| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:在稳态动力学测量中,-天仙碱将 GTP 酶活性的周转数从 0.19 min-1 增加到 2.11 min-1。 R-(+)-hyoscyamine 导致与毒蕈碱乙酰胆碱受体亚型 (m1-m5) 结合的 [3H]NMS 发生置换,pKi 值分别为 8.67、8.51、7.46、8.56 和 8.53。 Hyoscyamine 可防止 CHO 细胞中激动剂诱导的 cAMP 产生刺激,EC50 为 7.8 nM。 S-(-)-hyoscyamine 可将大鼠心脏(心房和心室)膜中毛喉素刺激的环 AMP 合成增强高达 24%。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
L-Hyoscyamine(曼陀林;5–20 mg/kg;IV)可延长 MMC 迁移周期的长度[1]。
|
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Rats[1]
Doses: 5, 10, 20 mg/kg Route of Administration: IV Experimental Results: Prolonged the migrating myoelectric complex (MMC) cycle length. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Hyoscyamine is completely absorbed by sublingual and oral routes, though exact data regarding the Cmax, Tmax, and AUC are not readily available. The majority of hyoscyamine is eliminated in the urine as the unmetabolized parent compound. Metabolism / Metabolites Hyoscyamine is largely unmetabolized, however a small amount is hydrolyzed into tropine and tropic acid. LIVER HOMOGENATES OF RABBITS CONTAINING (-)-HYOSCYAMINE ACYLHYDROLASE HYDROLYZED (-)-HYOSCYAMINE TO TROPINE AND(-)-TROPIC ACID BUT DID NOT CLEAVE (+)-HYOSCYAMINE. Biological Half-Life The half life of hyoscyamine is 3.5 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Despite widespread use over many decades, hyoscyamine has not been linked to episodes of liver enzyme elevations or clinically apparent liver injury. A major reason for its safety may relate to the low daily dose and limited duration of use. References on the safety and potential hepatotoxicity of anticholinergics are given together after the Overview section on Anticholinergic Agents. Drug Class: Gastrointestinal Agents; Anticholinergic Agents Interactions L-HYOSCYAMINE (0.3 MG/KG) PREVENTED THE SALIVATION INDUCED IN MICE BY CHOLINERGIC AND ADRENERGIC DRUGS WITHOUT AFFECTING THE ACCOMPANYING TEMP RESPONSES. WHEN GIVEN 30 MIN BEFORE THE INJECTION OF AN ADRENERGIC SIALAGOGUE, IT DID NOT INHIBIT THE SALIVATION INDUCED BY D-AMPHETAMINE SULFATE BUT STILL DIMINISHED THAT CAUSED BY L-ISOPROTERENOL BITARTRATE. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
(S)-atropine is an atropine with a 2S-configuration. It is functionally related to a (S)-tropic acid. It is a conjugate base of a (S)-atropinium.
Hyoscyamine is a tropane alkaloid and the levo-isomer of [atropine]. It is commonly extracted from plants in the Solanaceae or nightshade family. Research into the action of hyoscyamine in published literature dates back to 1826. Hyoscyamine is used for a wide variety of treatments and therapeutics due to its antimuscarinic properties. Although hyoscyamine is marketed in the United States, it is not FDA approved. Hyoscyamine as a natural plant alkaloid derivative and anticholinergic that is used to treat mild to moderate nausea, motion sickness, hyperactive bladder and allergic rhinitis. Hyoscyamine has not been implicated in causing liver enzyme elevations or clinically apparent acute liver injury. L-Hyoscyamine has been reported in Scopolia parviflora, Cyphanthera odgersii, and other organisms with data available. Hyoscyamine is a belladonna alkaloid derivative and the levorotatory form of racemic atropine isolated from the plants Hyoscyamus niger or Atropa belladonna, which exhibits anticholinergic activity. Hyoscyamine functions as a non-selective, competitive antagonist of muscarinic receptors, thereby inhibiting the parasympathetic activities of acetylcholine on the salivary, bronchial, and sweat glands, as well as the eye, heart, bladder, and gastrointestinal tract. These inhibitory effects cause a decrease in saliva, bronchial mucus, gastric juices, and sweat. Furthermore, its inhibitory action on smooth muscle prevents bladder contraction and decreases gastrointestinal motility. The 3(S)-endo isomer of atropine. See also: Atropine (annotation moved to); Hyoscyamine (annotation moved to). Drug Indication As a drug that is not FDA approved, hyscyamine has no official indications. Intravenous hysocyamine has been used to reduce gastric motility, reduce pancreatic pain and secretions, to facilitate imaging of the gastrointestinal tract, treat anticholinesterase toxicity, treat certain cases of partial heart block, improve visualization of the kidneys, and for symptomatic relief of biliary and renal colic. Intravenous hyoscyamine is also used pre-operatively to reduce secretions of the mouth and respiratory tract to facilitate intubation. Oral hyoscyamine is used to treat functional intestinal disorders, for symptomatic relief of biliary and renal colic, and symptomatic relief of acute rhinitis. Mechanism of Action Hyoscyamine competitively and non-selectively antagonises muscarinic receptors in the smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, sino-atrial node, atrioventricular node, exocrine nodes, gastrointestinal tract, and respiratory tract. Antagonism of muscarinic M1, M4, and M5 receptors in the central nervous system lead to cognitive impairment; antagonism of M2 in the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes leads to increases in heart rate and atrial contractility; and antagonism of M3 in smooth muscle results in reduced peristalsis, bladder contraction, salivary secretions, gastric secretions, bronchial secretions, sweating, increased bronchodilation, mydriasis, and cycloplegia. MAJOR ACTION OF ANTIMUSCARINIC AGENTS IS A COMPETITIVE ANTAGONISM OF THE ACTIONS OF ACETYLCHOLINE & OTHER MUSCARINIC AGONISTS. ... RECEPTORS AFFECTED ARE THOSE OF PERIPHERAL STRUCTURES THAT ARE...STIMULATED OR INHIBITED BY MUSCARINE, THAT IS, EXOCRINE GLANDS & SMOOTH & CARDIAC MUSCLE. RESPONSES TO POSTGANGLIONIC CHOLINERGIC NERVE STIMULATION ARE ALSO INHIBITED...BUT LESS READILY THAN RESPONSES TO INJECTED CHOLINE ESTERS. /ANTIMUSCARINIC DRUGS/ Therapeutic Uses Adjuvants, Anesthesia; Anti-Arrhythmia Agents; Antidotes; Bronchodilator Agents; Muscarinic Antagonists; Mydriatics; Parasympatholytics /L-HYOSCYAMINE IS/ THE LEVOROTATORY ISOMER OF THE RACEMIC MIXTURE.../DL-ATROPINE/, & THEREFORE 1/2 OF ATROPINE IS HYOSCYAMINE. SINCE DEXTROROTATORY ISOMER IS NEARLY INACTIVE, THE POTENCY OF HYOSCYAMINE IS APPROX TWICE THAT OF ATROPINE. ACTIONS /&/ USES...ARE SAME AS THOSE OF ANTIMUSCARINIC DRUGS IN GENERAL, EXCEPT THAT HYOSCYAMINE HAS NOT BEEN USED FOR OPHTHALMOLOGIC PURPOSES & IS OF LITTLE USE TO SUPPRESS GASTRIC SECRETION. ...ITS USE HAS MAINLY BEEN CONFINED TO THAT OF AN ANTISPASMODIC. TEN MALE PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC DUODENAL ULCERATION WERE EXAMINED WITH AN AUGMENTED HISTAMINE TEST BEFORE AND DURING TREATMENT WITH OPTIMAL EFFECTIVE DOSES OF LONG-ACTING L-HYOSCYAMINE 0.84 MG, GIVEN 3 TIMES DAILY. ACID OUTPUT WAS STIMULATED AND SECRETORY VOLUME WAS SIGNIFICANTLY REDUCED DURING TREATMENT, WHILE THE PEPSIN AND INTRINSIC FACTOR SECRETION WERE UNALTERED. IN HEALTHY VOLUNTEERS L-HYOSCYAMINE (0.6 MG, TWICE A DAY) AFFECTED SALIVARY SECRETION SIGNIFICANTLY. GASTRIC EMPTYING WAS SIGNIFICANTLY DELAYED BY L-HYOSCYAMINE COMPARED TO PIRENZEPINE. SWALLOWING-INDUCED ESOPHAGEAL PERISTALSIS WAS INHIBITED IN 51% BY L-HYOSCYAMINE. IT ALSO AFFECTED BOTH PUPIL-SIZE AND NEARPOINT DISTANCE. For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for (-)-HYOSCYAMINE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Hyoscyamine is not FDA approved, and so it has not official indications. However, it is used as an antimuscarinic agent in a number of treatments and therapies. Hyoscyamine has a short duration of action as it may need to be given multiple times per day. Patients should be counselled regarding the risks and signs of anticholinergic toxicity. |
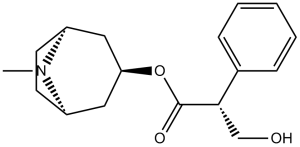
| 分子式 |
C17H23NO3
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
289.37
|
|
| 精确质量 |
289.167
|
|
| CAS号 |
101-31-5
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
L-Hyoscyamine sulfate;620-61-1;L-Hyoscyamine-d3
|
|
| PubChem CID |
154417
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
429.8±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
108.5ºC
|
|
| 闪点 |
213.7±28.7 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.581
|
|
| LogP |
1.53
|
|
| tPSA |
49.77
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
21
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
353
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
3
|
|
| SMILES |
CN1[C@@H]2CC[C@H]1CC(C2)OC(=O)[C@H](CO)C3=CC=CC=C3
|
|
| InChi Key |
RKUNBYITZUJHSG-VFSICIBPSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C17H23NO3/c1-18-13-7-8-14(18)10-15(9-13)21-17(20)16(11-19)12-5-3-2-4-6-12/h2-6,13-16,19H,7-11H2,1H3/t13-,14+,15?,16-/m1/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
[(1S,5R)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-yl] (2S)-3-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoate
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.64 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.64 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.64 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 30% Propylene glycol , 5% Tween 80 , 65% D5W: 5 mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4558 mL | 17.2789 mL | 34.5578 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6912 mL | 3.4558 mL | 6.9116 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3456 mL | 1.7279 mL | 3.4558 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。