| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Aurora A (Ki = 0.6 nM); Aurora B (Ki = 18 nM); Aurora C (Ki = 4.6 nM)
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
当用 ABL 或 FLT-3(突变型和野生型)激酶转染的 BaF3 细胞暴露于 tozasertib 时,除了相当的细胞毒性(IC50 约为 300 nM)外,细胞还表现出 G2/M 停滞、核内复制和凋亡。抑制表型类似于 AUR B。tozasertib 具有时间依赖性抑制 CAL-62 的生长。在 tozasertib 治疗 14 天后,8305C 的集落数量和大小显着减少约 70%,CAL-62、8505C 和 BHT-101 显着减少 90%。用 tozasertib 处理不同的 ATC 细胞系,可降低生长,IC50 范围为 25 至 150 nM。 Tozasertib 显着降低了许多细胞系在软琼脂中建立集落的能力。 Caspase-3 活性分析表明,Tozasertib 会导致多种细胞类型凋亡。暴露于tozasertib 12小时后,CAL-62细胞积累了DNA含量低于4N的细胞。延时成像显示,Tozasertib 处理的 CAL-62 细胞退出中期而不增殖。此外,使用 tozasertib 会消除组蛋白 H3 磷酸化 [2]。在患者来源的样本中,tozasertib 显着抑制带有 T315I 突变的 BCR-Abl [3]。
|
||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
VX-680 使人类 AML (HL-60) 异种移植模型中的肿瘤大小显着减小。在 mude 小鼠中,每天两次腹腔注射 (bidip) 75 mg/kg VX-680 治疗 13 天,平均肿瘤体积减少了 98%。肿瘤生长减少是剂量依赖性的,并且在 12.5 mg/kg bid 的剂量下显着,VX-680 具有良好的耐受性,仅在最高剂量时观察到体重小幅下降。 VX-680 还在胰腺和结肠异种移植模型中引发肿瘤消退。当静脉注射给携带 HCT116 肿瘤的 mude 大鼠时,VX-680 也显示出有效的抗肿瘤活性。更高剂量的 VX-680 (2 mg/kg/h) 可提高疗效,平均肿瘤体积减少 56%。
|
||
| 酶活实验 |
ABL2激酶结构域的蛋白表达与纯化[2]
用Sf9细胞培养获得的杆状病毒感染悬浮培养的Trichoplusia ni (Hi5)细胞,以2 × 106个/mL的密度表达该蛋白。感染后48 h,离心收获细胞,细胞微球保存于- 80℃。细胞重悬于由5mm咪唑、500 mM NaCl、50 mM Hepes、pH 7.4、5%甘油、0.5 mM三(2-羧基乙基)膦(TCEP)组成的缓冲液中,补充完整的蛋白酶抑制剂混合物,超声裂解。裂解液在45000g下,在4℃下离心1 h。过滤后的上清液上载于镍螯合树脂上。洗涤后,用上述缓冲液加50 ~ 300 mM咪唑洗脱蛋白,洗脱液混合。用TEV蛋白酶在4°C下处理过夜,去除六组氨酸标签。将消化后的ABL2浓缩至2.5 mL体积,上载于Superdex75凝胶过滤柱(hilload 16/60, GE Healthcare),在10 mM Hepes、pH 8.0、300 mM NaCl和0.5 mM TCEP中平衡。[2] 通过电喷雾电离飞行时间质谱法对该蛋白进行了鉴定。在去除六组氨酸标签之前,与计算质量33 502相比,观察到的质量为33 414 Da;质量的差异很可能是由于去除了n端蛋氨酸,然后乙酰化。去除六组氨酸标签后,观察到的质量为30 980 Da,与计算质量完全吻合。 结晶与数据收集[2] ABL2:伊马替尼复合物(PDB代码3GVU,表2)2)在4°C下从ABL2:伊马替尼(4 mg/mL含有1 mM伊马替尼的蛋白质)和储层溶液(20% PEG3350, 0.1 M柠檬酸盐,pH 5.5)的1:1比例滴入200 nL滴液中结晶。然后晶体在含20% (v/v) PEG300的储层溶液中冷冻,并在液氮中速冻。在瑞士光源(SLS)下,在X10SA光束线上采集了100 K下的x射线衍射数据。 |
||
| 细胞实验 |
免疫印迹[3]
细胞在RIPA缓冲液(50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), 1% NP-40, 0.5%脱氧胆酸钠,150 mM氯化钠,1 mM EDTA, 1×蛋白酶抑制剂鸡尾酒集III)中裂解,超声,然后在15 000 g下离心20分钟。用Bradford法测定蛋白浓度。50 μg细胞蛋白提取物等分液在12.5%聚丙烯酰胺凝胶上电泳,并转移到硝化纤维素膜上。然后用TBST (50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl, 0.05% twee -20)洗涤膜,用5%低脂牛奶在TBST中饱和,然后在4°C下与抗极光a(1:500),极光b(1:500),极光C(1:500)或肌动蛋白(1:100)抗体在TBS-T中孵育过夜。洗涤后,将膜与合适的山根过氧化物酶偶联抗小鼠或兔IgG二抗(1:20 000)在TBST中孵育,并使用化学发光超级信号试剂盒 进行开发。使用Bio-Rad 670型扫描密度计的Molecular Analyst PC软件,通过扫描密度测定法定量极光激酶和肌动蛋白免疫反应带。计算不同的极光激酶/肌动蛋白比值,得到Tozasertib (VX680;MK0457)处理的细胞与对照细胞中的细胞相比归一化,并报告为变异的倍数。 扩散试验[3] CAL-62细胞在不含(二甲基亚砜,DMSO)或500 nM Tozasertib (VX680;MK0457)的不同时间段(1-5天)。 用不同浓度的Aurora抑制剂(5-500 nM)处理不同的ATC细胞4天,观察Tozasertib (VX680;MK0457)对细胞增殖的影响。在孵育结束前,用30 mM BrdU脉冲标记细胞2小时。根据制造商的说明,使用细胞增殖ELISA试剂盒(罗氏应用科学)通过比色免疫分析法分析BrdU掺入。Tozasertib (VX680;MK0457)处理的细胞与对照细胞中观察到的细胞进行比较,表达为与对照相比的变异倍数。 流式细胞仪分析[3]< br > CAL-62细胞在DMSO缺失或250 nM Tozasertib (VX680;MK0457)持续6、12或72小时。在一些实验中,细胞在收获前20分钟用30 mM BrdU处理。用橡皮警棍刮擦,在PBS中收集细胞,并将其固定在冰冷的乙醇中。使用EPICS Elite流式细胞仪分析细胞样本的DNA含量(碘化丙啶)和/或BrdU含量(FITC),如前所述(30)。 软琼脂的菌落形成[3] 首先加入3 ml含0.4%软琼脂的完整培养基,制备直径为3.5 cm的培养皿。将贴壁ATC细胞培养物胰蛋白酶化并离心,获得150000个活细胞/ml的单细胞悬液。将悬浮液与含0.4%软琼脂的完全培养基按1:2的比例混合,然后分成两份,其中一份添加Tozasertib (VX680;MK0457) 250 nM,另一个与载具(DMSO)。将这些悬浮液涂于培养皿中,1 ml/皿,在37°C和5% CO2下孵育。处理过的和未处理过的板在电镀后几小时拍照,以排除细胞聚集物的存在(数据未显示),并在2周后再次拍照。利用MetaVue软件 测量菌落大小,对直径大于50 μm的菌落进行评分。 Caspase-3试验[3] 不同的ATC细胞在不含DMSO或存在250 nM Tozasertib (VX680;MK0457) 72 h。处理后,用PBS冲洗细胞,在PBS中刮取。然后使用caspase-3/CPP32荧光测定试剂盒评估细胞的caspase-3活性。 延时分析[3] CAL-62细胞在DMSO缺失或250 nM Tozasertib (VX680;MK0457),在配备孵育室的徕卡DM-IRBE显微镜下,在37°C和5% CO2条件下观察24 h。使用MetaVue软件每5分钟拍摄一次细胞图片。 免疫荧光(如果)[3] 玻璃片上培养的CAL-62细胞用250 nM Tozasertib (VX680;MK0457)或Vehicle(DMSO) 6小时。细胞在冷甲醇中固定2分钟,洗涤,在室温下用3% BSA在PBS中预孵育1小时。PBS洗涤三次后,细胞与抗tacc3抗体(1:100)、抗aurora - a抗体(1:200)、抗aurora - b抗体(1:200)、抗aurora - c抗体(1:200)、抗p -组蛋白H3抗体(1:100)、抗γ-微管蛋白抗体(1:200)、抗β-微管蛋白抗体(1:200)室温孵育2小时。 |
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Metabolism / Metabolites
Tozasertib has known human metabolites that include Unii-1S9W4WJ8WL and Unii-wuu5ros9AF. |
||
| 参考文献 |
|
||
| 其他信息 |
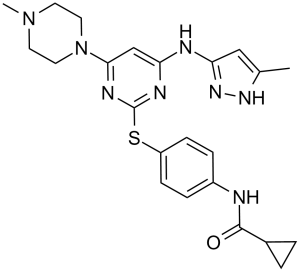
N-[4-[[4-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-6-[(5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)amino]-2-pyrimidinyl]thio]phenyl]cyclopropanecarboxamide is a N-arylpiperazine.
See also: Tozasertib Lactate (annotation moved to). ABL2 (also known as ARG (ABL related gene)) is closely related to the well-studied Abelson kinase cABL. ABL2 is involved in human neoplastic diseases and is deregulated in solid tumors. Oncogenic gene translocations occur in acute leukemia. So far no structural information for ABL2 has been reported. To elucidate structural determinants for inhibitor interaction, we determined the cocrystal structure of ABL2 with the oncology drug imatinib. Interestingly, imatinib not only interacted with the ATP binding site of the inactive kinase but was also bound to the regulatory myristate binding site. This structure may therefore serve as a tool for the development of allosteric ABL inhibitors. In addition, we determined the structures of ABL2 in complex with VX-680 and with an ATP-mimetic type I inhibitor, which revealed an interesting position of the DFG motif intermediate between active and inactive conformations, that may also serve as a template for future inhibitor design.[2] Anaplastic thyroid cancers (ATC) are aggressive tumors, which exhibit cell cycle misregulations leading to uncontrolled cellular proliferation and genomic instability. They fail to respond to chemotherapeutic agents and radiation therapy, and most patients die within a few months of diagnosis. In the present study, we evaluated the in vitro effects on ATC cells of VX-680, an inhibitor of the Aurora serine/threonine kinases involved in the regulation of multiple aspects of chromosome segregation and cytokinesis. The effects of VX-680 on proliferation, apoptosis, soft agar colony formation, cell cycle, and ploidy were tested on the ATC-derived cell lines CAL-62, 8305C, 8505C, and BHT-101. Treatment of the different ATC cells with VX-680 inhibited proliferation in a time- and dose-dependent manner, with the IC50 between 25 and 150 nM. The VX-680 significantly impaired the ability of the different cell lines to form colonies in soft agar. Analysis of caspase-3 activity showed that VX-680 induced apoptosis in the different cell lines. CAL-62 cells exposed for 12 h to VX-680 showed an accumulation of cells with > or =4N DNA content. Time-lapse analysis demonstrated that VX-680-treated CAL-62 cells exit metaphase without dividing. Moreover, histone H3 phosphorylation was abrogated following VX-680 treatment. In conclusion, our data demonstrated that VX-680 is effective in reducing cell growth of different ATC-derived cell lines and warrant further investigation to exploit its potential therapeutic value for ATC treatment.[3] |
| 分子式 |
C23H28N8OS
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
464.59
|
|
| 精确质量 |
464.21
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 59.46; H, 6.07; N, 24.12; O, 3.44; S, 6.90
|
|
| CAS号 |
639089-54-6
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
5494449
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.708
|
|
| LogP |
1.18
|
|
| tPSA |
127.37
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
33
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
650
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| InChi Key |
GCIKSSRWRFVXBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C23H28N8OS/c1-15-13-20(29-28-15)25-19-14-21(31-11-9-30(2)10-12-31)27-23(26-19)33-18-7-5-17(6-8-18)24-22(32)16-3-4-16/h5-8,13-14,16H,3-4,9-12H2,1-2H3,(H,24,32)(H2,25,26,27,28,29)
|
|
| 化学名 |
(N-[4({4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-6-[(3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5 -yl)amino]pyrimidin-2-yl}thio)phenyl]cyclopropanecarboxamide)
|
|
| 别名 |
Tozasertib, MK-0457; VX-680; MK 0457; MK-0457; VX680; VX 680; MK0457; VE 465; VE465; VE-465
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.48 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.48 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.48 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 30% PEG400+0.5% Tween80+5% propylene glycol:30mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1524 mL | 10.7622 mL | 21.5244 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4305 mL | 2.1524 mL | 4.3049 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2152 mL | 1.0762 mL | 2.1524 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT02532868 | Terminated | Drug: MK-0457 | Cancer | Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC | May 2005 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00099346 | Terminated | Drug: MK0457, VX-680 (Aurora Kinase Inhibitor) |
Colorectal Cancer Advanced Solid Tumors |
Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC | January 2005 | Phase 1 |
ABL2 bound to a type I inhibitor2. (A) ABL2:2, showing the compound bound to the ATP binding site, and the ordered activation loop. Compound2is shown in yellow.J Med Chem.2011 Apr 14;54(7):2359-67. |
Myristate binding pocket of ABL2. (A) Surface of the myristate binding pocket of ABL2, with imatinib shown as a yellow ball-and-stick representation.J Med Chem.2011 Apr 14;54(7):2359-67. |
Comparison of ABL2:imatinib and ABL2:1with ABL1:imatinib and ABL1:1.J Med Chem.2011 Apr 14;54(7):2359-67. |