| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Thrombin (Ki = 5-39 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
由于其对凝血酶的单一靶点特异性,阿加曲班 (MD-805) 可能具有避免血栓形成而不加重出血倾向的补充作用。为了治疗左心搭桥手术期间与多器官损伤相关的创伤性主动脉破裂,以 0.5 至 2 mcg/kg/分钟的速度注射一种安全的抗凝剂阿加曲班 (MD-805) [1]。与肝素相比,阿加曲班 (MD-805) 似乎可以改善 AMI 患者的 TPA 再灌注,尤其是那些晚于预期就诊的患者。阿加曲班治疗的患者严重出血事件较少,临床结果较差[2]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
阿加曲班可在大脑中动脉 (MCA) 闭塞后 3 小时内抑制微血栓的形成;超过3小时则无效。阿加曲班还可以显着减少 MCA 闭塞后 6 小时缺血性脑损伤的大小。在大鼠远端大脑中动脉闭塞模型中,阿加曲班(0.3 mg/h/大鼠)显着减少远端大脑中动脉(dMCA)闭塞后 1 天的微血栓数量。阿加曲班(0.1 和 0.3 mg/h/大鼠)可显着逆转远端大脑中动脉 (dMCA) 闭塞后 1 天局部脑血流量 (rCBF) 的减少。阿加曲班(0.3 mg/h/大鼠)还可显着减小脑梗塞的面积。
1.在三种大鼠血栓形成模型和尾部横断出血时间试验中研究了合成凝血酶抑制剂Argatroban的抗血栓作用。肝素被研究作为参考抗凝剂。2.在凝血活酶诱导的静脉血栓形成后腹腔静脉淤滞的模型中,当在注射凝血活酶前5分钟静脉推注阿加曲班时,其ED50为125微克kg-1:肝素的ED50为42微克kg-1,其中ED50是与对照组动物相比将血栓重量减少50%的剂量。当这两种化合物通过连续静脉输注给药时,阿加曲班(ED50=1.5微克kg-1 min-1)与肝素(ED50=1.2微克kg-1 cm-1)具有相同的效力。3.阿加曲班在动静脉分流模型中具有活性,当该化合物以丸剂形式给药时,ED50为0.6mg kg-1。在相同条件下,肝素的ED50为0.04 mg kg-1。当通过连续静脉输注给药时,这两种化合物的ED50值分别为6微克kg-1 min-1(阿加曲班)和3微克kg-1 min-1(肝素)。4.当通过电刺激左颈动脉来测试闭塞性动脉血栓形成时,静脉推注或连续输注这两种化合物都会导致病变后血管通畅持续时间的剂量依赖性增加。[1] 缺血性脑梗死会导致周围区域的高凝状态和微血栓形成,从而导致血管闭塞。我们确定了微血栓是否会导致血栓性大脑中动脉(MCA)闭塞后缺血性病变的扩散,还确定了选择性凝血酶抑制剂Argatroban是否会减少微血栓的形成和缺血性病变的面积。大鼠左大脑中动脉被玫瑰红与绿光发生光化学反应后形成的富含血小板的血栓闭塞。左半球组织学上发现微血栓。MCA闭塞后,缺血性病变和含微血栓纤维蛋白的程度呈时间依赖性增加。阿加曲班在MCA闭塞后3小时内抑制了微血栓的形成;3小时后无效。阿加曲班在MCA闭塞后6小时也显著(P<0.01)减小了缺血性脑损伤的大小。结论是,微血栓的形成有助于早期缺血性病变的进展。血栓性MCA闭塞后产生的凝血酶可能通过促进微血栓的形成来促进缺血性病变的进展。阿加曲班可以减少早期微血栓和缺血性病变的形成。[3] 为了阐明凝血酶在局灶性脑缺血期间脑损伤中的作用,我们使用大鼠血栓性大脑中动脉远端(dMCA)闭塞模型研究了选择性凝血酶抑制剂Argatroban对微血栓形成、局部脑血流(rCBF)、梗死区和神经功能缺损的影响。大鼠dMCA被玫瑰红与绿光发生光化学反应后形成的富含血小板的血栓闭塞。dMCA闭塞后一天,计数微血栓的数量。在单独的动物中,在dMCA闭塞后1天使用碘安替比林法测量rCBF。dMCA闭塞三天后,进行行为测试并确定脑梗死的大小。在本研究中,阿加曲班在dMCA闭塞后通过持续输注腹腔注射给药。阿加曲班(0.3mg/h/大鼠)显著降低了dMCA闭塞后1天的微血栓数量(P<0.05)。阿加曲班(0.1和0.3 mg/h/大鼠)显著(P<0.01)逆转了dMCA闭塞后1天rCBF的下降。阿加曲班(0.3mg/h/大鼠)也显著(P<0.01)减小了脑梗死的大小。阿加曲班(0.1和0.3 mg/h/大鼠)的给药导致dMCA闭塞后3天神经功能缺损的显著改善(分别为P<0.01和P<0.05)。阿加曲班在大鼠血栓性dMCA闭塞模型中减小了脑梗死的大小并改善了神经功能缺损。这些影响被认为是由于dMCA闭塞后rCBF的改善和继发血栓形成的减少[4]。 T2DM与心脏结构和功能紊乱有关,这可以从心脏功能参数受损和纤维化增加中得到证明。糖尿病诱导20周后,标准杆数表达显著增加。四周的阿加曲班治疗改善了代谢改变(降低了血糖和胆固醇)、心室功能障碍(改善了收缩和舒张功能)、心脏纤维化(减少了皮氏红染色中胶原蛋白的百分比面积)和凋亡(减少了TUNEL阳性核)。阿加曲班治疗组PAR1和PAR4的表达降低表明对凝血酶的抑制有反应。此外,阿加曲班治疗的糖尿病大鼠的AKT(Ser-473)、GSK-3β(Ser-9)、p-65 NFB磷酸化、TGF-β、COX-2和caspase-3表达显著降低,SERCA表达增加,这表明阿加曲班组在DCM中具有抗纤维化、抗炎和抗凋亡的潜力。 结论:本研究提示阿gatroban通过改善心室功能、减少纤维化、炎症、细胞凋亡和标准杆数表达,对糖尿病心肌病具有改善作用[5]。 阿加曲班适合构建诱导内源性肠血栓形成的动物模型。在肝切除的大鼠中,阿加曲班的药代动力学参数,如曲线下面积、分布体积和消除半衰期,显著增加4. 阿曲班在肾脏中从21-(R)异构体转化为21-(S)非对映异构体,后者表现出更强的抗血栓活性,并可能具有更高的肝清除率。 溶栓诱导 致病机制 阿加曲班是一种特异性凝血酶抑制剂,通过抑制动物体内的凝血酶活性建立溶栓模型。 建模方法 动物:Wistar ST•雄性•8周龄 管理:2毫克/千克/小时•静脉注射•1小时 注:溶栓实验前,允许自由饮水并禁食过夜 成功标准 血栓溶解相对速率↓ |
| 细胞实验 |
阿加曲班对肌球蛋白重链亚型mRNA表达的影响[2]
测试了特定凝血酶抑制剂Argatroban对培养的血管平滑肌细胞表型转化的影响。用0.01%胰蛋白酶-EDTA溶液孵育5分钟,分离培养的血管平滑肌细胞,并用1.5×105个细胞重新接种在25-cm2的烧瓶上。将细胞在10%胎牛血清-DMEM中培养9小时后,将培养基换成含有PDGF-BB(10和50 ng/ml)或阿加曲班(10和5 0μg/ml)的无血清DMEM,然后孵育3或24小时。孵育后,提取总RNA进行RT-PCR,用10%福尔马林-PBS固定细胞进行原位杂交,以检测肌球蛋白重链亚型的mRNA表达。 阿加曲班对SMemb蛋白表达的影响[2] 为了测量用Argatroban刺激培养的血管平滑肌细胞后SMemb的蛋白质水平,根据Towbin等人(1979)的方法进行了蛋白质印迹。刺激后3小时和24小时,根据Rovner等人(1986)的方法制备粗肌球蛋白提取物,并稍作修改。简而言之,Rubber Policeman从培养瓶中取出培养的血管平滑肌细胞(1.5×105个细胞),用PBS冲洗,并通过离心(1600 rpm,4°C)5分钟收集。将50μl提取缓冲液(50 mM NaH2PO4,1 mM EGTA,0.125 mMα-苯甲磺酰氟,pH 7.0)加入细胞沉淀中,用迷你无绳研磨机用一次性研杵均质化。离心(10000 rpm,4°C)10分钟后,将颗粒溶解在Gubba-Straub溶液(150 mM NaH2PO4、300 mM NaCl、1 mM EGTA、0.125 mMα-苯甲磺酰氟、1 mM 2-巯基乙醇、10 mM ATP,pH 6.7)中,然后在4°C下轻轻混合1小时。离心(10000 rpm,4°C)10分钟之后,收集上清液作为粗肌球蛋白提取物。为了分离粗肌球蛋白提取物中的蛋白质,使用Phast系统进行了8-25%梯度凝胶的十二烷基硫酸钠聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳(SDS-PAGE)。凝胶中的蛋白质通过PhastTransfer在15°C、20 V和25 mA下电印迹到聚偏二氟乙烯(PVDF)膜上90分钟。印迹后,在室温下用PBS中的3%脱脂乳封闭膜2小时,然后将膜与单克隆抗非肌肉肌球蛋白重链在4°C下孵育过夜,用PBS中3%脱脂乳稀释至1:1000。用PBS中0.1%吐温20洗涤5次,每次10分钟后,将膜与PBST中1%脱脂乳中1:3000稀释的羊抗小鼠IgG2b在室温下孵育1小时。通过PBS两次加入底物溶液(0.1mg/ml 3-氨基-9-乙基咔唑在0.1M磷酸钠缓冲液中)。通过NIH图像分析有色SMemb蛋白带的强度。 |
| 动物实验 |
Experimental Design and Pharmacological Interventions [5]
Argatroban is a direct thrombin inhibitor that binds to the catalytic site of thrombin reversibly and thereby inhibits its action. Argatroban was used and the doses (0.3 and 1 mg/kg) were selected based on previous literature. Argatroban was dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and administered daily through i.p. route. Similarly, DMSO was administered through i.p. route in the HFD + STZ group and control group to negate the effect of the vehicle. After the 16th week of STZ injection, presence of diabetes was again reconfirmed and animals with plasma glucose ≥250 mg/dl were considered for further study. Argatroban and vehicle were administered at the dose of 1 ml/kg of body weight. Animals were randomly assigned to the following groups. 1. Normal control group (Ctrl): Animals treated with vehicle dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) from the 16th to 20th week for 4 weeks to control animals on normal pellet diet (NPD). 2. High-fat diet + low-dose STZ 35 mg/kg group (T2DM): Vehicle (DMSO) was administered to T2DM animals for 4 weeks. 3.Low dose argatroban-treated diabetic animals group (T2DM + Arg 0.3 mg/kg): Argatroban was administered at the dose of 0.3 mg/kg, i.p. once daily for 4 weeks to T2DM animals. 4. High dose argatroban-treated diabetic animals group (T2DM + Arg 1 mg/kg): Argatroban was administered at the dose of 1 mg/kg, i.p. once daily for 4 weeks to T2DM animals. 5. Argatroban-treated per se group (Ctrl + Arg 1 mg/kg): Argatroban was administered at the dose of 1 mg/kg i.p., once daily for 4 weeks to control animals on NPD diet. Argatroban is suitable for constructing animal models to induce endogenous intestinal thrombosis. In hepatectomized rats, the pharmacokinetic parameters of Argatroban, such as area under the curve, volume of distribution, and elimination half-life, are significantly increased4. Argatroban is converted from the 21-(R) isomer to the 21-(S) diastereomer in the kidneys, with the latter exhibiting stronger antithrombotic activity and potentially higher hepatic clearance. Thrombolysis Induction Pathogenic Mechanism Argatroban is a specific thrombin inhibitor that establishes thrombolysis models by inhibiting thrombin activity in animals. Modeling Protocol Animal: Wistar ST • Male • 8 weeks old Administration: 2 mg/kg/h • IV • 1 h Note: Allow free access to water and fast overnight before thrombolysis experiments. Success Criteria Relative rate of thrombus dissolution ↓ |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Bioavailability is 100% (intravenous). Argatroban is excreted primarily in the feces (65%), presumably through biliary secretion; 22% is eliminated via urine. 174 mL/kg 12.18 L [70-kg adult] 5.1 L/kg/hr [infusion doses up to 40 mcg/kg/min] Argatroban is excreted primarily in the feces, presumably through biliary secretion. In a study in which (14)C-argatroban (5 ug/kg/min) was infused for 4 hours into healthy subjects, approximately 65% of the radioactivity was recovered in the feces within 6 days of the start of infusion with little or no radioactivity subsequently detected. Approximately 22% of the radioactivity appeared in the urine within 12 hours of the start of infusion. Little or no additional urinary radioactivity was subsequently detected. Average percent recovery of unchanged drug, relative to total dose, was 16% in urine and at least 14% in feces. It is not known if argatroban crosses the human placenta. the molecular weight (about 527 for the hydrated from), low metabolism, and moderate serum protein binding suggest that exposure of the embryo-fetus should be expected, especially sine the drug is given as a continuous infusion. Argatroban distributes mainly in the extra cellular fluid as evidenced by an apparent steady-state volume of distribution of 174 mL/kg (12.18 L in a 70 kg adult). Argatroban is 54% bound to human serum proteins, with binding to albumin and a1 - acid glycoprotein being 20% and 34%, respectively. /MILK/ Argatroban is detected in rat milk. Metabolism / Metabolites Liver via hydroxylation and aromatization of the 3-methyltetrahydroquinoline ring. Age and gender do not substantially affect the pharmacodynamic or pharmacokinetic profile of argatroban. The main route of argatroban metabolism is hydroxylation and aromatization of the 3-methyltetrahydroquinoline ring in the liver. The formation of each of the 4 known metabolites is catalyzed in vitro by the human liver microsomal cytochrome P450 enzymes CYP3A4/5. The primary metabolite (M1) exerts 3- to 5-fold weaker anticoagulant effects than argatroban. Unchanged argatroban is the major component in plasma. The plasma concentrations of M1 range between 0% and 20% of that of the parent drug. The other metabolites (M2 to M4) are found only in very low quantities in the urine and have not been detected in plasma or feces. These data, together with the lack of effect of erythromycin (a potent CYP3A4/5 inhibitor) on argatroban pharmacokinetics, suggest that CYP3A4/5-mediated metabolism is not an important elimination pathway in vivo. Argatroban is metabolized principally by the liver via hydroxylation and aromatization of the 3-methyltetrahydroquinoline ring. Biological Half-Life 39 and 51 minutes The terminal elimination half life is 39-51 minutes. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Because argatroban is poorly absorbed orally, it might not adversely affect a breastfeeding infant. However, no information is available on the use of argatroban during breastfeeding, so an alternate drug is preferred. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Toxicity Summary IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Argatroban is antithrombin, platelet aggregation inhibitor. Direct thrombin inhibitors including argatroban are commonly used anticoagulants in patients with known or suspected heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. HUMAN STUDIES: There are two case reports documenting safe use of argatroban during human pregnancy. Argatroban was not genotoxic in the WI-38 human fetal lung cell unscheduled DNA synthesis (UDS) test. ANIMAL STUDIES: Single intravenous doses of argatroban at 200, 124, 150, and 200 mg/kg were lethal to mice, rats, rabbits, and dogs, respectively. The symptoms of acute toxicity were loss of righting reflex, tremors, clonic convulsions, paralysis of hind limbs, and coma. Developmental studies performed in rats (during gestation Days 7 to 17) with argatroban at intravenous doses up to 27 mg/kg/day and in rabbits (during gestation Days 6 to 18) at intravenous doses up to 10.8 mg/kg/day have revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus. Argatroban was not genotoxic in the Ames test, the Chinese hamster ovary cell (CHO/HGPRT) forward mutation test, the Chinese hamster lung fibroblast chromosome aberration test, the rat hepatocyte or the mouse micronucleus test. Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Because argatroban is poorly absorbed orally, it might not adversely affect a breastfeeding infant. However, no information is available on the use of argatroban during breastfeeding, so an alternate drug is preferred. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding 54% Interactions A combined effect on the INR occurs with coadministration of argatroban and warfarin, and the relationship between INR and bleeding risk is altered. Daily INR determinations are recommended during concomitant use of argatroban and warfarin. Continue to monitor the effects of argatroban using aPTT during conversion to warfarin. Argatroban therapy can be discontinued when the INR exceeds 4 with combined therapy. Repeat INR determinations 4-6 hours after discontinuance of the argatroban infusion should be within the desired therapeutic range for warfarin monotherapy. Potential pharmacologic interaction (increased risk of hemorrhage) with concomitant use of thrombolytics, antiplatelet agents, or other anticoagulants. No pharmacokinetic or pharmacodynamic interaction demonstrated with low-dose oral aspirin (162.5 mg given 26 and 2 hours prior to argatroban infusion) or oral acetaminophen (1 g given every 6 hours for 5 doses beginning 12 hours prior to argatroban infusion). The manufacturer states that the safety and efficacy of concomitant therapy with argatroban and platelet glycoprotein (GP) IIb/IIIa-receptor antagonists has not been established. Heparin is contraindicated in patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT). Prior to initiation of argatroban therapy, allow sufficient time for effect of heparin on activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) to decrease. Pharmacodynamic interaction (increased prothrombin time (PT) and international normalized ratio (INR) relative to warfarin alone). |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Argatroban is an Anti-coagulant and Direct Thrombin Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of argatroban is as a Thrombin Inhibitor.
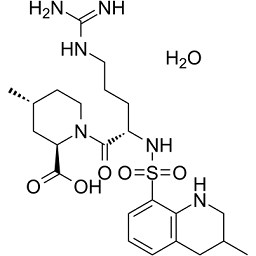
Argatroban is a synthetic derivative of L-arginine with antithrombotic activity. Argatroban is a univalent and direct inhibitor of fibrin-bound thrombin. This agent reversibly binds to the thrombin active site thereby preventing the thrombin-dependent reactions, which include conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin; the activation of factors V, VIII and XI; the activation of protein C; and platelet aggregation. Argatroban is highly selective for thrombin and is able to inhibit the action of both free and clot-associated thrombin. As a result, stabilization of blood clots and coagulation is inhibited. (2R,4R)-1-[(2S)-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)-2-[(3-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolin-8-yl)sulfonylamino]-1-oxopentyl]-4-methyl-2-piperidinecarboxylic acid is a peptide. Argatroban is a direct, selective thrombin inhibitor. The American College of Cardiologists (ACC) recommend using bivalirudin or argatroban in patients who have had, or at risk for, heparin induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) and are undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Argatroban is a non-heparin anticoagulant shown to both normalize platelet count in patients with HIT and prevent the formation of thrombi. Parental anticoagulants must be stopped and a baseline activated partial thromboplastin time must be obtained prior to administering argatroban. Argatroban anhydrous is an Anti-coagulant and Direct Thrombin Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of argatroban anhydrous is as a Thrombin Inhibitor. Argatroban is a synthetic derivative of L-arginine with antithrombotic activity. Argatroban is a univalent and direct inhibitor of fibrin-bound thrombin. This agent reversibly binds to the thrombin active site thereby preventing the thrombin-dependent reactions, which include conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin; the activation of factors V, VIII and XI; the activation of protein C; and platelet aggregation. Argatroban is highly selective for thrombin and is able to inhibit the action of both free and clot-associated thrombin. As a result, stabilization of blood clots and coagulation is inhibited. Argatroban Anhydrous is the anhydrous form of argatroban, a synthetic derivative of L-arginine with antithrombotic activity. Argatroban is a univalent and direct inhibitor of fibrin-bound thrombin. This agent reversibly binds to the thrombin active site, thereby preventing the thrombin-dependent reactions, which include the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin; the activation of factors V, VIII and XI; the activation of protein C; and platelet aggregation. Argatroban is highly selective for thrombin and is able to inhibit the action of both free and clot-associated thrombin. As a result, stabilization of blood clots occurs and coagulation is inhibited. Drug Indication Argatroban is indicated for prevention and treatment of thrombosis caused by heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT). It is also indicated for use in patients with, or at risk for, HIT who are undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. FDA Label Mechanism of Action Argatroban exerts its anticoagulant effects by inhibiting thrombin-catalyzed or -induced reactions, including fibrin formation; activation of coagulation factors V, VIII, and XIII; protein C; and platelet aggregation. Therapeutic Uses Antithrombins; Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors /CLINICAL TRIALS/ ClinicalTrials.gov is a registry and results database of publicly and privately supported clinical studies of human participants conducted around the world. The Web site is maintained by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Each ClinicalTrials.gov record presents summary information about a study protocol and includes the following: Disease or condition; Intervention (for example, the medical product, behavior, or procedure being studied); Title, description, and design of the study; Requirements for participation (eligibility criteria); Locations where the study is being conducted; Contact information for the study locations; and Links to relevant information on other health Web sites, such as NLM's MedlinePlus for patient health information and PubMed for citations and abstracts for scholarly articles in the field of medicine. Argatroban is included in the database. Argatroban injection is indicated as an anticoagulant in adult patients with or at risk for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). /Included in US product label/ Argatroban injection is indicated for prophylaxis or treatment of thrombosis in adult patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT). /Included in US product label/ For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Argatroban (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings Other nonhemorrhagic adverse effects occurring in at least 2% of argatroban-treated patients with HIT/HITTS undergoing PCI include chest pain, back pain, headache, bradycardia, and myocardial infarction. Adverse hemorrhagic effects reported in 2% or more of nonsurgical patients with HIT/HITSS receiving argatroban include major or minor GI bleeding, minor genitourinary bleeding or hematuria, minor decrease in hemoglobin/hematocrit, minor groin or brachial bleeding (e.g., catheter insertion site), and hemoptysis;9 nonhemorrhagic effects include dyspnea, hypotension, fever, diarrhea, sepsis, cardiac arrest, nausea, ventricular tachycardia, pain, urinary tract infection, vomiting, infection, pneumonia, atrial fibrillation, coughing, abnormal renal function, abdominal pain, and cerebrovascular disorder. Safety and efficacy of argatroban not fully established in pediatric patients; however, the drug has been evaluated in a limited number of seriously ill pediatric patients younger than 16 years of age with HIT or HITTS. In a small, multicenter open-label study, 18 seriously ill pediatric patients with a clinical condition requiring alternative nonheparin anticoagulation received argatroban at an initial dosage of 1 ug/kg per minute titrated to maintain a target aPTT of 1.5-3 times the baseline value. During the 30-day study period, thrombotic events occurred in 5 patients and major bleeding (intracranial hemorrhage) was reported in 2 patients. All of the patients had serious comorbid conditions and were receiving multiple concomitant medications; most were diagnosed with documented or suspected HIT. Pharmacokinetic analysis of the data indicated that argatroban clearance was reduced by 50% in seriously ill pediatric patients compared with healthy adults and by approximately 80% in pediatric patients with elevated bilirubin concentrations compared to pediatric patients with normal bilirubin concentrations. Based on these results, reduced dosages of argatroban are recommended in pediatric patients. There are no data on the presence of argatroban in human milk, or its effects on milk production. Argatroban is present in rat milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for Argatroban and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from Argatroban or from the underlying maternal condition. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Argatroban (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Argatroban is a synthetic direct thrombin inhibitor derived from L-arginine indicated as an anticoagulant for prophylaxis or treatment of thrombosis in patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Argatroban is a direct thrombin inhibitor that reversibly binds to the thrombin active site. Argatroban does not require the co-factor antithrombin III for antithrombotic activity. Argatroban exerts its anticoagulant effects by inhibiting thrombin-catalyzed or -induced reactions, including fibrin formation; activation of coagulation factors V, VIII, and XIII; protein C; and platelet aggregation. Argatroban is highly selective for thrombin with an inhibitory constant (Ki) of 0.04 µM. At therapeutic concentrations, Argatroban has little or no effect on related serine proteases (trypsin, factor Xa, plasmin, and kallikrein). Argatroban is capable of inhibiting the action of both free and clot-associated thrombin. Purpose: Chronic diabetes is associated with cardiovascular dysfunctions. Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) is one of the serious cardiovascular complications associated with diabetes. Despite significant efforts in understanding the pathophysiology of DCM, management of DCM is not adequate due to its complex pathophysiology. Recently, involvement of protease-activated receptors (PARs) has been postulated in cardiovascular diseases. These receptors are activated by thrombin, trypsin, or other serine proteases. Expression of PAR has been shown to be increased in cardiac diseases such as myocardial infarction, viral myocarditis, and pulmonary arterial hypertension. However, the role of PAR in DCM has not been elucidated yet. Therefore, in the present study, we have investigated the role of PAR in the condition of DCM using a pharmacological approach. We used argatroban, a direct thrombin inhibitor for targeting PAR. Methods: Type-2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) was induced by high-fat feeding along with low dose streptozotocin (STZ 35 mg/kg, i.p. single dose) in male Sprague-Dawley rats. After 16 weeks of diabetes induction, animals were treated with argatroban at 0.3 and 1 mg/kg dose daily for 4 weeks. After 20 weeks, ventricular functions were measured using ventricular catheterization. Cardiac histology, TUNEL staining, and immunoblotting were performed to evaluate cardiac fibrosis, DNA fragmentation, and expression level of different proteins, respectively. Results: T2DM was associated with cardiac structural and functional disturbances as evidenced from impaired cardiac functional parameters and increased fibrosis. There was a significant increase in PAR expression after 20 weeks of diabetes induction. Four weeks argatroban treatment ameliorated metabolic alterations (reduced plasma glucose and cholesterol), ventricular dysfunctions (improved systolic and diastolic functions), cardiac fibrosis (reduced percentage area of collagen in picro-sirius red staining), and apoptosis (reduced TUNEL positive nuclei). Reduced expression of PAR1 and PAR4 in the argatroban-treated group indicates a response towards inhibition of thrombin. In addition, AKT (Ser-473), GSK-3β (Ser-9), p-65 NFĸB phosphorylation, TGF-β, COX-2, and caspase-3 expression were reduced significantly along with an increase in SERCA expression in argatroban-treated diabetic rats which indicated the anti-fibrotic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic potential of argatroban in DCM. Conclusion: This study suggests the ameliorative effects of argatroban in diabetic cardiomyopathy by improving ventricular functions and reducing fibrosis, inflammation, apoptosis, and PAR expression.5] |
| 分子式 |
C23H38N6O6S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
526.653
|
| 精确质量 |
508.24679
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 52.45; H, 7.27; N, 15.96; O, 18.23; S, 6.09
|
| CAS号 |
141396-28-3
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Argatroban;74863-84-6
|
| PubChem CID |
92721
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.5±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
801.3±75.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
-41.5 °C
|
| 闪点 |
438.4±37.1 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±3.0 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.674
|
| LogP |
2.56
|
| tPSA |
195.32
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
6
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
9
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
9
|
| 重原子数目 |
36
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
887
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
3
|
| SMILES |
S(C1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C2=C1N([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C2([H])[H])(N([H])[C@@]([H])(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])/N=C(\N([H])[H])/N([H])[H])C(N1C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[C@@]([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[C@]1([H])C(=O)O[H])=O)(=O)=O.O([H])[H]
|
| InChi Key |
AIEZTKLTLCMZIA-CZSXTPSTSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C23H36N6O5S.H2O/c1-14-8-10-29(18(12-14)22(31)32)21(30)17(6-4-9-26-23(24)25)28-35(33,34)19-7-3-5-16-11-15(2)13-27-20(16)19;/h3,5,7,14-15,17-18,27-28H,4,6,8-13H2,1-2H3,(H,31,32)(H4,24,25,26);1H2/t14-,15?,17+,18-;/m1./s1
|
| 化学名 |
(2R,4R)-1-[(2S)-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)-2-[(3-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolin-8-yl)sulfonylamino]pentanoyl]-4-methylpiperidine-2-carboxylic acid;hydrate
|
| 别名 |
MCI-9038; MCI9038; MCI9038; MD-805; MD 805; MD805; DK-7419; DK7419; DK 7419; GN1600; GN-1600; GN 1600; MMTQAP; MPQA; Novastan; Argatroban; OM 805; Argipidine; Slonnon
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (~189.88 mM)
H2O : ~1 mg/mL (~1.90 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.75 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.75 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.75 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8988 mL | 9.4940 mL | 18.9879 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3798 mL | 1.8988 mL | 3.7976 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1899 mL | 0.9494 mL | 1.8988 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Anticoagulation in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19 (The IMPACT Trial)
CTID: NCT04406389
Phase: Phase 4 S
A pilot trial to assess the efficacy of Argatroban (Argatra®) in critically ill patients with heparin resistance
CTID: null
Phase: Phase 2 Status: Completed
Date: 2012-05-18