| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Natural flavonoid
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
建立了以桑皮素为分析试剂,柱前络合反相高效液相色谱法测定不稳定单体铝的荧光检测方法。采用Spherisorb ODS 2色谱柱分离高荧光铝-桑色素配合物(激发波长418 nm,发射波长490 nm),洗脱液为30%甲醇和70%水(pH为1.0的高氯酸)。该方案最值得注意的一点是,只有毒性最大的铝种,即游离的水铝离子及其单体氢氧配合物离子,在各种铝配合物之间选择性反应。该策略已成功应用于天然水体和生物样品中有毒铝的直接分馏,而无需任何预处理。[2]
在过去的几十年里,被诊断患有癌症的人数每年都在急剧增加,使其成为当今死亡的主要原因。结肠癌是世界上第三大常见癌症,死亡率第二。由于癌症干细胞(CSCs)的残留,目前的癌症治疗不能完全治疗结肠癌。在无花果(Ficus carica)和其他植物来源中发现的桑酮类黄酮对结肠癌模型和细胞系具有抗增殖作用,但尚未研究其对结肠CSCs的影响。在本研究中,我们测试了桑辣素抑制CSCs的效力。我们发现桑辣素以剂量依赖的方式显著降低结肠癌细胞增殖、集落形成、迁移和结肠球形成。Pumilio-1 (PUM1)已被证明在结肠CSCs的维持中发挥重要作用。我们发现桑皮素与PUM1蛋白具有良好的结合亲和力,具有1个疏水性和2个氢键相互作用。此外,免疫荧光结果也显示桑肽治疗后结肠癌细胞系中PUM1的表达降低。CD133在结肠CSCs中过表达,桑肽治疗降低了HCT116和CT26结肠癌细胞系中CD133的表达。我们的研究成果通过靶向PUM1蛋白,进一步减少结肠癌细胞中结肠球状体的形成和降低CD133的表达,探索了桑酸素的抗癌干细胞效力[3]。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
大鼠口服桑色素(50和100mg/kg体重)10天。第5天,通过单次腹腔注射MTX(20mg/kg体重)诱导肝毒性。MTX相关肝损伤与MDA增加有关,而GSH水平、内源性抗氧化剂(谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶、超氧化物歧化酶和过氧化氢酶)的活性以及肝组织中HO-1和Nrf2的mRNA水平降低有关。MTX治疗还通过增加Bax、caspase-3、Apaf-1的mRNA转录水平和下调Bcl-2导致肝组织凋亡。相反,不同剂量(50和100mg/kg)的桑色素治疗显著减轻了MTX诱导的肝组织氧化应激和凋亡。桑色素还减轻了MTX诱导的ALT、ALP和AST水平的升高,下调了基质金属蛋白酶(MMP-2和MMP-9)、MAPK14和MAPK15、JNK、Akt2和FOXO1基因的mRNA表达[4]。
黄酮类化合物是一种多酚类化合物,通过多种还原能力具有潜在的抗氧化活性。细胞脂质氧化与许多疾病有关。因此,本研究评估了几种膳食类黄酮苷元抑制肝微粒体脂质过氧化的能力,这些微粒体来自缺乏主要脂溶性抗氧化剂d - α-生育酚的大鼠。抗氧化效果为高良姜素>槲皮素>山奈酚>非瑟素>杨梅素>莫里素>儿茶素>芹菜素。然而,没有一种黄酮类化合物像d - α-生育酚那样有效,特别是在使用最低浓度时。此外,黄酮类化合物的体外抗氧化效果与其体内氧化指标的抑制能力之间似乎存在重要的区别。与d - α-生育酚相比,槲皮素、山奈酚和杨梅素对维生素E缺乏大鼠的脂质过氧化和组织损伤指标无显著影响。黄酮类化合物在体内的直接抗氧化作用不明显,可能是由于其生物利用度低,但不能排除通过刺激抗氧化反应元件而产生的间接氧化还原作用。[1] |
| 酶活实验 |
迈瑞Perfect Plus 400用于测量血清中天冬氨酸转氨酶(AST)、碱性磷酸酶(ALP)和丙氨酸转氨酶(ALT)的活性。结果以U/L[2]为单位给出。
|
| 细胞实验 |
MTT细胞增殖试验[1]
使用基于3-(4,5-二甲基噻唑-2-YI)-2,5-二苯基四唑溴化物(MTT)的比色法测定桑色素对HCT116和CT26增殖的影响。用5000个细胞/孔接种孔,并让其生长过夜。用不同浓度的桑色素(50μM、100μM、150μM、200μM和400μM)处理细胞并孵育48小时。孵育时间结束后,加入MTT试剂并在培养箱中孵育4小时。然后加入DMSO溶解甲酰胺晶体并在黑暗中孵育30分钟,测量570 nm处的吸光度。 菌落形成试验[1] 将HCT116和CT26细胞(500个细胞/孔)接种在6孔板上,并使其生长过夜。第二天,用IC50浓度的桑色素处理各细胞系的平板。孵育48小时后,更换培养基并孵育10天。用10%福尔马林固定菌落,用10%乙醇中的1%结晶紫染色。使用ImageJ软件记录图像并计数菌落,使用GraphPad Prism绘制图表。 伤口愈合试验[1] 对于伤口愈合试验,将1×105个细胞接种在6孔板的每个孔中,并培养至融合率达到75-80%。使用100μl移液管尖端制作伤口,用PBS洗涤分离的细胞,并用还原血清培养基覆盖细胞。在0小时、24小时和48小时拍摄图像,使用ImageJ软件定量测量伤口面积。 |
| 动物实验 |
35 male Wistar albino rats (weighing between 280 and 300 g, 11–12 weeks old) were separated into five groups of 7 male rats each at random:[4]
Control group: The animals received 0.9% saline via oral gavage for 10 days and a single intraperitoneal injection of saline on day 5 only. Morin group: The animals were given 100 mg/kg morin hydrate orally for 10 days and intraperitoneal saline injection was given on the 5th day of the experiment. MTX group: The animals were administered saline orally for 10 days and on the 5th day of the experiment, a single dose of 20 mg/kg MTX was injected intraperitoneally. MTX + Morin 50 group: Rats were given 50 mg/kg morin hydrate orally for 10 days and a single dose of 20 mg/kg MTX was injected intraperitoneally on the 5th day of the experiment. MTX + Morin 100 group: Rats were given 100 mg/kg morin hydrate orally for 10 days and a single dose of 20 mg/kg MTX was injected intraperitoneally on the 5th day of the experiment. Following day, the rats were sacrificed under mild sevoflurane anesthesia. Blood serum was separated by centrifugation at 3000×g for 10 min, and the serum samples were then tested for liver function analysis. Livers were immediately removed and washed with ice-cold physiological saline solution for biochemical and molecular analysis and then stored at -20 °C. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Metabolism / Metabolites
Morin has known human metabolites that include (2S,3S,4S,5R)-6-[2-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-4-oxochromen-3-yl]oxy-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
mouse LD50 intraperitoneal 555 mg/kg BEHAVIORAL: SOMNOLENCE (GENERAL DEPRESSED ACTIVITY); BEHAVIORAL: MUSCLE WEAKNESS; LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamie et de Therapie., 123(395), 1960 [PMID:13796312]
Adverse Effects Occupational hepatotoxin - Secondary hepatotoxins: the potential for toxic effect in the occupational setting is based on cases of poisoning by human ingestion or animal experimentation. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
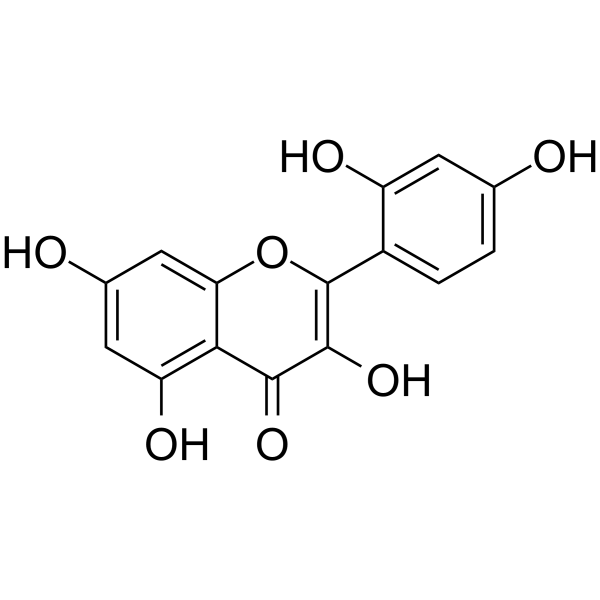
Morin is a pentahydroxyflavone that is 7-hydroxyflavonol bearing three additional hydroxy substituents at positions 2' 4' and 5. It has a role as an antioxidant, a metabolite, an antihypertensive agent, a hepatoprotective agent, a neuroprotective agent, an anti-inflammatory agent, an antineoplastic agent, an antibacterial agent, an EC 5.99.1.2 (DNA topoisomerase) inhibitor and an angiogenesis modulating agent. It is a pentahydroxyflavone and a 7-hydroxyflavonol.
Morin has been reported in Maclura pomifera, Petasites formosanus, and other organisms with data available. See also: Maclurin (annotation moved to). Flavonoids are polyphenolic compounds with potential antioxidant activity via multiple reduction capacities. Oxidation of cellular lipids has been implicated in many diseases. Consequently, this study has assessed the ability of several dietary flavonoid aglycones to suppress lipid peroxidation of hepatic microsomes derived from rats deficient in the major lipid soluble antioxidant, dα-tocopherol. Antioxidant effectiveness was galangin > quercetin > kaempferol > fisetin > myricetin > morin > catechin > apigenin. However, none of the flavonoids were as effective as dα-tocopherol, particularly at the lowest concentrations used. In addition, there appears to be an important distinction between the in vitro antioxidant effectiveness of flavonoids and their ability to suppress indices of oxidation in vivo. Compared with dα-tocopherol, repletion of vitamin E deficient rats with quercetin, kaempferol, or myricetin did not significantly affect indices of lipid peroxidation and tissue damage. Direct antioxidant effect of flavonoids in vivo was not apparent probably due to low bioavailability although indirect redox effects through stimulation of the antioxidant response element cannot be excluded.[1] |
| 分子式 |
C15H10O7
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
302.24
|
| 精确质量 |
302.042
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 59.61; H, 3.34; O, 37.05
|
| CAS号 |
480-16-0
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Morin monohydrate;6202-27-3; 654055-01-3 (hydrate);480-16-0
|
| PubChem CID |
5281670
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to yellow solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.8±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
645.5±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
299-300 °C (dec.)(lit.)
|
| 闪点 |
249.3±25.0 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.823
|
| LogP |
1.61
|
| tPSA |
131.36
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
5
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
1
|
| 重原子数目 |
22
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
488
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
YXOLAZRVSSWPPT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C15H10O7/c16-6-1-2-8(9(18)3-6)15-14(21)13(20)12-10(19)4-7(17)5-11(12)22-15/h1-5,16-19,21H
|
| 化学名 |
2-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxychromen-4-one
|
| 别名 |
NSC-19801; 480-16-0; Aurantica; 2',3,4',5,7-Pentahydroxyflavone; 2-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-4H-chromen-4-one; Calico Yellow; Al-Morin; Toxylon Pomiferum; NSC 19801; Morin
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~125 mg/mL (~413.58 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (6.88 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (6.88 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3086 mL | 16.5431 mL | 33.0863 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6617 mL | 3.3086 mL | 6.6173 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3309 mL | 1.6543 mL | 3.3086 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。