| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:Nisoldipine 是 L 型钙通道的有效阻断剂。尼索地平直接与非活性钙通道结合,稳定其非活性构象,与其他 DHP CCB 类似。由于大量不活跃的通道和通道的 α1 亚基,尼索地平对动脉平滑肌细胞表现出选择性。尼索地平对延迟整流 K+ 通道的选择性比 L 型 Ca2+ 通道低约 30 倍,它抑制 IKr(快速激活延迟整流 K+ 电流),IC50 为 23 μM,以及 IKs(缓慢激活延迟整流 K+ 电流)在豚鼠心室肌细胞中的 IC50 为 40 μM。尼索地平在添加活性氧之前和之后还表现出抗氧化效力,IC50 为 28.2 μM。这是通过使用非酶活性氧生成系统 (DHF/FeCl3-ADP) 的大鼠心肌膜脂质过氧化来测试的。激酶测定:在不同浓度的尼索地平存在下,在无血清培养基中培养表达电压依赖性L型Ca2+通道亚基的CHO细胞。然后,使用 List EPC-7 膜片钳放大器和 pClamp 软件,通过膜片钳方法的全细胞配置,在室温下记录从 -100 mV 或 -50 mV 的保持电位引起的 Ca2+ 通道电流。抑制 50% 特异性结合的竞争剂浓度代表 IC50。细胞测定:将肌细胞浸泡在正常 Tyrodes 溶液中,保持在 -80 mV,并在 200 毫秒预脉冲 (-40 mV) 后去极化至更正电位,持续 500 毫秒,频率为 0.1 Hz,在复极化至 -40 mV 时记录尾电流。将肌细胞暴露于 10-100 mM 尼索地平 8-10 分钟。然后使用 EPC-7 放大器记录全细胞膜电流。
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
尼索地平通过抑制钙离子通过 L 型钙通道的流入来降低动脉平滑肌收缩力和随后的血管收缩。这会导致血管舒张和血压总体下降,因此尼索地平用于治疗轻度至中度原发性高血压、慢性稳定型心绞痛和 Prinzmetals 变异型心绞痛。尼索地平在具有 Cav1.2 错义突变 G406R 的蒂莫西综合征患者中显示出一定的能力,IC50 为 267 nM,有助于治疗 TS。
|
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Relatively well absorbed into the systemic circulation with 87% of the radiolabeled drug recovered in urine and feces. The absolute bioavailability of nisoldipine is about 5%. Although 60-80% of an oral dose undergoes urinary excretion, only traces of unchanged nisoldipine are found in urine. Metabolism / Metabolites Pre-systemic metabolism in the gut wall, and this metabolism decreases from the proximal to the distal parts of the intestine. Nisoldipine is highly metabolized; 5 major urinary metabolites have been identified. The major biotransformation pathway appears to be the hydroxylation of the isobutyl ester. A hydroxylated derivative of the side chain, present in plasma at concentrations approximately equal to the parent compound, appears to be the only active metabolite and has about 10% of the activity of the parent compound. Cytochrome P450 enzymes are believed to play a major role in the metabolism of nisoldipine. The particular isoenzyme system responsible for its metabolism has not been identified, but other dihydropyridines are metabolized by cytochrome P450 IIIA4. Nisoldipine has known human metabolites that include 2,6-Dimethyl-5-(2-methylpropoxycarbonyl)-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid, Dehydro Nisoldipine, and 5-O-(1-hydroxy-2-methylpropyl) 3-O-methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate. Biological Half-Life 7-12 hours |
||
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Because no information is available on the use of nisoldipine during breastfeeding, an alternate drug may be preferred. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding 99% |
||
| 参考文献 | |||
| 其他信息 |
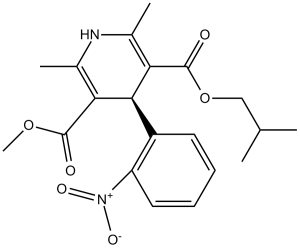
Methyl 2-methylpropyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate is a dihydropyridine that is 1,4-dihydropyridine which is substituted by methyl groups at positions 2 and 6, a methoxycarbonyl group at position 3, an o-nitrophenyl group at position 4, and an isobutoxycarbonyl group at position 5. The racemate, a calcium channel blocker, is used in the treatment of hypertension and angina pectoris. It is a C-nitro compound, a diester, a dihydropyridine, a methyl ester and a member of dicarboxylic acids and O-substituted derivatives.
Nisoldipine is a 1,4-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker. It acts primarily on vascular smooth muscle cells by stabilizing voltage-gated L-type calcium channels in their inactive conformation. By inhibiting the influx of calcium in smooth muscle cells, nisoldipine prevents calcium-dependent smooth muscle contraction and subsequent vasoconstriction. Nisoldipine may be used in alone or in combination with other agents in the management of hypertension. Nisoldipine is a Dihydropyridine Calcium Channel Blocker. The mechanism of action of nisoldipine is as a Calcium Channel Antagonist. The physiologic effect of nisoldipine is by means of Decreased Blood Pressure. Nisoldipine is a second generation calcium channel blocker and commonly used antihypertensive agent. Nisoldipine therapy is associated with a low rate of serum enzyme elevations, but has not been specifically linked to instances of clinical apparent acute liver injury. Nisoldipine is a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocking agent. Nisoldipine inhibits the transmembrane influx of extracellular calcium ions into myocardial and vascular smooth muscle cells, causing dilatation of the main coronary and systemic arteries and decreasing myocardial contractility. This agent also inhibits the drug efflux pump P-glycoprotein which is overexpressed in some multi-drug resistant tumors and may improve the efficacy of some antineoplastic agents. (NCI04) A dihydropyridine calcium channel antagonist that acts as a potent arterial vasodilator and antihypertensive agent. It is also effective in patients with cardiac failure and angina. Drug Indication For the treatment of hypertension. It may be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents. Mechanism of Action By deforming the channel, inhibiting ion-control gating mechanisms, and/or interfering with the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, Nisoldipine inhibits the influx of extracellular calcium across the myocardial and vascular smooth muscle cell membranes The decrease in intracellular calcium inhibits the contractile processes of the myocardial smooth muscle cells, causing dilation of the coronary and systemic arteries, increased oxygen delivery to the myocardial tissue, decreased total peripheral resistance, decreased systemic blood pressure, and decreased afterload. Pharmacodynamics Nisoldipine, a dihydropyridine calcium-channel blocker, is used alone or with an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, to treat hypertension, chronic stable angina pectoris, and Prinzmetal's variant angina. Nisoldipine is similar to other peripheral vasodilators. Nisoldipine inhibits the influx of extra cellular calcium across the myocardial and vascular smooth muscle cell membranes possibly by deforming the channel, inhibiting ion-control gating mechanisms, and/or interfering with the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The decrease in intracellular calcium inhibits the contractile processes of the myocardial smooth muscle cells, causing dilation of the coronary and systemic arteries, increased oxygen delivery to the myocardial tissue, decreased total peripheral resistance, decreased systemic blood pressure, and decreased afterload. |
| 分子式 |
C20H24N2O6
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
388.4144
|
|
| 精确质量 |
388.163
|
|
| CAS号 |
63675-72-9
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Nisoldipine-d6;1285910-03-3;Nisoldipine-d4;1219795-47-7;Nisoldipine-d7;1189718-34-0
|
|
| PubChem CID |
4499
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to yellow solid powder
|
|
| LogP |
3.3
|
|
| tPSA |
110
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
28
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
704
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
O(C([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])C(C1=C(C([H])([H])[H])N([H])C(C([H])([H])[H])=C(C(=O)OC([H])([H])[H])C1([H])C1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C1[N+](=O)[O-])=O
|
|
| InChi Key |
VKQFCGNPDRICFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C20H24N2O6/c1-11(2)10-28-20(24)17-13(4)21-12(3)16(19(23)27-5)18(17)14-8-6-7-9-15(14)22(25)26/h6-9,11,18,21H,10H2,1-5H3
|
|
| 化学名 |
3-isobutyl 5-methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.44 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.44 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5746 mL | 12.8730 mL | 25.7460 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5149 mL | 2.5746 mL | 5.1492 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2575 mL | 1.2873 mL | 2.5746 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT00979537 | Completed | Drug: Nisoldipine Extended-release Tablets, 40 mg |
Healthy | Mylan Pharmaceuticals Inc | March 2007 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00985660 | Completed | Drug: Nisoldipine Extended-release Tablets, 30 mg |
Healthy | Mylan Pharmaceuticals Inc | June 2007 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00730197 | Completed | Drug: Albuterol Sulfate Extended- Release Tablets 8 mg |
Healthy | Mylan Pharmaceuticals Inc | February 2007 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00311870 | Completed | Drug: nisoldipine Drug: lisinopril |
Diabetic Nephropathy | Steno Diabetes Center Copenhagen | March 1993 | Phase 4 |
|
|
|