| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Delta6 desaturase (D6D, FADS2) (IC50=0.2 μM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
SC-26196 (200 nM) 会抑制外周血单核细胞 (PBMC) 的增殖,但不会抑制 Jurkat 细胞的增殖 [2]。
由于技术原因,[13C]18:3n-3不能在实验中用于测试SC-26196对PBMCs中PUFA合成的影响。因此,结果以n-3 PUFA总量的比例表示。SC26196显著降低了受刺激的PBMC中20:4n-3的比例,同时伴有20:3n-3比例增加的非显著趋势(P=0.07)。20:5n-3和22:5n-3的比例也有降低的趋势(P<0.01)(图2B)。 用SC-26196(200 nmoles/l)处理Jurkat细胞显著增加了18:3n-3(59%;P=0.009)和20:3n-3(2倍;P=0.001)的[13C]富集,降低了20:4n-3的富集度(30%;P=0.04),20:5n-3(19%;P=0.02),22:5n-3(33%;P=0.0004)(图2D)。SC26196对18:4n-3和22:6n-3的[13C]富集没有显著影响。[2] SC-26196和甾体酸分别以0.1微M和0.9微M的IC(50)值特异性抑制Delta6D和Delta9D活性。这种中等通量细胞测定为鉴定特定的去饱和酶和延长酶抑制剂提供了一种有效的工具[4]。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
随着饮食中添加 SC-26196(剂量为 0、0.07、0.21 或 0.7 mg/kg,以获得 0、10、30 和 100 mg 剂量),计算出的脂肪组织和肝脏中的 Δ6-去饱和酶指数下降/千克每天)。当每天每公斤体重喂食 100 毫克 SC-26196 时,Δ6-去饱和酶会受到抑制 [3]。
通过抑制Delta6或Delta5去饱和酶减少花生四烯酸的合成被评估为减轻炎症的一种手段。使用定量体外和体内放射分析,鉴定出代表五类Delta5去饱和酶抑制剂和一类Delta6去饱和酶抑制物的新化合物。Delta6去饱和酶抑制剂SC-26196在小鼠体内具有药代动力学和药效学特征,可以评估慢性抑制去饱和酶活性的药理作用。SC-26196在小鼠角叉菜胶足肿胀模型中与吲哚美辛或必需脂肪酸缺乏症相同程度地减轻了水肿。SC-26196的抗炎特性与其作为Delta6去饱和酶抑制剂的作用机制一致:1)抑制肝脏Delta6去饱和度酶活性与水肿减轻之间存在相关性。2) 水肿减轻的开始具有时间依赖性。3) 花生四烯酸在肝脏、血浆和腹膜细胞中的选择性减少呈剂量依赖性。4) 在SC-26196存在的情况下,控制花生四烯酸的再喂养,而不是油酸,逆转了去饱和酶抑制引起的变化。Delta6去饱和酶可能是开发抗炎药物的靶点,其作用机制是独特的[1]。 |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞增殖测定 [2]
细胞类型: PBMC 和 Jurkat 细胞 测试浓度: 200 nM 孵育时间: PBMC 96 小时; Jurkat细胞144小时 实验结果: PBMC处理 分裂细胞比例、分裂指数和增殖指数显着降低。 Jurkat 细胞的细胞增殖没有显着改变。 细胞增殖的测量[2] 采用染料稀释法测定外周血单个核细胞增殖。将冷冻保存的PBMCs解冻,将40×106个活细胞悬浮在含有5%(v/v)FBS的1ml PBS中。PBMCs未经处理或用Con.A(终浓度5µg/ml)刺激,并保持在37°C、5%CO2气氛的加湿细胞培养箱中。根据制造商的说明,用羧基荧光素琥珀酰亚胺酯对细胞进行染色。 通过细胞计数测量Jurkat细胞的增殖。将细胞以5×105个细胞/ml的速度接种在含有10%(v/v)FBS的RPMI-1640培养基中,并在有或没有SC-26196(200 nM)或DMSO(终浓度0.02%(v/v))的情况下孵育长达144小时。以24小时的间隔收集等分试样,并使用库尔特Z1细胞计数器测定细胞数[2]。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Male mice (12 or 15 weeks old) [3]
Doses: 0, 10, 30 and 100 mg/kg daily Doses: included in the diet at 0, 0.07, 0.21 or 0.7 mg/kg diet to achieve doses of 0, 10, 30 and 100 mg/kg per day. Experimental Results: Caused a decrease in calculated Δ6-desaturase index in adipose tissue and liver. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are important for immune function. Limited evidence indicates that immune cell activation involves endogenous PUFA synthesis, but this has not been characterised. To address this, we measured metabolism of 18:3n-3 in quiescent and activated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), and in Jurkat T cell leukaemia. PBMCs from men and women (n = 34) were incubated with [1-13C]18:3n-3 with or without Concanavalin A (Con. A). 18:3n-3 conversion was undetectable in unstimulated PBMCs, but up-regulated when stimulated. The main products were 20:3n-3 and 20:4n-3, while 18:4n-3 was undetectable, suggesting initial elongation and Δ8 desaturation. PUFA synthesis was 17.4-fold greater in Jurkat cells than PBMCs. The major products of 18:3n-3 conversion in Jurkat cells were 20:4n-3, 20:5n-3, and 22:5n-3. 13C Enrichment of 18:4n-3 and 20:3n-3 suggests parallel initial elongation and Δ6 desaturation. The FADS2 inhibitor SC26196 reduced PBMC, but not Jurkat cell, proliferation suggesting PUFA synthesis is involved in regulating mitosis in PBMCs. Con. A stimulation increased FADS2, FADS1, ELOVL5 and ELOVL4 mRNA expression in PBMCs. A single transcript corresponding to the major isoform of FADS2, FADS20001, was detected in PBMCs and Jurkat cells. PBMC activation induced hypermethylation of a 470bp region in the FADS2 5'-regulatory sequence. This region was hypomethylated in Jurkat cells compared to quiescent PBMCs. These findings show that PUFA synthesis involving initial elongation and Δ8 desaturation is involved in regulating PBMC proliferation and is regulated via transcription possibly by altered DNA methylation. These processes were dysregulated in Jurkat cells. This has implications for understanding the regulation of mitosis in normal and transformed lymphocytes.[2]
Objective: To determine whether conjugated linoleic acid (CLA)-induced body fat loss is dependent upon metabolism of CLA by Delta6-desaturase, cyclooxygenase, or lipoxygenase. Methods and procedures: Mice were fed diets with or without CLA and inhibitors to either Delta6-desaturase (SC-26196), cyclooxygenase (aspirin), or lipoxygenase (nordihydroguaiaretic acid (NDGA)) for 2 weeks. Body fat percent, lean mass, fat pad weights, liver weight, and fatty acid concentrations were determined. A Delta6-desaturase index was calculated, and adipose tissue prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)) and leukotriene B(4) (LTB(4)) concentrations were determined to confirm enzyme inhibition. Results: Inhibition of Delta6-desaturase and cyclooxygenase were confirmed. CLA caused a loss of body fat (P < 0.001). The body fat loss was blocked (P = 0.08) by the Delta6-desaturase inhibitor at a dose that decreased (P < 0.05) the calculated index. Aspirin and NDGA had no effect on body fat and did not interact with CLA. Discussion: Inhibition of Delta6-desaturase prevented CLA from being able to cause a body fat loss. Therefore, a desaturated metabolite of CLA appears to be involved in the CLA antiobesity effect. This effect of CLA does not seem dependent upon cyclooxygenase. Because lipoxygenase activity was not blocked by NDGA, we cannot draw conclusions about its importance in mediating the antiobesity effect of CLA. [3] A multiplexed cell assay has been optimized to measure the activities of fatty acyl-CoA elongase, delta-5 desaturase (Delta5D), delta-6 desaturase (Delta6D), and delta-9 desaturase (Delta9D) together using (14)C-labeled tracers in HepG2 cells, which express the human stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 isoform (SCD1) exclusively. The Delta5 and Delta9 desaturase activities are indexed by the efficient conversion of [1-(14)C]-eicosatrienoic acid (C20:3, cis-8,11,14) to (14)C-arachidonic acid (C20:4, cis-5,8,11,14) and the conversion of [1-(14)C]-stearic acid to (14)C-oleic acid (C18:1, cis-9), respectively. CP-74006 potently blocks the Delta5D activity with an IC(50) value of 20 nM and simplifies the metabolism of [1-(14)C]-alpha-linolenate (C18:3, cis-9,12,15) by accumulating (14)C-eicosatetraenoic acid (C20:4, cis-8,11,14,17) as the major (14)C-eicosatrienoic acid (C20:3, cis-11,14,17) and (14)C-docosatetraenoic acid (C22:4, cis-10,13,16,19) as the minor metabolites through Delta6 desaturation and elongation. This simplified metabolite spectrum enables the delineation of the Delta6D activity by comparing the combined Delta6D/elongase activity index of the (14)C-(C20:4/C18:3) ratio with the corresponding elongation index of the (14)C-(C20:3/C18:3) ratio following compound treatment. SC-26196 and sterculic acid specifically inhibit the Delta6D and Delta9D activities with an IC(50) value of 0.1 microM and 0.9 microM, respectively. This medium-throughput cell assay provides an efficient tool in the identification of specific desaturase and elongase inhibitors. [4] |
| 分子式 |
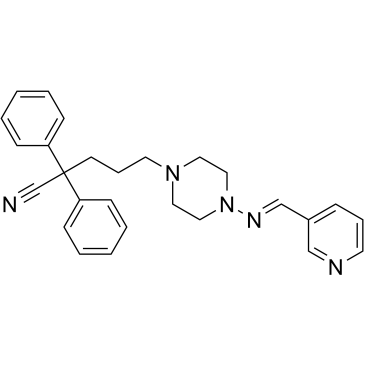
C27H29N5
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
423.55266
|
| 精确质量 |
423.242
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 76.56; H, 6.90; N, 16.53
|
| CAS号 |
218136-59-5
|
| PubChem CID |
9845201
|
| 外观&性状 |
Off-white to yellow solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.1±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
650.2±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
347.0±31.5 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.9 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.607
|
| LogP |
3.2
|
| tPSA |
55.5
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
| 重原子数目 |
32
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
599
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
C1CN(CCN1CCCC(C#N)(C2=CC=CC=C2)C3=CC=CC=C3)/N=C/C4=CN=CC=C4
|
| InChi Key |
QFYKXKMYVYOUNJ-JBASAIQMSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C27H29N5/c28-23-27(25-10-3-1-4-11-25,26-12-5-2-6-13-26)14-8-16-31-17-19-32(20-18-31)30-22-24-9-7-15-29-21-24/h1-7,9-13,15,21-22H,8,14,16-20H2/b30-22+
|
| 化学名 |
2,2-diphenyl-5-[4-[(E)-pyridin-3-ylmethylideneamino]piperazin-1-yl]pentanenitrile
|
| 别名 |
218136-59-5; SC-26196; (E)-2,2-Diphenyl-5-(4-((pyridin-3-ylmethylene)amino)piperazin-1-yl)pentanenitrile; 2,2-Diphenyl-5-(4-((pyridin-3-ylmethylene)amino)piperazin-1-yl)pentanenitrile; 2,2-diphenyl-5-[4-[(E)-pyridin-3-ylmethylideneamino]piperazin-1-yl]pentanenitrile; CHEMBL4554790; SCHEMBL20580676; CHEBI:232585;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~5 mg/mL (~11.80 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 10 mg/mL (23.61 mM) in 15% Cremophor EL 85% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浮液;超声助溶。
*生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 5 mg/mL (11.80 mM) in 0.5% CMC-Na/saline water (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浮液; 需要超声助溶并加热至 40°C。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3610 mL | 11.8050 mL | 23.6100 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4722 mL | 2.3610 mL | 4.7220 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2361 mL | 1.1805 mL | 2.3610 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。