| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Adenosine diphosphate/ADP receptor
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:盐酸噻氯匹定是噻吩并吡啶家族的一种抗血小板药物。盐酸噻氯匹定通过阻断 ADP 受体来改变血小板膜的功能,从而抑制血小板聚集。这可以防止糖蛋白 IIb/IIIa 的构象变化,从而使血小板与纤维蛋白原结合。 Ticlopidine HCl 通过激活环化酶的基础活性和 PGE1 刺激的活性,抑制血小板聚集和内源性底物合成前列腺素,防止 PGE2 诱导的环化酶活性抑制,从而增加血小板 c-AMP 水平。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
盐酸噻氯匹定可抑制男性血小板聚集,IC50 约为 2 μM。当大鼠口服盐酸噻氯匹定时,通过增加血小板膜中的环化酶与 PGE1 的亲和力,导致基础和前列腺素 E1 (PGE1) 刺激的腺苷酸环化酶活性的激活,尽管它不能影响腺苷或氟化钠刺激的腺苷酸环化酶活性。
当对大鼠口服噻氯匹啶时,通过增加血小板膜中环化酶对PGE1的亲和力,导致基础和前列腺素E1(PGE1)刺激的腺苷酸环化酶活性的激活,尽管它没有影响腺苷或氟化钠刺激的酶活性。在洗涤过的血小板中,噻氯匹啶还激活了基础和PGE1刺激的环化酶活性,并防止了低浓度PGE2引起的环化活性降低。此外,噻氯匹啶抑制了凝血酶诱导的血小板丙二醛的形成,但未能抑制外源性花生四烯酸引起的丙二醛的形成。腺苷3',5'-环磷酸(c-AMP):噻氯匹啶治疗对血小板裂解物的磷酸二酯酶活性没有显著影响。这些发现表明,噻氯匹啶通过激活环化酶的基础和PGE1刺激的活性,抑制血小板聚集和内源性底物前列腺素合成,防止PGE2诱导的环化酶活性降低,从而增加血小板c-AMP水平[2]。 |
| 酶活实验 |
盐酸噻氯匹啶是噻氯匹定的盐酸盐形式,噻氯匹定是一种具有抗凝血特性的噻吩并吡啶衍生物。盐酸噻氯匹啶通过与糖蛋白(GP)IIb/IIIA复合物结合,不可逆地抑制二磷酸腺苷(ADP)诱导的血小板纤维蛋白原结合,糖蛋白是ADP激活的两种嘌呤能受体之一。受体激活的抑制会导致腺苷酸环化酶的抑制,导致环磷酸腺苷水平降低,从而干扰血小板膜功能和随后的血小板-血小板相互作用、血小板颗粒成分的释放和出血时间的延长。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞增殖测定[4]
细胞类型: 人内皮细胞 测试浓度: 30 和 150 µM 孵育时间: 2, 6; 10 天 实验结果:与对照组相比,处理过的细胞生长较慢,这种效应与培养基中噻氯匹定的浓度相关。 |
| 动物实验 |
Ticlopidine, when orally administered to rats, resulted in activation of basal and prostaglandin E1 (PGE1)-stimulated adenylate cylase activity through increase in affinity of the cyclase in platelet membrane to PGE1, although it failed to affect adenosine- or sodium fluoride-stimulated activity of the enzyme. In washed platelets, Ticlopidine also activated basal and PGE1-stimulated activity of the cyclase and prevented reduction in the cyclase activity caused by low concentrations of PGE2. Furthermore, Ticlopidine inhibited malondialdehyde formation in platelets induced by thrombin but failed to inhibit that caused by exogenous arachidonic acid. Adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate (c-AMP): phosphodiesterase activity of platelet lysate was not significantly affected by Ticlopidine treatment. These findings indicate that Ticlopidine inhibits platelet aggregation and prostaglandin synthesis from endogenous substrate through activating basal and PGE1-stimulated activity of the cyclase, preventing PGE2-induced depression of the cyclase activity and thus increasing platelet c-AMP level.[2]
Ticlopidine is a new platelet aggregation inhibitor. The effect of this drug was studied on 55 subjects, healthy volunteers and hospitalized patients. The action requires 24 to 48 hr to appear, and lasts more than 3 days. A dose-effect relationship was studied with oral daily doses ranging from 250 to 1,000 mg during 1 wk; it showed a 50% inhibition on adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-induced aggregation at 2 muM concentration on an oral daily dose of 450 mg. No action was found on collagen-induced aggregation, and a mild effect was observed on platelet adhesiveness. Clinical tolerance was assessed in patients given ticlopidine in oral doses up to 500 mg/day during several weeks, showing no overt side effects and no change in the safety parameters.[1] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption
Absorption is greater than 80%. Food increases absorption by approximately 20%. Route of Elimination Ticlopidine is eliminated mostly in the urine (60%) and somewhat in the feces (23%). Volume of Distribution The volume of distribution was not quantified. Clearance Ticlopidine clearance was not quantified, but clearance decreases with age. Metabolism / Metabolites Ticlopidine is metabolized extensively by the liver with only trace amounts of intact drug detected. At least 20 metabolites have been identified. Ticlopidine has known human metabolites that include Ticlopidine S-oxide and Thienodihydropyridinium. Biological Half-Life Half-life following a single 250-mg dose is approximately 7.9 hours in subjects 20 to 43 years of age and 12.6 hours in subjects 65 to 76 years of age. With repeated dosing (250 mg twice a day), half-life is about 4 days in subjects 20 to 43 years of age and about 5 days in subjects 65 to 76 years of age. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Ticlopidine has been associated with serum enzyme elevations in approximately 4% of patients during therapy. These elevations are usually mild, asymptomatic and rarely require dose modification or stopping. Ticlopidine has also been associated with clinically apparent, acute liver injury. While these reactions are rare, more than 50 instances have been reported in the literature and some have been severe. The onset of symptoms is typically within 6 weeks (range 1 to 24 weeks) and marked by onset with fatigue, jaundice and itching. The usual pattern of liver enzyme elevations is cholestatic (~75%), but cases with mixed or hepatocellular enzyme elevations have also been described. Immunoallergic features such as fever, rash and eosinophilia can occur but are not common and, if present, are usually mild. Autoantibody formation is rare. Liver biopsy usually shows cholestatic hepatitis with mixed cellular infiltrates. Most cases are self-limited with recovery within 1 to 3 months, but isolated cases of prolonged jaundice or liver test abnormalities have been described, including at least one case of probable vanishing bile duct syndrome that eventually required liver transplantation. Ticlopidine therapy has also been associated with aplastic anemia and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) that can be severe and lead to death; these patients may also have accompanying cholestatic liver injury. Protein Binding Binds reversibly (98%) to plasma proteins, mainly to serum albumin and lipoproteins. The binding to albumin and lipoproteins is nonsaturable over a wide concentration range. Ticlopidine also binds to alpha-1 acid glycoprotein (about 15% or less). women TDLo oral 350 mg/kg/5W-I women TDLo oral 1896 mg/kg/26W 65335 women TDLo oral 1896 mg/kg/26W LIVER: JAUNDICE, CHOLESTATIC; GASTROINTESTINAL: NAUSEA OR VOMITING Clinical Pharmacy., 12(398), 1993 [PMID:8403812] 65335 women TDLo oral 49 mg/kg/1W-I LIVER: JAUNDICE, CHOLESTATIC; LIVER: LIVER FUNCTION TESTS IMPAIRED American Journal of Hospital Pharmacy., 51(1821), 1994 [PMID:7942916] 65335 women TDLo oral 189 mg/kg/17D- LIVER: JAUNDICE, CHOLESTATIC; LIVER: LIVER FUNCTION TESTS IMPAIRED American Journal of Hospital Pharmacy., 51(1821), 1994 [PMID:7942916] 65335 women LDLo unreported 180 mg/kg/18D- LIVER: LIVER FUNCTION TESTS IMPAIRED; BLOOD: APLASTIC ANEMIA; SKIN AND APPENDAGES (SKIN): DERMATITIS, OTHER: AFTER SYSTEMIC EXPOSURE American Journal of Hematology., 59(260), 1998 65335 rat LD50 oral 1780 mg/kg Medical Pharmacy., 15(272), 1981 |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
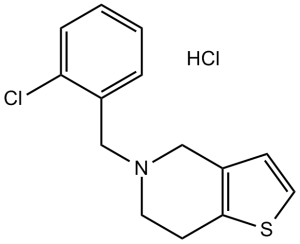
Ticlopidine Hydrochloride is the hydrochloride salt form of ticlopidine, a thienopyridine derivative with anticoagulant property. Ticlopidine hydrochloride irreversibly inhibits adenosine-diphosphate (ADP)-induced platelet-fibrinogen binding by binding to the glycoprotein (GP) IIb/IIIA complex, one of the two purinergic receptors activated by ADP. Inhibition of the receptor activation causes the inhibition of adenylyl cyclase, results in decreased levels of cyclic adenosine monophosphate and thereby interferes with platelet membrane function and subsequent, platelet-platelet interaction, release of platelet granule constituents and prolongation of bleeding time.
An effective inhibitor of platelet aggregation commonly used in the placement of STENTS in CORONARY ARTERIES. See also: Ticlopidine (has active moiety). Ticlopidine is a new platelet aggregation inhibitor. The effect of this drug was studied on 55 subjects, healthy volunteers and hospitalized patients. The action requires 24 to 48 hr to appear, and lasts more than 3 days. A dose-effect relationship was studied with oral daily doses ranging from 250 to 1,000 mg during 1 wk; it showed a 50% inhibition on adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-induced aggregation at 2 muM concentration on an oral daily dose of 450 mg. No action was found on collagen-induced aggregation, and a mild effect was observed on platelet adhesiveness. Clinical tolerance was assessed in patients given ticlopidine in oral doses up to 500 mg/day during several weeks, showing no overt side effects and no change in the safety parameters.[1] |
| 分子式 |
C14H14CLNS.HCL
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
300.25
|
| 精确质量 |
299.03
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 56.01; H, 5.04; Cl, 23.61; N, 4.67; S, 10.68
|
| CAS号 |
53885-35-1
|
| 相关CAS号 |
55142-85-3; 53885-35-1 (HCl)
|
| PubChem CID |
65335
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| 沸点 |
367.3ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
205°C
|
| 闪点 |
175.9ºC
|
| LogP |
4.699
|
| tPSA |
31.48
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
2
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
| 重原子数目 |
18
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
261
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
ClC1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C1C([H])([H])N1C([H])([H])C2C([H])=C([H])SC=2C([H])([H])C1([H])[H].Cl[H]
|
| InChi Key |
MTKNGOHFNXIVOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C14H14ClNS.ClH/c15-13-4-2-1-3-11(13)9-16-7-5-14-12(10-16)6-8-17-14;/h1-4,6,8H,5,7,9-10H2;1H
|
| 化学名 |
5-(2-chlorobenzyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine hydrochloride
|
| 别名 |
Ticlodix; Ticlodone; Panaldine; TICLOPIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE; 53885-35-1; Ticlopidine HCL; Panaldine; Tiklid; 5-(2-chlorobenzyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine hydrochloride; Tiklyd; EINECS 258-837-4; Tiklid; Ticlopidine; Ticlopidine HCl; 53 32C; 53-32C; 5332C; trade name Ticlid
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.33 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.33 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液添加到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: 8.33 mg/mL (27.74 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶 (<60°C). 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3306 mL | 16.6528 mL | 33.3056 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6661 mL | 3.3306 mL | 6.6611 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3331 mL | 1.6653 mL | 3.3306 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。