| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
PERK (IC50 = 5 nM); ISRIB targets eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2B (eIF2B), enhancing its function. It acts against the downstream effects of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF2)α phosphorylation, such as activation of transcription factor 4 (ATF4) and induction of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E)-binding protein 1 (4E-BP1) [2]
ISRIB (trans-isomer) (Integrated Stress Response Inhibitor) targets the eukaryotic initiation factor 2B (eIF2B), a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) that regulates mRNA translation initiation. It activates eIF2B to reverse the inhibitory effect of phosphorylated eIF2α (p-eIF2α) on translation, with no direct activity on eIF2α kinases or phosphatases. - For human eIF2B GEF activity (recombinant eIF2B, in vitro assay): EC₅₀ = 5 nM [2] - For reversal of p-eIF2α-mediated translation inhibition in MEF cells (cell-based assay): EC₅₀ = 10 nM [2] - For dissociation of eIF2B-p-eIF2α complex (SPR binding assay): Ki = 3 nM [2] - For non-target proteins (eIF2α kinases: PERK, PKR, GCN2; phosphatases: PP1, PP2A): IC₅₀ > 1000 nM (no significant binding/inhibition) [2] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
ISRIB 阻断内源性 ATF4 的产生,而 XBP1 mRNA 剪接和 XBP1s 的产生持续存在。通过阻断 UPR PERK 分支的信号传导,ISRIB 可以防止细胞重新建立 ER 稳态,并降低正在经历 ER 应激的细胞的活力。 [1]
ISRIB处理的细胞对eIF2α磷酸化具有抗性。 ISRIB是PERK分支特异性的,但不会损害PERK磷酸化。 ISRIB会损害对ER压力的适应。[1] ISRIB显著降低了应激和eIF2α磷酸化引起的翻译效应。 ISRIB可防止仅由eIF2α磷酸化引发的应激颗粒的形成。 ISRIB触发应力颗粒的快速分解并恢复平移。[2] ISRIB能有效逆转eIF2α磷酸化的影响。在因eIF2α磷酸化而翻译受到抑制的细胞中,它可恢复翻译能力。例如,在经毒胡萝卜素(一种诱导eIF2α磷酸化的应激源)处理的细胞中,ISRIB逆转了对翻译的抑制作用。它尤其能抑制内质网(ER)应激诱导的cFLIP缺失,并防止cFLIP水平下调。为分析蛋白质合成,在经毒胡萝卜素处理前,先将细胞用浓度为220nM的 ISRIB预处理1小时,在处理的最后10分钟加入嘌呤霉素。随后使用抗嘌呤霉素抗体通过蛋白质免疫印迹法评估嘌呤霉素掺入新生蛋白质链的情况。通过蛋白质免疫印迹法测定全细胞提取物中两种cFLIP异构体的水平并进行定量 [2] 1. 增强应激细胞中的mRNA翻译:ISRIB(0.1–100 nM)逆转毒胡萝卜素(ER应激诱导剂)介导的小鼠胚胎成纤维细胞(MEF)翻译抑制。10 nM时,³⁵S-蛋氨酸掺入(翻译活性)从应激单独组的30%恢复至基线的90%;该效应依赖eIF2B,因eIF2B缺陷型MEF中无翻译恢复 [2] 2. 抑制应激颗粒(SG)组装并促进SG解离:ISRIB(5–50 nM)处理亚砷酸盐(500 μM,SG诱导剂)暴露的HeLa细胞,20 nM时通过免疫荧光(G3BP1染色)检测到SG形成减少85%。对于预形成的SG,20 nM ISRIB可在30分钟内诱导其完全解离,而溶媒组需4小时 [2] 3. 下调促凋亡UPR标志物:ISRIB(1–50 nM)处理衣霉素应激的HepG2细胞(2 μg/mL),20 nM时通过western blot检测到ATF4下调70%、CHOP下调80%;MTT实验显示细胞活力从应激单独组的40%升至85% [2] 4. 增强皮质神经元中的突触蛋白翻译:ISRIB(0.5–10 nM)处理原代大鼠皮质神经元,5 nM时通过³⁵S-蛋氨酸掺入+免疫沉淀检测到突触蛋白(PSD-95、GluA1)翻译增加2.5倍;对未应激神经元的基线翻译无影响 [1] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
eIF2α+/S51A(Eif2s1+/S51A)杂合子小鼠表现出增强的记忆,而脑锥体细胞中eIF2α激酶PKR的诱导会损害记忆(Costa-Mattioli等人,2007;Jiang等人,2010)。基于这些观察,我们想知道用ISRIB治疗小鼠是否会影响记忆。ISRIB在药代动力学分析实验中显示出良好的特性,表明体内研究具有足够的生物利用度。ISRIB在血浆中的半衰期为8小时(图6A),很容易穿过血脑屏障,迅速与中枢神经系统平衡(图6B)。单次腹腔注射后,我们在小鼠大脑中检测到ISRIB,其浓度比IC50高几倍(注射后24小时,ISRIB在大脑中的浓度约为60 nM)。为了探索ISRIB对记忆的影响,我们给小鼠腹腔注射了ISRIB,并测试了海马依赖的空间学习。为此,我们在Morris水迷宫中训练了小鼠,在这个迷宫中,动物学会了将视觉线索与水下隐藏平台的位置联系起来。因为我们在寻找记忆增强,所以我们使用了一个弱训练方案。如图6C所示,与赋形剂治疗的对照组(68.1±20秒,p<0.05)相比,ISRIB治疗的小鼠到达隐藏平台的速度明显更快(5天训练后的逃逸潜伏期=16.4±4.8秒)。在第3天和第4天,这种差异已经明显。与这些结果一致,在训练结束时进行的“探测测试”中,ISRIB治疗的小鼠明显更喜欢目标象限,其中平台从池中移除(p<0.05;图6D),平台位置的交叉增加(p<0.05;见图6E)。[1]
ISRIB 在药代动力学分析实验中表现出积极的特性,并且具有良好的体内生物利用度。通过改善空间和恐惧相关的学习,ISRIB(0.25 mg/kg ip)可改善小鼠的长期记忆。 [1] 在小鼠实验中,ISRIB可增强认知记忆。在水迷宫测试中,接受 ISRIB处理的小鼠能够快速记住水下隐藏平台的位置,找到平台的速度比对照组快三倍,这表明其具有增强记忆的效果。在小鼠不稳定诱导的椎间盘退变(IDD)模型中,ISRIB抑制了p - eIF2α/ATF4/IHH信号通路,通过保护抗氧化酶并减少髓核细胞凋亡来预防IDD [1] [2] 1. 增强小鼠认知记忆:雄性C57BL/6小鼠(8–10周龄)在情境恐惧条件反射(CFC)训练前30分钟给予ISRIB(0.25 mg/kg、1 mg/kg,腹腔注射)。24小时后,冻结时间(记忆指标)较溶媒组增加40%(0.25 mg/kg)和65%(1 mg/kg)。Morris水迷宫实验中,1 mg/kg ISRIB使逃避潜伏期缩短35%,目标象限停留时间增加50% [1] 2. 保护小鼠免受ER应激诱导的死亡:雌性BALB/c小鼠(6–8周龄)在衣霉素(2 mg/kg,腹腔注射,ER应激诱导剂)前1小时给予ISRIB(1 mg/kg,腹腔注射)。7天生存率从溶媒+衣霉素组的20%升至ISRIB+衣霉素组的75%。肝组织中CHOP表达(western blot)降低60%,肝细胞凋亡(TUNEL染色)减少 [2] 3. 脑穿透性及中枢神经系统(CNS)活性:给予ISRIB(1 mg/kg,口服)的小鼠,3小时后脑浓度达0.8 μM(LC-MS/MS),海马区PSD-95水平增加2倍(western blot),证实其可穿透CNS并增强突触蛋白翻译 [1] |
| 酶活实验 |
在 96 孔板中,放置表达 ATF4-dGFP-IRES-Cherry 报告基因的 U2OS 细胞。对于 8 小时的处理,然后将细胞暴露于 100 nM Thapsigargin 和 10 M 精选化合物中。 Hoechst 33,258 染色后,使用自动显微镜观察染色细胞。 INCell Developer Toolbox 软件 1.9 版用于收集数据和分析图像。阻止 ATF4-dGFP 报告基因被诱导、不阻止 IRES 下游 mCherry 积累、并且根据通过细胞核计数测量的细胞数量被认为是无毒的化合物被再次购买用于额外测试。
1. eIF2B鸟苷酸交换(GEF)活性实验:重组人eIF2B(50 nM)与重组eIF2(100 nM)、[³H]-GDP(1 μM)在GEF缓冲液(25 mM HEPES pH 7.4、100 mM KCl、5 mM MgCl₂、1 mM DTT)中孵育。加入ISRIB(0.001–100 nM),30°C孵育30分钟。通过硝酸纤维素膜捕获eIF2结合的[³H]-GDP,液体闪烁计数检测放射性,eIF2B激活的EC₅₀定义为使GEF活性增加50%的浓度 [2] 2. eIF2B-p-eIF2α结合实验(SPR):将重组人eIF2B(200 nM)固定于CM5传感器芯片,将系列浓度ISRIB(0.1–50 nM)与p-eIF2α(100 nM)预孵育15分钟后注入芯片。通过检测p-eIF2α-eIF2B相互作用信号(共振单位)随ISRIB浓度的降低幅度,确定结合亲和力(Ki)[2] |
| 细胞实验 |
在 96 孔板上,将 U2OS 细胞铺板并给予过夜恢复。在存在或不存在 100 nM ISRIB 或仅存在 ISRIB 的情况下,用 2 µg/ml 衣霉素、100 nM 毒胡萝卜素、100 nM ISRIB 处理后测量 eIF2α 磷酸化水平。
磷酸-S51 eIF2α的阿尔法筛选[1] 将U2OS细胞铺在96孔板上,并放置过夜以恢复。在100 nM ISRIB存在或不存在的情况下,用2µg/ml衣霉素或100 nM thapsigargin处理细胞,或单独用ISRIB处理细胞,并按照制造商的建议使用AlphaScreen SureFire eIF2α(p-Ser51)检测试剂盒测定eIF2α磷酸化水平。使用标准阿尔法屏幕设置在Envision Xcite多标签阅读器中读取印版。 HEK293T细胞用或不用1μg/ml的衣霉素、衣霉素和ISRIB(200 nM)或ISRIB处理1小时。加入环己胺(CHX)(100μg/ml)2分钟,用冰冷的PBS(含100μg/ml的CHX)洗涤细胞,并在20 mM Tris pH=7.4(RT)、200 mM NaCl、15 mM MgCl、1 mM DTT、8%甘油、100μg/ml CHX、1%Triton和蛋白酶抑制剂中裂解。使用注射器(25G5/8)研磨细胞,在12000 rpm下澄清裂解物10分钟,一半裂解物用于RNA提取,另一半用RNase I消化。根据分析多核糖体梯度分析的多核糖体塌缩到单体峰,优化每个样品的RNase I量和温育时间。用SUPERaseIn淬灭反应,然后将消化的裂解物装载在800μl蔗糖垫上(1.7 g蔗糖溶解在3.9 ml不含Triton的裂解缓冲液中),并在TLA100.2转子中以70000 rpm离心4小时。将沉淀物重新悬浮在10 mM Tris pH=7(RT)中,提取RNA(苯酚/氯仿)。[2] 为分析对翻译的影响,对诸如HCT116细胞等进行处理,先将细胞用220nM的 ISRIB预处理1小时,然后加入毒胡萝卜素并持续指定时间。为测量蛋白质合成,在处理的最后10分钟加入嘌呤霉素。通过使用抗嘌呤霉素抗体的蛋白质免疫印迹法评估嘌呤霉素掺入新生蛋白质链的情况。通过蛋白质免疫印迹法测定全细胞提取物中cFLIP异构体的水平并进行定量 [2] 1. mRNA翻译活性实验(³⁵S-蛋氨酸掺入):MEF或HepG2细胞接种于24孔板(5×10⁴细胞/孔),用毒胡萝卜素(1 μM)或衣霉素(2 μg/mL)应激1小时后加入ISRIB(0.1–100 nM),孵育2小时。细胞用[³⁵S]-蛋氨酸(10 μCi/mL)脉冲标记30分钟,裂解后通过液体闪烁计数检测总蛋白中的放射性,翻译活性以未应激溶媒组为对照标准化 [2] 2. 应激颗粒检测(免疫荧光):HeLa细胞接种于盖玻片(2×10⁴细胞/盖玻片),用亚砷酸盐(500 μM)±ISRIB(5–50 nM)处理1小时。细胞用4%多聚甲醛固定,0.1% Triton X-100透化,用抗G3BP1抗体(SG标志物)和DAPI染色。荧光显微镜下计数SG,抑制率以亚砷酸盐单独组为对照计算 [2] 3. UPR及突触蛋白western blot实验:原代皮质神经元或小鼠海马组织用含蛋白酶/磷酸酶抑制剂的RIPA缓冲液裂解,30 μg蛋白经10% SDS-PAGE分离后转膜,用抗ATF4、CHOP、p-eIF2α、PSD-95、GluA1及β-actin抗体孵育,ECL发光显示条带并通过光密度法定量 [1, 2] |
| 动物实验 |
Mice: Female CD-1 mice that are 6-7 weeks old are given medication via the intra-peritoneal (ip) route. Groups of three mice/compound/route of administration receive a single dose of 5 mg/kg of animals. DMSO is used to dissolve ISRIB, which is then diluted 1:1 in super-refined PEG 400. Following dosing, blood (80 μL) is drawn from the saphenous vein in EDTA-containing collection tubes at intervals of 20 minutes, 1 hour, 3 hours, 8 hours, and 24 hours. Plasma is then prepared for analysis. Time-of-flight mass spectroscopy is used to find substances.[1]
\n\nMorris water maze[1] \nMice were trained in a water pool of 100 cm diameter with a hidden platform of 10 cm diameter. Mice were handled daily for 3 days before the experiment, and the training protocol consisted of one swimming trial per day. Each mouse swam until it found the hidden platform or 120 s, when it was gently guided to the platform and stayed there for 10 s before being returned to the cage. Immediately after the swimming trial the mice were injected intraperitoneally with ISRIB (0.25 mg/kg in saline, 1% DMSO). For the probe test, the platform was removed and each mouse was allowed to swim for 60 s, while its swimming trajectory was monitored with a video tracking system.[1] \n\nContextual fear conditioning[1] \nMice were trained with a protocol that consisted of a 2-min period of context exploration, followed by a single foot shock of 0.35 mA for 1 s. Mice received a single injection of ISRIB (2.5 mg/kg in 50% DMSO, 50% PEG 400, IP) immediately after training and were returned to their home cage. One and 24 hr after training, the mice were tested for contextual fear memory by placing the animals in the conditioning context for a 4-min period. The incidence of freezing was scored in 5-s intervals as either ‘freezing’ or ‘not freezing’. Percent of freezing indicates the number of intervals in which freezing was observed divided by total number of 5-s intervals. Statistical analyses were done by Student’s t tests and one-way ANOVA followed by between-group comparisons using Tukey’s posthoc test.\n \n\nCannulation and auditory fear conditioning[1] \nMale Sprague Dawley rats (275–350 g) were used for cannulation as described in Migues et al., 2010 (Migues et al., 2010). ISRIB (0.05 mg/ml, 0.5 μl) was infused bilaterally into the amygdala immediately after auditory fear conditioning training. The infusion was performed with a microinjector (28 gauge) connected to a Hamilton syringe with plastic tubing at a rate of 0.25 μl/min. To allow for the solution containing ISRIB to diffuse from the tip of the cannula into the tissue, the microinjector stayed in the cannula for one additional minute. Training protocol for auditory fear conditioning consisted of a 2-min period of context A exploration, followed by one pairing of a tone (5000 Hz, 75 dB, 30 s) with a co-terminating foot shock (0.75 mA, 1 s). Rats were returned to their home cage 1 min after the shock. Test for auditory fear memory consisted of a 2 min acclimatizing period to the context B (pre-CS), followed by tone presentation (CS) (2800 Hz, 85 dB, 30 s). Freezing time was measured and percent of freezing was calculated. At the end of the experiment, cannula placement was checked by examining 50 μm brain sections stained with formal-thionin under a light microscope. \n\nIn cognitive - related animal experiments, ISRIB is administered to mice, and their performance in tasks like the water - maze test is observed. In the water - maze test, mice need to use clues to remember the location of a hidden rest platform. Their ability to find the platform is measured to assess the effect of ISRIB on cognitive function. In the instability - induced intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) model in mice, ISRIB is administered, and the levels of p - eIF2α/ATF4/IHH are measured, along with the evaluation of anti - oxidative enzyme protection and nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis [1] [2] 1. Mouse Cognitive Memory Assay (Fear Conditioning): Male C57BL/6 mice (8–10 weeks old, 20–22 g) were acclimated for 7 days. ISRIB was formulated in 10% DMSO/90% saline and administered via intraperitoneal injection (0.25 mg/kg, 1 mg/kg) or oral gavage (1 mg/kg) 30 minutes before contextual fear conditioning (CFC). CFC training involved a 2-minute habituation, 2-second foot shock (0.7 mA), and 1-minute post-shock period. 24 hours later, freezing time in the training context was measured for 5 minutes. For Morris water maze, mice were trained to find a hidden platform over 5 days; escape latency and target quadrant time were recorded [1] 2. Mouse ER Stress Survival Assay: Female BALB/c mice (6–8 weeks old, 18–20 g) were randomized into 3 groups (n=8/group): vehicle (10% DMSO/90% saline, ip), ISRIB alone (1 mg/kg, ip), vehicle + tunicamycin (2 mg/kg, ip), ISRIB + tunicamycin. ISRIB was administered 1 hour before tunicamycin. Mice were monitored daily for survival for 7 days. On day 3, 3 mice per group were euthanized; liver tissue was collected for western blot (CHOP) and TUNEL staining [2] 3. Mouse Pharmacokinetic Study: Male CD-1 mice (n=3 per time point) received ISRIB (1 mg/kg, oral or iv). Blood was collected at 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12 hours post-dose; brains were harvested at 3 hours. Drug concentration was measured via LC-MS/MS to determine pharmacokinetic parameters [2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
ISRIB showed favorable properties in pharmacokinetic profiling experiments indicating sufficient bioavailability for in vivo studies. ISRIB displayed a half-life in plasma of 8 hr (Figure 6A) and readily crossed the blood-brain barrier, quickly equilibrating with the central nervous system (Figure 6B). After a single intraperitoneal injection, we detected ISRIB in the brain of mice at concentrations several fold higher than its IC50 (24 hr after injection, the ISRIB concentration in the brain was approximately 60 nM).[1]
Pharmacokinetics of ISRIB[1] Intra-peritoneal (ip) route of administration was performed on 6–7 wk old female CD-1 mice. Animals received a single, 5 mg/kg dose in groups of three mice/compound/route of administration. ISRIB was dissolved in DMSO then diluted 1:1 in Super-Refined PEG 400. Blood (80 μl) was collected from the saphenous vein at intervals post-dosing (20 min, 1 hr, 3 hr, 8 hr, 24 hr) in EDTA containing collection tubes (Sarstadt CB300) and plasma was prepared for analysis. Compounds were detected by time-of-flight mass spectroscopy. Intra-peritoneal (ip) route of administration was performed at a single dose of 2.5 mg/kg in groups of three for each time-point (2, 6, 24 and 36 hr). Brain tissue samples were individually homogenized with a Tissue Tearor. Approximately 300 mg of tissue was placed in 5-ml polypropylene tube, and four volumes of water were then added to mix. The speed scale of Tissue Tearor was set at 3 for 2 min. After homogenization, the supernatant was analyzed by LC-MS/MS to determine their brain concentration. Plasma samples were collected prior to extraction of brain samples. 1. Oral Bioavailability and Pharmacokinetics in Mice: Male CD-1 mice administered ISRIB (1 mg/kg, oral) showed: Cmax = 1.2 μM, Tmax = 1.5 hours, terminal half-life (t₁/₂) = 6.8 hours, oral bioavailability (F) = 48% (vs. iv microdose). Intravenous administration (1 mg/kg) showed CL = 9.2 mL/min/kg, Vdss = 0.7 L/kg [2] 2. Tissue Distribution: Mice (1 mg/kg, oral) euthanized at 3 hours post-dose had tissue concentrations: brain (0.8 μM), liver (2.5 μM), hippocampus (0.9 μM), plasma (1.0 μM). Brain/plasma ratio = 0.8, hippocampus/plasma ratio = 0.9, confirming CNS penetration [1, 2] 3. Metabolism: ISRIB was minimally metabolized in human liver microsomes (HLMs); <5% of parent drug was metabolized after 2 hours of incubation. The main metabolite was identified as a monohydroxylated derivative (LC-MS/MS), with no significant contribution to pharmacologic activity [2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
1. In Vitro Cytotoxicity: ISRIB (up to 1 μM) had no significant cytotoxicity in MEFs, HeLa cells, HepG2 cells, or primary cortical neurons (cell viability > 90% vs. vehicle, MTT/NeuN assay). No induction of excessive UPR activation (e.g., ATF4 overexpression) was observed at concentrations up to 500 nM [1, 2]
2. In Vivo Acute Toxicity: Mice treated with ISRIB (1–30 mg/kg, oral or ip) showed no mortality, weight loss (<5% vs. baseline), or abnormal behavior (lethargy, ataxia) within 7 days. Serum biochemical markers (ALT, AST, BUN, creatinine) were within normal ranges, and histopathological examination of liver, kidney, and brain showed no lesions [2] 3. Subacute Toxicity: Mice treated with ISRIB (1 mg/kg, oral, daily for 28 days) had no significant changes in body weight, organ weight, CBC (WBC, RBC, platelets), or liver/kidney function. Hippocampal tissue showed no neuronal loss (NeuN staining) or synaptic protein dysregulation [2] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Phosphorylation of the α-subunit of initiation factor 2 (eIF2) controls protein synthesis by a conserved mechanism. In metazoa, distinct stress conditions activate different eIF2α kinases (PERK, PKR, GCN2, and HRI) that converge on phosphorylating a unique serine in eIF2α. This collection of signaling pathways is termed the 'integrated stress response' (ISR). eIF2α phosphorylation diminishes protein synthesis, while allowing preferential translation of some mRNAs. Starting with a cell-based screen for inhibitors of PERK signaling, we identified a small molecule, named ISRIB, that potently (IC50 = 5 nM) reverses the effects of eIF2α phosphorylation. ISRIB reduces the viability of cells subjected to PERK-activation by chronic endoplasmic reticulum stress. eIF2α phosphorylation is implicated in memory consolidation. Remarkably, ISRIB-treated mice display significant enhancement in spatial and fear-associated learning. Thus, memory consolidation is inherently limited by the ISR, and ISRIB releases this brake. As such, ISRIB promises to contribute to our understanding and treatment of cognitive disorders. DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.00498.001.[1]
Previously, we identified ISRIB as a potent inhibitor of the integrated stress response (ISR) and showed that ISRIB makes cells resistant to the effects of eIF2α phosphorylation and enhances long-term memory in rodents (Sidrauski et al., 2013). Here, we show by genome-wide in vivo ribosome profiling that translation of a restricted subset of mRNAs is induced upon ISR activation. ISRIB substantially reversed the translational effects elicited by phosphorylation of eIF2α and induced no major changes in translation or mRNA levels in unstressed cells. eIF2α phosphorylation-induced stress granule (SG) formation was blocked by ISRIB. Strikingly, ISRIB addition to stressed cells with pre-formed SGs induced their rapid disassembly, liberating mRNAs into the actively translating pool. Restoration of mRNA translation and modulation of SG dynamics may be an effective treatment of neurodegenerative diseases characterized by eIF2α phosphorylation, SG formation, and cognitive loss.[2] ISRIB is an integrated stress response (ISR) inhibitor. It works by restarting the protein - production mechanism in cells that has been inhibited due to a certain stress response, namely the integrated stress response. The integrated stress response is a cellular quality - control mechanism that monitors problems in protein production in cells, such as virus infections or cancer - causing gene mutations, and responds by halting the cell's protein - synthesis mechanism. ISRIB can penetrate the blood - brain barrier. It has shown potential in treating various conditions, including reversing cognitive impairments in mice after traumatic brain injury, improving cognitive function in aged mice, and showing efficacy in animal models related to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). In 2015, the technology related to ISRIB was licensed to Calico. Based on ISRIB, the investigational therapy ABBV - CLS - 7262 has entered clinical development for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, with Calico collaborating with AbbVie for its development [1] [2] 1. Background: ISRIB (trans-isomer) is a first-in-class small-molecule inhibitor of the Integrated Stress Response (ISR), discovered via high-throughput screening in 2013. Unlike PERK inhibitors (e.g., GSK2606414), it does not block eIF2α phosphorylation but instead activates eIF2B to overcome p-eIF2α-mediated translation inhibition [1, 2] 2. Mechanism of Action: ISRIB binds to the regulatory subunit of eIF2B (eIF2Bε), inducing a conformational change that increases eIF2B’s GEF activity. This reverses the inhibitory interaction between p-eIF2α and eIF2B, restoring mRNA translation, reducing stress granule formation, and suppressing pro-apoptotic UPR signaling (e.g., CHOP) [2] 3. Therapeutic Potential: Preclinical data support ISRIB for cognitive disorders (e.g., Alzheimer’s disease, age-related memory decline) via enhancing synaptic protein translation, and stress-related diseases (e.g., ER stress-induced liver injury, neurodegeneration) via ISR modulation. It has been tested in preclinical models but not advanced to clinical trials [1, 2] 4. Advantages: ISRIB has high potency (EC₅₀ ~10 nM), good oral bioavailability (48%), and effective CNS penetration (brain/plasma ratio ~0.8), making it suitable for CNS applications. It has low toxicity and does not disrupt baseline translation in unstressed cells [1, 2] 5. Limitations: ISRIB is ineffective in eIF2B-deficient cells/tissues, limiting utility in disorders with eIF2B mutations (e.g., leukoencephalopathy). No FDA-approved indications exist, and long-term effects on cognitive plasticity remain to be fully characterized [2] |
| 分子式 |
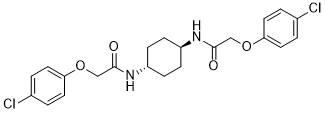
C22H24CL2N2O4
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
451.344
|
| 精确质量 |
450.111
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 58.55; H, 5.36; Cl, 15.71; N, 6.21; O, 14.18
|
| CAS号 |
1597403-47-8
|
| 相关CAS号 |
ISRIB;548470-11-7
|
| PubChem CID |
1011240
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
719.0±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
388.6±32.9 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.603
|
| LogP |
4.49
|
| tPSA |
76.66
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
| 重原子数目 |
30
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
493
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
ClC1C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=1[H])OC([H])([H])C(N([H])C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])C1([H])[H])N([H])C(C([H])([H])OC1C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=1[H])Cl)=O)=O
|
| InChi Key |
HJGMCDHQPXTGAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C22H24Cl2N2O4/c23-15-1-9-19(10-2-15)29-13-21(27)25-17-5-7-18(8-6-17)26-22(28)14-30-20-11-3-16(24)4-12-20/h1-4,9-12,17-18H,5-8,13-14H2,(H,25,27)(H,26,28)
|
| 化学名 |
2-(4-chlorophenoxy)-N-[4-[[2-(4-chlorophenoxy)acetyl]amino]cyclohexyl]acetamide
|
| 别名 |
ISRIB; 1597403-47-8; trans-ISRIB; 548470-11-7; ISRIB (trans-isomer); 1597403-48-9; N,N'-(cis-Cyclohexane-1,4-diyl)bis(2-(4-chlorophenoxy)acetamide); ISRIB trans-isomer; trans-ISRIB
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 0.83 mg/mL (1.84 mM) in 50% PEG300 +50% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浮液; 超声助溶 (<60°C).
*生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2156 mL | 11.0781 mL | 22.1562 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4431 mL | 2.2156 mL | 4.4312 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2216 mL | 1.1078 mL | 2.2156 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
|