| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Pyruvate kinase (PK), including wild-type (WT) PK-R and various mutant PK-R (mtPK-R) enzymes encoded by PKLR genotypes
[1] Pyruvate kinase (PK), including wild-type (WT) PK and mutant PK enzymes[3] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在健康供体红细胞中,mitapivat(0.1 nM-100 μM;16 小时)可激活 WT PK-R[1]。在红细胞中,mitapivat(0.01 nM-10 μM;16 小时)以剂量依赖性方式刺激 ATP 生成 [1]。
用 5 μM 的 Mitapivat 处理重组 WT PK-R 酶,经 PEP 刺激后,酶活性得到增强。PK-R 四聚体与 Mitapivat 形成的共晶复合物晶体结构显示,药物在变构结合口袋中存在关键相互作用,且结构中还含有 PEP 和 FBP[1] - Mitapivat 可激活多种重组 mtPK-R 酶。在 10 μM 浓度下,其对不同 mtPK-R 酶表现出不同的激活倍数和 AC₅₀ 值。例如,用 5 μM Mitapivat 预孵育重组 R532W mtPK-R 酶后,经 PEP 刺激,酶活性增强;在相同浓度(PEP = 0.05 mM)下,与 FBP 相比,Mitapivat 孵育可使该酶活性更高。此外,5 μM 的 Mitapivat 可提高 WT 或 R510Q 重组酶在 53°C 孵育后的残余活性,且对重组 R510Q 酶具有特定的解离速率(终 assay 浓度 5 μM,PEP = 2 mM)[1] - 健康供体的红细胞(RBCs)与不同浓度的 Mitapivat 过夜孵育后,WT PK-R 活性(PEP = 0.1 mM)和 ATP 水平均有所升高[1] - PK 缺乏症患者的 RBCs 经 Mitapivat 体外处理 24 小时后,大多数患者样本的 PK-R 活性(PEP = 0.5 mM)升高(平均升高 1.8 倍,范围 1.2-3.4),ATP 水平也有所增加(平均升高 1.5 倍,范围 1.0-2.2),这与对照细胞的 ATP 升高水平(平均升高 1.6 倍,范围 1.4-1.8)相近。PK 缺乏症 RBCs 中的 PK 热稳定性显著降低,但 Mitapivat 处理后,残余活性较溶媒处理组增加 1.4 至 >10 倍。在一半的患者中,该处理还与 RBC 变形能力的提高相关。然而,在 PK-R 蛋白水平极低或检测不到的患者细胞中,治疗效果微乎其微[3] - 用 Mitapivat 体外处理 β-地中海贫血患者的红系前体细胞,可增强红细胞生成、促进红系成熟并减少凋亡[2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在β-地中海贫血小鼠模型中,mitapivat(50 mg/kg;口服;每天两次,持续 21 天)可改善贫血[2]。
小鼠按不同剂量水平每日两次给予 Mitapivat,连续 7 天,药物在血浆中可检测到,且每个剂量水平均计算出 AUC₀₋₁₂ 小时。检测小鼠 RBCs 中的 PK-R 活性(PEP = 0.1 mM)、ATP 水平以及全血中的 2,3-DPG 水平,并计算每个参数的 AUC₀₋₁₂ 小时(清晰展示 150 mg/kg 剂量水平的数据)[1] - 给 Hbbᵗʰ³/⁺ 小鼠(β-地中海贫血小鼠模型)口服 Mitapivat(50 mg/kg,每日两次),可改善无效红细胞生成和贫血。该药物能提高 ATP 水平,减少活性氧(ROS)产生,改善线粒体清除,从而降低线粒体功能障碍标志物。治疗还增强了对促红细胞生成素的反应性,导致可溶性红细胞生成素受体(erythroferrone)减少、肝脏 Hamp 表达增加,进而减轻肝脏铁过载。此外,Mitapivat 可能通过激活丙酮酸激酶 M2-HIF2α 轴降低十二指肠 Dmt1 表达,与 Hamp 共同调控铁吸收,预防肝脏铁过载。该治疗还能改善红细胞存活、减少溶血,并提高小鼠体内谷胱甘肽/谷胱甘肽二硫化物比率[2] |
| 酶活实验 |
将重组 PK-R 酶与不同浓度的 Mitapivat 孵育(PEP 设定为 0.065 mM),检测酶活性以评估 Mitapivat 的激活作用。进行技术重复实验,并记录平均值、标准差、范围和重复次数[1]
- 重组 WT PK-R 酶经 PEP 刺激,分为预先用 5 μM Mitapivat 孵育组和未孵育组,检测酶活性,采用 3 次技术重复的平均值进行数据分析[1] - 多种重组 mtPK-R 酶用 10 μM Mitapivat 处理(PEP 浓度见补充表格),测定激活倍数和 AC₅₀ 值,以评估 Mitapivat 对突变酶的激活效果[1] - 重组 R532W mtPK-R 酶经 PEP 刺激,分为预先用 5 μM Mitapivat 孵育组和未孵育组,检测酶活性(3 次技术重复的平均值)[1] - 重组 R532W mtPK-R 酶与不同浓度的 FBP 或 Mitapivat 孵育(PEP = 0.05 mM),检测酶活性以比较两种化合物的激活作用[1] - WT 或 R510Q 重组酶与 5 μM Mitapivat 在 53°C 孵育(PEP = 2 mM),随时间检测残余活性,以评估 Mitapivat 对酶热稳定性的影响[1] - 测定 Mitapivat 或 FBP(终 assay 浓度均为 5 μM,PEP = 2 mM)从重组 R510Q 酶上的解离速率,以评估药物与突变酶的结合动力学[1] - 采用偶联酶分光光度法检测健康供体、PK 缺乏症患者和小鼠 RBCs 中的 PK 活性(患者 B 除外,其活性通过液相色谱-串联质谱法直接测定丙酮酸生成量来评估)。在特定 PEP 浓度(如 0.1 mM、0.5 mM)下进行实验,以确定 Mitapivat 对 PK 活性的影响[1, 3] |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定[1]
细胞类型: RBC 细胞 测试浓度: 0.1 nM-100 µM 孵育时间: 16 小时(孵育过夜) 实验结果: PK-R 活性以剂量依赖性方式增加至 DMSO 对照的约 2.5 倍,AC50 为 62 nM。 细胞活力测定[1] 细胞类型: RBC 细胞 测试浓度: 0.01 nM-10 µM 孵育时间:16 小时(孵育过夜) 实验结果:以剂量依赖性方式持续增加 ATP 水平,比 DMSO 对照平均增加 60%,AC50 为10.9纳米。 健康供体的 RBCs 与不同浓度的 Mitapivat 过夜孵育后,检测 PK-R 活性(PEP = 0.1 mM)和 ATP 水平,以评估药物对健康 RBCs 的体外作用[1] - PK 缺乏症患者的 RBCs 与 Mitapivat 孵育 24 小时后,检测 PK-R 活性(PEP = 0.5 mM)和 ATP 水平。此外,将 PK 缺乏症患者的 RBC 裂解液与 2 mM Mitapivat 孵育(或不孵育)2 小时(37°C),随后在 53°C 下热处理不同时间(5、10、20、40、60 分钟),检测残余 PK 活性,以评估 PK 热稳定性[3] - 采用渗透扫描曲线评估 PK 缺乏症患者的 RBC 变形能力,并确定 Mitapivat 体外处理(20 mM,24 小时)对 RBC 变形能力的影响[3] - PK 缺乏症患者和健康对照的红系细胞体外培养,分为加入 2 mM Mitapivat 组和未加入组。观察增殖和分化不同阶段的细胞形态,检测细胞增殖(细胞数量百分比),并测定 PK/己糖激酶(HK)比率,以评估 Mitapivat 对红系细胞功能的影响[3] - 用 Mitapivat 体外处理 β-地中海贫血患者的红系前体细胞,评估其对红细胞生成、红系成熟和凋亡的影响[2] |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: WT C57B6 and Hbbth3/+ mice (both are 2-month-old female mice; β-thalassemia model)[2].
Doses: 50 mg/kg Route of Administration: In animal feedings; single daily for 3 weeks. Experimental Results: Increased the expression of pyruvate kinase isoforms in both red cells and erythroid precursors from Hbbth3/+ mice. Elevated pyruvate kinase activity in cells from Hbbth3/+ mice, and markedly increased ROS level in erythrocytes. Increased the expression of PKM2 in polychromatic and orthochromatic erythroblasts of Hbbth3/+ mice. Animal/Disease Models: WT C57B6 and Hbbth3/+ mice (both are 2-month-old female mice; β-thalassemia model)[2]. Doses: 50 mg/kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage), twice (two times) daily for 21 days. Experimental Results: Ameliorated ineffective erythropoiesis and anemia in Hbbth3/+ mice and increased ATP, decreased ROS production, as well as decreased markers of mitochondrial dysfunction associated with improved mitochondrial clearance. Mice were dosed with Mitapivat twice daily for 7 days at different dose levels. Blood samples were collected at specific time points to measure plasma concentrations of Mitapivat and calculate AUC₀₋₁₂ hours. RBCs and whole blood were also collected to determine PK-R activity, ATP levels, and 2,3-DPG levels[1] - WT and Hbbᵗʰ³/⁺ mice (β-thalassemia model) were treated with vehicle or Mitapivat at 50 mg/kg twice daily via oral administration. The treatment duration was 21 days. Various parameters were measured, including erythrocyte morphology, hemoglobin (Hb) levels, mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), reticulocyte count, α-globin/β-globin ratio, total and soluble Hb, ROS levels, glutathione/glutathione disulfide ratio, red cell survival (using CFSE-labeled red cells), plasma erythropoietin (EPO) levels, spleen weight/mouse weight ratio, flow cytometry analysis of bone marrow and spleen erythroid cells, ATP content in sorted erythroblasts, mRNA expression of Erfe, soluble plasma ERFE levels, mitochondrial content (using MitoTracker), mRNA expression of mitochondrial genes (Atp6, Mtco1, Cytb, Pgc1a, Yme1l), liver iron staining (Perl’s Prussian blue), liver protein oxidation (OxyBlot), mRNA expression of hepcidin (Hamp) and Id1, Western blot analysis of liver proteins (phospho NF-κB p65, NF-κB p65, pSTAT3, STAT3, pNRF2, NRF2), duodenal iron staining, Western blot analysis of duodenal proteins (PKR, PKM2, HIF2α, pNF-κB p65, NF-κB p65), and mRNA expression of Dmt1-IRE[2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
The absolute bioavailability of mitapivat after a single dose is approximately 73%. Mitapivat exposure increases dose-proportionally. Following twice-daily oral administration of mitapivat at the dose of 5 mg, 20 mg, and 50 mg, the mean (CV%) Cmax at steady state were 101.2 (17%) ng/mL, 389.9 (18%) ng/mL, and 935.2 (18%) ng/mL, respectively. The mean (CV%) AUC were 450.4 (28%) ng x h/mL, 1623.8 (28%) ng x h/mL, and 3591.4 (28%) ng x h/mL, respectively. The median Tmax values at steady state were 0.5 to 1.0 hour post-dose across the dose range of 5 mg to 50 mg twice daily. In healthy subjects, a high-fat meal did not affect the drug exposure but reduced the rate of mitapivat absorption, with a 42% reduction in Cmax and a delay in Tmax of 2.3 hours when compared to dosing under fasted conditions. Mitapivat is primary eliminated via hepatic metabolism. After a single oral administration of radiolabeled mitapivat in healthy subjects, the total recovery of administered radioactive dose was 89.2%. About 49.6% of radioactivity was recovered in the urine with 2.6% excreted as unchanged mitapivat. About 39.6% of radioactivity was recovered in the feces with less than 1% being the unchanged drug. The mean volume of distribution at steady state (Vss) was 42.5 L. Population pharmacokinetics derived median CL/F at steady state was 11.5, 12.7, and 14.4 L/h for the 5 mg twice daily, 20 mg twice daily, and 50 mg twice daily regimens, respectively. Metabolism / Metabolites According to _in vitro_ studies, mitapivat is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4. It is also a substrate of CYP1A2, CYP2C8, and CYP2C9. Following a single oral dose administration of 120 mg of radiolabeled mitapivat in healthy subjects, unchanged mitapivat was the major circulating component in plasma. Biological Half-Life In patients with pyruvate kinase deficiency receiving multiple doses of 5 mg mitapivat twice daily to 20 mg twice daily, the mean effective half-life (t1/2) of mitapivat ranged from 3 to 5 hours. Plasma concentrations of Mitapivat were measured in mice after twice-daily dosing for 7 days at different dose levels, and AUC₀₋₁₂ hours was calculated for each dose level[1] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding
Mitapivat is 97.7% bound to plasma proteins, with an RBC-to-plasma ratio of 0.37. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Pharmacodynamics
Mitapivat is a pyruvate kinase activator that works to increase the activity of erythrocyte pyruvate kinase, an enzyme responsible for energy production for and survival of red blood cells. It is effective in upregulating the activity of both wild-type and mutant forms of erythrocyte pyruvate kinase. Interestingly, mitapivat is a mild-to-moderate inhibitor of the aromatase enzyme (CYP19A1), which is an enzyme involved in biosynthesis of estrogens from androgen precursors. Inhibition of aromatase is associated with bone density loss, as estrogen mediates suppressive, antiresorptive effects on osteoclasts and generally favours bone formation over resorption. Thus, low estrogen levels can increase bone turnover and osteoclast activity, resulting in net bone loss and decreased bone quality. Inhibition of aromatase by mitapivat may have some clinical implications, as patients with pyruvate kinase deficiency have considerably high rate of osteopenia and osteoporosis. The long-term effect of mitapivant on bond mineral density requires further investigation. One study suggests that this off-target effect may have negligible clinical effects on adults, but may potentially have some clinical implications in developing children. Mitapivat (AG-348) is an allosteric activator of pyruvate kinase[1, 2, 3] - PK deficiency is a rare genetic disease that causes chronic hemolytic anemia, and there are currently no targeted therapies for this condition. Mitapivat has the potential to restore the glycolytic pathway activity in patients with PK deficiency by increasing PK enzyme activity, thereby leading to clinical benefit[1] - Anemia in β-thalassemia is related to ineffective erythropoiesis and reduced red cell survival. Excess free heme and accumulation of unpaired α-globin chains impose substantial oxidative stress on β-thalassemic erythroblasts and erythrocytes. Mitapivat reduces chronic hemolysis and ineffective erythropoiesis through stimulation of red cell glycolytic metabolism[2] - Mitapivat is currently in clinical trials for the treatment of PK deficiency (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT02476916, NCT03853798, NCT03548220, NCT03559699)[3] |
| 分子式 |
C24H26N4O3S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
450.56
|
| 精确质量 |
450.173
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 63.98; H, 5.82; N, 12.44; O, 10.65; S, 7.12
|
| CAS号 |
1260075-17-9
|
| 相关CAS号 |
2151847-10-6 (sulfate hydrate);1260075-17-9 (free);2329710-91-8 (sulfate); 2559738-69-9 (HCl); 2559738-74-6
|
| PubChem CID |
59634741
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| LogP |
4.233
|
| tPSA |
90.99
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
32
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
750
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
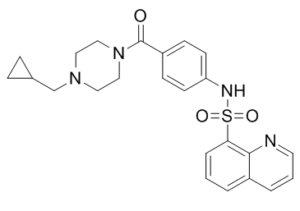
C1CC1CN2CCN(CC2)C(=O)C3=CC=C(C=C3)NS(=O)(=O)C4=CC=CC5=C4N=CC=C5
|
| InChi Key |
XAYGBKHKBBXDAK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C24H26N4O3S/c29-24(28-15-13-27(14-16-28)17-18-6-7-18)20-8-10-21(11-9-20)26-32(30,31)22-5-1-3-19-4-2-12-25-23(19)22/h1-5,8-12,18,26H,6-7,13-17H2
|
| 化学名 |
N-{4-[4-(cyclopropylmethyl)piperazine-1-carbonyl]phenyl}quinoline-8-sulfonamide
|
| 别名 |
PKM2 activator 1020; AG348; Mitapivat; PKM2 activator; 1260075-17-9; PKR-IN-1; AG-348; 2WTV10SIKH; PKR-IN-1; AG-348; PKR-IN-1; trade name Pyrukynd
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (5.55 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浮液;超声助溶。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.55 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.55 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2195 mL | 11.0973 mL | 22.1946 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4439 mL | 2.2195 mL | 4.4389 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2219 mL | 1.1097 mL | 2.2195 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
A Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Mitapivat in Pediatric Participants With Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency (PKD) Who Are Not Regularly Transfused, Followed by a 5-Year Extension Period
CTID: NCT05175105
Phase: Phase 3 Status: Active, not recruiting
Date: 2024-11-15