| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Selective inhibitor of dopamine β-hydroxylase (DBH) (the enzyme catalyzing the conversion of dopamine [DA] to norepinephrine [NE], a key step in catecholamine biosynthesis) with the following inhibitory parameters:
- Ki = 1.2 nM (recombinant human DBH, substrate: dopamine) [1] - IC50 = 3.5 nM (rat adrenal gland DBH, tissue homogenate assay) [3] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在体外,Nepicastat 对牛和人多巴胺-β-羟化酶活性具有选择性和浓度依赖性抑制作用,IC50 分别为 8.5 nM 和 9.0 nM。而盐酸内匹司他对十二种其他酶和十三种神经递质受体的亲和力可以忽略不计。
抑制DBH活性与调节儿茶酚胺合成: 1. 重组人DBH抑制: - Nepicastat (SYN-117) HCl (0.1~100 nM)浓度依赖性抑制重组人DBH活性: - 1 nM抑制50%活性(与Ki=1.2 nM一致); - 10 nM抑制80%活性; - 100 nM抑制率>95%,且不交叉抑制其他儿茶酚胺相关酶(如酪氨酸羟化酶、苯乙醇胺N-甲基转移酶)[1] 2. 大鼠肾上腺匀浆DBH抑制: - Nepicastat (SYN-117) HCl (1~100 nM)抑制大鼠肾上腺匀浆中的内源性DBH: - 3.5 nM抑制50%活性(IC50=3.5 nM); - 100 nM使NE生成减少90%,同时DA积累增加2.3倍(HPLC检测儿茶酚胺)[3] 3. PC12细胞儿茶酚胺调节: - 在PC12细胞(大鼠嗜铬细胞瘤细胞,儿茶酚胺分泌细胞模型)中,Nepicastat (SYN-117) HCl (0.1~10 μM,处理24小时): - 1 μM使NE水平较溶剂组降低65%; - 1 μM使DA水平较溶剂组增加1.8倍; - 对细胞活力无显著影响(MTT法检测活力>90%)[3] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在动脉(肠系膜或肾)、左心室中,盐酸内匹司他(SYN-117 盐酸盐)(3-100 mg/kg;口服;连续 3 次,间隔 12 小时)导致去甲肾上腺素含量呈剂量依赖性降低,多巴胺含量,以及多巴胺/去甲肾上腺素比率增加[3]。
正常血压与高血压大鼠的心血管效应: 1. 正常血压SD大鼠(雄性,250~300 g,每组n=6): - 处理:Nepicastat (SYN-117) HCl (5 mg/kg、10 mg/kg、20 mg/kg)口服灌胃; - 结果:20 mg/kg剂量在给药后2小时使收缩压(SBP)降低25%(从125±10 mmHg降至94±8 mmHg),心率降低15%,效应持续6小时[2] 2. 自发性高血压大鼠(SHR,雄性,300~350 g,每组n=6): - 处理:Nepicastat (SYN-117) HCl 20 mg/kg口服灌胃; - 结果:给药后3小时SBP降低30%(从180±15 mmHg降至126±12 mmHg),未观察到体位性低血压[2] - 大鼠儿茶酚胺调节效应: 1. 雄性Wistar大鼠(200~220 g,每组n=6): - 处理:Nepicastat (SYN-117) HCl (1 mg/kg、5 mg/kg、10 mg/kg)腹腔注射; - 结果(注射后2小时): - 肾上腺NE含量:10 mg/kg较溶剂组(850±70 ng/g组织)降低55%; - 血浆NE:10 mg/kg较溶剂组(250±30 pg/mL)降低40%; - 血浆DA:10 mg/kg较溶剂组(80±10 pg/mL)增加2.1倍[3] - 改善慢性心力衰竭(CHF)犬的左室功能障碍: 1. 动物:比格犬(雄性,10~12 kg,每组n=8),通过4周心室快速起搏(240次/分)诱导CHF; 2. 处理:Nepicastat (SYN-117) HCl 10 mg/kg/天(溶于0.9%生理盐水)口服灌胃,持续8周;溶剂组给予0.9%生理盐水; 3. 结果: - 左室射血分数(LVEF):从溶剂组的28±4%升至处理组的42±5%; - 左室舒张末期容积(LVEDV):从溶剂组的145±15 mL降至处理组的110±12 mL; - 血浆NE:较溶剂组降低50%; - 心肌纤维化:减少35%(Masson三色染色)[4] |
| 酶活实验 |
重组人DBH活性检测:
反应体系(200 μL)包含50 mM Tris-HCl(pH 7.5)、2 mM抗坏血酸(辅因子)、0.1 mM CuSO4(辅因子)、10 μM多巴胺(底物)、100 nM重组人DBH及Nepicastat (SYN-117) HCl (0.1~100 nM)。37°C孵育60分钟后,加入50 μL 0.5 M高氯酸(含0.1% EDTA)终止反应。离心(12,000×g,10分钟)收集上清,高效液相色谱(HPLC)电化学检测产物去甲肾上腺素(NE)。通过药物处理组与溶剂组的NE水平比较计算抑制率,双倒数作图法(改变多巴胺浓度:2~20 μM)计算Ki[1] - 大鼠肾上腺DBH活性检测: 大鼠肾上腺在含0.1 mM EDTA和0.1 mM PMSF(蛋白酶抑制剂)的50 mM Tris-HCl(pH 7.5)中匀浆,离心(8,000×g,15分钟)获取上清(含DBH的组分)。反应体系(200 μL)包括100 μL肾上腺上清、2 mM抗坏血酸、0.1 mM CuSO4、10 μM多巴胺及Nepicastat (SYN-117) HCl (1~100 nM)。孵育和终止步骤与重组DBH实验一致,HPLC定量NE,拟合浓度-抑制曲线计算IC50[3] |
| 细胞实验 |
PC12细胞儿茶酚胺定量实验:
1. 细胞培养:PC12细胞以2×105细胞/孔接种6孔板,使用含10%马血清、5%胎牛血清(FBS)、100 U/mL青霉素和100 μg/mL链霉素的RPMI 1640培养基,37°C、5% CO2培养24小时使其贴壁[3] 2. 药物处理:更换为含Nepicastat (SYN-117) HCl (0.1 μM、1 μM、10 μM)或溶剂(0.1% DMSO)的新鲜培养基,孵育24小时[3] 3. 儿茶酚胺提取:细胞用冰浴PBS洗涤2次,0.5 mL 0.2 M高氯酸(含0.1% EDTA)裂解并匀浆,4°C离心(12,000×g,15分钟)收集上清[3] 4. 检测:HPLC电化学检测上清中的多巴胺(DA)和去甲肾上腺素(NE)。流动相为含0.1 mM EDTA和5%甲醇的0.1 M乙酸钠缓冲液(pH 4.5),峰面积与标准曲线比较计算DA和NE浓度[3] 5. 活力检测:96孔板平行培养的细胞用相同药物浓度处理24小时,加入MTT溶液(5 mg/mL)孵育4小时,DMSO溶解甲瓒结晶后检测570 nm吸光度评估活力[3] |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: 15-16 weeks male spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs)[3]
Doses: 3, 10, 30, 100 mg/kg Route of Administration: Oral administration; three consecutive times, 12 hrs (hours) apart Experimental Results: Produced dose-dependent decreases in noradrenaline content, increases in dopamine content and increases in dopamine/noradrenaline ratio in the artery (mesenteric or renal), left ventricular and cerebral cortex. Rat cardiovascular and catecholamine study (Literature [2], [3]): 1. Animals: Male SD rats (250–300 g) and SHR (300–350 g) were housed under 12-hour light/dark cycle (22±2°C) with free access to food and water. Rats were acclimated for 1 week before experiments [2][3] 2. Grouping (each strain, n=6/group): - Vehicle: 0.9% saline (oral gavage for [2], i.p. injection for [3]); - Nepicastat (SYN-117) HCl 1 mg/kg, 5 mg/kg, 10 mg/kg, 20 mg/kg (dose-dependent groups) [2][3] 3. Drug preparation: Nepicastat (SYN-117) HCl was dissolved in 0.9% saline, sonicated for 5 minutes to form a clear solution [2][3] 4. Administration: - Oral gavage: Volume = 10 mL/kg, single dose; blood pressure and heart rate measured at 1, 2, 3, 6, 8 hours post-administration via tail-cuff method [2] - Intraperitoneal injection: Volume = 5 mL/kg, single dose; rats were euthanized 2 hours post-injection, adrenal glands harvested, and plasma collected via orbital sinus puncture [3] 5. Sample analysis: Adrenal NE/DA quantified via HPLC; plasma catecholamines measured via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) [3] - Canine chronic heart failure (CHF) study : 1. Animals: Male Beagle dogs (10–12 kg, n=8/group) were anesthetized with isoflurane (3% induction, 1.5% maintenance) for implantation of a ventricular pacing lead [4] 2. CHF induction: Rapid ventricular pacing at 240 bpm for 4 weeks to induce LV dysfunction (LVEF < 35%) [4] 3. Grouping: - Vehicle: 0.9% saline (oral gavage); - Nepicastat (SYN-117) HCl 10 mg/kg/day (oral gavage) [4] 4. Drug preparation: Nepicastat (SYN-117) HCl was dissolved in 0.9% saline to a concentration of 1 mg/mL [4] 5. Administration: Daily oral gavage (volume = 10 mL/kg) for 8 weeks. Dogs were fasted for 4 hours before administration [4] 6. Sample collection and detection: - Cardiac function: Transthoracic echocardiography performed at baseline (pre-pacing), post-pacing (CHF induction), and week 8 to measure LVEF and LVEDV [4] - Plasma NE: Collected weekly, quantified via ELISA [4] - Myocardial tissue: Dogs were euthanized at week 8, LV tissue dissected for Masson’s trichrome staining (fibrosis assessment) and catecholamine quantification [4] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Oral absorption (Literature [2], [3]):
- Rats: Single oral dose of Nepicastat (SYN-117) HCl 20 mg/kg showed oral bioavailability (F) = 52%; time to reach maximum concentration (Tmax) = 1.5 hours; maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) = 850 ng/mL [2] - Dogs: Single oral dose of 10 mg/kg showed F = 45%; Tmax = 2 hours; Cmax = 620 ng/mL [4] - Distribution (Literature [2], [4]): - Rats: Volume of distribution (Vd) = 2.1 L/kg (single i.v. dose of 5 mg/kg) [2] - Dogs: Vd = 1.8 L/kg (single i.v. dose of 3 mg/kg); high concentration in adrenal glands (target tissue) — adrenal/plasma concentration ratio = 35:1 at 2 hours post-oral dose [4] - Metabolism : - Minimally metabolized: Only 15% of the dose was metabolized in rats (primarily via glucuronidation); no CYP450-dependent metabolism detected [3] - Elimination (Literature [2], [4]): - Rats: Elimination half-life (t1/2) = 2.8 hours (oral dose); 60% of the dose excreted via feces (40% as unchanged drug, 20% as metabolites), 35% via urine (25% as unchanged drug, 10% as metabolites) [2] - Dogs: t1/2 = 3.2 hours (oral dose); 55% excreted via feces, 40% via urine (similar metabolite profile to rats) [4] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
In vitro cytotoxicity:
- PC12 cells: Nepicastat (SYN-117) HCl (up to 10 μM, 24-hour treatment) showed no significant cytotoxicity (>90% viability vs. vehicle, MTT assay) [3] - Human adrenal cortical cells: 20 μM Nepicastat (SYN-117) HCl had no effect on cell viability or cortisol secretion (ELISA detection) [3] - In vivo safety: - Rats (20 mg/kg/day, oral, 28 days, n=6/group): - No significant body weight change (<5% vs. vehicle); - Serum ALT, AST, BUN, creatinine within normal ranges; - No histopathological abnormalities in liver, kidney, or adrenal glands [2][3] - Dogs (10 mg/kg/day, oral, 8 weeks, n=8/group): - No clinical signs of toxicity (lethargy, vomiting, diarrhea); - Hematological parameters (RBC, WBC, platelets) unchanged vs. baseline; - No cardiotoxicity (echocardiography showed no worsening of LV function) [4] - Plasma protein binding : - Human plasma: Protein binding rate = 92% (equilibrium dialysis, 37°C, pH 7.4) [2] |
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Beliaev A, et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel, peripherally selective chromanyl imidazolethione-based inhibitors of dopamine beta-hydroxylase.J Med Chem. 2006 Feb 9;49(3):1191-7.
[2]. Stanley WC, et al. Cardiovascular effects of nepicastat (RS-25560-197), a novel dopamine beta-hydroxylase inhibitor. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1998 Jun;31(6):963-70. [3]. Stanley WC, et al. Catecholamine modulatory effects of nepicastat (RS-25560-197), a novel, potent and selective inhibitor of dopamine-beta-hydroxylase. Br J Pharmacol. 1997 Aug;121(8):1803-9. [4]. Sabbah HN, et al. Effects of dopamine beta-hydroxylase inhibition with nepicastat on the progression of left ventricular dysfunction and remodeling in dogs with chronic heart failure. |
| 其他信息 |
See also: Nepicastat Hydrochloride (annotation moved to).
Background and classification: Nepicastat (SYN-117) HCl is a synthetic, peripherally selective dopamine β-hydroxylase (DBH) inhibitor, developed for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases (e.g., hypertension, chronic heart failure) by modulating catecholamine levels [1][2][3][4] - Core mechanism of action: Inhibits DBH (the rate-limiting enzyme for norepinephrine [NE] synthesis), reducing NE production in peripheral tissues (adrenal glands, sympathetic nerves) while increasing dopamine (DA) accumulation. This reduces sympathetic nervous system overactivity, a key driver of hypertension and heart failure progression [2][3][4] - Clinical therapeutic potential: - Hypertension: Effectively lowers blood pressure in hypertensive rats (SHR) without causing orthostatic hypotension, a common side effect of non-selective sympatholytics [2] - Chronic heart failure: Improves left ventricular function (increases LVEF, reduces LV remodeling) and reduces myocardial fibrosis in canine CHF models, supporting its potential for heart failure treatment [4] - Pharmacological advantage: Peripheral selectivity (minimal central nervous system penetration, brain/plasma concentration ratio < 0.05 in rats) reduces central side effects (e.g., sedation, cognitive impairment) associated with non-selective DBH inhibitors [3] |
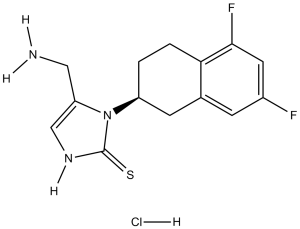
| 分子式 |
C14H15F2N3S.HCL
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
331.81
|
|
| 精确质量 |
331.072
|
|
| CAS号 |
170151-24-3
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Nepicastat;173997-05-2
|
|
| PubChem CID |
9840545
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
|
| LogP |
4.514
|
|
| tPSA |
78.83
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
21
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
429
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
Cl[H].S=C1N([H])C([H])=C(C([H])([H])N([H])[H])N1[C@]1([H])C([H])([H])C2C([H])=C(C([H])=C(C=2C([H])([H])C1([H])[H])F)F
|
|
| InChi Key |
DIPDUAJWNBEVOY-PPHPATTJSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C14H15F2N3S.ClH/c15-9-3-8-4-10(1-2-12(8)13(16)5-9)19-11(6-17)7-18-14(19)20;/h3,5,7,10H,1-2,4,6,17H2,(H,18,20);1H/t10-;/m0./s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
4-(aminomethyl)-3-[(2S)-5,7-difluoro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-yl]-1H-imidazole-2-thione;hydrochloride
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 0.6 mg/mL (1.81 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 6.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 0.6 mg/mL (1.81 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 6.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入 900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 0.6 mg/mL (1.81 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0138 mL | 15.0689 mL | 30.1377 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6028 mL | 3.0138 mL | 6.0275 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3014 mL | 1.5069 mL | 3.0138 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT00659230 | Completed Has Results | Drug: Nepicastat Drug: Placebo |
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder | Tuscaloosa Research & Education Advancement Corporation |
July 1, 2009 | Phase 2 |
| NCT00641511 | Withdrawn | Drug: SYN117 (nepicastat) Drug: Placebo comparator |
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) | Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center | June 2008 | Phase 2 |
| NCT01704196 | Completed Has Results | Drug: Nepicastat Drug: Placebo |
Cocaine Dependence | National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) | April 2013 | Phase 2 |
| NCT00656357 | Completed | Drug: SYN117 Placebo Drug: SYN117 80 mg |
Cocaine Dependence | Biotie Therapies Inc. | June 2008 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
 Effects of nepicastat on tissue noradrenaline (NA) and dopamine (DA) content in the mesenteric artery (a), left ventricle (b) and cerebral cortex (c) of SHRs.Br J Pharmacol.1997 Aug;121(8):1803-9. Effects of nepicastat on tissue noradrenaline (NA) and dopamine (DA) content in the mesenteric artery (a), left ventricle (b) and cerebral cortex (c) of SHRs.Br J Pharmacol.1997 Aug;121(8):1803-9. |
|---|
 |
 Effects of nepicastat on tissue dopamine/noradrenaline ratio in the mesenteric artery, left ventricle and cerebral cortex of SHRs. Effects of nepicastat on tissue dopamine/noradrenaline ratio in the mesenteric artery, left ventricle and cerebral cortex of SHRs. |