| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
| 靶点 |
Arginase
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
nor-NOHA(0.1-1 mM,72 h)在缺氧(1.5% O2)条件下以剂量依赖性方式诱导 K562 细胞凋亡[1]。nor-NOHA(1 mM,72 h)可以减弱 K562 或 KCL22 细胞中缺氧介导的伊马替尼耐药性[1]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
nor-NOHA(100 mg/kg,静脉注射,一次)可显著减少雄性 Sprague-Dawley 大鼠的梗死面积 [2]。nor-NOHA(100 mg/kg,静脉注射,一次)可增加雄性 Sprague-Dawley 大鼠血浆瓜氨酸和亚硝酸盐水平,并降低血浆鸟氨酸水平 [2]
|
| 酶活实验 |
精氨酸酶活性测定[1]
精氨酸酶活性经修饰后按描述进行分析。计数细胞,等量细胞在50μl裂解缓冲液(PBS加1mM EDTA, 0.1% Triton X−100和蛋白酶抑制剂)中裂解,4℃下14000 g离心15分钟。将上清液与50μl新配制的活化缓冲液(10mM MnCl2, 50mM Tris-HCl pH7.5)和50μl 0.5M精氨酸混合,在56℃下加热10分钟。然后,加入800μl酸性溶液(H2SO4 (96%)/H3PO4 (85%)/H2O, 1/3/7, v/v/v)和25μl 9% α -异硝基丙烯酮(乙醇),在100℃下加热15 min。让这种混合物在黑暗中显色。最后将250μl转移到96孔板上,在550nm处测量外径。 |
| 细胞实验 |
Seahorse分析仪测量细胞呼吸[1]
0.1x106 K562细胞每孔镀于聚L -赖氨酸包被的XF - 24孔细胞培养微孔板上,XF Assay培养基中添加4.5 g/L葡萄糖和1mM丙酮酸钠。将细胞自旋固定在200g的微孔板上1分钟。细胞耗氧率(OCR)、细胞外酸化率(ECAR)和光子产生率(PPR)采用Seahorse Bioscience公司的XF24分析仪进行测定。根据制造商的说明进行测量,使用低霉素,羰基氰化物- 4 -(三氟甲氧基)苯腙(FCCP)和鱼藤酮&抗霉素A (R/A;所有来自Sigma - Aldrich)在指定的浓度。数据分析使用Seahorse XF软件。 |
| 动物实验 |
Sprague-Dawley rats were subjected to 30 min of coronary artery ligation, followed by 2 h of reperfusion. The animals were given either saline, or the arginase inhibitor N-omega-hydroxy-nor-l-arginine (nor-NOHA) with or without the NO scavenger carboxy-2-phenyl-4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-imidazoline-1-oxyl-3-oxide (cPTIO) or the NOS inhibitor N(G)-monomethyl-l-arginine (l-NMMA) iv 15 min before ischaemia. The infarct size was 79 +/- 4% of the area at risk in the control group. Nor-NOHA treatment reduced the infarct size to 39 +/- 7% (P < 0.001). Administration of cPTIO or l-NMMA completely abolished the protective effect of nor-NOHA. Expression of arginase I was significantly (P < 0.05) increased in ischaemic myocardium. Nor-NOHA treatment resulted in higher plasma levels of nitrite (P < 0.05) and a 10-fold increase in the citrulline/ornithine ratio (P < 0.001), indicating a shift in arginine utilization towards NOS.
Conclusion: Inhibition of arginase protects from myocardial infarction by a mechanism that is dependent on NOS activity and bioavailability of NO by shifting arginine utilization from arginase towards NOS. These findings suggest that targeting of arginase is a promising future therapeutic strategy for protection against myocardial IR injury.[2] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
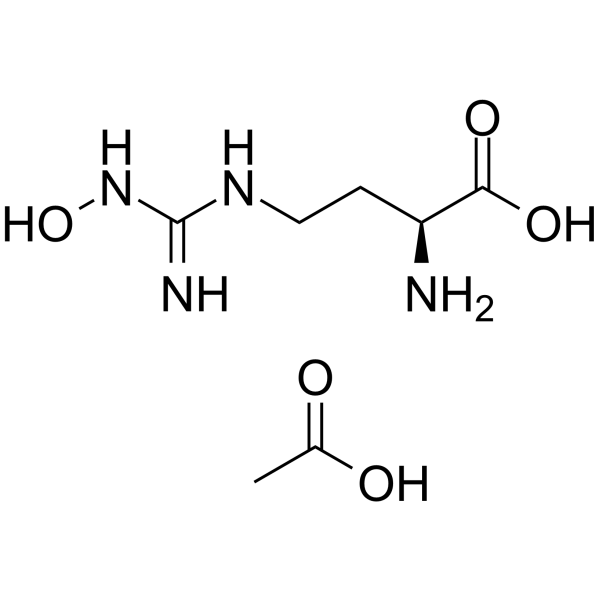
Nomega-hydroxy-nor-l-arginine is a L-alpha-amino acid. N-Hydroxy-nor-L-arginine (nor-NOHA) is under investigation in clinical trial NCT02009527 (Arginase Inhibition in Ischemia-reperfusion Injury).
Cancer cells, including in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), depend on the hypoxic response to persist in hosts and evade therapy. Accordingly, there is significant interest in drugging cancer-specific hypoxic responses. However, a major challenge in leukemia is identifying differential and druggable hypoxic responses between leukemic and normal cells. Previously, we found that arginase 2 (ARG2), an enzyme of the urea cycle, is overexpressed in CML but not normal progenitors. ARG2 is a target of the hypoxia inducible factors (HIF1-α and HIF2-α), and is required for the generation of polyamines which are required for cell growth. We therefore explored if the clinically-tested arginase inhibitor Nω-hydroxy-nor-arginine (nor-NOHA) would be effective against leukemic cells under hypoxic conditions. Remarkably, nor-NOHA effectively induced apoptosis in ARG2-expressing cells under hypoxia but not normoxia. Co-treatment with nor-NOHA overcame hypoxia-mediated resistance towards BCR-ABL1 kinase inhibitors. While nor-NOHA itself is promising in targeting the leukemia hypoxic response, we unexpectedly found that its anti-leukemic activity was independent of ARG2 inhibition. Genetic ablation of ARG2 using CRISPR/Cas9 had no effect on the viability of leukemic cells and their sensitivity towards nor-NOHA. This discrepancy was further evidenced by the distinct effects of ARG2 knockouts and nor-NOHA on cellular respiration. In conclusion, we show that nor-NOHA has significant but off-target anti-leukemic activity among ARG2-expressing hypoxic cells. Since nor-NOHA has been employed in clinical trials, and is widely used in studies on endothelial dysfunction, immunosuppression and metabolism, the diverse biological effects of nor-NOHA must be cautiously evaluated before attributing its activity to ARG inhibition.[1] |
| 分子式 |
C7H16N4O5
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
236.225741386414
|
| 精确质量 |
236.112
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 35.59; H, 6.83; N, 23.72; O, 33.86
|
| CAS号 |
2250019-93-1
|
| 相关CAS号 |
189302-40-7; 1140844-63-8 (acetate); 291758-32-2 (HCl); 2250019-93-1 (nor-NOHA monoacetate)
|
| PubChem CID |
131648256
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| tPSA |
171
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
6
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
16
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
213
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
OC([C@H](CC/N=C(\N)/NO)N)=O.OC(C)=O
|
| InChi Key |
RYUGHGOGNIYFKU-DFWYDOINSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C5H12N4O3.C2H4O2/c6-3(4(10)11)1-2-8-5(7)9-12;1-2(3)4/h3,12H,1-2,6H2,(H,10,11)(H3,7,8,9);1H3,(H,3,4)/t3-;/m0./s1
|
| 化学名 |
acetic acid;(2S)-2-amino-4-[[amino-(hydroxyamino)methylidene]amino]butanoic acid
|
| 别名 |
Nor NOHA monoacetate; 2250019-93-1; nor-NOHA (monoacetate); nor-NOHA monoacetate; N-OMega-hydroxy-L-norarginine acetate salt; AKOS032962868; HY-112885B; N-OMega-hydroxy-L-norarginineacetatesalt;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~423.32 mM)
H2O : ~50 mg/mL (~211.66 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (10.58 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (10.58 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (10.58 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 100 mg/mL (423.32 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶 (<60°C). 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.2332 mL | 21.1658 mL | 42.3316 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8466 mL | 4.2332 mL | 8.4663 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4233 mL | 2.1166 mL | 4.2332 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。