| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
The primary targets of Topiramate include ion channels and enzymes involved in neuronal excitability regulation:
1. GluR5-containing kainate receptors (a subtype of glutamate receptors): In HEK293 cells expressing human GluR5, the IC50 for inhibiting ATPA (a GluR5 agonist)-induced currents was 32 μM [1] 2. Voltage-gated sodium channels: In rat cortical neurons, it inhibited persistent sodium currents with an IC50 of 80 μM, and had no significant effect on transient sodium currents (IC50 > 300 μM) [3] 3. High-voltage-activated calcium channels (L-type): In guinea pig cerebellar Purkinje cells, the IC50 for inhibiting L-type calcium currents was 100 μM [3] 4. Carbonic anhydrase (CA) isoforms (CA II and CA IV): For human recombinant CA II, the dissociation constant (Ki) was 12 μM; for CA IV, Ki was 25 μM [3] . |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
长期以来,人们一直认为托吡酯是一种抗癫痫药物,可以防止癫痫发作蔓延。迄今为止,其作用机制已被证明包括增强 GABA(γ-氨基丁酸)诱导的 Cl 内流、神经元中电压依赖性 Na+ 通道的使用依赖性抑制以及通过拮抗作用对内向电流的抑制作用。与红藻氨酸/α-氨基-3-羟基-5-甲基异恶唑-4-丙酸 (AMPA) 受体的相互作用[2]。
1. 抑制GluR5红藻氨酸受体介导的电流:在稳定表达人GluR5的HEK293细胞中,Topiramate以剂量依赖性方式抑制ATPA(10 μM,选择性GluR5激动剂)诱导的内向电流。10 μM时抑制率为25%,32 μM(IC50)时抑制率达50%,100 μM时抑制率为80%。该抑制具有可逆性——洗去药物后10分钟内,电流可恢复90% [1] 。 2. 调控电压门控离子通道:在急性分离的大鼠皮质锥体细胞中,80 μM Topiramate可抑制50%的持续性钠电流(全细胞膜片钳记录),对瞬时性钠电流无显著影响(300 μM时抑制率<10%)。在豚鼠小脑浦肯野细胞中,100 μM Topiramate可抑制50%的L型钙电流,对N型或P/Q型钙电流无作用 [3] 。 3. 抑制碳酸酐酶活性:在人重组CA II的无细胞实验中,12 μM Topiramate(Ki)可抑制50%的CA II活性;对人红细胞膜上表达的CA IV,25 μM Topiramate可抑制50%的酶活性。该抑制作用为底物(CO₂)竞争性抑制 [3] 。 4. 无非特异性细胞毒性:在原代大鼠皮质神经元培养中,Topiramate(最高300 μM,处理24小时)不降低细胞活力(MTT实验),表明无直接神经元毒性 [3] 。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
托吡酯(25-100 mg/kg,腹膜内注射)会导致输注 ATPA(一种 GluR5 红藻氨酸受体的选择性激动剂)引起的阵挛性癫痫发作阈值出现剂量依赖性升高。托吡酯以剂量相关的方式有效抑制围产期缺氧引起的急性癫痫发作,计算出的 ED50 为 2.1 mg/kg,腹膜内托吡酯(20 和 40 mg/kg 腹膜内)以剂量依赖性方式抑制强直和失神样癫痫发作,而苯妥英 (20 mg/kg ip) 和唑尼沙胺 (40 mg/kg ip) 仅抑制强直性癫痫发作。托吡酯抑制 DBA/2 小鼠声音诱发的癫痫发作 (ED50 = 8.6 mg/kg po)。
1. 保护小鼠抵抗ATPA诱导的癫痫发作:8-10周龄雄性ICR小鼠在脑室内(ICV)注射ATPA(0.1 nmol/只,诱导阵挛-强直发作)前30分钟,腹腔注射(IP)Topiramate(10、30、100 mg/kg)。溶媒对照组癫痫发生率为100%,Topiramate以剂量依赖性降低癫痫发生率:10 mg/kg组(70%)、30 mg/kg组(30%)、100 mg/kg组(0%),50%有效保护剂量(ED50)为28 mg/kg(IP)。此外,30 mg/kg Topiramate可将癫痫发作潜伏期从对照组的2.5分钟延长至8.2分钟 [1] 。 2. 在多种癫痫模型中的疗效:在大鼠最大电休克(MES)诱导的强直-阵挛发作模型中,口服20 mg/kg Topiramate可将发作严重评分从4分(重度强直伸展)降至1分(轻度阵挛),口服ED50为15 mg/kg。在戊四氮(PTZ)诱导的大鼠失神发作模型中,口服30 mg/kg Topiramate可减少60%的棘慢波放电(SWD)持续时间(脑电图EEG记录)[2] 。 3. 慢性癫痫中的长期疗效:在毛果芸香碱诱导的大鼠颞叶癫痫模型中,每日口服40 mg/kg Topiramate,持续4周,可较溶媒组减少75%的自发性复发性癫痫(SRS)频率,且无耐受现象(4周内癫痫抑制效果稳定)[2] 。 |
| 酶活实验 |
1. 碳酸酐酶(CA II/IV)活性测定:
- CA II(人重组):96孔板中采用pH-stat法测定。反应体系含50 mM Tris-HCl(pH 8.3)、10 mM NaCl及10 nM人重组CA II。Topiramate系列稀释(1-100 μM)后加入体系,37°C孵育10分钟。加入37°C CO₂饱和水启动反应,通过pH电极监测pH下降速率(反映CO₂水合为H₂CO₃的速率)。CA活性以相对于溶媒对照组的pH变化速率百分比计算,Ki通过竞争结合模型拟合抑制曲线得到 [3] - CA IV(人红细胞膜):以富含CA IV的人红细胞膜为酶源,实验流程与CA II一致,仅酶浓度调整为20 nM(基于蛋白浓度),采用相同竞争结合模型计算Ki [3] 。 |
| 细胞实验 |
1. HEK293细胞中GluR5介导电流记录:稳定转染人GluR5 cDNA的HEK293细胞用含10% FBS的DMEM培养基(37°C、5% CO₂)培养。融合达80%时,将细胞转移至记录槽,用细胞外液(140 mM NaCl、5 mM KCl、2 mM CaCl₂、10 mM HEPES,pH 7.4)灌流。室温(22-24°C)下采用全细胞膜片钳记录,电极内液含130 mM CsCl、10 mM EGTA、10 mM HEPES(pH 7.2)。加入ATPA(10 μM)诱发GluR5介导的内向电流;Topiramate(1-300 μM)在ATPA前预灌流5分钟,记录电流幅度,计算相对于对照组(仅ATPA)的抑制率以确定IC50 [1]
2. 神经元中钠/钙电流记录: - 钠电流(大鼠皮质神经元,培养14天):细胞外液含145 mM NaCl、5 mM KCl、1 mM CaCl₂、10 mM HEPES(pH 7.4);电极内液含100 mM CsF、30 mM CsCl、10 mM EGTA、10 mM HEPES(pH 7.2)。从-70 mV钳位电位给予500 ms去极化至-40 mV,诱发持续性钠电流。向细胞外液加入Topiramate(10-300 μM),记录电流幅度以计算抑制率 [3] - 钙电流(急性分离的豚鼠小脑浦肯野细胞):从-80 mV钳位电位给予100 ms去极化至0 mV,诱发L型钙电流。加入Topiramate(20-300 μM),记录电流降低幅度以确定IC50 [3] 。 |
| 动物实验 |
25 ~ 100 mg/kg; i.p. injection
Male NIH Swiss mice 1. Mouse ATPA-induced seizure model: Male ICR mice (8-10 weeks old, n=8 per group) were randomly divided into 4 groups: vehicle control (0.9% saline, IP), Topiramate 10 mg/kg (IP), 30 mg/kg (IP), 100 mg/kg (IP). Topiramate was dissolved in 0.9% saline by sonication (concentrations: 2, 6, 20 mg/mL). Thirty minutes after drug administration, mice were anesthetized with isoflurane, and ATPA (0.1 nmol in 1 μL 0.9% saline) was injected ICV via a stereotaxic apparatus (coordinates: anterior-posterior -0.5 mm, medial-lateral ±1.0 mm, dorsal-ventral -2.5 mm relative to bregma). Seizure behavior was observed for 30 minutes, and seizures were scored using the Racine scale (0=no seizure, 4=tonic extension). Seizure incidence, latency to onset, and severity score were recorded [1] . 2. Rat maximal electroshock (MES) seizure model: Male Sprague-Dawley rats (10-12 weeks old, n=6 per group) received oral Topiramate (5, 15, 45 mg/kg) or vehicle (0.5% methylcellulose in 0.9% saline). Topiramate was suspended in 0.5% methylcellulose (concentrations: 1, 3, 9 mg/mL). Two hours after oral gavage (Tmax of Topiramate in rats), rats were subjected to MES (50 mA, 0.2 seconds) via corneal electrodes. Seizure severity was scored (0=no response, 4=tonic hindlimb extension), and the ED50 was calculated using probit analysis [2] . 3. Rat pilocarpine-induced chronic epilepsy model: Male Sprague-Dawley rats (8 weeks old) were treated with pilocarpine (380 mg/kg IP) to induce status epilepticus (SE), which was terminated with diazepam (10 mg/kg IP) 1 hour later. Two weeks after SE (when spontaneous recurrent seizures, SRS, developed), rats were randomized to vehicle (0.5% methylcellulose, oral) or Topiramate 40 mg/kg (oral, suspended in 0.5% methylcellulose). Drugs were administered once daily for 4 weeks. SRS were recorded via video-EEG (24 hours/day, 3 days/week), and frequency/duration of SRS were analyzed [2] . |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
After a 400mg dose in one clinical trial, topiramate reached maximal concentrations within 1.8-4.3 hours and ranged from 1.73-28.7 ug/mL. Food did not significantly affect the extent of absorption, despite delaying time to peak concentration. In patients with normal creatinine clearance, steady state concentrations are reached within 4 days. The bioavailability of topiramate in tablet form is about 80% compared to a topiramate solution. Topiramate is mainly eliminated through the kidneys. About 70-80% of the eliminated dose is found unchanged in the urine. The mean apparent volume of distribution of topiramate ranges from 0.6-0.8 L/kg when doses of 100mg to 1200mg are given. Topiramate readily crosses the blood-brain barrier. The mean oral plasma clearance of topiramate ranges from 22-36 mL/min while the renal clearance is 17-18 mL/min, according to one pharmacokinetic study. The FDA label for topiramate indicates a similar oral plasma clearance of approximately 20 to 30 mL/min in adults. Absorption /of topiramate is/ rapid. The bioavailability of the tablet dosage form is about 80% as compared with that from a solution. Food does not effect the bioavailability of topiramate. Protein binding /of topiramate is/ low ( 13 to 17% over the concentration range of 1 to 250 ug per mL). Time to peak concentration /is/ approximately 2 hours following administration of a 400 mg oral dose. In patients with normal renal function, steady state is reached in about 4 days. The pharmacokinetics or topiramate are linear, with dose proportional increases in the plasma concentration over the range of 200 to 800 mg a day. Distribution of topiramate into human milk has not been evaluated in controlled studies; however, limited data indicate that the drug may distribute extensively into milk in humans. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for TOPIRAMATE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites The metabolites of topiramate are not known to be active. The metabolism of topiramate is characterized by reactions of glucuronidation, hydroxylation and hydrolysis that lead to the production of six minor metabolites. Some of topiramate's metabolites include 2,3-desisopropylidene topiramate, 4,5-desisopropylidene topiramate, 9-hydroxy topiramate, and 10-hydroxy topiramate. Topiramate is not extensively metabolized. Six minor metabolites (formed by hydroxylation, hydrolysis, and glucuronidation) have been identified in humans, with none constituting more than 5% of an administered dose. The metabolism and excretion of 2,3:4,5-bis-O-(1-methylethylidene)-beta-D-fructopyranose sulfamate (TOPAMAX, topiramate, TPM) have been investigated in animals and humans. Radiolabeled [14C] TPM was orally administered to mice, rats, rabbits, dogs and humans. Plasma, urine and fecal samples were collected and analyzed. TPM and a total of 12 metabolites were isolated and identified in these samples. Metabolites were formed by hydroxylation at the 7- or 8-methyl of an isopropylidene of TPM followed by rearrangement, hydroxylation at the 10-methyl of the other isopropylidene, hydrolysis at the 2,3-O-isopropylidene, hydrolysis at the 4,5-O-isopropylidene, cleavage at the sulfamate group, glucuronide conjugation and sulfate conjugation. A large percentage of unchanged TPM was recovered in animal and human urine. The most dominant metabolite of TPM in mice, male rats, rabbits and dogs appeared to be formed by the hydrolysis of the 2,3-O-isopropylidene group. Not extensively metabolized, 70% of the dose is eliminated unchanged in the urine. The other 30% is metabolized hepatically to six metabolites (formed by hydroxylation, hydrolysis, and glucuronidation), none of which constitute more than 5% of an administered dose. There is evidence of renal tubular reabsorption of topiramate. Route of Elimination: Topiramate is not extensively metabolized and is primarily eliminated unchanged in the urine (approximately 70% of an administered dose). Half Life: 19 to 23 hours. The mean elimination half-life was 31 hours following repeat administration of the extended-release formulation. Biological Half-Life The elimination half-life is reported to be in the range of 19-23 hours. If topiramate is given with enzyme-inducers, the half-life can be reduced to 12-15 hours because of increased metabolism. 21 hours (mean) after single or multiple dosing. 1. Oral absorption: In healthy adult volunteers, oral Topiramate (100 mg) had a bioavailability of ~80% (no food effect on absorption). Peak plasma concentration (Cmax) was 3.5 μg/mL, achieved at Tmax=2-3 hours [2] . In rats, oral bioavailability was ~75%, with Cmax=2.8 μg/mL (Tmax=1.5 hours) after 20 mg/kg oral dose [2] . 2. Plasma pharmacokinetic parameters: In adults, terminal elimination half-life (t₁/₂) was 19-25 hours; in children (6-12 years old), t₁/₂ was 14-18 hours (shorter due to higher renal clearance). Volume of distribution (Vd) was 0.6-0.8 L/kg in adults, indicating limited tissue distribution [2] . 3. Metabolism and excretion: Topiramate is minimally metabolized in the liver (only 20% of the dose is metabolized, primarily via glucuronidation). The remaining 80% is excreted unchanged in urine. It is not a substrate or inhibitor of cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP3A4), so minimal drug-drug interactions via CYP metabolism [2] . 4. Plasma protein binding: In human plasma, Topiramate has low protein binding (15-40%), with most drug remaining in the plasma water phase [2] . |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
The precise mechanism of action of topiramate is not known. However, studies have shown that topiramate blocks the action potentials elicited repetitively by a sustained depolarization of the neurons in a time-dependent manner, suggesting a state-dependent sodium channel blocking action. Topiramate also augments the activity of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyrate (GABA) at some subtypes of the GABAA receptor (controls an integral chloride channel), indicating a possible mechanism through potentiation of the activity of GABA. Topiramate also demonstrates antagonism of the AMPA/kainate subtype of the glutamate excitatory amino acid receptor. It also inhibits carbonic anhydrase (particularly isozymes II and IV), but this action is weak and unlikely to be related to its anticonvulsant actions. Interactions Alcohol or central nervous system depression-producing medications administered concurrently with /topiramate/ may enhance CNS depression. 12 % increase in amitriptyline AUC and Cmax with concommitant use /of topiramate; some patients may experience large increases in amitriptyline concentration in the presents of topiramate; amitriptyline dosage adjustments should be made according to patient's clinical response and not on the basis of plasma levels. Anticholinergic /agents/ or carbonic anhydrase inhibitors such as acetazolamide or dichlorphenamide predispose patients to heat-related disorders; caution should be used when administered concurrently with topiramate. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors may create a physiological environment that increases the risk of renal stone formation; concommitant use should be avoided. Mean carbamazepine area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) was unchanged or changed by less than 10%, whereas the AUC of topiramate was decreased by 40% when these two medications were given concurrently during controlled clinical studies. For more Interactions (Complete) data for TOPIRAMATE (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page. 1. Adverse effects in humans: Common dose-related adverse effects included central nervous system (CNS) symptoms: (15% of patients at 100 mg/day), dizziness (12%), and cognitive impairment (e.g., word-finding difficulty, 8%). Gastrointestinal effects (nausea, 5%) were mild and transient. Serious but rare adverse effects included nephrolithiasis (kidney stones, 1-2% at doses >200 mg/day) and metabolic acidosis (due to carbonic anhydrase inhibition, 0.5%) [2] . 2. Animal toxicity: In a 28-day chronic toxicity study in rats, oral Topiramate (100 mg/kg/day) caused mild weight loss (5-7%) but no changes in hematological parameters (WBC, RBC, platelets) or serum biochemistry (ALT, AST, creatinine). At 300 mg/kg/day, rats developed mild renal tubular vacuolation (reversible after drug withdrawal) [2] . 3. Drug-drug interactions: Co-administration with phenytoin or carbamazepine (antiepileptic drugs that induce renal clearance) reduced Topiramate plasma AUC by 25-30%. Conversely, Topiramate (200 mg/day) increased phenytoin plasma concentration by 10% (due to reduced phenytoin renal excretion) [2] . 4. In vitro toxicity: Topiramate (up to 300 μM) did not induce apoptosis in primary rat cortical neurons (Annexin V-FITC/PI staining) or cause DNA damage (comet assay) [3] . |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
Topiramate is indicated as initial monotherapy in patients 10 years of age and older with partial onset or primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures. /Included in US product label/ Topiramate is indicated for use in the adjunctive treatment of partial onset seizures in adults and pediatric patients ages 2 to 16 years. Topiramate is also indicated for use in the treatment of primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures in adults and in pediatric patients ages 2 to 16 years. /Included in US product label/ Topiramate is indicated for use in the treatment of seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome in patients 2 years of age and older. /Included in US product label/ Topiramate is indicated for adults for the prophylaxis of migraine headache. /Included in US product label/ The usefulness of topiramate in the acute treatment of migraine headache has not been studied. /NOT included in US product label/ Drug Warnings Nervous system effects are the most frequently reported adverse effects of topiramate in adults and generally can be classified into 3 categories: cognitive-related dysfunction (e.g., confusion, psychomotor slowing, difficulty with concentration or attention, difficulty with memory, speech or language problems, particularly word-finding difficulties); psychiatric or behavioral disturbances (e.g., depression, mood problems); and somnolence or fatigue. Cognitive-related adverse effects frequently occur in isolation and often in association with a rapid titration rate and higher initial dosages. Although generally mild or moderate in severity, many of these cognitive-related adverse effects have resulted in discontinuance of topiramate therapy. Psychiatric or behavioral disturbances (including rare cases of suicide attempts) appear to be dose-related in patients receiving topiramate for seizure disorders as well as for migraine prophylaxis. Somnolence and fatigue are the most commonly reported adverse effects in patients receiving topiramate for seizure disorders. In patients receiving topiramate as initial monotherapy for seizure disorders, the frequency of somnolence (but not fatigue) appears to be dose related. In patients receiving topiramate as adjunctive therapy for seizure disorders, the frequency of somnolence does not appear to be dose related; however, fatigue tends to occur with increasing frequency in patients receiving topiramate at dosages exceeding 400 mg daily. In patients receiving topiramate for migraine prophylaxis, somnolence and fatigue appear to be dose related and occur more frequently during the titration phase. Other common dose-related adverse nervous system effects of topiramate (at dosages of 200-1000 mg daily) include nervousness and anxiety. Frequently reported adverse nervous system effects that do not appear to be dose related include dizziness, ataxia, and paresthesia. Paresthesia occurred more frequently in patients receiving topiramate as initial monotherapy for management of seizure disorders or for migraine prophylaxis; however, in most instances, this adverse effect did not result in discontinuance of therapy. Other common dose-related adverse effects of topiramate, in addition to adverse nervous system effects, include anorexia and weight loss. Frequently reported adverse effects that do not appear to be dose related include abnormal vision and diplopia. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for TOPIRAMATE (20 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Topiramate prevents the occurrence of seizures and prevents migraine symptoms by reducing neural pathway excitability. It is important to note that this drug may cause metabolic acidosis, mood changes, suicidal thoughts and attempts, as well as kidney stones. When topiramate is combined with [valproic acid], it is known to cause hypothermia. 1. Chemical class and development background: Topiramate is a sulfamate-substituted monosaccharide derivative (chemically: 2,3:4,5-di-O-isopropylidene-β-D-fructopyranose sulfamate), developed as a broad-spectrum antiepileptic drug (AED) with a unique multi-target mechanism (distinct from traditional AEDs like phenytoin or valproate) [2, 3] . 2. Antiepileptic mechanism of action: Topiramate exerts its effects via four complementary mechanisms: (1) Inhibiting GluR5 kainate receptors to reduce glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity; (2) Stabilizing voltage-gated sodium channels to limit repetitive neuronal firing; (3) Inhibiting L-type calcium channels to reduce calcium influx and neuronal hyperexcitability; (4) Weakly inhibiting carbonic anhydrase to modulate brain pH and synaptic transmission [1, 2, 3] . 3. Clinical indications: Approved for the treatment of: (1) Partial-onset seizures (with or without secondary generalization) in adults and children ≥2 years old; (2) Primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures in adults and children ≥6 years old; (3) Adjunctive therapy for Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (a severe pediatric epilepsy syndrome) [2] . 4. Formulation: Available as oral tablets (25, 50, 100 mg) and oral sprinkle capsules (15, 25 mg) for pediatric patients or those unable to swallow tablets. It is soluble in water (13 mg/mL at 25°C) and stable in acidic and neutral solutions [2] . |
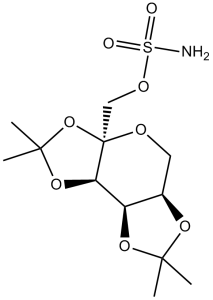
| 分子式 |
C12H21NO8S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
339.36
|
|
| 精确质量 |
339.098
|
|
| CAS号 |
97240-79-4
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Topiramate lithium;488127-53-3
|
|
| PubChem CID |
5284627
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
438.7±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
125ºC
|
|
| 闪点 |
219.1±31.5 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.497
|
|
| LogP |
2.97
|
|
| tPSA |
123.92
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
9
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
22
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
556
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
4
|
|
| SMILES |
CC1(O[C@@H]2CO[C@@]3([C@H]([C@@H]2O1)OC(O3)(C)C)COS(=O)(=O)N)C
|
|
| InChi Key |
KJADKKWYZYXHBB-XBWDGYHZSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C12H21NO8S/c1-10(2)18-7-5-16-12(6-17-22(13,14)15)9(8(7)19-10)20-11(3,4)21-12/h7-9H,5-6H2,1-4H3,(H2,13,14,15)/t7-,8-,9+,12+/m1/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
[(1R,2S,6S,9R)-4,4,11,11-tetramethyl-3,5,7,10,12-pentaoxatricyclo[7.3.0.02,6]dodecan-6-yl]methyl sulfamate
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.37 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.37 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.37 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 16.67 mg/mL (49.12 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9467 mL | 14.7336 mL | 29.4672 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5893 mL | 2.9467 mL | 5.8934 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2947 mL | 1.4734 mL | 2.9467 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT06282783 | Not yet recruiting | Drug: Topiramate | HIV-1-infection Hiv |
Erasmus Medical Center | September 2024 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
| NCT04986631 | Recruiting | Drug: Topiramate Tablets | Obesity, Childhood | University of Minnesota | April 4, 2022 | Early Phase 1 |
| NCT01682681 | Completed Has Results | Drug: Topiramate | Epilepsy | Janssen Korea, Ltd., Korea | July 2007 | |
| NCT06248931 | Recruiting | Drug: Valproic acid Drug: Topiramate 50 MG |
Migraine Disorders | Kafrelsheikh University | February 1, 2024 | Phase 3 |