| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
L-type voltage-gated calcium channels (L-VGCCs) [2]
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
拉西地平(0.01-100 μM;24 小时)在体外以浓度依赖性方式抑制 HKC 增殖[1]。通过控制 caspase-3 通路,拉西地平(0.01-100 μM;24 小时)可保护 HKC 免受 ATP 耗竭和恢复引起的细胞凋亡[1]。
在人肾细胞中,拉西地平(GX-1048, GR-43659X, SN-305, Lacipil, Motens)(1 μM、5 μM、10 μM)呈浓度依赖性抑制细胞凋亡。Annexin V-FITC/PI双染色检测显示,与凋亡对照组相比,凋亡率分别降低32%(1 μM)、58%(5 μM)和72%(10 μM)。该药物抑制caspase-3激活(10 μM浓度时活性降低45%),下调促凋亡蛋白Bax,同时在mRNA和蛋白水平上调抗凋亡蛋白Bcl-2 [1] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在 apoE 缺陷动物中,拉西地平(0.3、1.0、3.0 mg/kg;口服;每日一次,持续 10 周)可降低血浆内皮素浓度,并具有抗动脉粥样硬化特性[2]。
在载脂蛋白E缺陷小鼠(动脉粥样硬化模型)中,口服给予拉西地平(1 mg/kg、3 mg/kg,每日一次,连续12周)可减少动脉粥样硬化病灶形成。与对照组相比,主动脉病灶面积分别减少38%(1 mg/kg)和65%(3 mg/kg),同时3 mg/kg剂量使血清总胆固醇(TC)降低25%、甘油三酯(TG)降低22%,对高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)无显著影响 [2] - 拉西地平(3 mg/kg)处理减少主动脉病灶中的巨噬细胞浸润和脂质蓄积,组织学染色及免疫荧光分析可证实这一结果 [2] |
| 酶活实验 |
L型钙通道活性实验:从血管平滑肌细胞中制备富含L-VGCCs的膜组分,将其与系列浓度的拉西地平(0.01 μM-10 μM)在含荧光钙指示剂的反应缓冲液中共同孵育。通过检测去极化诱导的荧光强度变化评估钙内流,对比对照组计算L-VGCCs的抑制率 [2]
- Caspase-3活性实验:人肾细胞经拉西地平(1 μM、5 μM、10 μM)处理24小时后裂解,提取总蛋白。将蛋白提取物与caspase-3特异性荧光底物在37°C孵育60分钟,检测荧光强度,以对照组为标准进行活性归一化分析 [1] |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞增殖测定[1]
细胞类型: HKC 细胞 测试浓度: 0.01-100 μM 孵育时间: > 24 小时 实验结果:以浓度依赖性方式证明抗增殖活性。 细胞凋亡分析[1] 细胞类型: HKC 细胞(肾缺血再灌注 (I/R) 模型) 测试浓度: 1, 10 μM 孵育时间: 24 h 实验结果: AA诱导HKC细胞凋亡,早期凋亡细胞比例分别为1.47%和0.30分别为 1 和 10 μM 剂量的%。 蛋白质印迹分析[1] 细胞类型: HKC 细胞(肾缺血再灌注 (I/R) 模型) 测试浓度: > 1, 10 μM 孵育时间: 24 小时(预处理) 实验结果: ATP 耗尽和恢复后受损细胞的细胞色素 c 表达减少。显着增加 Bcl-2 蛋白的表达,但减少 Bax 蛋白的表达。 人肾细胞凋亡实验:细胞接种于6孔板,培养24小时后用促凋亡刺激剂(未明确)诱导凋亡,同时加入拉西地平(1 μM、5 μM、10 μM),继续孵育48小时。Annexin V-FITC/PI染色结合流式细胞术检测凋亡细胞;提取总RNA和蛋白,通过RT-PCR和Western blot检测Bax、Bcl-2及caspase-3的表达 [1] |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Female C57BL/6 mice (Homozygous ; apoE-deficient; atherosclerosis model)[2].
Doses: 0.3, 1.0, 3.0 mg/kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage); single daily for 10 weeks. Experimental Results: Induced a significant dose-dependent decrease in plasma endothelin levels. Dramatically decreased the mean lesion area in a dose-related manner by 10, 17 and 53% for 0.3, 1.0, 3.0 mg/kg, respectively. ApoE-deficient mouse atherosclerosis model: Male apoE-deficient mice were randomly divided into control and Lacidipine-treated groups. Lacidipine was dissolved in corn oil and administered via oral gavage at doses of 1 mg/kg and 3 mg/kg once daily for 12 weeks. Control mice received an equal volume of corn oil. At the end of the experiment, mice were sacrificed, aortic tissues were collected for |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Since it is a highly lipophilic compound, lacidpine is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract following oral administration with the peak plasma concentrations reached between 30 and 150 minutes of dosing. The peak plasma concentrations display large interindividual variability, with the values ranging from 1.6 to 5.7 μg/L following single-dose oral administration of lacidipine 4mg in healthy young volunteers. Absolute bioavailability is less than 10% due to extensive first-pass metabolism in the liver. Approximately 70% of the administered dose is eliminated as metabolites in the faeces and the remainder as metabolites in the urine. Metabolism / Metabolites Lacidipine undergoes complete CYP3A4-mediated hepatic metabolism, with no parent drug detected in the urine or faeces. The 2 main metabolites have no pharmacological activity. Biological Half-Life The average terminal half-life of lacidipine ranges from between 13 and 19 hours at steady state. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding
Lacidipine is highly protein-bound (more than 95%) to predominantly albumin and to a lesser extent, alpha-1-glycoprotein. No significant in vitro cytotoxicity was observed in human kidney cells at Lacidipine concentrations ≤10 μM [1] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
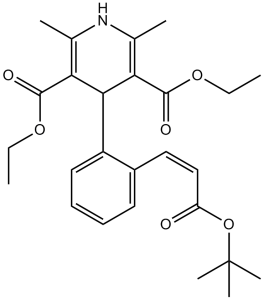
Lacidipine is a cinnamate ester and a tert-butyl ester.
Lacidipine is a lipophilic dihydropyridine calcium antagonist with an intrinsically slow onset of activity. Due to its long duration of action, lacidipine does not lead to reflex tachycardia. It displays specificity in the vascular smooth muscle, where it acts as an antihypertensive agent to dilate peripheral arterioles and reduce blood pressure. Compared to other dihydropyridine calcium antagonists, lacidipine exhibits a greater antioxidant activity which may confer potentially beneficial antiatherosclerotic effects. Lacidipine is a highly lipophilic molecule that interacts with the biological membranes. Through radiotracer analysis, it was determined that lacidipine displays a high membrane partition coefficient leading to accumulation of the drug in the membrane and slow rate of membrane washout. When visualized by small-angle X-ray diffraction with angstrom resolution to examine its location within the membranes, lacidipine was found deep within the membrane's hydrocarbon core. These results may explain the long clinical half-life of lacidipine. In randomised, well-controlled trials, administration of daily single-dose lacidipine ranging from 2-6 mg demonstrated comparable antihypertensive efficacy similar to that of other long-acting dihydropyridine calcium antagonists, thiazide diuretics, atenolol (a beta-blocker) and enalapril (an ACE inhibitor). It is available as once-daily oral tablets containing 2 or 4 mg of the active compound commonly marketed as Lacipil or Motens. It is not currently FDA-approved. Drug Indication Indicated for the treatment of hypertension either alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents, including β-adrenoceptor antagonists, diuretics, and ACE-inhibitors. Mechanism of Action By blocking the voltage-dependent L-type calcium channels, it prevents the transmembrane calcium influx. Normally, calcium ions serve as intracellular messengers or activators in exictable cells including vascular smooth muscles. The influx of calcium ultimately causes the excitation and depolarization of the tissues. Lacidipine inhibits the contractile function in the vascular smooth muscle and reduce blood pressure. Due to its high membrane partition coefficient, some studies suggest that lacidipine may reach the receptor via a two-step process; it first binds and accumulates in the membrane lipid bilayer and then diffuses within the membrane to the calcium channel receptor. It is proposed that lacidipine preferentially blocks the inactivated state of the calcium channel. Through its antioxidant properties shared amongst other dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers, lacidipine demonstrates an additional clinical benefit. Its antiatherosclerotic effects are mediated by suppressing the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and subsequent inflammatory actions by chemokines, cytokines and adhesion molecules, thus reducing atherosclerotic lesion formation. Lacidipine may also suppress cell proliferation and migration in smooth muscle cells and suppress the expression of matrix metalloproteinases, which affects the stability of atheromatous plaques. Pharmacodynamics acidipine is a specific and potent calcium antagonist with a predominant selectivity for calcium channels in the vascular smooth muscle. Its main action is to dilate predominantly peripheral and coronary arteries, reducing peripheral vascular resistance and lowering blood pressure. Following the oral administration of 4 mg lacidipine to volunteer subjects, a minimal prolongation of QTc interval has been observed (mean QTcF increase between 3.44 and 9.60 ms in young and elderly volunteers). Lacidipine is a dihydropyridine-class L-type calcium channel blocker [2] - Its primary mechanism of action involves inhibiting L-VGCCs, reducing calcium influx into vascular smooth muscle cells, and inducing vasodilation [2] - It exhibits anti-apoptotic effects in human kidney cells via a caspase-3-dependent pathway, regulating the Bax/Bcl-2 balance [1] - Clinically, it is indicated for the treatment of hypertension, and has potential anti-atherosclerotic effects in animal models [2] - It is marketed under the brand names Lacipil and Motens, with multiple developmental codes including GX-1048, GR-43659X, and SN-305 [1][2] |
| 分子式 |
C26H33NO6
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
455.54
|
|
| 精确质量 |
455.23
|
|
| CAS号 |
103890-78-4
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Lacidipine-13C8;1261432-01-2
|
|
| PubChem CID |
5311217
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.1±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
558.4±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
174-175°C
|
|
| 闪点 |
291.5±30.1 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.540
|
|
| LogP |
5.49
|
|
| tPSA |
90.93
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
11
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
33
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
805
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
CCOC(=O)C1=C(NC(=C(C1C2=CC=CC=C2/C=C/C(=O)OC(C)(C)C)C(=O)OCC)C)C
|
|
| InChi Key |
GKQPCPXONLDCMU-CCEZHUSRSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C26H33NO6/c1-8-31-24(29)21-16(3)27-17(4)22(25(30)32-9-2)23(21)19-13-11-10-12-18(19)14-15-20(28)33-26(5,6)7/h10-15,23,27H,8-9H2,1-7H3/b15-14+
|
|
| 化学名 |
diethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-[(E)-3-[(2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxy]-3-oxoprop-1-enyl]phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.49 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.49 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1952 mL | 10.9760 mL | 21.9520 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4390 mL | 2.1952 mL | 4.3904 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2195 mL | 1.0976 mL | 2.1952 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。