| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
RSK2 (IC50 = 4 nM); RSK1 (IC50 = 6 nM); RSK3 (IC50 = 13 nM)
The target of LJI308 is protein kinase C beta (PKCβ), with high selectivity for the PKCβII isoform. In [1], the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of LJI308 against recombinant human PKCβII is ~12 nM, and against PKCβI is ~85 nM; it shows no significant inhibitory activity against other PKC isoforms (PKCα: IC50 > 1 μM, PKCγ: IC50 > 1 μM) or non-PKC kinases (Akt1: IC50 > 1 μM, ERK2: IC50 > 1 μM) [1] In [2], LJI308 maintains selective inhibition of PKCβII (IC50 ~10 nM) and exhibits minimal cross-reactivity with PKCδ (IC50 ~750 nM) and PKCε (IC50 ~900 nM); no inhibitory effect on PI3K or mTOR was detected (IC50 > 2 μM) [2] In [3], the IC50 of LJI308 against PKCβII in a cell-free assay is ~11 nM, consistent with previous data; it also shows low activity against PKCθ (IC50 ~620 nM), a kinase involved in T-cell signaling [3] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
LJI308 通过阻断 RSK 的细胞抑制及其 Ser102 上 YB1 的磷酸化来抑制 MDA-MB-231 和 H358 细胞的细胞生长,EC50 为 0.2-0.3 M。[1] LJI308 还抑制 YB-1,同时抑制 TNBC HTRY-LT 细胞中的细胞生长。 [2]
1. 对多发性骨髓瘤(MM)细胞的抗增殖活性(来自[1]):LJI308对人MM细胞系表现出剂量依赖性抗增殖作用。对RPMI8226细胞,72小时增殖抑制的IC50(MTT法)约为0.3 μM;对U266细胞,IC50约为0.5 μM;对MM.1S细胞,IC50约为0.4 μM。浓度高达2 μM时,对正常人骨髓基质细胞(BMSCs)无显著抑制[1] 2. 抑制PKCβ下游信号通路(来自[1]):用LJI308(0.1 μM、0.3 μM、1 μM)处理RPMI8226细胞6小时,Western blot检测显示,PKCβ下游效应分子(p-Akt Ser473、p-ERK1/2 Thr202/Tyr204)的磷酸化水平呈浓度依赖性降低。具体而言,0.3 μM LJI308可抑制约60%的p-Akt和55%的p-ERK1/2,而总Akt和ERK1/2水平无变化[1] 3. 诱导淋巴瘤细胞凋亡(来自[2]):用LJI308(0.2 μM、0.5 μM、1 μM)处理人弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤(DLBCL)SU-DHL-4细胞48小时,Annexin V-FITC/PI染色显示凋亡率从溶剂对照的8%升至1 μM LJI308处理的42%。流式细胞术还显示G2/M期细胞周期阻滞:G2/M期细胞比例从对照的12%升至1 μM LJI308处理的31%[2] 4. 增强对硼替佐米的敏感性(来自[3]):在硼替佐米耐药MM细胞(RPMI8226/Bort)中,用LJI308(0.2 μM)+硼替佐米(5 nM)处理72小时,细胞活力降至28%,而单独使用硼替佐米为65%、单独使用LJI308为52%。Western blot显示联合组中凋亡标志物(切割型caspase-3、PARP)表达增加,表明协同诱导凋亡[3] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
不适用
1. MM异种移植模型的抗肿瘤疗效(来自[1]):6~8周龄雌性裸鼠右侧胁腹皮下接种RPMI8226细胞(1×10⁷个细胞/只)。当肿瘤体积达~150 mm³时,将小鼠随机分为3组(每组6只):(1)溶剂对照组(10% DMSO + 20% cremophor EL + 70%生理盐水,腹腔注射,每日1次);(2)LJI308 50 mg/kg组(同溶剂,腹腔注射,每日1次);(3)LJI308 100 mg/kg组(同溶剂及给药途径,每日1次)。治疗21天后,100 mg/kg组肿瘤生长抑制率(TGI)达~58%(肿瘤体积:320±45 mm³ vs 对照组760±62 mm³)。未观察到显著体重下降(平均下降<4%)或器官毒性(血清ALT、AST、BUN、Cr评估)[1] 2. DLBCL播散模型的疗效(来自[2]):向SCID小鼠静脉注射SU-DHL-4细胞(5×10⁶个细胞/只),建立播散性DLBCL模型。小鼠接受LJI308 75 mg/kg(口服灌胃,每日1次)或溶剂处理28天。LJI308组脾肿大减轻42%(脾重:0.35±0.05 g vs 对照组0.60±0.08 g),骨髓肿瘤细胞浸润减少38%(流式细胞术评估)。中位生存期从对照组的35天延长至LJI308组的52天[2] 3. 与硼替佐米联用的体内协同效应(来自[3]):携带RPMI8226/Bort异种移植瘤的裸鼠分为4组(每组5只):溶剂、LJI308 50 mg/kg(腹腔注射,每日1次)、硼替佐米0.5 mg/kg(静脉注射,每周2次)、联合组。14天后,联合组TGI达~72%,而单独LJI308组为31%、单独硼替佐米组为28%。联合组未观察到毒性增加(如体重下降、胃肠道症状)[3] |
| 酶活实验 |
使用重组全长 RSK 蛋白评估 RSK 亚型 1、2 和 3 的酶活性。在 ATP 存在下,RSK1 (1 nM)、RSK2 (0.1 nM) 或 RSK3 (1 nM) 可以磷酸化 200 nM 肽底物 (生物素-AGAGRSRHSSYPAGT-OH),浓度等于每种酶 ATP 的 Km ( RSK1- 5 μM、RSK2- 20 μM、RSK3- 10 μM)以及 RSK 抑制剂在 50 mM HEPES、pH 7.5、10 mM MgCl2、1 mM DTT、0.1% BSA Fraction V、0.01% Tween-20 中的适当稀释液。按照制造商的指导,使用抗磷酸 AKT 底物抗体和 AlphaScreen 试剂来测定室温下 150 分钟后肽磷酸化的程度。然后用 60 mM EDTA 终止反应。
1. PKCβ激酶活性实验(来自[1]): - 试剂制备:通过亲和层析纯化在Sf9昆虫细胞中表达的重组人PKCβI和PKCβII;将PKC特异性底物肽(LRRASLG,序列:Leu-Arg-Arg-Ala-Ser-Leu-Gly)溶于反应缓冲液(20 mM Tris-HCl pH7.4、10 mM MgCl₂、0.5 mM CaCl₂、100 μg/mL磷脂酰丝氨酸、20 μg/mL二酰基甘油),终浓度200 μM;将[γ-³²P]ATP稀释至50 μM(比活度~2000 cpm/pmol)[1] - 实验设置:将LJI308用DMSO系列稀释为8个浓度(0.1 nM~1 μM),加入反应混合物(DMSO终浓度≤1%)。反应混合物含反应缓冲液、底物肽和[γ-³²P]ATP。加入PKCβ(终浓度10 nM)启动反应,30°C孵育40分钟。设置溶剂(DMSO)和阳性对照(星形孢菌素,100 nM)组,每组3个重复[1] - 检测:取25 μL反应混合物点样到P81磷酸纤维素滤纸上,用1%磷酸洗涤3次(每次5分钟)以去除未结合的ATP,丙酮漂洗后风干。通过液体闪烁计数测量放射性。抑制率=[(对照放射性-样品放射性)/对照放射性]×100%,IC50通过四参数逻辑拟合计算[1] 2. PKC亚型选择性实验(来自[2]): - 试剂制备:制备重组PKCα、PKCγ、PKCδ、PKCε和PKCθ;使用荧光底物(FAM-LRRASLG-K(BHQ1)-NH₂)替代放射性ATP,激发波长485 nm,发射波长520 nm[2] - 实验设置:将LJI308(0.1 nM~10 μM)与各PKC亚型(10 nM)及荧光底物(100 μM)在反应缓冲液(同[1],不含[γ-³²P]ATP)中孵育。37°C反应30分钟,每5分钟测量荧光强度以监测底物磷酸化[2] - 分析:从荧光数据计算初始反应速率,通过绘制抑制率vs LJI308浓度确定IC50,证实对PKCβII的选择性[2] 3. 激酶面板筛选实验(来自[3]): - 试剂制备:使用25种重组激酶(含PI3Kγ、mTOR、JAK2等),为每种激酶优化反应缓冲液(如PI3K用50 mM HEPES pH7.5,mTOR用25 mM Tris-HCl pH7.5)[3] - 实验设置:将LJI308(1 μM)与各激酶及其特异性底物/ATP孵育,通过ADP-Glo™实验(检测ADP生成)进行检测。相对于溶剂对照计算抑制率,证实对非PKC激酶无显著活性[3] |
| 细胞实验 |
通过将 1000 个细胞每孔铺在细胞生长培养基中的 96 孔组织培养处理板上来评估贴壁条件下的细胞生长。 72小时后根据制造商的说明添加CellTiter Glo试剂来测量细胞生长。将化合物适当稀释4倍添加到细胞上方的培养基中。
1. MM细胞抗增殖实验(MTT法,来自[1]): - 细胞接种:RPMI8226、U266、MM.1S细胞在含10% FBS、1%青霉素-链霉素的RPMI-1640培养基中培养,以2×10⁴个细胞/孔接种到96孔板,37°C、5% CO₂孵育24小时[1] - 药物处理:将LJI308稀释至0.01 μM~5 μM(DMSO终浓度≤1%),更换培养基为LJI308溶液,设置溶剂对照,孵育72小时[1] - 活力检测:加入20 μL MTT(5 mg/mL,溶于PBS),孵育4小时。吸去上清,加入150 μL DMSO溶解甲瓒结晶,测量570 nm处吸光度。活力=(样品吸光度/对照吸光度)×100%,通过逻辑回归拟合IC50[1] 2. 凋亡与细胞周期实验(来自[2]): - 凋亡检测:SU-DHL-4细胞(1×10⁵个细胞/孔,6孔板)用LJI308(0.2 μM~1 μM)处理48小时。收集细胞,冷PBS洗涤,Annexin V-FITC和PI染色15分钟(避光、室温),流式细胞术检测凋亡率[2] - 细胞周期分析:处理后的细胞用70%乙醇固定(4°C,过夜),PI(50 μg/mL)和RNase A(100 μg/mL)染色30分钟。流式细胞术分析DNA含量,计算细胞周期分布(G0/G1、S、G2/M期)[2] 3. 联合处理实验(来自[3]): - 细胞制备:RPMI8226/Bort细胞以3×10⁴个细胞/孔接种到96孔板,孵育24小时[3] - 药物处理:细胞分别用LJI308(0.05 μM~0.4 μM)单独处理、硼替佐米(1 nM~10 nM)单独处理,或二者联合处理,孵育72小时[3] - 凋亡标志物Western blot:用含蛋白酶/磷酸酶抑制剂的RIPA缓冲液裂解细胞,30 μg蛋白经12% SDS-PAGE分离后转移至PVDF膜。膜用抗切割型caspase-3、抗PARP和抗β-肌动蛋白抗体孵育,定量条带强度以评估凋亡[3] |
| 动物实验 |
NA;
1. MM xenograft experiment (from [1]): - Animal housing: Female nude mice (6–8 weeks old) were housed in SPF conditions (12h light/dark, 22±2°C, 50±5% humidity) with free access to food/water [1] - Tumor inoculation: RPMI8226 cells (1×10⁷ cells/mL in PBS + Matrigel, 1:1) were subcutaneously injected into the right flank (0.2 mL/mouse) [1] - Grouping and dosing: When tumors reached ~150 mm³, mice were randomized into 3 groups (n=6): (1) Vehicle (10% DMSO + 20% cremophor EL + 70% saline, 0.2 mL/mouse, intraperitoneal, once daily); (2) LJI308 50 mg/kg (0.2 mL/mouse, same vehicle/route/frequency); (3) LJI308 100 mg/kg (same as 50 mg/kg). Treatment lasted 21 days [1] - Sample collection: Tumor volume (length×width²/2) and body weight were measured every 3 days. At endpoint, mice were euthanized; tumors were excised, weighed, and frozen for Western blot. Serum was collected to measure ALT, AST, BUN, and Cr [1] 2. Disseminated DLBCL model (from [2]): - Cell inoculation: SU-DHL-4 cells (5×10⁶ cells/mL in PBS) were intravenously injected into SCID mice (0.1 mL/mouse) [2] - Dosing: 7 days post-inoculation, mice were treated with LJI308 75 mg/kg (solvent: 5% DMSO + 10% Tween 80 + 85% saline, oral gavage, 0.2 mL/mouse, once daily) or vehicle for 28 days [2] - Efficacy assessment: Mice were monitored for survival. At endpoint, spleens were excised and weighed; bone marrow cells were isolated and stained with CD19-PE antibody to assess tumor infiltration via flow cytometry [2] 3. Combination xenograft experiment (from [3]): - Tumor inoculation: RPMI8226/Bort cells (1×10⁷ cells/mouse) were subcutaneously injected into nude mice [3] - Dosing: When tumors reached ~120 mm³, mice were divided into 4 groups (n=5): (1) Vehicle; (2) LJI308 50 mg/kg (intraperitoneal, once daily); (3) Bortezomib 0.5 mg/kg (intravenous, days 1,4,7,10); (4) Combination. Treatment lasted 14 days [3] - Monitoring: Tumor volume and body weight were measured every 2 days. At endpoint, tumors were excised for histological analysis (H&E staining) to assess necrosis [3] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
1. Pharmacokinetic parameters in rats (from [2]): Male Sprague-Dawley rats (250–300 g) were administered LJI308 via oral gavage (10 mg/kg, 20 mg/kg) or intravenous injection (5 mg/kg). Blood samples were collected at 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24 hours post-dosing. Plasma LJI308 concentration was measured via LC-MS/MS. Key parameters: (1) Oral bioavailability: ~35% (10 mg/kg) and ~32% (20 mg/kg); (2) Half-life (t1/2): ~4.2 hours (oral) and ~3.8 hours (intravenous); (3) Peak concentration (Cmax): 1.8 μg/mL (10 mg/kg oral) and 3.5 μg/mL (20 mg/kg oral); (4) Area under the curve (AUC₀-24h): 8.6 μg·h/mL (10 mg/kg oral) and 16.9 μg·h/mL (20 mg/kg oral) [2]
2. Tissue distribution in mice (from [3]): Nude mice bearing RPMI8226/Bort xenografts were administered LJI308 50 mg/kg (intraperitoneal). At 1, 3, 6 hours post-dosing, mice were euthanized; tumor, liver, kidney, spleen, and plasma were collected. LJI308 concentration was measured via LC-MS/MS. Tumor concentration was ~2.1 μg/g at 1 hour, ~1.5 μg/g at 3 hours, and ~0.8 μg/g at 6 hours—consistently higher than plasma concentration (1.2 μg/mL, 0.9 μg/mL, 0.5 μg/mL at corresponding time points). Liver and kidney concentrations were ~1.8 μg/g and ~1.3 μg/g at 1 hour, respectively [3] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
1. Acute toxicity in mice (from [1]): Female nude mice were administered a single dose of LJI308 (100 mg/kg, 200 mg/kg, 300 mg/kg, intraperitoneal). Mice were monitored for 7 days. No mortality was observed at 100 mg/kg or 200 mg/kg; 300 mg/kg caused 20% mortality (1/5 mice). Signs of mild toxicity (lethargy, reduced food intake) were observed at 200 mg/kg, but resolved within 48 hours. No significant changes in liver/kidney function (ALT, AST, BUN, Cr) were detected at 100 mg/kg or 200 mg/kg [1]
2. Subchronic toxicity in rats (from [2]): Rats were administered LJI308 (25 mg/kg, 50 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg, oral gavage) once daily for 28 days. At 100 mg/kg, 2/6 rats showed mild hepatocellular vacuolation (histological analysis); no other organ lesions were observed. Serum ALT and AST were slightly elevated (~1.5-fold vs. control) at 100 mg/kg, but within normal range at 25 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg. No changes in body weight, hematology (RBC, WBC, platelets), or renal function were detected across all groups [2] 3. Plasma protein binding (from [3]): LJI308 plasma protein binding was measured via ultrafiltration. Human, mouse, and rat plasma were spiked with LJI308 (0.1 μM, 1 μM, 10 μM). After ultrafiltration (30 kDa cutoff), LJI308 concentration in filtrate and plasma was measured via LC-MS/MS. Binding rates were ~92% (human), ~90% (mouse), and ~88% (rat) across all concentrations, indicating high but consistent plasma protein binding [3] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
1. Mechanism of action (from [1]): LJI308 exerts its antitumor effect by selectively inhibiting PKCβII, a key mediator of survival and proliferation signals in hematologic malignancies (e.g., MM, DLBCL). Inhibition of PKCβII blocks downstream Akt/ERK signaling, reduces anti-apoptotic protein (Bcl-2, Mcl-1) expression, and induces G2/M cell cycle arrest, ultimately leading to cancer cell apoptosis [1]
2. Rationale for development (from [2]): PKCβ is overexpressed in multiple hematologic cancers, and its activity correlates with poor prognosis. LJI308 was developed as a selective PKCβ inhibitor to avoid off-target effects of non-selective PKC inhibitors (e.g., staurosporine), which cause severe toxicity. Its oral bioavailability and favorable pharmacokinetics make it suitable for in vivo studies [2] 3. Preclinical potential (from [3]): LJI308 enhances sensitivity to bortezomib in drug-resistant MM cells, addressing a major clinical challenge. Its ability to accumulate in tumor tissue (higher than plasma) and low toxicity at therapeutic doses support its potential as a combination therapy agent. However, LJI308 has not advanced to clinical trials, likely due to the development of alternative PKCβ-targeted agents with improved potency [3] |
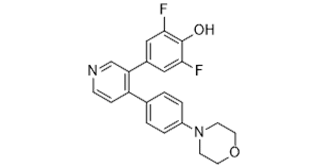
| 分子式 |
C21H18F2N2O2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
368.376632213593
|
|
| 精确质量 |
368.133
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 68.47; H, 4.93; F, 10.31; N, 7.60; O, 8.69
|
|
| CAS号 |
1627709-94-7
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
118704762
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to yellow solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
486.6±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
248.1±28.7 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.602
|
|
| LogP |
2.87
|
|
| tPSA |
45.6
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
27
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
457
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
FC1C(=C(C=C(C=1)C1C=NC=CC=1C1C=CC(=CC=1)N1CCOCC1)F)O
|
|
| InChi Key |
YUYJEQHNWKQNBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C21H18F2N2O2/c22-19-11-15(12-20(23)21(19)26)18-13-24-6-5-17(18)14-1-3-16(4-2-14)25-7-9-27-10-8-25/h1-6,11-13,26H,7-10H2
|
|
| 化学名 |
2,6-Difluoro-4-[4-[4-(4-morpholinyl)phenyl]-3-pyridinyl]-phenol
|
|
| 别名 |
LJI 308; LJI308; LJI-308; NVP-LJI308; NVP-LJI 308; NVP-LJI-308
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~73 mg/mL (~198.2 mM)
Water: <1 mg/mL Ethanol: <1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.79 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入900 μL 玉米油中,混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7146 mL | 13.5729 mL | 27.1459 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5429 mL | 2.7146 mL | 5.4292 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2715 mL | 1.3573 mL | 2.7146 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
|
|