| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 靶点 |
Raf-1 (IC50 = 2.5 nM); Tie2 (IC50 = 311 ± 46 nM); VEGFR2 (IC50 = 4.2 nM); VEGFR1 (IC50 = 13 nM); BRafV600E (IC50 = 19 nM); PDGFRβ (IC50 = 22 nM); Braf (IC50 = 28 nM); VEGFR3 (IC50 = 46 nM)
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Regorafenib 一水合物(0–10 μM,96 小时)在 GIST 882、甲状腺 TT、MDA-MB-231、HepG2、A375 和 SW620 细胞中表现出抗增殖活性[1]。 Regorafenib 一水合物(0–3000 nM,30 分钟)抑制 FGFR 和 pERK1/2 以及 VEGFR2、TIE2 和 PDGFR– 自磷酸化 [1]。 Regorafenib 一水合物的 IC50 为 5 μM,以浓度依赖性方式抑制 Hep3B 细胞生长。然后,瑞戈非尼会提高 Hep3B 细胞(JNK 靶标)中的磷酸化 c-Jun 水平,但不会提高总 c-Jun 水平[3]。
Regorafenib(0-10 μM,96 小时)在 GIST 882、甲状腺 TT、MDA-MB-231、HepG2、A375 和 SW620 细胞中表现出抗增殖活性[1]。 Regorafenib(BAY 73-4506)是一种新型口服多激酶抑制剂,在生化和细胞激酶磷酸化测定中能有效抑制这些内皮细胞激酶。此外,瑞格非尼还能抑制其他血管生成激酶(VEGFR1/3、血小板衍生生长因子受体β和成纤维细胞生长因子受体1)以及突变致癌激酶KIT、RET和B-RAF。 雷戈非尼以浓度和时间依赖的方式抑制人Hep3B、PLC/PRF/5和HepG2细胞的生长。多种信号通路发生了改变,包括MAP激酶磷酸化ERK和磷酸化JNK及其靶点磷酸化c-Jun。有证据表明FACS导致细胞凋亡、胱天蛋白酶切割和Bax水平升高;以及通过增加Beclin-1和LC3(II)水平来判断自噬的诱导。长时间接触药物会导致细胞静止。与阿霉素化疗不同,药物去除后生长完全恢复。雷戈非尼是一种强效的细胞生长抑制剂。在雷戈非尼治疗中存活的细胞仍然存活,但处于静止状态,在药物去除后能够再生。药物去除后肿瘤细胞生长抑制的可逆性可能具有临床意义。[3] Regorafenib(0–3000 nM,30 分钟)抑制 FGFR 和 pERK1/2 以及 VEGFR2、TIE2 和 PDGFR-β 的自身磷酸化。 Regorafenib 的 IC50 为 5 μM,以浓度依赖性方式抑制 Hep3B 细胞生长。然后,瑞戈非尼会提高 Hep3B 细胞(JNK 靶标)中的磷酸化 c-Jun 水平,但不会提高总 c-Jun 水平[3]。 |
||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Rogafenib 一水合物(10 mg/kg,口服,单剂量或每天服用 4 天)可抑制大鼠 GS9L 胶质母细胞瘤模型中的肿瘤脉管系统和肿瘤生长[1]。 Rogafenib 一水合物(0-100 mg/kg,口服,qd × 9)在 Colo-205、MDA-MB-231 和 786-O 模型中表现出抗肿瘤和抗血管生成作用[1]。
动态增强磁共振成像在体内证明了瑞格非尼的抗血管生成作用。雷戈非尼以10mg/kg的剂量口服一次,显著减少了Gadomer在大鼠GS9L胶质母细胞瘤异种移植物血管系统中的外渗。在每日(qd)×4次给药研究中,药效作用在最后一次给药后持续48小时,并与肿瘤生长抑制(TGI)相关。在10和30 mg/kg的qd×5给药后,在人类结直肠异种移植物中观察到肿瘤微血管面积的显著减少。雷戈非尼在小鼠的各种临床前人类异种移植物模型中表现出强烈的剂量依赖性TGI,在乳腺MDA-MB-231和肾786-O癌模型中观察到了肿瘤缩小。乳腺模型的药效学分析显示,增殖标志物Ki-67和磷酸化细胞外调节激酶1/2的染色显著减少。这些数据表明,瑞格非尼是一种耐受性良好、口服活性的多激酶抑制剂,具有独特的靶点特征,可能对人类恶性肿瘤具有治疗益处[1]。 |
||
| 酶活实验 |
Raf-1 (aa305-aa648)、PDGFRβ (aa561-aa1106)、VEGFR2 (鼠类 aa785-aa1367)、VEGFR3 (鼠类 aa818-aa1363) 和 BRafV600E (aa409-aa765) 激酶结构域用于体外测试。初始 1 μM 瑞戈非尼浓度用于体外激酶抑制分析。选定的响应激酶,例如 VEGFR1 和 RET,用于测定 IC50 值,即 50% 的抑制浓度。通过使用谷胱甘肽-S-转移酶的重组融合蛋白、TIE2的胞内结构域和肽生物素-Ahx-EPKDDAYPLYSDFG作为底物,使用均相时间分辨荧光(HTRF)测定来测量TIE2激酶抑制。
|
||
| 细胞实验 |
GIST 882 和 TT 细胞在含有 L-谷氨酰胺的 RPMI 培养基中生长以进行增殖测定,而 MDA-MB-231、HepG2 和 A375 细胞在始终补充有 10% hiFBS 的 DMEM 中生长。胰蛋白酶处理的细胞以每孔 5 104 个细胞的密度接种在含有含 10% FBS 的完全培养基的 96 孔板中,并在 37 °C 下生长过夜。第二天,添加媒介物或瑞格非尼,并在完全生长培养基中连续稀释至最终浓度在 10 M 至 5 nM 之间,以及 0.2% DMSO,并继续孵育另外 96 小时。量化细胞增殖。[1]
通过酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)和蛋白质印迹分析VEGFR2磷酸化[1] 将转染有人VEGFR2的NIH-3T3细胞以30000个细胞/孔的速度接种在含有10%FBS的Dulbecco改良Eagle培养基的96孔板中;接种后6小时,将培养基换成0.1%BSA/DMEM,继续孵育24小时。细胞在37°C下用0.1%BSA/DMEM/0.1%二甲亚砜(DMSO)中的载体或不同浓度的雷戈非尼处理1小时,然后用终浓度为30 ng/mL的重组VEGF165刺激5分钟。细胞用冷磷酸盐缓冲盐水(PBS)洗涤,并在100μL裂解缓冲液(50 mM HEPES,pH 7.2,1%Triton X-100,1 mM Na3VO4,150 mM NaCl,10%甘油,1.5 mM乙二醇四乙酸和完全蛋白酶抑制剂混合物)中裂解。这是因为。 雷戈非尼治疗[3] 每株细胞系以0.3×105个细胞/2ml含10%FBS的DMEM接种在35mm组织培养皿中。将细胞孵育24小时以允许附着,然后用含有浓度逐渐增加(1μM、2.5μM、5μM、7.5μM和10μM)的雷戈非尼的新鲜培养基替换培养基。在这些实验条件下,允许细胞生长72或96小时。 在Hep3B细胞上进行短期(15、60、180分钟)、中期(24、48、72和96小时)或长期(长达7天)的7.5μMRegorafenib时间过程实验。当细胞被长时间处理时,药物被替换为新鲜的。每个实验都包括一个对照组,其DMSO浓度(溶剂对照组)与用于添加雷戈非尼的浓度相等。每个实验进行三次,重复3次。在特定浓度和孵育时间下进行后续分析。 恢复/可逆性[3] 为了研究停药后细胞增殖的恢复,Hep3B细胞用雷戈非尼5或7.5μM处理3-7天,然后取出培养基,用不含药物的新鲜培养基替换。在不同的后续时间点通过MTT试验评估细胞恢复率。 以0.01、0.05或0.1μM的阿霉素治疗作为阳性对照,研究凋亡过程。 细胞凋亡的FACS分析[3] 按照供应商的规定,使用FITC膜联蛋白V试剂盒检测细胞凋亡。简而言之,收获用不同浓度的雷戈非尼处理48小时的1×106个细胞,并用PBS洗涤。将细胞重新悬浮在结合缓冲液中,然后在5μl AnnexinV-FITC和10μl 7-氨基放线菌素D(7AAD)插入DNA后,在室温下在黑暗中孵育5分钟。将完整细胞与凋亡细胞区分开来。 |
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Cmax = 2.5 μg/mL; Tmax = 4 hours; AUC = 70.4 μg*h/mL; Cmax, steady-state = 3.9 μg/mL; AUC, steady-state = 58.3 μg*h/mL; The mean relative bioavailability of tablets compared to an oral solution is 69% to 83%. Approximately 71% of a radiolabeled dose was excreted in feces (47% as parent compound, 24% as metabolites) and 19% of the dose was excreted in urine (17% as glucuronides) within 12 days after administration of a radiolabeled oral solution at a dose of 120 mg. Regorafenib undergoes enterohepatic circulation with multiple plasma concentration peaks observed across the 24-hour dosing interval. Metabolism / Metabolites Regorafenib is metabolized by CYP3A4 and UGT1A9. The main circulating metabolites of regorafenib measured at steady-state in human plasma are M-2 (N-oxide) and M-5 (N-oxide and N-desmethyl), both of them having similar in vitro pharmacological activity and steady-state concentrations as regorafenib. M-2 and M-5 are highly protein bound (99.8% and 99.95%, respectively). Regorafenib is an inhibitor of P-glycoprotein, while its active metabolites M-2 (N-oxide) and M-5 (N-oxide and N-desmethyl) are substrates of P-glycoprotein. Biological Half-Life Regorafenib, 160 mg oral dose = 28 hours (14 - 58 hours); M2 metabolite, 160 mg oral dose = 25 hours (14-32 hours); M5 metabolite, 160 mg oral dose = 51 hours (32-72 hours); |
||
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In large clinical trials of regorafenib, elevations in serum aminotransferase levels were common, occurring in 39% to 45% of patients, and were greater than 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) in 3% to 6%. In addition, there have been several reports of clinically apparent liver injury arising during regorafenib therapy which was often severe and occasionally fatal, estimated to occur in 0.3% of treated subjects. For these reasons, routine monitoring of liver enzymes is recommended. Regorafenib induced liver injury can present in several different patterns or phenotypes. Some patients present within a few days of starting regorafenib with acute hepatic necrosis, high levels of serum aminotransferase and lactic dehydrogenase with mild jaundice, but prolongation of INR and signs of hepatic failure. The injury can be severe but is generally self-limited and recovery is rapid and complete. Other patients present with an acute viral hepatitis like pattern, hepatocelllar (or mixed) serum enzyme elevations and jaundice that can be prolonged and has been fatal in several instances. Autoimmune and immunoallergic features are uncommon. In addition, rare instances of regorafenib associated liver injury have presented with a sinusoidal obstruction-like syndrome or pseudocirrhosis, with marked hepatic nodularity and ascites that eventually improves or resolves. Finally, regorafenib, like other multi-kinase inhibitors [sunitinib, imatinib, sorafenib], has also been associated with episodes of hyperammonemic coma generally arising within a few days or weeks of starting and with rapid reversal upon stopping treatment. Likelihood score: B (highly likely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the clinical use of regorafenib during breastfeeding. Because regorafenib is 99.5% bound to plasma proteins, the amount in milk is likely to be low. However, one of its metabolites has a half-life of up to 70 hours, and might accumulate in the infant. The manufacturer recommends that breastfeeding be discontinued during regorafenib therapy and for 2 weeks after the final dose. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Regorafenib is highly bound (99.5%) to human plasma proteins. |
||
| 参考文献 |
|
||
| 其他信息 |
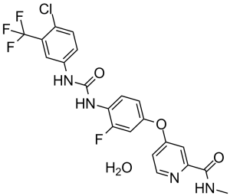
Regorafenib is a pyridinecarboxamide obtained by condensation of 4-[4-({[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]carbamoyl}amino)-3-fluorophenoxy]pyridine-2-carboxylic acid with methylamine. Used for for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer in patients who have previously received chemotherapy, anti-EGFR or anti-VEGF therapy. It has a role as an antineoplastic agent, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor and a hepatotoxic agent. It is an aromatic ether, a pyridinecarboxamide, a member of monochlorobenzenes, a member of (trifluoromethyl)benzenes, a member of monofluorobenzenes and a member of phenylureas.
Regorafenib is an orally-administered inhibitor of multiple kinases. It is used for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer, advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumours, and hepatocellular carcinoma. FDA approved on September 27, 2012. Approved use of Regorafenib was expanded to treat Hepatocellular Carcinoma in April 2017. Regorafenib anhydrous is a Kinase Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of regorafenib anhydrous is as a Kinase Inhibitor, and Cytochrome P450 2C9 Inhibitor, and Breast Cancer Resistance Protein Inhibitor, and UGT1A9 Inhibitor, and UGT1A1 Inhibitor. Regorafenib is an oral multi-kinase inhibitor that is used in the therapy of refractory metastatic colorectal cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma and gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Regorafenib has been associated with frequent serum aminotransferase elevations during therapy and with rare, but sometimes severe and even fatal instances of clinically apparent liver injury. Regorafenib Anhydrous is the anhydrous form of regorafenib, an orally bioavailable small molecule with potential antiangiogenic and antineoplastic activities. Regorafenib binds to and inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFRs) 2 and 3, and Ret, Kit, PDGFR and Raf kinases, which may result in the inhibition of tumor angiogenesis and tumor cell proliferation. VEGFRs are receptor tyrosine kinases that play important roles in tumor angiogenesis; the receptor tyrosine kinases RET, KIT, and PDGFR, and the serine/threonine-specific Raf kinase are involved in tumor cell signaling. Regorafenib is the hydrate form of regorafenib, an orally bioavailable small molecule with potential antiangiogenic and antineoplastic activities. Regorafenib binds to and inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFRs) 2 and 3, and Ret, Kit, PDGFR and Raf kinases, which may result in the inhibition of tumor angiogenesis and tumor cell proliferation. VEGFRs are receptor tyrosine kinases that play important roles in tumor angiogenesis; the receptor tyrosine kinases RET, KIT, and PDGFR, and the serine/threonine-specific Raf kinase are involved in tumor cell signaling. See also: Regorafenib Monohydrate (active moiety of). Drug Indication Regorafenib is indicated for the treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC) who have been previously treated with fluoropyrimidine-, oxaliplatin- and irinotecan-based chemotherapy, an anti-VEGF therapy, and, if KRAS wild type, an anti-EGFR therapy. Regorafenib is also indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced, unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumour (GIST) who have been previously treated with imatinib mesylate and sunitinib malate. Regorafenib is also indicated for the treatment of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) previously treated with sorafenib. FDA Label Stivarga is indicated as monotherapy for the treatment of adult patients with: metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC) who have been previously treated with, or are not considered candidates for, available therapies - these include fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy, an anti-VEGF therapy and an anti-EGFR therapy; unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) who progressed on or are intolerant to prior treatment with imatinib and sunitinib; hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who have been previously treated with sorafenib. Treatment of all conditions contained in the category of malignant neoplasms (except haematopoietic and lymphoid tissue) Mechanism of Action Regorafenib is a small molecule inhibitor of multiple membrane-bound and intracellular kinases involved in normal cellular functions and in pathologic processes such as oncogenesis, tumor angiogenesis, and maintenance of the tumor microenvironment. In in vitro biochemical or cellular assays, regorafenib or its major human active metabolites M-2 and M-5 inhibited the activity of RET, VEGFR1, VEGFR2, VEGFR3, KIT, PDGFR-alpha, PDGFR-beta, FGFR1, FGFR2, TIE2, DDR2, TrkA, Eph2A, RAF-1, BRAF, BRAFV600E , SAPK2, PTK5, and Abl at concentrations of regorafenib that have been achieved clinically. In in vivo models, regorafenib demonstrated anti-angiogenic activity in a rat tumor model, and inhibition of tumor growth as well as anti-metastatic activity in several mouse xenograft models including some for human colorectal carcinoma. |
| 分子式 |
C₂₁H₁₇CLF₄N₄O₄
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
500.83
|
| 精确质量 |
500.087
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 50.36; H, 3.42; Cl, 7.08; F, 15.17; N, 11.19; O, 12.78
|
| CAS号 |
1019206-88-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Regorafenib;755037-03-7;Regorafenib Hydrochloride;835621-07-3;Regorafenib mesylate;835621-08-4
|
| PubChem CID |
11167602
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to orange solid powder
|
| LogP |
6.102
|
| tPSA |
105.07
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
33
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
686
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
ClC1C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=1C(F)(F)F)N([H])C(N([H])C1C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=1F)OC1C([H])=C([H])N=C(C(N([H])C([H])([H])[H])=O)C=1[H])=O.O([H])[H]
|
| InChi Key |
ZOPOQLDXFHBOIH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C21H15ClF4N4O3.H2O/c1-27-19(31)18-10-13(6-7-28-18)33-12-3-5-17(16(23)9-12)30-20(32)29-11-2-4-15(22)14(8-11)21(24,25)26;/h2-10H,1H3,(H,27,31)(H2,29,30,32);1H2
|
| 化学名 |
4-[4-[[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]carbamoylamino]-3-fluorophenoxy]-N-methylpyridine-2-carboxamide;hydrate
|
| 别名 |
BAY-734506 monohydrate; BAY 734506; BAY734506; regorafenib monohydrate; 1019206-88-2; Regorafenib hydrate; Regorafenib (monohydrate); Regorafenib hydrate [JAN]; Regorafenib HCl. Brand name: Stivarga
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.99 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.99 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液添加到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: 30% PEG400+0.5% Tween80+5% Propylene glycol : 30mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9967 mL | 9.9834 mL | 19.9669 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3993 mL | 1.9967 mL | 3.9934 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1997 mL | 0.9983 mL | 1.9967 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT03878524 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Afatinib Drug: Regorafenib |
Metastatic Breast Carcinoma Anemia |
OHSU Knight Cancer Institute | April 1, 2020 | Phase 1 |
|
|---|
Regorafenib inhibits key kinase targets in cells expressing VEGFR2, TIE2, PDGFR‐β, or FGFR.Int J Cancer.2011 Jul 1;129(1):245-55. |
Regorafenib inhibits tumor vasculature and tumor growth in a rat GS9L glioblastoma model: time‐course analysis by DCE‐MRI.Int J Cancer.2011 Jul 1;129(1):245-55. |
Regorafenib significantly reduces tumor MVA in the Colo‐205 CRC xenograft model.Int J Cancer.2011 Jul 1;129(1):245-55. |
|---|
Regorafenib exhibits antitumorigenic and antiangiogenic effects in the MDA‐MB‐231 breast xenograft model.Int J Cancer.2011 Jul 1;129(1):245-55. |
In vivoantitumor efficacy of regorafenib.Int J Cancer.2011 Jul 1;129(1):245-55. |