| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 靶点 |
AMPK; Autophagy; Mitophagy; Human Endogenous Metabolite
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
HepG2 细胞分别用不同剂量的 AICAR (0.1-1.0 mM) 处理 12、24 和 48 小时。使用 0.25、0.5 和 1.0 mM AICAR 后 48 小时,IR-β 的表达水平分别显着降低至对照的 50%、53% 和 46% [1]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
将 0.5 mg AMP 激活激酶 (AMPK) 激活剂 AICAR (A) *g 体重 wt-1*day-1 或生理盐水对照 (C) 注射到 14 周龄雄性瘦肉动物 (L; 31.3克体重)野生型和ob/ob(O;59.6克体重)小鼠。最后一次注射后 24 小时(其中包括 12 小时禁食)取出腓肠肌、比目鱼肌和跖屈肌复合体的跖肌进行分析。然后对所有动物实施安乐死。无论体重变化如何,与 LC、LA 和 OA 小鼠(分别为 176±10、178±9 和 166±16 mg)相比,OC 小鼠的肌肉质量减少(159±12 mg)[3]。与运动组和AICAR(0.5毫克/克体重)组相比,未治疗组的肾脏重量明显更高。运动组的心脏重量高于其他组,但 AICAR 治疗组的肝脏重量明显大于运动组和未治疗组 [4]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
在半固体甲基纤维素培养基中,向 K562 细胞系或原代细胞(103 CD34+ 细胞/mL)给予阿卡地辛。细胞系和原代 CD34+ 细胞分别用 MethoCult H4100 或 H4236 培养。培养 10 天后,通过添加 1 mg/mL 3-(4,5-二甲基噻唑-2-基)-2,5-二苯基四唑溴化物 (MTT) 试剂发现菌落,并使用 Image J 对它们进行评分量化软件。
|
| 细胞实验 |
将 HepG2 细胞(5×105 个细胞)接种到 6 孔培养板中,然后在转染前在无血清培养基中培养 12 小时。 FuGENE6转染试剂用于转染一微克质粒。转染5小时后,除去培养基,然后将添加或不添加AICAR (0.1-1.0 mM)的培养基添加到每个孔中。每 24 小时更换一次刺激介质[。
|
| 动物实验 |
Lifexstyle interventions including exercise programs are cornerstones in the prevention of obesity-related diabetes. The AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) has been proposed to be responsible for many of the beneficial effects of exercise on glucose and lipid metabolism. The effects of long-term exercise training or 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-d-riboruranoside (AICAR) treatment, both known AMPK activators, on the development of diabetes in male Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rats were examined. Five-week-old, pre-diabetic ZDF rats underwent daily treadmill running or AICAR treatment over an 8-week period and were compared with an untreated group. In contrast to the untreated, both the exercised and AICAR-treated rats did not develop hyperglycemia during the intervention period. Whole-body insulin sensitivity, as assessed by a hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp at the end of the intervention period, was markedly increased in the exercised and AICAR-treated animals compared with the untreated ZDF rats (P < 0.01). In addition, pancreatic beta-cell morphology was almost normal in the exercised and AICAR-treated animals, indicating that chronic AMPK activation in vivo might preserve beta-cell function. Our results suggest that activation of AMPK may represent a therapeutic approach to improve insulin action and prevent a decrease in beta-cell function associated with type 2 diabetes.[4]
|
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
The liver is one of the major target organs of insulin in which the expression of insulin receptor is abundant. We analyzed the effect of AICAR, an AMPK activator, on the expression of insulin receptor in a human hepatoma cell line, HepG2 cells. AICAR treatment for 48 h significantly decreased the expression of the insulin receptor protein in a dose-dependent manner, however, this same effect of AICAR was not observed in either 3T3-L1 adipocytes or CHO cells. The expression of insulin receptor mRNA also decreased after AICAR treatment. In addition, the transcriptional activity of the insulin receptor gene promoter investigated with a luciferase assay was down-regulated by AICAR treatment. Dipyridamole, an adenosine transporter inhibitor, and 5'-amino-5'-deoxyadenosine, an adenosine kinase inhibitor, blocked the effect of AICAR on the down-regulation of the insulin receptor protein, mRNA, and promoter activity. Our findings suggest, for the first time, that AMPK activation could reduce the expression of insulin receptor, at least in part, by a down-regulation of the transcriptional level, and this effect may be liver specific.[1]
The aim of this study was to determine the effect of 14 days of 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1β-4-ribofuranoside (AICAR) treatment on mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling and mTOR-regulated processes (i.e., translation initiation) in obese mouse skeletal muscle. Our hypothesis was that daily treatment (14 days) with AICAR would normalize obesity-induced alterations in skeletal muscle mTOR signaling and mTOR-regulated processes to lean levels and positively affect muscle mass. Fourteen-week-old male, lean (L; 31.3 g body wt) wild-type and ob/ob (O; 59.6 g body wt) mice were injected with the AMP-activated kinase (AMPK) activator AICAR (A) at 0.5 mg·g body wt(-1)·day(-1) or saline control (C) for 14 days. At 24 h after the last injection (including a 12-h fast), all mice were killed, and the plantar flexor complex muscle (gastrocnemius, soleus, and plantaris) was excised for analysis. Muscle mass was lower in OC (159 ± 12 mg) than LC, LA, and OA (176 ± 10, 178 ± 9, and 166 ± 16 mg, respectively) mice, independent of a body weight change. A decrease in obese muscle mass corresponded with higher muscle cross section staining intensity for lipid and glycogen, higher blood glucose and insulin levels, and lower nuclear-enriched fractions for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α protein expression in OC skeletal muscle, which was normalized with AICAR treatment. AMPK and acetyl-cocarboxylase phosphorylation was reduced in OC mice and augmented by AICAR treatment in OA mice. Conversely, OC mice displayed higher activation of downstream targets (S6 kinase-1 and ribosomal protein S6) of mTOR and lower raptor-associated mTOR than LC mice, which were reciprocally altered after 14 days of AICAR treatment. Dysregulation of translational capacity was improved in OA mice, as assessed by sucrose density gradient fractionation of ribosomes, total and ribosome-associated RNA content, eukaryotic initiation factor 4F complex formation, and eukaryotic initiation factor 4G phosphorylation. These data show that short-term (14 days) AMPK agonist treatment augments regulatory processes in atrophic obese mouse skeletal muscle through the normalization of mTOR signaling and mRNA translation closer to lean levels.[3] |
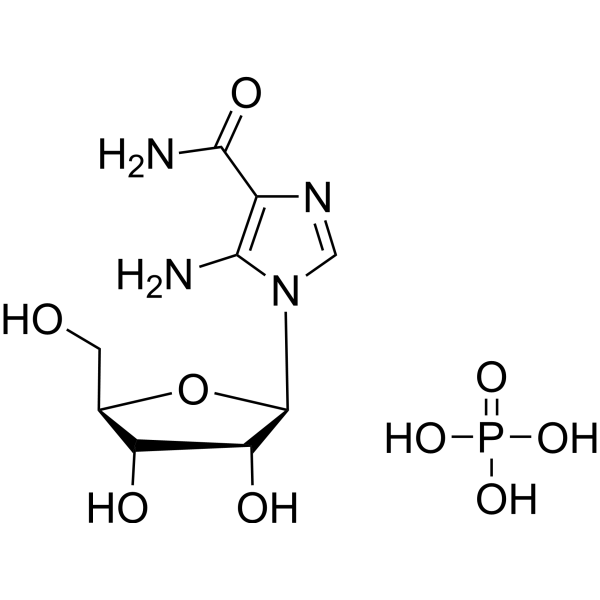
| 分子式 |
C9H17N4O9P
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
356.2264
|
| 精确质量 |
356.073
|
| CAS号 |
681006-28-0
|
| 相关CAS号 |
AICAR;2627-69-2
|
| PubChem CID |
67675098
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| tPSA |
235
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
8
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
11
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
| 重原子数目 |
23
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
380
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
4
|
| SMILES |
P(=O)(O[H])(O[H])O[H].O1[C@]([H])(C([H])([H])O[H])[C@]([H])([C@]([H])([C@]1([H])N1C([H])=NC(C(N([H])[H])=O)=C1N([H])[H])O[H])O[H]
|
| InChi Key |
BPVGMEHURDEDAZ-GWTDSMLYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C9H14N4O5.H3O4P/c10-7-4(8(11)17)12-2-13(7)9-6(16)5(15)3(1-14)18-9;1-5(2,3)4/h2-3,5-6,9,14-16H,1,10H2,(H2,11,17);(H3,1,2,3,4)/t3-,5-,6-,9-;/m1./s1
|
| 化学名 |
5-amino-1-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]imidazole-4-carboxamide;phosphoric acid
|
| 别名 |
AICAR (phosphate); AICAR phosphate; 681006-28-0; 5-amino-1-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]imidazole-4-carboxamide;phosphoric acid; SCHEMBL8722270;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
H2O : ~100 mg/mL (~280.72 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.84 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.84 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.84 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 33.33 mg/mL (93.56 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8072 mL | 14.0359 mL | 28.0718 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5614 mL | 2.8072 mL | 5.6144 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2807 mL | 1.4036 mL | 2.8072 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。