| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
mGlu2 Receptor (Ki = 149 nM); hmGluR3 (Ki = 92 nM)
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在神经元表达天然 mGlu2/3 受体 (Ki=88 nM) 的大鼠中,Pomaglumetad/LY404039 是一种纳摩尔级强效激动剂 [1]。 LY404039 作为毛喉素刺激的 cAMP 形成的有效抑制剂,作用于表达人 mGlu2 (EC50=23 nM) 和 mGlu3 (EC50=48 nM) 受体的细胞 [1]。根据电生理学研究,LY404039 抑制前额皮质中血清素诱导的 L-谷氨酸释放以及纹状体中电诱发的兴奋活动。 LY404039 在 1 μM 时表现出最大抑制率为 85.6%,有效抑制 5-HT 诱导的兴奋性突触后电流 (EPSC) 的频率,EC50 为 82.3 nM [1]。 LY404039 阻断人克隆 D2 受体与 D2 特异性拮抗剂 [3H]多潘立酮的结合,高 D2 的解离常数为 8.2 nM,低 D2 的解离常数为 1640 nM。使用大鼠纹状体组织测定 LY404039 的解离常数,D2 高时为 12.6 nM,D2 低时为 2100 nM [2]。
与LY354740类似,Pomaglumetad/LY404039是重组人mGlu2和mGlu3受体(Ki = 149和92)和表达天然mGlu2/3受体的大鼠神经元(Ki = 88)的纳摩尔强效激动剂。LY404039对mGlu2/3受体具有高度选择性,与已知抗焦虑和抗精神病药物靶向的离子性谷氨酸受体、谷氨酸转运体和其他受体相比,LY404039对这些受体的选择性超过100倍。在功能上,LY404039能有效抑制福斯克林刺激的表达人mGlu2和mGlu3受体的细胞中cAMP的形成。电生理研究表明,LY404039抑制纹状体的电诱发兴奋活动和前额叶皮层中血清素诱导的l-谷氨酸释放;LY341495逆转了这些效应。[1] Pomaglumetad/LY404039在D2High (D2的功能态)解离常数为8.2 nM和12.6 nM;Seeman, 2006), LY404039在人代谢-2和-3谷氨酸受体上的解离常数为92 nM - 149 nM (Rorick-Kehn et al., 2007),这表明在临床剂量下,D2High受体会被谷氨酸受体所占据。 |
||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
LY404039/Pomaglumetad分别减少安非他明 (3-30 mg/kg) 和苯环己哌啶 (10 mg/kg) 引起的运动过度。 LY404039 (3–10 mg/kg) 可抑制条件性回避反应。此外,LY404039 均可减少小鼠的大理石埋藏(3-10 mg/kg)和大鼠的恐惧增强惊吓(3-30 μg/kg),表明具有抗焦虑样作用。此外,LY404039 (10 mg/kg) 可增强前额皮质中的血清素和多巴胺释放/周转 [3]。给禁食大鼠口服 1、3 或 10 mg/kg 剂量的 LY404039 后,暴露量随剂量成比例增加。在用 LY404039(10 mg/kg;口服)治疗的大鼠中,Cmax 为 1528.5 ng/mL,Tmax 为 2 小时 [1]。
目的:本研究的目的是评估一种结构新颖、强效、选择性的mGlu2/3受体激动剂的生物利用度(Pomaglumetad/LY404039)在动物模型中预测抗精神病和抗焦虑疗效的有效性。 材料和方法:Pomaglumetad/LY404039在安非他明和苯环利定诱导的过度运动、条件回避反应、恐惧增强惊吓、大理石掩埋和旋转棒行为测试中进行评估。通过微透析和离体组织水平评估单胺释放和转化。 结果:Pomaglumetad/LY404039减轻安非他明和苯环利定诱导的过度运动(分别为3-30和10 mg/kg)。LY404039 (3 ~ 10 mg/kg)抑制条件回避反应。LY404039还减少了大鼠的恐惧增强惊吓(3-30 mg/kg)和小鼠的大理石掩埋(3-10 mg/kg),表明类似焦虑的作用。重要的是,LY404039不产生镇静作用或运动障碍,通过旋转杆性能和条件回避任务中缺乏逃避失败来测量(剂量分别高达30和10 mg/kg)。LY404039 (10 mg/kg)也增加了前额皮质多巴胺和血清素的释放/周转。 结论:这些结果表明Pomaglumetad/LY404039在多种动物模型中的抗精神病和抗焦虑作用具有广泛的临床前疗效。此外,该化合物调节中皮层神经传递,为治疗精神疾病提供了一种新的机制,可能与提高疗效和减少不良副作用的发生率有关。由于谷氨酸能功能障碍与精神分裂症的病因有关,临床研究更有效的mGlu2/3激动剂,如LY404039,可能有助于探索这一假设的有效性。[3] |
||
| 酶活实验 |
受体结合试验。[1]
表达人mGlu2、mGlu3、mGlu1a、mGlu5a、mGlu4a、mGlu6、mGlu7a和mGlu8受体的细胞系按照先前描述(Schoepp etal ., 1997)获得,并在Dulbecco改良Eagle培养基中培养,培养基中加入5%透析胎牛血清、1mm谷氨酰胺、1mm丙酮酸钠、50mg /ml遗传素和0.2 mg/ml湿霉素b。这些细胞被称为大鼠谷氨酸转运体(RGT)... |
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
LY404039/Pomaglumetad demonstrated higher plasma exposure and better oral bioavailability in pharmacokinetic experiments. [1]
Due to the poor oral bioavailability of previous generation mGlu2/3 receptor agonists, we discovered LY404039/Pomaglumetad, a novel agent with improved potency and bioavailability (Monn et al. 2007) that represents a potentially viable clinical investigational tool. [3] |
||
| 参考文献 |
|
||
| 其他信息 |
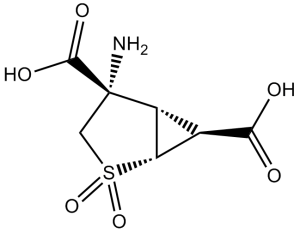
LY404039/Pomaglumetad is an organic heterobicyclic compound that is (1S,5R)-2-thiabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane carrying oxo, oxo, amino, carboxy, and carboxy groups at positions 2, 2, 4S, 4S, and 6S, respectively. It is a potent agonist of group II metabotropic glutamate receptors mGluR2 mGluR3 (Ki = 149 nM and 92 nM, respectively) and exhibits antipsychotic and anxiolytic efficacy in animal models. It has a role as a metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist, an antipsychotic agent, an anxiolytic drug and a dopamine agonist. It is a dicarboxylic acid, a bridged compound, an organic heterobicyclic compound, a sulfone and a non-proteinogenic amino acid derivative.
Receptor Binding Assays. Group II mGlu receptor binding affinities for LY354740 and Pomaglumetad/LY404039 were determined by displacement of specific [3H]LY341495 binding in RGT cells expressing recombinant human mGlu2 and mGlu3 receptor subtypes and in cortical tissue prepared from rat forebrain under conditions selectively labeling group II mGlu receptors. As shown in Table 2 and Fig. 2, both LY354740 and LY404039 displaced [3H]LY341495 binding with nanomolar potencies: (LY354740: mGlu2, Ki = 99 ± 7 nM; The current report details the in vitro pharmacological and pharmacokinetic profile of a structurally novel group II metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist Pomaglumetad/LY404039. We report here that, similar to LY354740 (Schoepp et al., 1997), LY404039 is a nanomolar potent agonist at recombinant human mGlu2/3 receptors and in rat neurons expressing native mGlu2/3 receptors. Also similar to LY354740, LY404039 is highly selective for mGlu2/3 receptors, showing virtually no affinity for group I or group III... [1] The clinical data show that 80 mg of Pomaglumetad/LY404039 twice per day did not reduce the clinical symptoms more than the placebo, while the comparator drug olanzapine reduced the positive symptoms and the negative signs (Kinon et al., 2011; Seeman, 2012). The dissociation constant of 8.2 nM at the D2High receptor indicates that LY404039 is weaker than aripiprazole, which has a dissociation constant of 0.2 nM at D2High (Seeman, 2008). Nevertheless, LY404039 may act as a partial agonist. In discussions on LY404039, it is essential to avoid comparisons with the pharmacology of related LY congeners, because of the different selectivities that each drug has for various receptors. Finally, it should be noted that the removal of the metabotropic-2 or -3 glutamate receptors leads to behavioural and biochemical dopamine supersensitivity (Seeman et al., 2009), indicating that an underactive glutamate neurotransmission is intimately associated with dopamine hyperactivity. [2] LY404039/Pomaglumetad resulted from an effort to discover selective, potent, orally active mGlu2/3 receptor agonists for the treatment of psychiatric disorders. In this paper, we demonstrated that oral administration of LY404039 produced antipsychotic- and anxiolytic-like effects in several animal models and increased monoamine turnover and release in the prefrontal cortex at lower oral doses than those previously reported for LY354740. Specifically, while LY354740 failed to reverse PCP-induced hyperlocomotion at oral doses up to 100 mg/kg (Rorick-Kehn et al. 2006), LY404039 was effective at doses as low as 1 mg/kg when administered orally (Monn et al. 2007). Using another model of schizophrenia, we report here that LY404039 effectively reversed amphetamine-induced hyperlocomotion at an oral dose of 3 mg/kg. In previous experiments, parenteral routes were required to observe anxiolytic effects with LY354740 (Rorick-Kehn et al. 2006), whereas the current results demonstrate oral anxiolytic-like effects at a dose of 3 μg/kg in the fear-potentiated startle paradigm, demonstrating markedly improved oral potency in vivo. The increased bioavailability observed in rats (63%) relative to LY354740 (~10%; Monn et al. 2007; Johnson et al. 2002) suggests that LY404039 may be an attractive candidate for clinical development in the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders. Although not addressed in the current experiments, the relative contribution of mGlu2 versus mGlu3 receptors is an issue that should be examined in future studies, particularly as more selective ligands are discovered. For example, a recent report demonstrated that an mGlu2 receptor potentiator produced behavioral effects similar to those produced by mGlu2/3 receptor agonists in animal models predictive of antipsychotic efficacy, suggesting that mGlu2 receptors may be primarily responsible for the behavioral effects (Galici et al. 2005). Further support is provided by the demonstration that the racemate of LY354740 reversed PCP-induced hyperlocomotion in wild-type, but not mGlu2 receptor knock-out mice (Spooren et al. 2000). Whether the activation of mGlu3 receptors further contributes to the in vivo efficacy of group II mGlu agonists requires further exploration. Pathological glutamatergic and dopaminergic neurotransmission in limbic and cortical areas is hypothesized to underlie the production of both positive and negative symptoms in schizophrenic patients (Goldman-Rakic 1999; Heresco-Levy 2005). Stress and anxiety disorders are also associated with altered glutamatergic activity in limbic and cortical regions (Bergink et al. 2004; Moghaddam 2002). Many clinically effective antipsychotics are believed to alleviate the positive symptoms of schizophrenia by reducing mesolimbic dopamine release and concomitantly increasing dopamine activity in mesocortical pathways (Goldman-Rakic 1999; Heresco-Levy 2005). However, recent experiments support the contention that the most effective atypical antipsychotics do not work solely through the dopaminergic system, but rather interact through a broad class of neurotransmitter systems (Heresco-Levy 2005; Krystal et al. 2005b). Anxiolytics produce their effects by increasing inhibitory activity in the brain, but a converse approach is to decrease excessive central excitatory activity through modulatory metabotropic glutamatergic mechanisms (Swanson et al. 2005). Described herein is a demonstration of the broad preclinical efficacy of the structurally novel, potent selective mGlu2/3 receptor agonist Pomaglumetad/LY404039. The results also indicate that Pomaglumetad/LY404039 modulates mesocortical glutamatergic and dopaminergic neurotransmission and, in doing so, may provide a novel mechanism for the treatment of psychiatric disorders that is associated with improved efficacy and reduced incidence of undesirable side effects. As glutamatergic dysfunction has been linked to the etiology of schizophrenia, clinical studies with more potent mGlu2/3 agonists, such as LY404039, may be useful to explore the validity of this hypothesis in the clinic. [3] The current treatment of schizophrenia by antipsychotics is based on their ability to interfere with the neurotransmission of dopamine (Seeman, 2006). In fact, the clinical daily doses of antipsychotics and their therapeutic concentrations in the spinal fluid can be precisely predicted by their dissociation constants at the cloned dopamine D2 receptor and by the calculation to occupy between 60% and 80% of the human brain D2 receptors (Seeman, 2006). These data suggest that schizophrenia is associated with a hyperactive neurotransmission of dopamine. It has also been suggested, however, that schizophrenia may be based on an underactive glutamate neurotransmission, based on the observation that phencyclidine, a glutamate antagonist, can elicit temporary psychosis. Based on this hypoglutamate hypothesis, Patil et al. (2007) effectively treated schizophrenia patients with a glutamate receptor agonist, pomaglumetad methionil (LY2140023, the parent substance of which is Pomaglumetad/LY404039). A subsequent clinical trial of LY2140023 on schizophrenia patients, however, was “inconclusive” as to the drug's efficacy (Kinon et al., 2011; see also Kinon and Gómez, 2012). Considering that LY404039 was the first apparently non-dopamine-interfering effective drug for psychosis, it was important to test whether LY404039 was indeed free of anti-dopamine action. It was found that LY404039 inhibited the binding of the D2-specific antagonist, [3H]domperidone, to the human cloned D2 receptor with dissociation constants of 8.2 nM at D2High and 1640 nM at D2Low (Fig. 1; Seeman and Guan, 2009). Using rat striatal tissue, LY404039 had dissociation constants of 12.6 nM at D2High and 2100 nM at D2Low. The addition of guanilylimidodiphosphate eliminated the high-affinity component, consistent with an expected agonist action at the D2 receptor. Moreover, the drug stimulated the incorporation of [35S]GTP-γ-S into the tissue (Fig. 1, bottom), as expected for an agonist. [1] |
| 分子式 |
C7H9NO6S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
235.22
|
|
| 精确质量 |
235.015
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 35.75; H, 3.86; N, 5.96; O, 40.81; S, 13.63
|
|
| CAS号 |
635318-11-5
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
9834591
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to gray solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.9±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
600.3±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
316.8±31.5 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±3.7 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.661
|
|
| LogP |
-2.02
|
|
| tPSA |
143.14
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
15
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
451
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
4
|
|
| SMILES |
C1[C@]([C@@H]2[C@H]([C@@H]2S1(=O)=O)C(=O)O)(C(=O)O)N
|
|
| InChi Key |
AVDUGNCTZRCAHH-MDASVERJSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C7H9NO6S/c8-7(6(11)12)1-15(13,14)4-2(3(4)7)5(9)10/h2-4H,1,8H2,(H,9,10)(H,11,12)/t2-,3-,4+,7+/m1/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
(1R,4S,5S,6S)-4-amino-2,2-dioxo-2λ6-thiabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-4,6-dicarboxylic acid
|
|
| 别名 |
LY-404039; LY 404039; 635318-11-5; LY404039; Pomaglumetad; LY-404039; (1R,4S,5S,6S)-4-Amino-2-thiabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-4,6-dicarboxylic acid 2,2-dioxide; LY 404039; UNII-531QUG7P9E; 531QUG7P9E; Pomaglumetad;LY404039; LY-404,039; LY404,039; LY 404,039
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 2 mg/mL (8.50 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶。 (<60°C).
配方 2 中的溶解度: 30% propylene glycol, 5% Tween 80, 65% D5W: 30 mg/mL 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.2513 mL | 21.2567 mL | 42.5134 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8503 mL | 4.2513 mL | 8.5027 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4251 mL | 2.1257 mL | 4.2513 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT03106571 | Terminated | Drug: Pomaglumetad methionil Drug: Placebo Drug: Methamphetamine |
Methamphetamine Use Disorder | University of California, Los Angeles | August 1, 2017 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01487083 | Terminated | Drug: Pomaglumetad methionil | Schizophrenia | Eli Lilly and Company | December 2011 | Phase 3 |
| NCT02919774 | Completed | Drug: POMA Drug: placebo |
Healthy Controls | New York State Psychiatric Institute | October 2016 | Phase 1 |
| NCT02234687 | Terminated Has Results | Drug: Pomaglumetad Methionil 160mg Drug: Pomaglumetad Methionil 40mg Drug: Placebo |
Post-traumatic Stress Disorder | NYU Langone Health | September 2014 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01606436 | Completed Has Results | Drug: LY2140023 Drug: Placebo Drug: Moxifloxacin |
Schizophrenic Disorders | Denovo Biopharma LLC | June 2012 | Phase 1 |
|
|---|
|
|