| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 靶点 |
Thrombin (Ki = 4.5 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:达比加群选择性且可逆地抑制人凝血酶(Ki:4.5 nM)以及凝血酶诱导的血小板聚集(IC50:10 nM),同时对其他血小板刺激剂没有抑制作用。达比加群选择性且可逆地抑制人凝血酶 (Ki: 4.5 nM) 以及凝血酶诱导的血小板聚集 (IC50: 10 nM),同时对其他血小板刺激剂没有抑制作用。达比加群抑制贫血小板血浆 (PPP) 中的凝血酶生成,IC50 为 0.56 μM,以内源性凝血酶电位 (ETP) 测量。达比加群在体外对多种物种具有浓度依赖性抗凝作用,在浓度为 0.23、0.83 和 0.18 μM 时,人 PPP 中的活化部分凝血活酶时间 (aPTT)、凝血酶原时间 (PT) 和 ecarin 凝血时间 (ECT) 分别加倍。
体外活性:Dabigatran/BIBR 953 是一种非常有效的抗凝血剂。 BIBR 953 表明末端苯基可以被更亲水的 2-吡啶基取代,而不会显着损失活性。 BIBR 953 抑制凝血酶、纤溶酶、因子 Xa、胰蛋白酶、tPA 和活化蛋白 C,Ki 分别为 4.5 nM、1.7 μM、3.8 μM、50 nM、45 μM 和 20 μM。 BIBR 953 特异性且可逆地抑制凝血酶。 达比加群是一种可逆、选择性的直接凝血酶抑制剂(DTI),作为其口服活性前药达比加群组酯正在进行高级临床开发。本研究旨在确定达比加群及其前药达比加群组酯的分子效力和抗凝功效。这是通过酶抑制和选择性分析、表面等离子体共振研究、血小板聚集、凝血酶产生和体外凝血试验实现的。这些研究表明,达比加群选择性和可逆地抑制人凝血酶(Ki:4.5 nM)以及凝血酶诱导的血小板聚集(IC(50):10 nM),而对其他血小板刺激剂没有抑制作用。以内源性凝血酶电位(ETP)测量的血小板缺乏血浆(PPP)中凝血酶的产生受到浓度依赖性抑制(IC(50):0.56微M)。达比加群在体外各种物种中表现出浓度依赖性抗凝作用,在0.23、0.83和0.18微M的浓度下,人PPP中的活化部分凝血活酶时间(aPTT)、凝血酶原时间(PT)和埃卡蛋白凝血时间(ECT)分别加倍。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
大鼠(0.3、1和3 mg/kg)和恒河猴(0.15、0.3和0.6 mg/kg)静脉注射后,达比加群以剂量依赖性方式延长aPTT。与依诺肝素相比,达比加群酯(20 mg/kg,口服)对猪的 K 值延长较小,角度和最大幅度降低较小。达比加群 (0.01-0.1 mg/kg) 减少血栓形成呈剂量依赖性,ED50(有效剂量的 50%)为 0.033 mg/kg,在 0.1 mg/kg 时完全抑制。达比加群酯 (5-30 mg/kg) 以剂量和时间依赖性方式抑制血栓形成,在预处理后 30 分钟内达到最大抑制,表明作用迅速起效。
BIBR 953/Dabigatran 在对大鼠进行静脉注射后表现出最有利的活性。达比加群酯口服给药后Dabigatran/达比加群的生物利用度为7.2%。口服治疗后达比加群主要通过粪便排泄,静脉注射治疗后达比加群主要通过尿液排泄。达比加群的平均终末半衰期约为 8 小时。口服和静脉注射给药后,达比加群酰基葡萄糖醛酸苷分别占尿液中剂量的 0.4% 和 4%。 在体内,大鼠(0.3、1和3 mg/kg)和恒河猴(0.15、0.3和0.6 mg/kg)静脉注射Dabigatran/达比加群后, 剂量依赖性地延长aPTT。对清醒大鼠(10、20和50mg/kg)或恒河猴(1、2.5或5mg/kg)口服Dabigatran/达比加群酯,观察到剂量和时间依赖性抗凝作用,分别在给药后30至120分钟观察到最大作用。这些数据表明,达比加群是一种强效的选择性凝血酶抑制剂,也是一种口服活性抗凝剂,作为前药,达比加群酯。[1] 达比加群是一种可逆的直接、选择性凝血酶抑制剂,正在作为其口服活性前药达比加群组酯进行临床开发。本试验旨在评估达Dabigatran和Dabigatran酯在静脉血栓形成大鼠模型中的抗血栓和抗凝作用。为了做到这一点,使用改良的Wessler模型来评估静脉注射(i.v.)达比加群和口服达比加群组酯的抗血栓和抗凝作用。此外,使用大鼠尾部出血时间模型来研究达比加群的抗止血作用。该研究表明,大剂量服用达比加群(0.01-0.1 mg/kg)可剂量依赖性地减少血栓形成,ED50(有效剂量的50%)为0.033 mg/kg,在0.1 mg/kg时完全抑制。相比之下,肝素(0.03-0.3 mg/kg)、水蛭素(0.01-0.5 mg/kg)和美拉加群的ED50值分别为0.07、0.15和0.12 mg/kg。口服达比加群酯(5-30mg/kg)以剂量和时间依赖的方式抑制血栓形成,在预处理后30分钟内抑制作用最强,表明作用起效迅速。静脉注射达比加群(0.1-1.0 mg/kg)后,观察到出血时间在统计学上显著延长,剂量分别比ED50和ED100(有效剂量的100%)剂量大至少15倍和5倍;在最大治疗有效剂量(0.1mg/kg)下,出血倾向没有显著增加。可以得出结论,达比加群及其口服前药达比加群组酯在血栓栓塞性疾病的治疗中显示出希望[3]。 由于其强大的体外活性和相对于相关丝氨酸蛋白酶的良好选择性(表3),对达比加群/Dabigatran/24进行了深入的生物学研究,结果证明它是一种非常有效的体内抗凝剂。在这类结构的所有抑制剂中,静脉注射给药后,它在麻醉大鼠中表现出最强的活性和最长的作用持续时间。与化合物2不同,它在这些动物中耐受性良好,最高给药剂量为10mg/kg。然而,它没有口服活性,考虑到它是一种极性很强、永久带电的分子,logP为-2.4(正辛醇/缓冲液,pH 7.4),这并不奇怪[2]。 在30天时,我们观察到无抗凝组有638±895 mg血栓,依诺肝素组有121±128 mg血栓,Dabigatran/达比加群酯组有19±31 mg血栓(P=0.01依诺肝素vs达比加群组酯)。达比加群酯组瓣膜上沉积的血小板(2.7×108)少于依诺肝素组(1.8×109,P=0.03)。未观察到重大或隐性出血或栓塞事件。通过血栓弹性分析,达比加群酯的K值延长(P=.01)和角度(P=.01)和最大振幅(P=.001)的降低均小于依诺肝素。 达比加群酯与依诺肝素在机械瓣膜短期血栓预防方面同样有效。它可以在30天内防止瓣膜血栓和血小板沉积,而不会增加不良事件。这些有希望的结果为达比加群酯作为双叶机械主动脉瓣患者华法林替代品的前瞻性临床试验奠定了基础。[4] 剂量研究[4] 每日两次口服20mg/kg的达比加群酯,可将APTT增加到正常值的2至2.5倍(图2,A)。每天两次皮下注射2.0 mg/kg依诺肝素,可将抗Xa水平可重复地提高到至少0.6(图2,B)。这些剂量用于研究的剩余时间。 抗凝治疗的测量[4] 连续的血液学检测证实了两个治疗组的适当剂量和药物效果。接受Dabigatran/达比加群酯治疗的动物APTT升高,凝血酶原时间也显著增加。(图3,A和B)。正如预期的那样,我们观察到,与未抗凝组和达比加群酯组相比,接受依诺肝素的动物在所有时间点的抗Xa水平都有所升高(图3,C)。在研究的所有3个时间点,我们观察到达比加群酯组的循环纤维蛋白原明显减少(图3,D)。 瓣膜血栓[4] 术后第6天,非抗凝组有1人因严重败血症而过早死亡。当动物被杀死时,两组之间的平均血栓重量存在统计学差异。我们观察到638±895 mg血栓,未使用抗凝药物,121±128 mg使用依诺肝素,19±31 mg使用达比加群酯(P=0.04;图4A)。这表示达比加群酯组的平均瓣膜血栓比未抗凝组减少了30倍。比较两个治疗组,我们发现接受达比加群酯治疗的动物瓣膜血栓明显减少(P=0.02;图4,B)。同样,达比加群酯组瓣膜假体上沉积的血小板平均数(2.7×108)低于依诺肝素组(1.8×109,(P=0.03;图4,C)。无抗凝、依诺肝素和达比加群酯组移植瓣膜的代表性尸检照片如图5所示。 血栓弹性成像[4] 在基线和抗凝期间进行了天然和高岭土血栓弹性测定。我们观察到,至少在体内,接受达比加群酯治疗的动物的血栓弹性凝血曲线(R和K时间、角度和最大振幅)看起来更像没有抗凝治疗的动物,而不是接受依诺肝素治疗的动物(图6)。高岭土和天然血栓弹性分析都是如此(天然数据未显示),这表明尽管血栓弹性分析结果正常,但抗凝治疗充分。 |
| 酶活实验 |
凝血酶抑制的测量。[2]
用市售的显色法测定化合物的凝血酶抑制作用(IC50)。将人凝血酶(0.042 U/mL)在37°C下与溶解在DMSO中的10种不同稀释液(浓度范围为0.003-100μM)的试验化合物或DMSO作为对照预孵育10分钟。在将预孵育混合物添加到显色底物甲苯磺酰-甘氨酰-脯氨酰-精氨酸-4-硝基苯胺乙酸酯中后,硝基苯胺被凝血酶裂解,并在分光光度计中测量与游离硝基苯胺相关的405nm处吸光度的增加。通过绘制405nm处的吸光度与测试化合物浓度的关系图,计算出诱导50%凝血酶抑制的浓度(IC50)。所有测量均进行了两次,并表示了两次测定的平均值。 aPTT的测量。[2] aPTT在凝血仪中测量,作为相应化合物抗凝血作用的量度。在柠檬酸钠溶液(终浓度0.313%)中收集血液样本。将每份天然血液样本(0.1 mL)移入预热至37°C的试管中。加入PTT试剂(0.1 mL),混合并孵育3分钟。加入预热至37°C的氯化钙溶液(0.1 mL。 |
| 动物实验 |
Male rats (280-350 g) and rhesus monkeys of either sex (3-8 kg)
10, 20 and 50 mg/kg for rats and 1, 2.5 and 5 mg/kg for monkeys Oral Thirty swine underwent implantation of modified bileaflet mechanical valved conduit bypassing the ligated, native descending thoracic aorta. Animals randomly received no anticoagulation (n = 10), enoxaparin 2 mg/kg subcutaneously twice daily (n = 10), or Dabigatran etexilate 20 mg/kg orally twice daily. Primary end point was amount of valve thrombus at 30 days. Secondary end points included quantitative measurement of platelet deposition on valve prosthesis, thromboelastography, and hemorrhagic and embolic events. [4] Dosing study [4] Dabigatran etexilate is a novel, orally administered prodrug of the direct thrombin inhibitor Dabigatran. Unlike warfarin, it has a rapid clinical onset with a predictable dose response. Additionally, there are no known food or drug interactions, and it does not require frequent monitoring for therapeutic effect. Its half-life is approximately 12 hours, and it has no other active metabolites. Dabigatran is predominantly eliminated by renal excretion. To identify the most effective doses of Dabigatran etexilate and enoxaparin in swine, we first performed a dosing study. Animals were dosed with either Dabigatran etexilate or enoxaparin, and appropriate hematologic assay samples were drawn at 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, 24, 36, 48, and 72 hours.11 Our aim was to find the doses of Dabigatran etexilate and enoxaparin that corresponded to therapeutic levels in our strain of animals. For Dabigatran etexilate, we aimed to increase the activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) 2 to 2.5 times normal. For enoxaparin, we sought an anti-Xa level of at least 0.6 at 4 hours.12 In vivo thromboprophylaxis of mechanical valves [4] Specific details regarding this model of heterotopic aortic valve prostheses have been reported elsewhere.9, 13 Briefly, 30 swine were randomly sorted into 3 treatment arms of postoperative anticoagulation. These treatments consisted of no anticoagulation (n = 10), enoxaparin at 2.0 mg/kg administered subcutaneously twice daily (n = 10), and Dabigatran etexilate at 20 mg/kg by mouth twice daily (n = 10). The clinical formulation of Dabigatran etexilate (small tartaric acid pellets coated with drug in capsules) was used in the study. The low–molecular weight heparin enoxaparin was used as the standard for anticoagulation because of the difficulty in maintaining a therapeutic window with warfarin in swine.14 Additionally, low–molecular weight heparins are used to bridge patients to warfarin anticoagulation and as an alternative to warfarin for some patients unable to take warfarin.15, 16 These doses were determined from the results of our dosing studies. Animals received their assigned treatment medication beginning on postoperative day 1. Coagulation profile [4] We used several hematologic and anticoagulation assays to assess the effects of Dabigatran etexilate on the coagulation system. At baseline (before valve implantation), on days 10 and 20, and when the animal was killed (30 days), we performed a complete blood cell count; measured prothrombin time, APTT, fibrinogen, and anti-Xa levels; and performed thromboelastography. We used the TEG 5000 device with native and kaolin cups and pins (Haemoscope Corporation, Niles, Ill). Measurements obtained included R time (minutes), K time (minutes), angle (degrees), and maximal amplitude (mm). R time measures time to initial fibrin formation, K time measures time to strong clot formation and cross-linking, angle measures the speed of clot strengthening, and maximum amplitude measures final clot strength. We included thromboelastography because it evaluates the entire coagulation system and is becoming more widely used in managing cardiovascular surgical patients. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Oral dabigatran has a bioavailability of 3-7%, although the relative bioavailability of dabigatran pellets is 37% higher than that for capsules and the bioavailability increases to 75% when the capsule shell is removed; dabigatran capsules should not be tampered with in any way prior to administration. The Cmax is achieved by one hour following oral dosing, which is extended to two hours if accompanied by a high-fat meal. Dabigatran can be taken with or without food. Dabigatran pharmacokinetics are approximately linear over a range of 10-400 mg in healthy adults and adult patients and it has an accumulation factor of two in adult and pediatric patients. Dabigatran is primarily eliminated in the urine. Following oral administration of radiolabeled dabigatran, 7% of the radioactivity is recovered in urine and 86% is recovered in feces. Dabigatran has a volume of distribution of 50-70L. Following intravenous administration, renal clearance constitutes ~80% of total dabigatran clearance. Metabolism / Metabolites Dabigatran is administered as the orally available prodrug dabigatran etexilate that is subsequently metabolized to the active form. _In vitro_ studies and observations regarding the oral bioavailability and levels of plasma prodrug suggest extensive first-pass metabolism by carboxylesterases, first by intestinal CES2 to form BIBR0951 (also known as M2) and then subsequently by hepatic CES1 to form [dabigatran]. Dabigatran etexilate can also first undergo CES1-mediated hydrolysis to BIBR1087 (M1) followed by CES2-mediated hydrolysis to [dabigatran], though it is hypothesized that the former pathway accounts for most of the active form in plasma. Dabigatran can undergo 1-_O_-acyl glucuronidation by UGT1A9, UGT2B7, and UGT2B15 followed by acyl migration to form the corresponding 2-_O_-, 3-_O_-, and 4-_O_-acyl glucuronides; all of these acyl glucuronides exhibit activity similar to [dabigatran] but account for a small fraction of recovered metabolites. In addition to these better characterized metabolic pathways, detailed LC/MS characterization suggests a wide variety of possible metabolites following oral or intravenous administration, most of which are present in only trace amounts in plasma, urine, or feces. These include a variety of oxidation, hydrolysis, and conjugation products, including through the addition of mannitol. Biological Half-Life Dabigatran has a half-life of 12-17 hours in adult patients and 12-14 hours in pediatric patients. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Chronic therapy with dabigatran is associated with moderate ALT elevations (greater than 3 times the upper limit of normal) in 1.5% to 3% of patients, an overall rate which is slightly lower than with low molecular weight heparin and similar to the rates with warfarin. While case reports of clinically apparent liver injury due to dabigatran have not been published, several instances of ALT elevations with jaundice occurred during the large, prelicensure clinical trials of dabigatran. These cases were mild and self-limited, resolving completely once therapy was stopped. However, other causes of liver injury could not always be identified and the relationship of the injury to dabigatran therapy remains unclear. The clinical features of these cases were not described. In one large clinical trial, these unexplained cases of liver injury with bilirubin elevations occurred in approximately 1 in 2000 patients treated. In a subsequent case report, liver injury with jaundice and a mixed pattern of serum enzyme elevations arose within 4 weeks of starting dabigatran and resolved rapidly with its discontinuation. Immunoallergic and autoimmune features were not present. There have been multiple spontaneous reports of liver injury, some of which were fatal, made to WHO and FDA surveillance databases, but the relatedness of the episodes has not been clearly defined. Thus, clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice due to dabigatran occurs but is rare and typically mild and self-limited. Likelihood score: D (possible rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury). One reason why dabigatran was subjected to close scrutiny for evidence of hepatotoxicity was that the initial oral, direct thrombin inhibitor developed and evaluated in clinical trials was ximelagatran (zye" mel a gat' ran), which subsequently was found to be associated with rare but potentially severe cases of liver injury, typically arising after 1 to 6 months of treatment with a hepatocellular pattern of serum enzyme elevations and potentially severe and fatal course. Ximelagatran did not receive approval for use in the United States because of concerns about hepatotoxicity. After several further cases of clinically apparent hepatic injury were found in patients taking ximelagatran, it was also withdrawn from use in Europe. Risk of serum ALT elevations during ximelagatran therapy were later shown to be linked to HLA-DRB1*07 and DQA1*-02. Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation In adults, less than 7% of dabigatran is absorbed orally in its prodrug form of dabigatran etexilate mesylate; dabigatran itself is not absorbed orally. Preliminary data from 2 individuals indicate that dabigatran is poorly excreted into breastmilk and unlikely to affect the breastfed infant. If the mother requires dabigatran, it is not a reason to discontinue breastfeeding. Because data are limited, monitor preterm or newborn infants for signs of bleeding. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Samples of newborn and preterm infant blood spiked with of dabigatran in the concentrations found in breastmilk after a 220 mg dose of dabigatran etexilate indicate that no effect on coagulation would occur. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Interactions The concomitant use of a CYP3A4 isoenzyme substrate (atorvastatin) and dabigatran did not have clinically relevant effects on the pharmacokinetics of either drug. Also, the concomitant use of a CYP2C9 substrate (diclofenac) and dabigatran did not have clinically relevant effects on the pharmacokinetics of either drug. Administration of rifampin for 7 days followed by a single dose of dabigatran resulted in decreases of 66 and 67% in dabigatran area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) and peak plasma concentration, respectively. Within 7 days of rifampin discontinuance, dabigatran exposure approached levels expected without concurrent use of rifampin. Concomitant use should be avoided. Concomitant use of dabigatran with P-glycoprotein inhibitors may increase systemic exposure to dabigatran. While clinical data and pharmacokinetic studies indicate that concomitant use of dabigatran with certain P-glycoprotein inhibitors (i.e., amiodarone, clarithromycin, ketoconazole, quinidine, verapamil) does not necessitate dosage adjustments, the manufacturer states that these results should not be extrapolated to all P-glycoprotein inhibitors. Concomitant use of P-glycoprotein transport inhibitors and dabigatran in patients with renal impairment is expected to increase systemic exposure to dabigatran compared with that resulting from either factor alone. Reduction of dabigatran dosage should be considered in patients with moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance of 30-50 mL/minute) who are receiving concomitant dronedarone or systemic ketoconazole. Concomitant use of dabigatran and P-glycoprotein transport inhibitors in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance of 15-30 mL/minute) should be avoided. For more Interactions (Complete) data for Dabigatran (20 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Protein Binding Dabigatran is ~35% bound to plasma proteins, including human serum albumin. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Dabigatran etexilate is an oral prodrug that is hydrolyzed to the competitive and reversible direct thrombin inhibitor [dabigatran]. Dabigatran etexilate may be used to decrease the risk of venous thromboembolic events in patients in whom anticoagulation therapy is indicated. In contrast to warfarin, because its anticoagulant effects are predictable, lab monitoring is not necessary. Dabigatran etexilate was approved by the FDA in 2010.
A THROMBIN inhibitor which acts by binding and blocking thrombogenic activity and the prevention of thrombus formation. It is used to reduce the risk of stroke and systemic EMBOLISM in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. See also: Dabigatran (has active moiety); Dabigatran Etexilate Mesylate (has salt form). Drug Indication Dabigatran etexilate is available in both oral pellet and capsule form. Dabigatran etexilate pellets are indicated for the treatment of venous thromboembolic events (VTE) in pediatric patients between three months and 12 years of age who have been treated with a parenteral anticoagulant for at least 5 days. They are also indicated in the same age group to reduce the risk of recurrence of VTE in patients who have been previously treated. In capsule form, dabigatran etexilate is indicated in adults to reduce the risk of stroke and systemic embolism associated with non-valvular atrial fibrillation and for the treatment of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) in patients who have been treated with a parenteral anticoagulant for 5-10 days. It is also indicated in adults to reduce the risk of recurrence of DVT and PE in patients who have been previously treated and for the prophylaxis of DVT and PE in patients who have undergone hip replacement surgery. Lastly, it is indicated in pediatric patients between eight and 18 years of age for the treatment of venous thromboembolic events (VTE) in patients who have been treated with a parenteral anticoagulant for at least 5 days and to reduce the risk of recurrence of VTE in patients who have been previously treated. Dabigatran etexilate is also approved by the EMA to prevent VTE in adult patients. For pediatric patients, Dabigatran etexilate is used to treat TVE and prevent recurrent TVE for patients from birth to less than 18 years of age. FDA Label Mechanism of Action Hemostasis is a complex process that balances coagulation to prevent excessive thrombus formation or excessive bleeding. Central to the coagulation process is the serine protease thrombin (FIIa), which is synthesized as inactive prothrombin (FII) and subsequently activated by FXa/FVa, leading to a positive feedback loop and the production of large quantities of thrombin; once enough thrombin is formed, it cleaves soluble fibrinogen to form insoluble fibrin fibres that, together with aggregated platelets, form a clot. Although beneficial in wound healing, aberrant thrombus formation can lead to serious health consequences. Dabigatran is a univalent reversible direct thrombin inhibitor (DTI) that competitively inhibits thrombin with a Ki of 4.5 ± 0.2 nmol/L. Furthermore, the reversible nature of the inhibition is believed to allow for some normal physiological thrombin function, which may help alleviate some adverse effects associated with anticoagulation therapy. In addition, dabigatran has several glucuronidated metabolites, all of which have been shown to possess _in vitro_ activity similar to the parent compound. In addition to a direct effect on thrombin activity, dabigatran has also been shown to inhibit platelet aggregation, another step in the coagulation pathway. However, the mechanism remains unclear as dabigatran inhibits platelet aggregation stimulated by thrombin and von Willebrand factor (vWF), but not by other pathways such as ADP- or thromboxane A2-induced aggregation. Pharmacodynamics Dabigatran etexilate is a double prodrug that is hydrolyzed to the active [dabigatran] by intestinal and hepatic carboxylesterases. Dabigatran is a reversible competitive thrombin inhibitor that directly inhibits the conversion by thrombin of fibrinogen to fibrin, impairing the clotting process and acting as an anticoagulant. Dabigatran use prolongs coagulation markers such as the activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), ecarin clotting time (ECT), thrombin time (TT), and dilute thrombin time (dTT), but not the international normalized ratio (INR), which cannot be used in this context as it can in [warfarin] monitoring. As with all anticoagulant therapies, dabigatran carries a risk of bleeding, which may increase with concomitant use of antiplatelet agents, fibrinolytic therapy, heparins, or chronic NSAID use, and should be monitored for. Premature discontinuation of dabigatran, in the absence of an alternative anticoagulant, also carries an increased risk of thromboembolic events. Due to the risk of an epidural or spinal hematoma, dabigatran should generally not be used in the context of neuraxial anesthesia or spinal puncture; if such use is unavoidable, careful monitoring should be employed. Dabigatran should not be used in patients with prosthetic heart valves due to an increased occurrence of major bleeding and thromboembolic events. Dabigatran is a substrate of the P-gp transporter and should generally not be administered together with P-gp inhibitors or inducers, especially in patients with impaired renal function. Lastly, dabigatran or any other direct-acting oral anticoagulant should not be administered in patients with triple-positive antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) due to an increased risk of recurrent thrombotic events. In case of the need for emergency reversal, [idarucizumab] is available for use in adult patients; the safety and efficacy of [idarucizumab] has not been established in pediatric patients yet, for whom reversal may be achieved through hemodialysis, prothrombin complex concentrates, or recombinant FVIIa. However, none of these have been sufficiently evaluated in clinical trials. Dabigatran is an aromatic amide obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of 2-{[(4-carbamimidoylphenyl)amino]methyl}-1-methyl-1H-benzimidazole-5-carboxylic acid with the secondary amoino group of N-pyridin-2-yl-beta-alanine. The active metabolite of the prodrug dabigatran etexilate, it acts as an anticoagulant which is used for the prevention of stroke and systemic embolism. It has a role as an anticoagulant, an EC 3.4.21.5 (thrombin) inhibitor and an EC 1.10.99.2 [ribosyldihydronicotinamide dehydrogenase (quinone)] inhibitor. It is an aromatic amide, a member of benzimidazoles, a carboxamidine, a member of pyridines and a beta-alanine derivative. Dabigatran is the active form of the orally bioavailable prodrug [dabigatran etexilate]. Dabigatran is a Direct Thrombin Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of dabigatran is as a Thrombin Inhibitor. Dabigatran is a direct inhibitor of thrombin and anticoagulant which is used for prevention of stroke and venous embolism in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. Dabigatran therapy has been associated with a low rate of serum enzyme elevations and rare instances of liver enzyme elevations and jaundice. Dabigatran is a benzimidazole and direct thrombin inhibitor, with anticoagulant activity. Upon administration, dabigatran reversibly binds to and inhibits the activity of thrombin, a serine protease that converts fibrinogen into fibrin. This disrupts the coagulation cascade and inhibits the formation of blood clots. A THROMBIN inhibitor which acts by binding and blocking thrombogenic activity and the prevention of thrombus formation. It is used to reduce the risk of stroke and systemic EMBOLISM in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. See also: Dabigatran Etexilate (is active moiety of); Dabigatran Etexilate Mesylate (active moiety of); Dabigatran Ethyl Ester (is active moiety of). Mechanism of Action Dabigatran and its acyl glucuronides are competitive, direct thrombin inhibitors. Because thrombin (serine protease) enables the conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin during the coagulation cascade, its inhibition prevents the development of a thrombus. Both free and clot-bound thrombin, and thrombin-induced platelet aggregation are inhibited by the active moieties. ... To evaluate the profibrinolytic effect of dabigatran, a new, direct thrombin inhibitor, using different in vitro models. The resistance of tissue factor-induced plasma clots to fibrinolysis by exogenous tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA) (turbidimetric method) was reduced by dabigatran in a concentration-dependent manner, with > or = 50% shortening of lysis time at clinically relevant concentrations (1-2 um). A similar effect was observed in the presence of low (0.1 and 1 nm) but not high (10 nm) concentrations of thrombomodulin. Acceleration of clot lysis by dabigatran was associated with a reduction in TAFI activation and thrombin generation, and was largely, although not completely, negated by an inhibitor of activated TAFI, potato tuber carboxypeptidase inhibitor. The assessment of the viscoelastic properties of clots showed that those generated in the presence of dabigatran were more permeable, were less rigid, and consisted of thicker fibers. The impact of these physical changes on fibrinolysis was investigated using a model under flow conditions, which demonstrated that dabigatran made the clots markedly more susceptible to flowing t-PA, by a mechanism that was largely TAFI-independent. Dabigatran, at clinically relevant concentrations, enhances the susceptibility of plasma clots to t-PA-induced lysis by reducing TAFI activation and by altering the clot structure. These mechanisms might contribute to the antithrombotic activity of the drug. Therapeutic Uses Benzimidazoles; beta-Alanine/analogs & derivatives Dabigatran is indicated to reduce the risk of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. /Included in US product label/ Drug Warnings /BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: PREMATURE DISCONTINUATION OF PRADAXA INCREASES THE RISK OF THROMBOTIC EVENTS. Premature discontinuation of any oral anticoagulant, including Pradaxa, increases the risk of thrombotic events. If anticoagulation with Pradaxa is discontinued for a reason other than pathological bleeding or completion of a course of therapy, consider coverage with another anticoagulant. /BOXED WARNING/ SPINAL/EPIDURAL HEMATOMA. Epidural or spinal hematomas may occur in patients treated with Pradaxa who are receiving neuraxial anesthesia or undergoing spinal puncture. These hematomas may result in long-term or permanent paralysis. Consider these risks when scheduling patients for spinal procedures. Factors that can increase the risk of developing epidural or spinal hematomas in these patients include: use of indwelling epidural catheters; concomitant use of other drugs that affect hemostasis, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), platelet inhibitors, other anticoagulants; a history of traumatic or repeated epidural or spinal punctures; a history of spinal deformity or spinal surgery; optimal timing between the administration of Pradaxa and neuraxial procedures is not known. Monitor patients frequently for signs and symptoms of neurological impairment. If neurological compromise is noted, urgent treatment is necessary. Consider the benefits and risks before neuraxial intervention in patients anticoagulated or to be anticoagulated. The FDA is evaluating post-marketing reports of serious bleeding events in patients taking dabigatran etexilate mesylate (Pradaxa). Bleeding that may lead to serious or even fatal outcomes is a well-recognized complication of all anticoagulant therapies. The dabigatran drug label contains a warning about significant and sometimes fatal bleeds. In a large clinical trial (18,000 patients) comparing dabigatran and warfarin, major bleeding events occurred at similar rates with the two drugs. FDA is working to determine whether the reports of bleeding in patients taking dabigatran are occurring more commonly than would be expected, based on observations in the large clinical trial that supported the approval of dabigatran. Dabigatran is a blood thinning (anticoagulant) medication used to reduce the risk of stroke in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation (AF), the most common type of heart rhythm abnormality. At this time, FDA continues to believe that dabigatran provides an important health benefit when used as directed and recommends that healthcare professionals who prescribe dabigatran follow the recommendations in the approved drug label. Patients with AF should not stop taking dabigatran without talking to their healthcare professional. Stopping use of blood thinning medications can increase their risk of stroke. Strokes can lead to permanent disability and death. Dabigatran is contraindicated in patients with: active pathological bleeding; history of a serious hypersensitivity reaction to dabigatran (e.g., anaphylactic reaction or anaphylactic shock). For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Dabigatran (14 total), please visit the HSDB record page. The clinical syndromes of thromboembolism are evoked by an excessive stimulation of the coagulation cascade. In this context, the serine protease thrombin plays a key role. Considerable efforts have therefore been devoted to the discovery of safe, orally active inhibitors of this enzyme. On the basis of the X-ray crystal structure of the peptide-like thrombin inhibitor NAPAP complexed with bovine thrombin, we have designed a new structural class of nonpeptidic inhibitors employing a 1,2,5-trisubstituted benzimidazole as the central scaffold. Supported by a series of X-ray structure analyses, we optimized the activity of these compounds. Thrombin inhibition in the lower nanomolar range could be achieved although the binding energy mainly results from nonpolar, hydrophobic interactions. To improve in vivo potency, we increased the overall hydrophilicity of the molecules by introducing carboxylate groups. The very polar compound 24 (BIBR 953/Dabigatran) exhibited the most favorable activity profile in vivo. This zwitterionic molecule was converted into the double-prodrug 31 (BIBR 1048), which showed strong oral activity in different animal species. On the basis of these results, 31 was chosen for clinical development.[1] Dabigatran etexilate, a new oral direct thrombin inhibitor, is safe and effective in reducing risk of stroke among patients with atrial fibrillation. No data exist in the setting of mechanical heart valves. We tested the hypothesis that dabigatran etexilate is as effective as heparin for thromboprophylaxis of mechanical valves in a porcine heterotopic aortic valve model. [4] The novel direct thrombin inhibitor dabigatran etexilate was effective for short-term thromboprophylaxis of mechanical heart valves in our porcine model. These animal data provide additional support for clinical trials evaluating dabigatran etexilate as an alternative to warfarin for appropriately selected patients with bileaflet mechanical valve aortic valves. [4] |
| 分子式 |
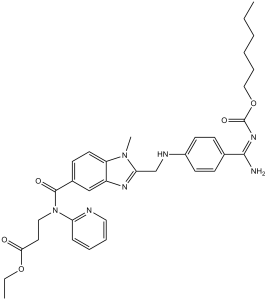
C34H41N7O5
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
627.73
|
|
| 精确质量 |
627.316
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 65.05; H, 6.58; N, 15.62; O, 12.74)
|
|
| CAS号 |
211915-06-9
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Dabigatran;211914-51-1;Dabigatran-d4 hydrochloride;Dabigatran etexilate mesylate;872728-81-9;Dabigatran etexilate-d13;Dabigatran (ethyl ester);429658-95-7;BIBR 1087 SE;212321-78-3
|
|
| PubChem CID |
135565674
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
827.9±75.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
128-129°
|
|
| 闪点 |
454.5±37.1 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±3.0 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.615
|
|
| LogP |
5.13
|
|
| tPSA |
154.03
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
9
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
18
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
46
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
991
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
O(C(/N=C(\C1C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=1[H])N([H])C([H])([H])C1=NC2C([H])=C(C(N(C3=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])=N3)C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C(=O)OC([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])=O)C([H])=C([H])C=2N1C([H])([H])[H])/N([H])[H])=O)C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H]
|
|
| InChi Key |
XETBXHPXHHOLOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C34H41N7O5.CH4O3S/c1-4-6-7-10-21-46-34(44)39-32(35)24-12-15-26(16-13-24)37-23-30-38-27-22-25(14-17-28(27)40(30)3)33(43)41(20-18-31(42)45-5-2)29-11-8-9-19-36-29;1-5(2,3)4/h8-9,11-17,19,22,37H,4-7,10,18,20-21,23H2,1-3H3,(H2,35,39,44);1H3,(H,2,3,4)
|
|
| 化学名 |
ethyl 3-[[2-[[4-(N-hexoxycarbonylcarbamimidoyl)anilino]methyl]-1-methylbenzimidazole-5-carbonyl]-pyridin-2-ylamino]propanoate;methanesulfonic acid
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.98 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.98 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.5930 mL | 7.9652 mL | 15.9304 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3186 mL | 1.5930 mL | 3.1861 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1593 mL | 0.7965 mL | 1.5930 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
A Study to Learn About How BAY2927088 Affects the Level of Dabigatran or Rosuvastatin in the Blood When These Drugs Are Taken Together in Healthy Participants
CTID: NCT06329895
Phase: Phase 1 Status: Completed
Date: 2024-07-05