗后四天和随机分组之前评估小鼠。当施用 (+)-JQ1 时,FDG 摄取显着减少。肿瘤体积的评估表明,JQ1 治疗抑制了肿瘤生长。 CD1 小鼠用于口服和静脉给药后 (+)-JQ1 的药代动力学研究。静脉注射(5 mg/kg)后(+)-JQ1 平均血浆浓度的时间曲线。静脉注射(+)-JQ1的半衰期(T1/2)约为1小时,其药代动力学特征显示出良好的药物暴露(AUC=2090 hr*ng/mL)。口服剂量(10 mg/kg)后,创建了 (+)-JQ1 的平均血浆浓度-时间曲线。口服(+)-JQ1药代动力学参数显示出良好的药物暴露(AUC=2090 hr*ng/mL)、血浆峰浓度(Cmax=1180 ng/mL)和口服生物利用度(F=49%)[1]。
1. AML异种移植瘤生长抑制:荷MOLM-13皮下异种移植瘤的裸鼠(肿瘤体积≈100 mm³,n=6/组),经(+)-JQ1(50 mg/kg,口服灌胃,每日1次,21天)或溶媒(5% DMSO+20% Cremophor EL+75%生理盐水)处理。第21天,处理组平均肿瘤体积≈210 mm³,溶媒组≈950 mm³,肿瘤生长抑制率(TGI)≈78%。肿瘤组织中MYC mRNA下降2.8倍,Western blot显示BRD4蛋白减少65%[1] 2. 可逆性男性避孕作用:8周龄雄性C57BL/6小鼠(n=8/组)经(+)-JQ1(25 mg/kg,腹腔注射,每日1次,28天)或溶媒(10% DMSO+90%生理盐水)处理。处理后,附睾精子数量从1.2×10⁷个/附睾降至0.3×10⁷个/附睾,精子活力从65%降至12%。停药4周后,精子数量和活力恢复至正常水平的85%,且无睾丸组织病理学损伤(HE染色)及血清睾酮水平变化[3] |
| 酶活实验 |
乙酰组蛋白结合测定。[1]
如前所述51进行分析,对制造商的方案(PerkinElmer,USA)稍作修改。将所有试剂在补充有0.05%CHAPS的50mM HEPES、100mM NaCl、0.1%BSA、pH 7.4中稀释,并在加入平板之前使其平衡至室温。在150–0μM的范围内制备配体的24点1:2系列稀释液,并将4μl转移到低体积384孔板中,然后加入4μl His标记蛋白(BRD4(1),250 nM,BRD4(2)和CREBBP,2000 nM)。将板密封并在室温下孵育30分钟,然后将4μl等摩尔浓度的生物素化肽添加到蛋白质中[BRD4(1)和BRD4(2)的肽:H4K5acK8acK12acK16ac,HSGRGK(Ac)GGK(Ac。在弱光条件下加入4μl链霉亲和素包被的供体珠(25μg/ml)和4μl镍螯合受体珠(25µg/ml)之前,将板密封并再孵育30分钟。将板箔密封以避光,在室温下孵育60分钟,并使用AlphaScreen 680激发/570发射滤光片组在PHERAstar FS板读取器上读取。对照相应的DMSO对照标准化后,在Prism 5(GraphPad Software,USA)中计算IC50值,并作为20μl反应体积中化合物的最终浓度给出。 1. BRD4结合SPR实验:采用胺偶联法将重组人BRD4 BD1(10 μg/mL)固定于CM5传感器芯片。(+)-JQ1 用运行缓冲液(10 mM HEPES pH7.4、150 mM NaCl、0.05% Tween-20)稀释为0.01–1 μM,以30 μL/min流速注入芯片,记录结合-解离曲线,计算平衡解离常数(Kd)≈0.05 μM[1] 2. ITC结合热力学实验:25°C条件下,将50 μM (+)-JQ1 逐滴加入5 μM BRD4 BD1溶液(缓冲液:20 mM Tris-HCl pH7.5、150 mM NaCl),记录热功率变化。推导结合参数:焓变(ΔH)≈-25 kJ/mol,结合常数(Ka)≈2×10⁷ M⁻¹[1] 3. BRD4抑制HTRF实验:将BRD4 BD1(20 nM)、生物素化组蛋白H4K5ac肽(10 nM)与(+)-JQ1(0.001–10 μM)在反应缓冲液中孵育1小时,加入链霉亲和素-铕与抗BRD4抗体-别藻蓝蛋白,检测665 nm/620 nm荧光比,计算BRD4 BD1的IC₅₀≈0.07 μM[1] |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞增殖测定。[1]
将细胞接种到白色384孔微量滴定板(Nunc)中,在总体积为50μl的培养基中,每孔500个细胞。797、TT和TE10细胞生长在含有1%青霉素/链霉素和10%FBS的DMEM中。Per403细胞生长在含1%青霉素/链霉菌和20%FBS的DMEM中。患者来源的NMC 11060细胞生长在具有10%FBS和1%青霉素/链球菌素的RPMI中。通过机器人销钉转移(PerkinElmer JANUS配备有V&P Scientific 100 nl销钉工具)将化合物递送至微量滴定分析板。在37ºC下孵育48小时后,裂解细胞,并使用商业增殖测定法评估孔的总ATP含量。根据剂量分析重复测量,并通过逻辑回归计算IC50的估计值。[1] 细胞生长测定。[1] 将细胞以每孔1.5×104个细胞的浓度接种在6孔组织培养皿中。细胞在2ml DMEM(797)或RPMI(11060)中生长,所述DMEM或RPMI含有10%胎牛血清、1%青霉素/链霉素和250nM(+)-JQ1或等效体积的DMSO(0.025%)。每天更换每口井中一半的介质。在第0天、第1天、第3天、第7天和第10天,将分配给每个时间点的细胞培养皿进行胰蛋白酶消化,以1:1的比例与0.4%台盼蓝混合,并使用Countess自动细胞计数器计数。 1. MOLM-13细胞MTT抗增殖实验:MOLM-13细胞以5×10³个/孔接种96孔板,用含10% FBS的RPMI 1640培养基过夜培养。加入0.01–1 μM (+)-JQ1,37°C、5% CO₂孵育72小时。每孔加MTT试剂(5 mg/mL,10 μL)孵育4小时,加二甲亚砜(100 μL/孔)溶解甲臜,检测570 nm吸光度,非线性回归计算IC₅₀[1] 2. MYC启动子结合ChIP-qPCR实验:MOLM-13细胞经0.5 μM (+)-JQ1 处理24小时后,用1%甲醛交联,超声破碎染色质。抗BRD4抗体免疫沉淀后,用MYC启动子特异性引物进行qPCR,以Input DNA为参照定量BRD4结合量[1] 3. HeLa细胞自噬检测:HeLa细胞经0.1–1 μM (+)-JQ1 处理48小时。Western blot实验:RIPA裂解细胞,检测LC3B、p62、LAMP1蛋白;免疫荧光实验:4%多聚甲醛固定细胞,抗LC3B抗体(荧光二抗标记)染色,共聚焦显微镜计数LC3B斑点[2] 4. 精原细胞分化实验:从小鼠睾丸分离原代精原细胞,接种6孔板,加入0.05–0.5 μM (+)-JQ1 培养72小时。细胞固定后,抗SYCP3抗体(减数分裂标志物)与DAPI(核染色)染色,荧光显微镜计数SYCP3阳性细胞比例[3] |
| 动物实验 |
\n1. Dissolved in 5% dextrose; 50 mg/kg; i.p. injection; Nature. 2010 Dec 23;468(7327):1067-73;
\n2. Dissolved in 10% DMSO and 90% of a 10% 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin solution; Leukemia. 2017 Oct;31(10):2037-2047.; \n3. Dissolved in 1% DMSO+5% Glucose+ddH2O; Cell. 2018 Sep 20;175(1):186-199.e19.; \n4. Dissolved in 20% hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin, 5% DMSO, 0.2% Tween-80 in saline; Mol Cancer Ther. 2016 Jun;15(6):1217-26.; \n5. Dissolved in 1:1 propylene glycol:water; J Biol Chem. 2016 Nov 4;291(45):23756-23768.; \n6. Dissolved in 5% DMSO in 10% 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin solution; Cancer Lett. 2017 Aug 28;402:100-109. \n\nXenograft Efficacy Studies.[1] \nNMC 797 xenografts were established by injecting NMC 797 cells (107) in 30 % Matrigel (BD Biosciences) into the flank of 6 week-old female NCr nude mice. Twelve days after injection, mice with measureable tumors were divided into cohorts to be treated with JQ1 at 50 mg kg-1 IP or vehicle (5 % DMSO in 5 % dextrose). For FDG-PET studies, mice with established tumors measuring approximately 1 cm in the largest linear dimension underwent baseline CT/PET imaging 1 h after injection of 250 μCi of FDG (Pre-treatment). Mice were then treated with four daily doses of 50 mg kg-1 of racemic JQ1 by intraperitoneal injection. Two hours after the fourth dose of JQ1 or vehicle, mice underwent repeat FDG-PET imaging (Post-treatment). The integrated signal encompassed within the entire tumor volume is expressed as the percent of injected dose per gram (% ID/gm). Tumors were fixed in 10 % buffered formalin for histopathological analysis. For tumor caliper studies, the average size of tumors in the JQ1 treatment group (n = 8) and vehicle group (n = 7) were similar (63.8 ± 17.1 and 73.6 ± 14.4 mm3 respectively) at the start of treatment. Animals were followed daily for clinical symptoms. Tumor measurements were assessed by caliper measurements, and volume calculated using the formula Vol = 0.5 x L x W2. After 2 weeks of treatment, all mice were humanely euthanized, and tumors were fixed in 10 % formalin for histopathological examination. Statistical significance of tumor volumes was calculated by two-sided Students t-test.[1] \nPrimary NMC Xenograft Studies.[1] \nA primary xenograft model of NMC was established by injecting NCr nude mice with primary cells (107 cells in 100 μl of 30 % Matrigel in 70 % PBS) collected from malignant pleural fluid obtained with IRB approval and informed consent from a patient at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Brigham & Women’s Hospital. As above, four mice with established tumors measuring approximately 1 cm in the largest linear dimension underwent baseline CT/PET imaging 1 h after injection of 250 μCi of FDG (Pre-treatment). Mice were then treated with four daily doses of 50 mg kg-1 of (+)-JQ1 by intraperitoneal injection. Animals were followed daily for clinical symptoms. Two hours after the fourth dose of (+)-JQ1 or vehicle, mice underwent repeat FDG-PET imaging (Post-treatment). The integrated signal encompassed within the entire tumor volume is expressed as the percent of injected dose per gram (%ID/gm). Tumors were fixed in 10 % buffered formalin for histopathological analysis. At the conclusion of the study, all mice were humanely euthanized, and tumors were fixed in 10 % formalin for histopathological examination. Survival (30 days) studies performed with NMC Per403 and 11060 xenografts were initiated as above. For these studies, (+)-JQ1 was administered at a dose of 50 mg kg-1 by daily intraperitoneal injection. The average size of tumors in the (+)-JQ1 treatment group (n = 10) and vehicle group (n = 10) were similar at the start of treatment. Animals were followed daily for clinical symptoms. Tumor measurements were assessed by caliper measurements, and volume calculated using the formula Vol = 0.5xLxW2. Statistical significance of tumor volumes was calculated by two-sided Students t-test. Comparative survival analysis was performed using the Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) Test, and data were presented as a Kaplain-Meier plot annotated with a measure of statistical significance (pvalue). All animal studies were approved by the IACUC of the DFCI. \nPharmacokinetic Studies in Mice.[1] Male CD1 mice (24 – 29 gm) were treated with a single dose of (+)-JQ1 at 5 mg kg-1 for intravenous tail vein injection studies and 10 mg kg-1 for oral gavage studies. Approximately 150 μl of blood were taken from animals by retro-orbital puncture under anesthesia with Isoflurane into EDTA tubes at pre-specified time intervals: 0.033, 0.083, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 5, 8 and 24 hours. Three animals were analyzed per time point. Blood samples were put on ice and centrifuged to obtain plasma samples (2000 x.g, 5 min under 4 °C) within 15 minutes post-sampling. Plasma samples were stored at approximately -70 °C until analysis was performed. Mice were provided free access to food and water throughout the study. Compound was formulated for intravenous injection in 10 % DMSO and 10 % HP-β-CD. Pharmcokinetic studies and pharmacologic assay development was performed at ChemPartner (Shanghai, CHINA). Data were analyzed by J.E.B. using Microsoft Excel and GraphPad Prism 5.02. \n In vivo formulations used (reported): 1. MOLM-13 AML xenograft model: Female nude mice (6–8 weeks old, 18–22 g) were subcutaneously injected with 5×10⁶ MOLM-13 cells (suspended in 0.2 mL PBS:Matrigel = 1:1) into the right flank. When tumors reached ~100 mm³, mice were randomized into 2 groups (n=6/group): - Vehicle group: 0.2 mL of 5% DMSO + 20% Cremophor EL + 75% saline, oral gavage, once daily for 21 days; - (+)-JQ1 group: 50 mg/kg (+)-JQ1 (dissolved in the above vehicle to 250 mg/mL), 0.2 mL oral gavage, once daily for 21 days. Tumor volume (length × width² / 2) and body weight were measured every 3 days. On day 22, mice were euthanized, and tumors were collected for mRNA and protein analysis [1] 2. Male contraception mouse model: Male C57BL/6 mice (8 weeks old, 22–25 g) were randomized into 2 groups (n=8/group): - Vehicle group: 0.1 mL of 10% DMSO + 90% saline, intraperitoneal injection, once daily for 28 days; - (+)-JQ1 group: 25 mg/kg (+)-JQ1 (dissolved in the above vehicle to 250 mg/mL), 0.1 mL intraperitoneal injection, once daily for 28 days. After treatment, epididymides were collected to count sperm and measure motility. Testes were fixed for HE staining. Four weeks after drug withdrawal, sperm parameters were re-evaluated [3] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
The bromodomain inhibitor (+)-JQ1 is a highly validated chemical probe; however, it exhibits poor in vivo pharmacokinetics.
The large differences between individual mice in this small study may lead to questions about the significance of the modest average differences obtained from this pharmacokinetic analysis. Given that our main goal was to assess the relative effects of deuteration on clearance of (+)-JQ1 rather than determining the absolute pharmacokinetic parameters of (+)-JQ1 and (+)-JQ1-D, we examined the isotopomeric ratios for (+)-JQ1 and for its major metabolite M19 from the pharmacokinetic time course for evidence of the effects of deuteration. In both male and female mice, the (+)-JQ1/(+)-JQ1-D ratio drops steadily over the examined time course (Figure 7), indicating that (+)-JQ1 is cleared more rapidly than (+)-JQ1-D.[https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10788937/] A plasma pharmacokinetic study of JQ1 was performed in non-tumor bearing mice dosed with 30 mg/kg JQ1 intraperitoneally. All JQ1 concentrations collected after 6 h post-dose fell under the LOQ. JQ1 total plasma concentration-time data were well captured with a linear one-compartment model, in which the intraperitoneal absorption was assumed immediate and total (Figure 6). The model parameter estimates are reported in Table 7. The limited sampling model determined the following informative time-points for plasma sampling during the cerebral microdialysis study: 15 min, 1 h, and 6 h post-dose. [https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8384680/] 1. Oral bioavailability: Male SD rats (250–300 g, n=3/time point) were administered (+)-JQ1 via oral gavage (50 mg/kg) or intravenous injection (10 mg/kg). Oral bioavailability was calculated as ~35% (based on AUC₀₋₂₄ₕ: oral ≈ 15 μM·h; intravenous ≈ 43 μM·h) [1] 2. Plasma pharmacokinetics: After oral administration (50 mg/kg) in rats, key parameters were: Cₘₐₓ ≈ 2.8 μM (Tₘₐₓ = 1.5 h), terminal half-life (t₁/₂) ≈ 3.2 h, clearance (CL) ≈ 18 mL/kg/min. After intravenous administration (10 mg/kg): Cₘₐₓ ≈ 12 μM, t₁/₂ ≈ 2.8 h, CL ≈ 15 mL/kg/min [1] 3. Tissue distribution: In rats 1.5 h after oral (+)-JQ1 (50 mg/kg), LC-MS/MS detected concentrations: liver ≈ 4.5 μM, kidney ≈ 3.2 μM, MOLM-13 xenograft tumor ≈ 3.8 μM, brain ≈ 0.3 μM (low blood-brain barrier penetration) [1] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
1. Subchronic toxicity in rats: Rats treated with oral (+)-JQ1 (50 mg/kg, 21 days) showed <5% body weight change vs. vehicle. Serum ALT/AST was ~1.1-fold of vehicle (within normal range), and creatinine was normal. Peripheral white blood cell count was ~0.9-fold of vehicle (no significant difference) [1]
2. Testicular safety in mice: Mice treated with intraperitoneal (+)-JQ1 (25 mg/kg, 28 days) had intact seminiferous tubule structure (HE staining) with no inflammation or necrosis. Serum testosterone levels were ~0.9-fold of vehicle (no significant difference) [3] 3. Plasma protein binding: (+)-JQ1 (1 μM) had ~85% plasma protein binding in human plasma (measured by ultrafiltration with 30 kDa cutoff membranes and LC-MS/MS) [1] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
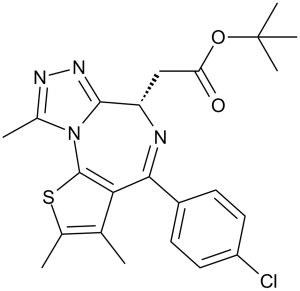
JQ1 is a member of the class of thienotriazolodiazepines that is the tert-butyl ester of [(6S)-4-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,3,9-trimethyl-6H-thieno[3,2-f][1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a][1,4]diazepin-6-yl]acetic acid. An inhibitor of bromodomain-containing protein 4 that exhibits anti-cancer and cardioprotective properties. It has a role as a bromodomain-containing protein 4 inhibitor, a cardioprotective agent, an antineoplastic agent, an anti-inflammatory agent, an angiogenesis inhibitor, an apoptosis inducer and a ferroptosis inducer. It is a thienotriazolodiazepine, an organochlorine compound, a carboxylic ester and a tert-butyl ester.
\n\nEpigenetic proteins are intently pursued targets in ligand discovery. So far, successful efforts have been limited to chromatin modifying enzymes, or so-called epigenetic 'writers' and 'erasers'. Potent inhibitors of histone binding modules have not yet been described. Here we report a cell-permeable small molecule (JQ1) that binds competitively to acetyl-lysine recognition motifs, or bromodomains. High potency and specificity towards a subset of human bromodomains is explained by co-crystal structures with bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) family member BRD4, revealing excellent shape complementarity with the acetyl-lysine binding cavity. Recurrent translocation of BRD4 is observed in a genetically-defined, incurable subtype of human squamous carcinoma. Competitive binding by JQ1 displaces the BRD4 fusion oncoprotein from chromatin, prompting squamous differentiation and specific antiproliferative effects in BRD4-dependent cell lines and patient-derived xenograft models. These data establish proof-of-concept for targeting protein-protein interactions of epigenetic 'readers', and provide a versatile chemical scaffold for the development of chemical probes more broadly throughout the bromodomain family.[1] \n\nAutophagy is a membrane-trafficking process that directs degradation of cytoplasmic material in lysosomes. The process promotes cellular fidelity, and while the core machinery of autophagy is known, the mechanisms that promote and sustain autophagy are less well defined. Here we report that the epigenetic reader BRD4 and the methyltransferase G9a repress a TFEB/TFE3/MITF-independent transcriptional program that promotes autophagy and lysosome biogenesis. We show that BRD4 knockdown induces autophagy in vitro and in vivo in response to some, but not all, situations. In the case of starvation, a signaling cascade involving AMPK and histone deacetylase SIRT1 displaces chromatin-bound BRD4, instigating autophagy gene activation and cell survival. Importantly, this program is directed independently and also reciprocally to the growth-promoting properties of BRD4 and is potently repressed by BRD4-NUT, a driver of NUT midline carcinoma. These findings therefore identify a distinct and selective mechanism of autophagy regulation.[2] \n\nA pharmacologic approach to male contraception remains a longstanding challenge in medicine. Toward this objective, we explored the spermatogenic effects of a selective small-molecule inhibitor (JQ1) of the bromodomain and extraterminal (BET) subfamily of epigenetic reader proteins. Here, we report potent inhibition of the testis-specific member BRDT, which is essential for chromatin remodeling during spermatogenesis. Biochemical and crystallographic studies confirm that occupancy of the BRDT acetyl-lysine binding pocket by JQ1 prevents recognition of acetylated histone H4. Treatment of mice with JQ1 reduced seminiferous tubule area, testis size, and spermatozoa number and motility without affecting hormone levels. Although JQ1-treated males mate normally, inhibitory effects of JQ1 evident at the spermatocyte and round spermatid stages cause a complete and reversible contraceptive effect. These data establish a new contraceptive that can cross the blood:testis boundary and inhibit bromodomain activity during spermatogenesis, providing a lead compound targeting the male germ cell for contraception.[3] 1. Mechanism of BET inhibition: (+)-JQ1 competitively binds to the acetyl-lysine binding pocket of BET bromodomains (e.g., BRD4), preventing BET proteins from associating with chromatin. This blocks transcription of BET-dependent oncogenes (e.g., MYC), which drive proliferation in multiple cancers [1] 2. Autophagy activation mechanism: BRD4 negatively regulates autophagy by binding to promoters of autophagy-related genes (e.g., ATG5) and suppressing their transcription. (+)-JQ1 inhibits BRD4, relieving this suppression and activating autophagy—enhancing cancer cell sensitivity to nutrient deprivation [2] 3. Male contraceptive potential: BRDT is essential for spermatogenesis (expressed exclusively in testicular germ cells during meiosis). (+)-JQ1 inhibits BRD4, blocking spermatogonial differentiation into spermatocytes and causing reversible oligoasthenospermia. It avoids hormonal side effects (unlike traditional contraceptives), making it a candidate for non-hormonal male contraception [3] |
| 分子式 |
C23H25CLN4O2S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
456.99
|
|
| 精确质量 |
456.138
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 60.45; H, 5.51; Cl, 7.76; N, 12.26; O, 7.00; S, 7.02
|
|
| CAS号 |
1268524-70-4
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
(R)-(-)-JQ1 Enantiomer;1268524-71-5;JQ-1 (carboxylic acid);202592-23-2
|
|
| PubChem CID |
46907787
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to yellow solid
|
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
610.4±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
322.9±34.3 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.657
|
|
| LogP |
4.49
|
|
| tPSA |
97.61
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
31
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
706
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
ClC1C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=1[H])C1C2C(C([H])([H])[H])=C(C([H])([H])[H])SC=2N2C(C([H])([H])[H])=NN=C2[C@]([H])(C([H])([H])C(=O)OC(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])N=1
|
|
| InChi Key |
DNVXATUJJDPFDM-KRWDZBQOSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C23H25ClN4O2S/c1-12-13(2)31-22-19(12)20(15-7-9-16(24)10-8-15)25-17(11-18(29)30-23(4,5)6)21-27-26-14(3)28(21)22/h7-10,17H,11H2,1-6H3/t17-/m0/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.47 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.47 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.47 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 2% DMSO+30% PEG 300+5% Tween 80+ddH2O:5mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1882 mL | 10.9412 mL | 21.8823 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4376 mL | 2.1882 mL | 4.3765 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2188 mL | 1.0941 mL | 2.1882 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Leukemia and lymphoma cell lines are broadly sensitive to BET-bromodomain inhibition.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2011 Oct 4;108(40):16669-74. |
Gene expression profiling of LP-1 and Raji cells treated with active or inactive BET inhibitors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2011 Oct 4;108(40):16669-74. |
Small molecule BET-bromodomain inhibition suppressesMYCtranscription.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2011 Oct 4;108(40):16669-74. |
MYC reconstitution significantly protects cells from BET-mediated effects.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2011 Oct 4;108(40):16669-74. |
BET-bromodomain inhibition decreases tumor load in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2011 Oct 4;108(40):16669-74. |
Integrated genomic rationale for BET bromodomains as therapeutic targets in MM.Cell.2011 Sep 16;146(6):904-17. |
Inhibition of Myc-dependent transcription by theJQ1BET bromodomain inhibitor.Cell.2011 Sep 16;146(6):904-17. |
BET inhibition suppressesMYCtranscription in MM.Cell.2011 Sep 16;146(6):904-17. |
Regulation ofMYCtranscription by BET bromodomains.Cell.2011 Sep 16;146(6):904-17. |
Anti-myeloma activity ofJQ1in vitro.Cell.2011 Sep 16;146(6):904-17. |
JQ1induces cell cycle arrest and cellular senescence in MM cells.Cell.2011 Sep 16;146(6):904-17. |
Translational implications of BET bromodomain inhibition in MM.Cell.2011 Sep 16;146(6):904-17. |
|
 |
 |