| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE); the inhibition constant (Ki) of Moexipril HCl (RS-10085) for human plasma ACE was 2.6 nM, and it inhibited rabbit lung ACE with an IC50 of 1.9 nM [3]
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
盐酸莫西普利对血小板功能影响很小,且无抗炎作用[2]。莫西普利拉是盐酸莫西普利的水解产物,其 IC50 分别为 2.6 和 4.9 nM,可抑制兔肺和豚鼠血清中的 ACE[2]。盐酸莫昔普利 (0.01 nM-0.1 mM) 的 IC50 分别为 2.7 mM 和 0.165 mM,对血浆 ACE 和兔肺分离的 ACE 具有强大的功效[3]。盐酸莫昔普利(0-100 μM,24 小时)以剂量依赖性方式显着降低受损神经元的百分比[4]。盐酸莫昔普利(0-100 μM,24 小时)可显着降低 Fe2+/3+ 引起的神经毒性[4]。凋亡神经元的比例不受盐酸莫昔普利剂量的显着影响[4]。
1. ACE抑制活性:以Hippuryl-His-Leu为底物的人血浆ACE实验中,Moexipril HCl (RS-10085) 呈剂量依赖性抑制ACE活性,Ki值为2.6 nM。在兔肺ACE实验中,其IC50为1.9 nM,抑制活性是依那普利(IC50=4.8 nM)的2–3倍 [3] 2. 抗自由基诱导的神经元损伤保护作用:在原代培养的大鼠皮质神经元中,Moexipril HCl (RS-10085)(1–10 μM)预处理2小时可减少过氧化氢(H₂O₂)诱导的神经元凋亡。浓度为10 μM时,凋亡率从模型组的42% ± 5%降至15% ± 3%(Annexin V-FITC染色检测),细胞活力提高38% ± 4%(MTT法检测)[4] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
盐酸莫昔普利不能穿过血脑屏障[1]。盐酸莫昔普利(分别为 3 mg/kg、30 mg/kg 和 10 mg/kg;口服;每日一次;5 天)对肾性高血压大鼠、自发性高血压大鼠和肾周高血压犬的影响呈剂量依赖性,并且抗高血压[3]。在 NMRI 小鼠中,盐酸莫昔普利(0.3 mg/kg,腹腔注射)可显着减少小鼠大脑表面的梗塞面积[4]。在 Long-Evans 大鼠中,盐酸莫昔普利(0.1 mg/kg,腹腔注射)可显着减少皮质梗塞体积[4]。
1. SHR大鼠降压效果:在12周龄自发性高血压大鼠(SHRs)中,口服Moexipril HCl (RS-10085)(10 mg/kg/天,溶解于饮用水)4周,收缩压从基线的185 ± 9 mmHg降至142 ± 7 mmHg,舒张压从132 ± 6 mmHg降至98 ± 5 mmHg;同时,左心室肥厚指数(LV/BW)从3.8 ± 0.2 mg/g降至3.1 ± 0.1 mg/g [3] 2. 脑缺血神经保护效果:在小鼠大脑中动脉阻塞(MCAO,阻塞60分钟后再灌注24小时)模型中,再灌注后立即腹腔注射Moexipril HCl (RS-10085)(3 mg/kg),脑梗死体积从模型组的35% ± 4%降至18% ± 3%(TTC染色),神经功能缺损评分从2.8 ± 0.3降至1.2 ± 0.2(0–4分制);同时,脑组织丙二醛(MDA)水平降低40% ± 5% [4] |
| 酶活实验 |
1. 人血浆ACE实验:
- 试剂制备:人血浆离心去除细胞后,通过硫酸铵沉淀法部分纯化ACE;Moexipril HCl (RS-10085) 溶于50 mM Tris-HCl缓冲液(pH 7.5),配制系列浓度(0.1–10 nM);底物Hippuryl-His-Leu用同缓冲液溶解至5 mM。 - 实验流程:反应体系(300 μL)含纯化ACE(10 μg蛋白)、Moexipril HCl (RS-10085)(不同浓度)和底物(终浓度5 mM),37℃孵育60分钟后,加100 μL 1 M HCl终止反应;用乙酸乙酯萃取反应液,蒸发有机相,残渣溶于水后检测228 nm吸光度,定量底物水解产物马尿酸。 - 数据分析:根据实验组与对照组的吸光度差异计算抑制率,通过Lineweaver-Burk双倒数作图法推导Ki值 [3] 2. 兔肺ACE实验: - 兔肺组织在50 mM Tris-HCl缓冲液(pH 7.5)中匀浆,离心获取上清液(ACE粗提液);实验流程同人血浆ACE实验,仅酶源替换为兔肺粗提液,通过量效曲线计算IC50值 [3] |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞培养:从1日龄Sprague-Dawley大鼠分离原代皮质神经元,用含B27添加剂的Neurobasal培养基培养;细胞接种于96孔板(5×10⁴细胞/孔),培养7天至成熟。
- 实验分组与处理:细胞分为三组: - 对照组:仅用培养基孵育。 - H₂O₂模型组:用200 μM H₂O₂处理24小时。 - Moexipril HCl (RS-10085)预处理组:1–10 μM Moexipril HCl (RS-10085)预处理2小时后,联合200 μM H₂O₂处理24小时。 - 检测方法:MTT法检测细胞活力(570 nm吸光度);Annexin V-FITC/PI双染色结合流式细胞术检测神经元凋亡 [4] |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Spontaneously hypertensive rats[3]
Doses: 30 mg/kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage); one time/day; 5 days Experimental Results: Caused a progressive lowering of mean blood pressure from pretreatment values of 180 +/- 7 mmHg to a trough on day 4 of 127 +/- 4 mmHg. Dose-dependently diminished arterial blood pressure, and inhibited plasma and tissue ACE activity. Animal/Disease Models: Renal hypertensive rats[3] Doses: 0.03-10 mg/kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage); one time/day; 5 days Experimental Results: Caused a dose-dependent decrease in blood pressure with a threshold dose of 0.3 mg/kg. Lowered mean blood pressure by about 70 mmHg of 3 mg/kg. Animal/Disease Models: Perinephritic hypertensive dogs[3] Doses: 10 mg/kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage); one time/day; 5 days Experimental Results: Caused a drop of mean blood pressure by 25 mmHg from pre-treatment control , which persisted for 24 h, by a rapid onset and a long duration of action. Animal/Disease Models: NMRI mice (male, Permanent focal ischemia)[4] Doses: 0, 0.03, 0.3, and 3 mg/kg Administration 1. SHR antihypertensive model: - Male spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs, 12 weeks old, 280–320 g) were randomly divided into two groups (n=8 per group): - SHR control group: Given plain drinking water for 4 weeks. - Moexipril HCl (RS-10085) group: Given drinking water containing Moexipril HCl (RS-10085) (adjusted to 10 mg/kg/day based on daily water intake) for 4 weeks. - Blood pressure was measured weekly using a tail-cuff plethysmograph (after rats were acclimated to the device for 3 consecutive days). At the end of treatment, rats were euthanized, and the left ventricle was weighed to calculate the left ventricular hypertrophy index (LV/BW, mg/g) [3] 2. Mouse MCAO cerebral ischemia model: - Male ICR mice (8–10 weeks old, 25–30 g) were randomly divided into two groups (n=8 per group): - MCAO control group: Intraperitoneally injected with normal saline (1 mL/kg) immediately after reperfusion. - Moexipril HCl (RS-10085) group: Intraperitoneally injected with Moexipril HCl (RS-10085) (3 mg/kg, dissolved in normal saline) immediately after reperfusion. - MCAO was induced by inserting a nylon suture into the middle cerebral artery for 60 minutes, followed by reperfusion. After 24 hours of reperfusion, neurological deficit scores were evaluated (0–4 scale: 0 = no deficit, 4 = severe deficit). Brains were removed, sliced into 2 mm coronal sections, and stained with 2% TTC to measure infarct volume (calculated as % of total brain volume) [4] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption: Moexipril HCl (RS-10085) is a prodrug; its oral bioavailability in healthy volunteers is approximately 13% (due to first-pass metabolism). Food intake reduces its absorption by ~40% (decreased Cmax of the active metabolite moexiprilat), so it is recommended to be taken 1 hour before meals. After oral administration of 15 mg Moexipril HCl (RS-10085), the Cmax of moexiprilat is 22 ± 5 ng/mL, reached at 1.5 hours [1][2]
- Distribution: The volume of distribution (Vd) of moexiprilat (active metabolite) in healthy volunteers is approximately 18 L. It does not penetrate the blood-brain barrier significantly [1] - Metabolism: Moexipril HCl (RS-10085) is rapidly hydrolyzed by hepatic esterases to its active metabolite moexiprilat (the main form exerting ACE inhibitory activity). No other active metabolites are detected [1][2] - Excretion: Moexiprilat is excreted mainly via the kidneys. Approximately 50% of the administered dose is excreted as moexiprilat in urine within 24 hours. The elimination half-life (t1/2) of moexiprilat is approximately 9 hours in healthy volunteers; in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min), t1/2 prolongs to 24 hours [1][2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Acute toxicity: The median lethal dose (LD50) of Moexipril HCl (RS-10085) was >2000 mg/kg in mice (oral administration) and >1000 mg/kg in rats (oral administration) [2]
- Chronic toxicity: In a 6-month oral toxicity study in rats (doses of 10, 30, 100 mg/kg/day), no significant changes in liver function (ALT/AST) or kidney function (creatinine/BUN) were observed, even at the highest dose [2] - Plasma protein binding: Moexiprilat (active metabolite) has a plasma protein binding rate of approximately 50% [1] - Adverse effects: The most common adverse effects in clinical trials included dry cough (incidence: 5%–8%), dizziness (3%–4%), and fatigue (2%–3%). Rare adverse effects included angioedema (incidence <0.1%) and hyperkalemia (more common in patients with renal impairment) [1] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Moexipril hydrochloride is a dipeptide.
Moexipril Hydrochloride is the hydrochloride salt form of moexipril, a prodrug and non-sulfhydryl angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor with antihypertensive activity. Moexipril hydrochloride is hydrolized into its active form moexiprilat, which competitively inhibits ACE, thereby blocking the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II. This prevents the actions of the potent vasoconstrictor angiotensin II and leads to vasodilatation. It also prevents angiotensin II-induced aldosterone secretion by the adrenal cortex, thereby promoting diuresis and natriuresis. Moexipril hydrochloride also directly suppresses renin release. See also: Moexiprilat (has active moiety); Hydrochlorothiazide; moexipril hydrochloride (component of). 1. Moexipril HCl (RS-10085) is an oral prodrug angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI) that exerts pharmacological effects after being metabolized to moexiprilat (active form) [1][3] 2. Compared with enalapril (another ACEI), Moexipril HCl (RS-10085) has higher ACE inhibitory potency (2–3-fold) and a longer duration of antihypertensive effect (24 hours with once-daily administration) [3] 3. Therapeutic indications: Moexipril HCl (RS-10085) is indicated for the treatment of essential hypertension (monotherapy or in combination with thiazide diuretics) [1] 4. Its neuroprotective effect in cerebral ischemia is proposed to be associated with reducing oxidative stress (decreasing MDA levels) and inhibiting neuronal apoptosis, independent of its ACE inhibitory activity [4] |
| 分子式 |
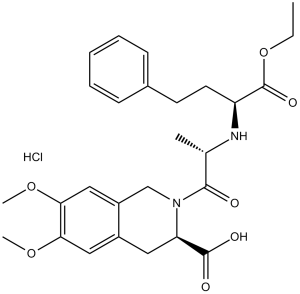
C₂₇H₃₅CLN₂O₇
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
535.03
|
| 精确质量 |
534.213
|
| CAS号 |
82586-52-5
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Moexipril;103775-10-6;Moexipril-d5;1356929-49-1;Moexipril-d5 hydrochloride
|
| PubChem CID |
54889
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 沸点 |
709.3ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
141-161ºC
|
| 闪点 |
382.8ºC
|
| LogP |
3.715
|
| tPSA |
114.4
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
12
|
| 重原子数目 |
37
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
742
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
3
|
| SMILES |
CCOC(=O)[C@H](CCC1=CC=CC=C1)N[C@@H](C)C(=O)N2CC3=CC(=C(C=C3C[C@H]2C(=O)O)OC)OC.Cl
|
| InChi Key |
JXRAXHBVZQZSIC-QGCARJLFSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C27H34N2O7.ClH/c1-5-36-27(33)21(12-11-18-9-7-6-8-10-18)28-17(2)25(30)29-16-20-15-24(35-4)23(34-3)14-19(20)13-22(29)26(31)32;/h6-10,14-15,17,21-22,28H,5,11-13,16H2,1-4H3,(H,31,32);1H/t17-,21-,22?;/m0./s1
|
| 化学名 |
2-(((S)-1-ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-yl)-L-alanyl)-6,7-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid hydrochloride
|
| 别名 |
SPM-925; SPM 925; SPM925; CI-925; CI 925; CI925;RS 10085; RS-10085; RS10085; Moexipril.
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.89 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.89 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.89 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 50 mg/mL (93.45 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8691 mL | 9.3453 mL | 18.6905 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3738 mL | 1.8691 mL | 3.7381 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1869 mL | 0.9345 mL | 1.8691 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。