| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在帕米膦酸盐浓度范围为 100 至 1000 μM 时,骨肉瘤细胞活力以浓度和时间依赖性方式显着降低,最大的降低在暴露 48 和 72 小时后最为一致。暴露于 1000 μM 帕米膦酸 72 小时后,治疗后的骨肉瘤细胞的细胞活力百分比最低为 34% [1]。 BMMSC 的成骨发育受 Wnt 和 β-catenin 信号传导调节,而帕酰胺酯二钠可抑制该信号传导。 BMMSC 的成骨异常可通过 Wnt3a 来挽救,Wnt3a 是 Wnt 和 β-catenin 信号传导的激活剂,可抵消帕米膦酸二钠的副作用 [2]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在早期骨关节炎的情况下,帕米膦酸可以有效预防甚至逆转软骨下骨丢失,从而减缓软骨的恶化。该过程可能与 RANKL、MMP-9 和 TLR-4 的下调以及 OPG 的上调有关[3]。
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
In patients with a creatinine clearance >90mL/min, a 90mg intravenous dose reached a Cmax of 1.92±1.08µg/mL, with a Tmax of 4h, and an AUC of 10.2±6.95µg\*h/mL. In patients with a creatinine clearance 61-90mL/min, a 90mg intravenous dose reached a Cmax of 1.86±0.50µg/mL, with a Tmax of 4h, and an AUC of 10.7—3.91µg\*h/mL.[A203264 In patients with a creatinine clearance 30-60mL/min, a 90mg intravenous dose reached a Cmax of 1.84±0.58µg/mL, with a Tmax of 4h, and an AUC of 10.1±3.38µg\*h/mL. In patients with a creatinine clearance <30mL/min, a 90mg intravenous dose reached a Cmax of 1.93±0.53µg/mL, with a Tmax of 4h, and an AUC of 34.0±8.37µg\*h/mL. Pamidronate is exclusively eliminated in the urine. By 120 hours after administration, 46±16% of the dose has been eliminated in the urine. The mean total clearance of pamidronate is 107±50mL/min and the mean renal clearance is 49±28mL/min. Metabolism / Metabolites Pamidronate is not metabolized _in vivo_. Pamidronate is not metabolized and is exclusively eliminated by renal excretion. Route of Elimination: Pamidronate is not metabolized and is exclusively eliminated by renal excretion. Half Life: The mean ± SD elimination half-life is 28 ± 7 hours Biological Half-Life The mean elimination half life of pamidronate is 28±7 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
The mechanism of action of pamidronate is inhibition of bone resorption. Pamidronate adsorbs to calcium phosphate (hydroxyapatite) crystals in bone and may directly block dissolution of this mineral component of bone. In vitro studies also suggest that inhibition of osteoclast activity contributes to inhibition of bone resorption. Pamidronate also targets farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) synthase. Nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates (such as pamidronate, alendronate, risedronate, ibandronate and zoledronate) appear to act as analogues of isoprenoid diphosphate lipids, thereby inhibiting FPP synthase, an enzyme in the mevalonate pathway. Inhibition of this enzyme in osteoclasts prevents the biosynthesis of isoprenoid lipids (FPP and GGPP) that are essential for the post-translational farnesylation and geranylgeranylation of small GTPase signalling proteins. This activity inhibits osteoclast activity and reduces bone resorption and turnover. In postmenopausal women, it reduces the elevated rate of bone turnover, leading to, on average, a net gain in bone mass. Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Limited information indicates that maternal doses of pamidronate of 30 mg intravenously produce very low levels in milk. Because pamidronate has a serum half-life of about 3 hours, is highly bound to calcium and is poorly absorbed orally (0.3 to 3% in adults), absorption of pamidronate by a breastfed infant is unlikely.[1] Until more data become available, withholding nursing for 12 to 24 hours after a dose should ensure that the breastfed infant is exposed to little or no pamidronate. Other evidence indicates that breastfeeding after cessation of long-term pamidronate treatment appears to have no adverse effects on the infant. Some experts recommend monitoring the infant's serum calcium during the first 2 months postpartum if the mother received pamidronate during pregnancy or nursing.[2] ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants A mother received intravenous pamidronate 30 mg once monthly beginning 6 months postpartum. She pumped her breasts and discarded the milk for 48 hours after each dose. The infant, who was about 80% breastfed throughout maternal pamidronate therapy, remained healthy and grew normally during this time.[1] Because pamidronate can persist in the body for years after long-term administration, the following cases may be relevant. Three women received pamidronate intravenously for osteogenesis imperfecta or McCune-Albright syndrome in cumulative dosages of 6, 7.5 and 9 mg/kg annually for 2 years, 4 years, and 2.2 years, respectively. Their last doses were 3 months, 3 and 48 months (2 infants), and 21 months prior to conception, respectively. None of the women resumed pamidronate during breastfeeding, but they all breastfed their infants postpartum, one for 18 months, two for undetermined times, and one for 6 weeks. None of the infants had any evidence of adverse effects of pamidronate.[3] Two other mothers received intravenous pamidronate infusions preconception and during pregnancy. On received a total of 240 mg with the final dose during the first trimester of pregnancy. She exclusively breastfed her infant for 6 months and continued breastfeeding until the infant was 12 months old. Her infant grew normally and had no adverse reactions.[4] Another woman received alendronate for 6 months, then pamidronate every 4 months for 1 year prior to conception. Her infant was breastfed (extent not stated) for 3 months. The infant had mild hypocalcemia at 2 months of age, but a normal calcium level and normal long bone development at 5 months of age.[5] A woman developed transient osteoporosis with foot pain during pregnancy. On days 3 and 8 postpartum and 2 months later, she received 30 mg of pamidronate intravenously. She was instructed to discard her breastmilk for 24 hours after each dose. Her breastfed (extent not stated) infant had normal growth and development at 15 months of age.[6] ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Pamidronate is approximately 54% protein bound in serum. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Pharmacodynamics
Pamidronic acid is a second generation, nitrogen containing bisphosphonate that inhibits osteoclast mediated bone loss It has a wide therapeutic index and a long duration of action as it can be given every 3-4 weeks for certain indications. Patients should be counselled regarding the risk of elevated blood urea nitrogen, renal tubular necrosis, and nephrotoxicity. |
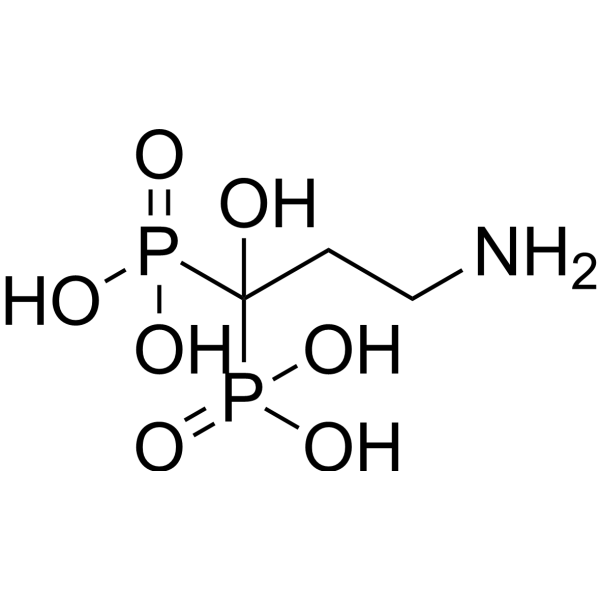
| 分子式 |
C3H11NO7P2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
235.0695
|
| 精确质量 |
235.001
|
| CAS号 |
40391-99-9
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Pamidronate Disodium;57248-88-1
|
| PubChem CID |
4674
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.998 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
658.7ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
226-228ºC
|
| 闪点 |
352.2ºC
|
| 折射率 |
1.611
|
| LogP |
-6.9
|
| tPSA |
180.93
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
6
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
13
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
243
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
WRUUGTRCQOWXEG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C3H11NO7P2/c4-2-1-3(5,12(6,7)8)13(9,10)11/h5H,1-2,4H2,(H2,6,7,8)(H2,9,10,11)
|
| 化学名 |
(3-amino-1-hydroxy-1-phosphonopropyl)phosphonic acid
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
H2O : ~5 mg/mL (~21.27 mM)
DMSO : ~1 mg/mL (~4.25 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 2 mg/mL (8.51 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶。
请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.2541 mL | 21.2703 mL | 42.5405 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8508 mL | 4.2541 mL | 8.5081 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4254 mL | 2.1270 mL | 4.2541 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。