| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Ro 61-8048 targets kynurenine 3-hydroxylase (KMO) (Ki = 1.3 nM for rat liver KMO; IC50 = 2.1 nM for human recombinant KMO) [1]
Ro 61-8048 targets KMO [2][3] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
沙鼠中的脑酶被 30 µmol/kg 口服剂量(12.64 µg/kg Ro 61-8048,化合物 16)抑制。这种抑制作用在 2 小时后达到峰值(约 85% 抑制)并持续长达 8 小时[1]。 Ro 61-8048 (0.1-100 μM) 显着抑制 QUIN 的形成,表明犬尿氨酸羟化酶活性是 QUIN 体外新合成所必需的[3]。
在纯化大鼠肝脏KMO酶实验中,Ro 61-8048 以竞争性方式抑制KMO活性,Ki值为1.3 nM,可选择性阻断L-犬尿氨酸向3-羟犬尿氨酸的转化[1] - 对人重组KMO,Ro 61-8048 表现出强效抑制活性,IC50为2.1 nM,对犬尿氨酸通路中其他酶(如犬尿氨酸转氨酶、色氨酸2,3-双加氧酶)及无关酶(如细胞色素P450亚型)的选择性超过1000倍[1] - 在脂多糖(LPS)激活的小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞中,Ro 61-8048(1-100 nM)剂量依赖性抑制喹啉酸(QA)生成,100 nM时最大抑制率约78%;该效应与细胞上清液中3-羟犬尿氨酸积累减少和犬尿氨酸水平升高相关[3] - Ro 61-8048(浓度高达1 μM)不影响巨噬细胞活力或LPS诱导的TNF-α/IL-6产生,表明无脱靶细胞毒性或免疫抑制作用[3] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在 dtsz 仓鼠中,Ro 61-8048(50、100 和 150 mg/kg ip)可显着减轻肌张力障碍的严重程度,且不会产生明显的中枢副作用[2]。在突变仓鼠的纹状体、小脑和脑干中,Ro 61-8048(100 mg/kg ip)会导致内源性广谱谷氨酸受体拮抗剂犬尿氨酸增加两到三倍[2]。
在dt sz突变小鼠(遗传性肌张力障碍模型)中,纹状体注射Ro 61-8048(1 μg/μL,总容积1 μL)可显著降低肌张力障碍严重程度:肌张力障碍评分从溶媒组的3.2 ± 0.4降至注射后2小时的1.1 ± 0.3,且效应持续长达4小时[2] - 在LPS诱导的免疫激活小鼠(腹腔注射LPS 5 mg/kg)中,口服Ro 61-8048(10 mg/kg/天,连续3天)较溶媒对照组降低脑内QA水平约62%,肝脏QA水平约58%;外周犬尿氨酸水平升高约45%,与KMO抑制作用一致[3] - Ro 61-8048(10 mg/kg/天,口服)不改变LPS诱导的小鼠发热或体重减轻,提示不干扰全身性免疫反应[3] |
| 酶活实验 |
在dt sz突变小鼠(遗传性肌张力障碍模型)中,纹状体注射Ro 61-8048(1 μg/μL,总容积1 μL)可显著降低肌张力障碍严重程度:肌张力障碍评分从溶媒组的3.2 ± 0.4降至注射后2小时的1.1 ± 0.3,且效应持续长达4小时[2]
- 在LPS诱导的免疫激活小鼠(腹腔注射LPS 5 mg/kg)中,口服Ro 61-8048(10 mg/kg/天,连续3天)较溶媒对照组降低脑内QA水平约62%,肝脏QA水平约58%;外周犬尿氨酸水平升高约45%,与KMO抑制作用一致[3] - Ro 61-8048(10 mg/kg/天,口服)不改变LPS诱导的小鼠发热或体重减轻,提示不干扰全身性免疫反应[3] |
| 细胞实验 |
LPS激活巨噬细胞QA生成实验:分离小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞,以2×10⁵个细胞/孔接种到24孔板中。用Ro 61-8048(1-100 nM)预处理细胞1小时,随后用LPS(1 μg/mL)刺激24小时。收集细胞上清液,衍生化后通过荧光检测HPLC(激发波长340 nm,发射波长450 nm)定量QA水平;采用紫外HPLC检测犬尿氨酸和3-羟犬尿氨酸水平,以验证KMO通路调控效果[3]
- 巨噬细胞活力实验:LPS激活的巨噬细胞用Ro 61-8048(0.1 nM-1 μM)处理24小时。MTT法测定细胞活力(570 nm处吸光度);ELISA法定量上清液中细胞因子(TNF-α/IL-6)水平,评估免疫抑制潜力[3] |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Male and female dtsz mutant Syrian golden hamsters[2].
Doses: 50, 100 and 150 mg /kg. Route of Administration: IP, one dose. Experimental Results: Dramatically decreased the individual maximum severity of dystonia reached at the end of the observation period of 3 h at doses of 50, 100 and 150 mg/kg ip. 100 and 150 mg/kg Dramatically diminished the severity, indicating a fast onset of action. A delayed onset of dystonic attacks was observed after treatment with 150 mg/kg but not after administration of 50 and 100 mg/kg. At lower doses of 10 and 25 mg/kg, the compound failed to exert any antidystonic effects. Caused a moderate sedation and hypolocomotion 5 to 70 min after administration of 100 and 150 mg/kg, while no central adverse effects were observable at a dose of 50 mg/kg or lower doses. dt sz mutant mouse dystonia model: Male dt sz mutant mice (8-12 weeks old) were anesthetized with isoflurane. Stereotaxic intrastriatal injection of Ro 61-8048 (0.5 μg or 1 μg in 1 μL sterile saline) was performed at coordinates: AP +0.5 mm, ML ±2.0 mm, DV -3.5 mm relative to bregma. Vehicle control mice received 1 μL sterile saline. Dystonic movements were scored on a 4-point scale (0 = no dystonia, 4 = severe, continuous dystonia) at 1, 2, 4, and 24 hours post-injection [2] - LPS-induced immune-activated mouse model: Female C57BL/6 mice (6-8 weeks old) were randomly divided into vehicle control, LPS alone, and LPS + Ro 61-8048 groups (n=6 per group). Ro 61-8048 was dissolved in 0.5% methylcellulose and administered by oral gavage at 10 mg/kg/day for 3 days, with the first dose given 1 hour before intraperitoneal injection of LPS (5 mg/kg). Mice were euthanized 24 hours after the last dose, and brain, liver, and serum samples were collected for QA, kynurenine, and 3-hydroxykynurenine quantification [3] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Acute toxicity: Single intrastriatal injection of Ro 61-8048 (up to 1 μg) in dt sz mice did not cause mortality or overt neurotoxicity (e.g., seizures, altered locomotor activity) [2]
- Chronic toxicity: Repeated oral administration of Ro 61-8048 (10 mg/kg/day for 3 days) in C57BL/6 mice did not affect body weight, liver function (ALT, AST), or kidney function (creatinine, BUN) [3] |
| 参考文献 |
[1]. S Röver, et al. Synthesis and biochemical evaluation of N-(4-phenylthiazol-2-yl)benzenesulfonamides as high-affinity inhibitors of kynurenine 3-hydroxylase. J Med Chem. 1997 Dec 19;40(26):4378-85.
[2]. Melanie Hamann, et al. Effects of the kynurenine 3-hydroxylase inhibitor Ro 61-8048 after intrastriatal injections on the severity of dystonia in the dt sz mutant. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 May 31;586(1-3):156-9. [3]. AlbertoChiarugi, et al. Quinolinic acid formation in immune-activated mice: studies with (m-nitrobenzoyl)-alanine (mNBA) and 3,4-dimethoxy-[-N-4-(-3-nitrophenyl) thiazol-2yl]-benzenesulfonamide (Ro 61-8048), two potent and selective inhibitors of kynureni |
| 其他信息 |
Ro 61-8048 is a C-nitro compound.
Ro 61-8048 is a potent, selective small-molecule inhibitor of kynurenine 3-hydroxylase (KMO), belonging to the N-(4-phenylthiazol-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide chemical class [1] - The therapeutic mechanism of Ro 61-8048 involves blocking the kynurenine pathway at the KMO-catalyzed step, reducing the formation of neurotoxic metabolites (3-hydroxykynurenine, quinolinic acid) and increasing the levels of neuroprotective kynurenine [1][3] - Ro 61-8048 has been used as a tool compound to study the role of the kynurenine pathway in neurological disorders, including dystonia and neuroinflammation [2][3] - In preclinical models, Ro 61-8048 exhibits efficacy in reducing dystonic symptoms and neurotoxic quinolinic acid accumulation, supporting its potential for the treatment of KMO-related neurological diseases [2][3] |
| 分子式 |
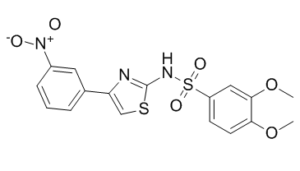
C17H15N3O6S2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
421.45
|
|
| 精确质量 |
421.04
|
|
| CAS号 |
199666-03-0
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
5282337
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
|
| 密度 |
1.5±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
627.4±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
333.3±34.3 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.8 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.641
|
|
| LogP |
3.38
|
|
| tPSA |
159.96
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
9
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
28
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
638
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
S(C1C([H])=C([H])C(=C(C=1[H])OC([H])([H])[H])OC([H])([H])[H])(N([H])C1=NC(=C([H])S1)C1C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C(C=1[H])[N+](=O)[O-])(=O)=O
|
|
| InChi Key |
NDPBMCKQJOZAQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C17H15N3O6S2/c1-25-15-7-6-13(9-16(15)26-2)28(23,24)19-17-18-14(10-27-17)11-4-3-5-12(8-11)20(21)22/h3-10H,1-2H3,(H,18,19)
|
|
| 化学名 |
3,4-dimethoxy-N-[4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]benzenesulfonamide
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.93 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (5.93 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: 20 mg/mL (47.46 mM) in 50% PEG300 50% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3728 mL | 11.8638 mL | 23.7276 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4746 mL | 2.3728 mL | 4.7455 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2373 mL | 1.1864 mL | 2.3728 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。